IJCRR - 13(12), June, 2021
Pages: 54-61
Date of Publication: 22-Jun-2021
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
Assessment and Interrelation of hs-CRP, Nitrosative Stress and Lipid Profile in Type-2 Diabetes Mellitus
Author: Bithika Ghosh, Saumyajit Maiti, Kasturi Mukherjee
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Introduction: The prevalence of type 2 Diabetes Mellitus, one of the major health problems, is increasing day by day, which is one of the important causes for the development of Cardiovascular Disease (CVD). Aim: To determine serum levels of hs-CRP, total nitrite, endogenous nitrite, Nitrate/Nitrite ratio and Lipid Profile as predictors of inflammation, nitrosative stress and dyslipidemia in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus patients and to evaluate the correlation among the above mentioned biochemical parameters with age-sex matched healthy controls. Materials and Methods: Current study was designed to estimate the level of fasting blood sugar, hs-CRP, parameters of lipid profile and different parameters of nitrosative stress (total nitrite, endogenous nitrite, nitrate and nitrate/nitrite ratio)in the Department of Biochemistry on diabetics screened from Department of Endocrinology and Metabolism, through proper inclusion and exclusion criteria, and compared with that of age-sex matched healthy controls. Result: Level of total nitrite, nitrate, nitrate/nitrite ratio parameters of nitrosative stress, hs-CRP and total cholesterol, LDL-cholesterol, VLDL-cholesterol and triglyceride are significantly high in the group of diabetics and statistically significant as compared with controls. Conclusion: Assessment of hs-CRP, marker of low-grade inflammation and parameters of nitrosative stress is necessary for the diabetics as they are established independent potent risk factors for CVD. A large study population from multiple centres are required for a better result to conclude the study.
Keywords: hs-CRP, Nitrosative stress, Nitrate, Nitrite, Lipid Profile, Type-2 Diabetes Mellitus
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION:
According to WHO reports, in this 21st century, the prevalence of type 2 Diabetes Mellitus (T2DM) has been increased worldwide very rapidly. T2DM, one of the major public health problems, accounts for approximately 85 to 95 percent of all diagnosed cases of diabetes. In India, the scenario is worsening day by day. Epidemiological data in India show the same upward trend and the projected figure for DM affected people is 33 million in 2025.1
Inflammation and endothelial dysfunction followed by oxidative stress – the sequence which is ultimately responsible for the development and progress of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and all sorts of its complications. In Type 2 Diabetes, 65 to 80 percent of deaths occur due to cardiovascular disease (CVD) whose aetiology cannot be explained by chronic hyperglycemia, dyslipidemia and traditional cardiac risk factors.2, 3
CVD is in part an inflammatory process; C - reactive protein (CRP) has been widely investigated in the context of atherosclerosis and subsequent vascular events. Mild elevation of high–sensitivity C – reactive protein (hs-CRP) associated with future cardiovascular risk. Chronic low-grade systemic inflammation plays a major role in the pathophysiology of both T2DM as well as atherosclerosis.4
Among the number of factors involved in maintaining proper vascular homeostasis, nitric oxide (NO) plays a pivotal role in guaranteeing physiological endothelial function. It is still a matter of controversy whether and in which way imbalance in glucose metabolism might affect NO synthesis and bioavailability.5Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus is a state of increased free radical activity. The roles of surplus Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) and Reactive Nitrogen Species (RNS) in the diabetic complications of multiple organ systems are widely documented.6The endothelial dysfunction associated with Diabetes has been attributed to a lack of bioavailable NO due to oxidative and nitrosative stress.
This study aims to assess serum levels of hs-CRP, total nitrite, endogenous nitrite, Nitrate/Nitrite ratio and Lipid Profile as predictors of inflammation, nitrosative stress and dyslipidemia in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus patients and find out the correlation among the above mentioned biochemical parameters with age-sex matched healthy controls.
MATERIALS AND METHODS:
This hospital-based case-control study was done in the Department of Biochemistry, Calcutta Medical College and Hospital, Kolkata and the patients were selected from the Out-Patient Department of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Calcutta Medical College and Hospital, Kolkata over one year (from January 2014 to January 2015). The problem is defined as chronic inflammatory endothelial damage; nitrosative stress and dyslipidemia are collectively responsible for multi-organ complications and death in patients of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Written informed consent was taken from the patients as per proforma. Detailed demographical data, history and clinical findings and laboratory investigations were recorded in the proforma.
The sample size was determined by using the correlation coefficient (Pearson’s) in Type 2 DM between hs-CRP and total cholesterol (r=0.72), triglyceride levels (r=0.58) and LDL Cholesterol (r=0.72) with type 1 error of 5%, and power 80% using statistical software Medcalc version 10.2.0.0. Considering correlation coefficient (Pearson’s) as 0.72 the minimum required sample size was 12, and considering 0.58 the size was 21. In our study, we took a total sample of 100 (case 50 and control 50).
Study Population:
-
Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus patients attending the Out Patient Department of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Medical College and Hospital, Kolkata, who fulfil the Inclusion Criteria.
-
Normal healthy age and sex-matched controls.
Inclusion Criteria:
-
Male and female newly diagnosed Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus patients aged between 30 to 65 years, having fasting blood glucose more than or equal to 126mg/dl.
-
The Control group includes age-matched healthy volunteers with fasting plasma glucose level less than 100mg/dl of both sexes.
-
Patients willing to participate in the study and gave proper consent.
Exclusion Criteria:
-
Diabetes was other than Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus.
-
History of insulin and or oral hypoglycaemic drugs.
-
History of any chronic inflammatory disorder.
-
History of renal or hepatic impairment.
-
History of recent trauma/surgery.
-
History of Infective Disease.
-
H/O Myocardial infarction, Hypertension.
-
Pregnant and lactating woman.
-
Subjects on any concomitant medication such as antioxidants, herbal treatment may interact with nitrosative stress parameter.
-
Cigarette smokers and alcoholics.
Collection of sample:
10 ml of venous blood was collected from newly diagnosed Diabetic patients at 12-hour fasting in the early morning with proper aseptic technique. Then the patients were instructed to take a meal that they take normally in their lunch and come again exactly after two hours. Blood was collected in two containers one having no anticoagulant for serum and the other having citrate-fluoride for plasma. The sample taken in clot activator without anticoagulant were allowed to clot and then all the containers were centrifuged at 1500 rpm speed for 3-5 minutes for separation of serum and plasma. The serum and plasma were separated and kept at 2-8?C until analysis.
Laboratory investigations parameters and procedures
-
Plasma glucose was estimated by Glucose Oxidase-Peroxidase Method. (Crest Biosystem a division of Coral-clinical systems)
-
Nitrate was assessed by the Cadmium Reduction method; Nitrite was determined by Diazotization of Sulphanilamide by coupling it to N-naphthyl ethylene diamine.
Principle
The nitrate was assayed by the Cadmium reduction method. The nitrite was determined by diazotization of Sulphanilamide & coupling it to N-naphthyl ethylene diamine dihydrochloride (NED). Since NO has an extremely short half-life of less than 10 sec, it cannot be measured directly. However as NO is rapidly metabolized to nitrite (NO2) and nitrate (NO3) in the cell, the concentration of these stable anions can be used to measure the amount of NO that was originally present in a sample. NO2 is converted to nitrous acid (HNO2) in an acidic solution. HNO2 is diazotized with the Sulphanilic acid and Sulphanilamide –Diazonium complex is formed. This is coupled with the amine of NED and a purpled coloured compound is obtained which can be measured spectrophotometrically at 545 nm.7
Calculations:
The individual reading was put on the Standard curve and the concentration was derived. The result was multiplied by 30 which is the final dilution factor. To obtain the Nitrate concentration, the concentration of endogenous nitrite is subtracted from total nitrite (endogenous nitrite + nitrate converted to nitrite). Finally, the nitrate nitrite ratio was calculated (serum nitrate/endogenous nitrite).
-
hs-CRP estimation by Immuno turbidimetric method. (Erba CRP –HS)
-
Estimation of serum total cholesterol by (CHOD/PAP) method. (Coral-clynical system)
-
Estimation of serum Triglyceride by (GPO/PAP) method. (Coral-clynical system)
-
Estimation of serum HDL- cholesterol by Direct Enzymatic method. Polyvinyl Sulfonic acid (PVS) and Polyethylene-glycol-methyl ether (PEGME) coupled classic precipitation method. (Kit used Erba XL system pack)
-
LDL- cholesterol and VLDL cholesterol values in mg/dl were indirectly calculated by using the formulae of Friedwald and Fredrickson (1972).
Statistical analysis:
Statistical analysis of the study was done by SPSS (statistical package for social sciences) software (version 21 original) after obtaining the data at the end of the study. P-value less than 0.05 was considered to be statistically significant.
This study was cleared by the Institutional Ethics committee as per ref no. MC/Kol/IEC/195/12-2013 Dt 21.12.2013 Proforma.
RESULT:
In this study, 50 newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes patients in the age group of 31-65 years of both sexes were selected from the outpatient department of Endocrinology considering the inclusion and exclusion criteria and 50 healthy age and sex-matched volunteers were selected as controls between January 2014 to January 2015.
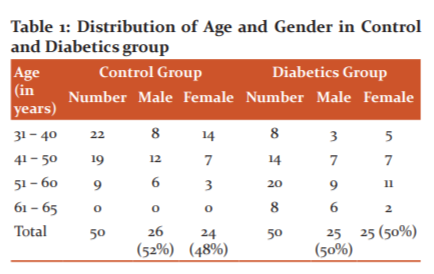
Table 1 describes the age-gender distribution of the control and case (diabetics) group. The control group consists of 26 (52%) male and 24 (48%) female volunteers whereas in the case group, amongst 50 cases, 25 (50%) were male and 25 (50%) were female.
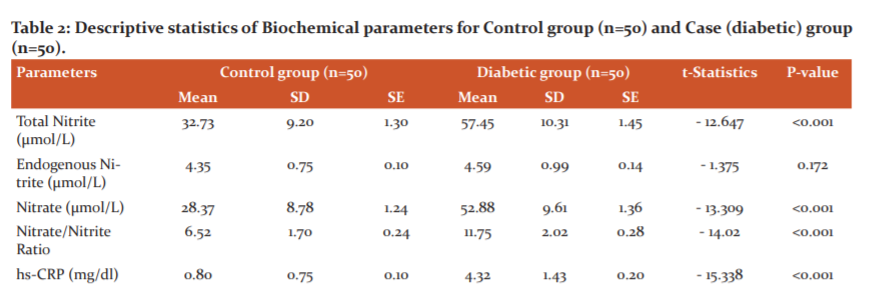
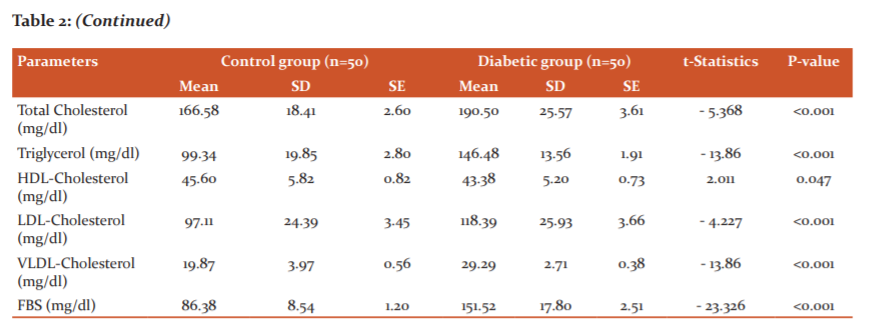
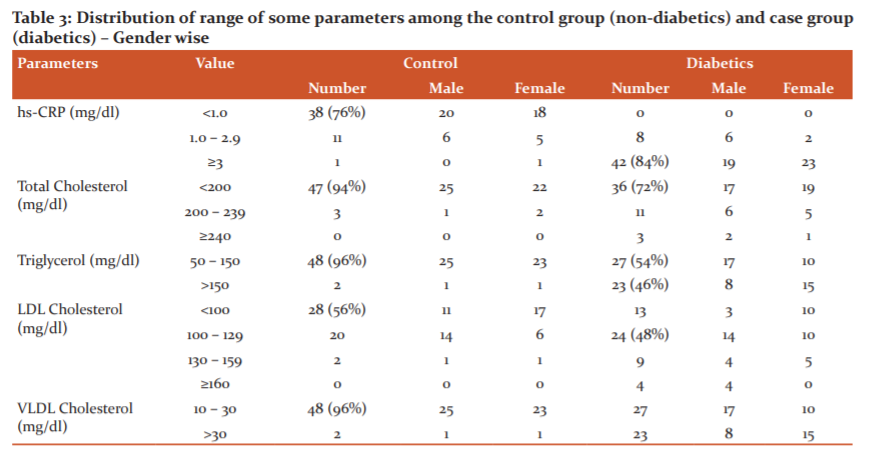
For both, the group's different biochemical variables were measured. Among the biochemical parameters FBS, hsCRP, Nitrate and Nitrites (NOx), Total cholesterol, Triglyceride, HDL-Cholesterol, LDL-Cholesterol, and VLDL-Cholesterol were done. All these data are thoroughly described in table 2, table 3 and table 4.
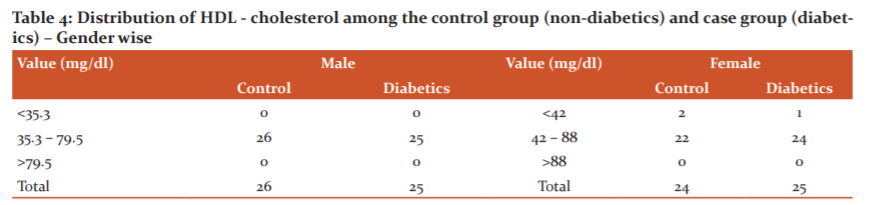
Inferential Statistics:
In the case (diabetics) group, different parameters were analyzed and the comparison was done which was in the tabular form below, p-value <0.05 is significant.
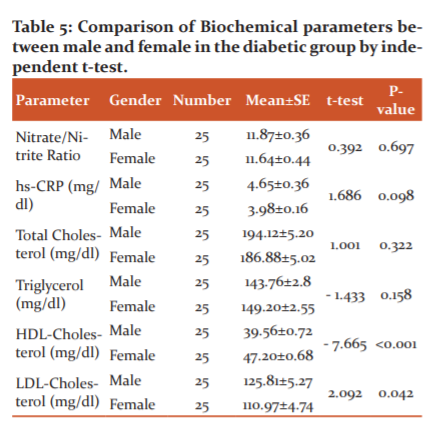
From this table 5, it is evident, only HDL-Cholesterol and LDL-Cholesterol; these two parameters are statistically significant when the parameters from male diabetics and female diabetics are analyzed.
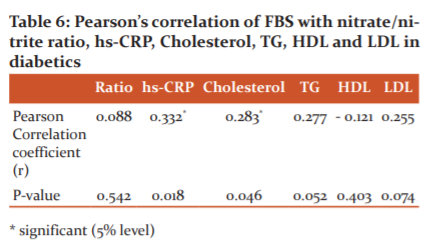
The above table 6 showed there is significant positive correlation of FBS with hs-CRP and total cholesterol. No significant correlation was found between FBS and Nitrate/Nitrite Ratio, TG, HDL & LDL.
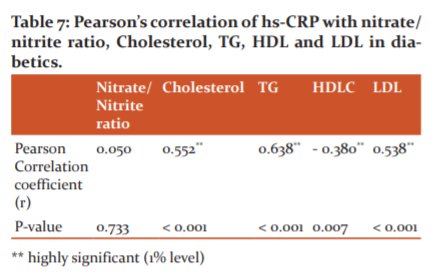
The above table 7 showed that hs-CRP has got highly significant positive correlation with total cholesterol, TG, LDL and a highly significant negative correlation with HDL. But it has got no significant relation with the Nitrate/Nitrite Ratio.

The above table 8 showed that the Nitrate /nitrite ratio(NO) were positively correlated with FBS, hs-CRP, total cholesterol, triglyceride and LDL but statistically not significant. Also, the Nitrate/ nitrite ratio (NO) with HDL-C were negatively correlated but statistically not significant.
DISCUSSION:
Diabetes mellitus (DM) is a group of metabolic diseases characterized by hyperglycemia resulting from defects in insulin secretion, insulin action, or both. The current global epidemiological evidence gives us a bitter but unavoidable message regarding the burden of Diabetes. Today, 382 million people are living with diabetes worldwide. This number is increasing day by day very rapidly and it is estimated that this number will reach 592 million by 2035. Recently Middle East, Western Pacific, sub-Saharan Africa and Southeast Asia – these regions are declared as a diabetic hotspot where economic development has transformed lifestyles.1 Temporary or permanent impairment in lifestyle and premature deaths due to diabetes and its associated complications, is increasing day by day very rapidly which reflects the burden of diabetes. The current NCEP III guidelines recommend treating patients of T2DM as coronary artery disease equivalents. It is associated with a two to fourfold excess risk of coronary heart disease, higher postinfarction fatality rate and sudden cardiac death.3
Endothelial dysfunction is regarded as a major cardiovascular risk factor in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (DM). Among the number of factors involved in maintaining proper vascular homeostasis, nitric oxide (NO) plays a pivotal role in guaranteeing physiological endothelial function.2 Various studies showed that plasma NO metabolites (nitrites and nitrates, collectively termed as NOx) levels were significantly higher in diabetics than in controls suggesting an association with excessive production and/or inactivation of NO.8, 9 The endothelial dysfunction associated with Diabetes has been attributed to lack of bioavailable NO due to oxidative and nitrosative stress.10
CRP is a classical acute phase reactant, synthesized by the liver in response to and as part of the inflammatory response.11, 12 In people with diabetes, high CRP levels (> 0.8 mg/dl) were associated with a two-fold increase in CV mortality after adjusting for age, sex, and glucose tolerance tests.4, 13, 14 Inflammation and endothelial dysfunction followed by oxidative stress – the sequence which is ultimately responsible for the development and progress of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and all sorts of its complications.
In lipid metabolism, several steps are influenced by insulin; so dyslipidemia (increased level of serum total cholesterol, LDL cholesterol and triglycerides and significantly reduced level of serum HDL cholesterol) is the most common features of diabetes.15
In this present study, the control group, 26 (52%) were male and 24 (48%) were female, whereas in the diabetic groups 25 (50%) were male and 25 (50%) were female (Table 1). The study subjects were age-sex matched. In this study, 8 (16%) diabetics are of intermediate risk and 42 (84%) are of high risk for CVD (Table 3). Comparison of serum hsCRP level by independent t-test in control (mean±SE; 0.80±0.10 mg/L) and diabetic (mean±SE; 4.32±0.20 mg/L) which is statistically significant, p-value <0.001.
In the studies of Yasufumi et al (2005)16, Simin et al (2007)17, Abbas et al (2007) 18 and Mohan et al (2005)19 done across the world have projected similar results of high hs-CRP level in the diabetics.
The values of parameters of lipid profile; total cholesterol (control group, mean±SE; 166.58±2.60 mg/dl and diabetic group, mean±SE; 190.50±3.61 mg/dl), LDL-cholesterol (control group, mean±SE; 97.11±3.45 mg/dl and diabetic group, mean±SE; 118.39±3.66 mg/dl), VLDL cholesterol (control group, mean±SE; 19.87±0.56 mg/dl and diabetic group, mean±SE; 29.29±0.38mg/dl), HDL cholesterol (control group, mean±SE; 45.60±0.82 mg/dl and diabetic group, mean±SE; 43.38±0.73mg/dl) and triglyceride (control group, mean±SE; 99.34±2.80 mg/dl and diabetic group, mean±SE; 146.48±1.91mg/dl) were analyzed by independent t-test. All are statistically significant.
Asegaonkar Shilpa B et al.3 Maryam J Jalali et al.20 Rhee EJ et al. 21 Palvasha Waheed.22 Abha Gupta et al.23 have shown similar results in their studies.
In this study, it has been observed that the level of mean Total nitrite (nitrate + endogenous nitrite) value (57.45 μmol/L), the mean nitrate value (52.88 μmol/L) and mean Nitrate/Nitrite ratio (11.75) in diabetics was in the higher side and is statistically significant in comparison with the same of the control group. The mean Endogenous Nitrite value in the diabetic group was higher than that of the control, but it is statistically not significant.
Hyperglycemia, insulin resistance and elevated free fatty acid triggers systemic inflammation and impaired NO bioavailability leading to impaired endothelial function.2 In some prospective studies, reduced level of NO bioavailability is established as a predictor of dyslipidemia as it is an endogenous anti-atherosclerotic molecule.24, 25 Rajlakshmi Sarangi et al.2 Konukoglu D et al.26 Cassone-Faldetta et al.27 Maryam J Jalali et al.20 have shown increase NOx level in the diabetics in comparison to healthy control.
Yugar-Toledo et al.28 found that patients with diabetes showed an increase in plasma Nitrite/nitrate level suggesting an association with excessive production and/or inactivation of NO. In contrast to the above studies, Amrita Ghosh et al.29 observed that serum NO was significantly low in diabetic participants as compared to control.
In our study, the mean HDL-C level of male diabetics was lower than females and the difference is statistically highly significant. The mean LDL-C is higher in male diabetics than females and the difference was weakly significant. But no significant difference found in the mean value of TG, Total cholesterol, hs-CRP and Nitrate/Nitrite Ratio between male and female diabetics (Table 5).
In Pearson correlation values, FBS with hsCRP and total cholesterol were positively correlated and statistically significant, but HDL-C were negatively correlated and statistically insignificant (TABLE 6). Pearson correlation values of hs-CRP with total cholesterol, triglyceride, with LDL were statistically significant in diabetics and a significant negative correlation was found with HDL-C (Table 7). Pearson correlation values of Nitrate/nitrite ratio (NO) with FBS, hs-CRP, total cholesterol, triglyceride, LDL-cholesterol and HDL-cholesterol were statistically not significant (Table 8).
CONCLUSION:
The hs-CRP is a marker of inflammation and a strong indicator of the risk of CVD. Its concentration is raised in Type 2 DM signifies that type 2DM is associated with low-grade inflammation. However rise in cholesterol, triglyceride, LDL-C and low HDL-C can only be explained by the loss of regulation in lipid metabolism. As cholesterol is a negative acute-phase reactant, a significant positive correlation between hs-CRP and cholesterol indicates that type 2 DM is not an acute inflammatory response but a low-grade systemic inflammation.
The significant rise of Nitrate/Nitrite ratio (NO) reflects that the Nitrosative stress is more in Type2 DM but its insignificant correlation with FBS, lipid profile and hs-CRP signify that the raised level of NO metabolites may be influenced by several other unidentified factors which were not addressed in the study.
LIMITATIONS OF THIS STUDY:
NO (predictor of nitrosative stress) measurement is complicated because its value represents the flux of production, degradation and excretion of NOx. Particularly the sources of NOx consist of endothelial production, cytotoxic injury via i-NOS and the intake of exogenous nitric oxides such as green vegetables, meat preservatives and so on. Additionally, serum NOx level is influenced by its distribution to extracellular fluid, plasma half-life and urinary excretion. So more standardized method for NOx determination is required. Moreover, this was a single centred study, which is situated in the eastern zone of India. However, a large sample size is required to establish the findings of the current study.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS:
I express my gratitude to all the faculty members and technical staffs of the Department of Biochemistry and Department of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Calcutta Medical College and Hospital, Kolkata who had helped to collect, analyse and compile huge data concerned with this work. The authors acknowledge the immense help received from the scholars whose articles are cited and included in references of this manuscript. The authors are also grateful to authors/editors/publishers of all those articles, journals and books from where the literature for this article has been reviewed and discussed.
Conflict of interest: No
Source of Funding: No internal/external funding/grant was received for the study. It was solely funded by principal investigator himself
AUTHORS’ CONTRIBUTION:
Dr. Bithika Ghosh: Concept and design of the study, reviewed the literature, Collection of the data, Final approval.
Dr. Saumyajit Maiti: Conceptualization of the study, manuscript preparation and editing
Dr. Kasturi Mukherjee: Critical revision of the manuscript, Literature search, Statistical analysis and its interpretation.
References:
-
IDF Diabetes atlas. 2013; 6th edition.
-
Sarangi R, Padhi S, Mahapatra S, Bhumika N. Serum Nitric Oxide metabolites and high-sensitivity C-reactive protein are important biomarkers in non-obese Indian Type 2 Diabetic males. Int Diabe
-
tes Dev Ctries. 2012 Sep; 32(3):163-168.
-
Asegaonkar SB, Bavikar JS, Marathe A, Tekade M, Asegaonkar BN, Bardapurkar J. High Sensitivity C-reactive protein is associated with Traditional Cardiovascular Risk Factors in Indians with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Int J Biomed Adv Res. 2013; 4(3): 160-66.
-
Pfutzner A, Forst T. High sensitivity C- reactive protein as a cardiovascular risk marker in patients with diabetes mellitus. Diab Techn Therap. 2006; 8(1): 28-36.
-
Savage DB, Petersen KF, Shulman GI. Disordered lipid metabolism and the pathogenesis of insulin resistance. Physiol Rev. 2007 Apr; 87(2):507-20
-
Ross HM. The Dangers of High Cholesterol and Diabetes. Updated July 22, 2011.
-
Cortas NK, Wakid NW. Determination of inorganic nitrate in serum and urine by a kinetic cadmium-reduction method. Clin Chem. 1990 Aug; 36 (8 Pt 1):1440-3.
-
Dejam A, Hunter CJ, Pelletier MM, Hsu LL, Macado RF et al. Erythrocytes are major intravascular storage sites of nitrite in human blood. Blood. 2005 Jul 15;106(2):734-9
-
Pawloski JR, Hess DT, Stamler JS. Export by red blood cells of nitric oxide bioactivity. Nature. 2001 Feb 1;409(6820):622-6.
-
Ghasemi A, Zahediasl S, Azimzadeh I, Azizi F. Increased serum nitric oxide metabolites in dysglycaemia. Ann Human Biol. 2011 Sep;38(5):577-82.
-
Asl SZ, Ghasemi A, Azizi F. Serum nitric oxide metabolites in subjects with metabolic syndrome. Clin Biochem. 2008 Nov; 41(16-17):1342-7.
-
Tsai DC, Chiou SH, Lee FL, Chou CK, Chen SJ, Peng CH, et al. Possible Involvement of Nitric Oxide in the Progression of Diabetic Retinop Ophthalm. 2003; 217: 342–6.
-
Chiriboga DE, Ma Y, Li W, Stanek EJ, Hebert JR, Merriam PA et al. Seasonal and sex variation of the high sensitivity C-reactive protein in healthy adults: A longitudinal study. Clinical Chemistry Clin Chem. 2009 Feb; 55(2): 313–321.
-
Jager A, Van Hinsberg VW, Kostense PJ. CRP and five-year mortality in diabetic subjects: The Hoorn study. Arteioscl Throm Vasc Biol.1999; 12: 3071-80.
-
Yoshimasa ASO, Wakabayashi S, Yamamoto R, Matsutomo R, Kohzo, Takebayashi, Inukai T. Metabolic syndrome accompanied by hypercholesterolemia is strongly associated with proinflammatory state and impairment of fibrinolysis in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2005;28:(9) 2211-6.
-
Doi Y, Kiyohara Y, Kubo MK, Ninomiya T, Wakugawa Y, Yonemoto Ket al., (2005). Elevated c-reactive protein, is a predictor of the development of diabetes in a normal Japanese population. Diabetes Care. 2005 Oct; 28(10): 2497-2500.
-
Liu S, Tinker L, Song Y, Rifai N, Bonds DE, Cook NR, et al. A prospective study of inflammatory cytokines and diabetes mellitus in multiethnic cohort of postmenopausal women. Arch Int Med. 2007 Aug 13-27;167(15):1676-85.
-
Dehghan A, Hoek MV, Eric J.G. Stijnen ST, Hofman A, Jacqueline C.M. Witteman. Risk of Type 2 diabetes attributable to C - reactive protein and other risk factors. Diabetes Care. 2007 Oct; 30(10): 2695-2699.
-
Mohan V, Deepa R, Velmurugan K, G. Premalatha. Association of C - reactive protein with body fat, diabetes and coronary artery disease in Asian Indian’s. The Chennai Urban Rural Epidemiology Study (CURES-6). Diab Med. 2005 July; 22(7):863-870.
-
Maryam J. Jalali, Madhavi S. Phadke. Assessment of Endothelial Dysfunction in Health and Disease; Using Various Parameters. Ind J Clin Biochem. (Oct-Dec 2011) 26(4):407–412.
-
Rhee EJ, Kim YC, Lee WY, Jung CH, Sung KC, Ryu SH, et al. Comparison of insulin resistance and serum high-sensitivity C-reactive protein levels according to the fasting blood glucose subgroups divided by the newly recommended criteria for fasting hyperglycemia in 10059 healthy Koreans. Metabol. 2006 Feb;55(2):183-7.
-
Waheed P, Naveed AK and Farooq F. Levels of Inflammatory Markers and their Correlation with Dyslipidemia in Diabetics. J Coll Physic Surg Pakis. 2009, Vol. 19 (4): 207-210.
-
Gupt A, Kumar D, Rajvanshi S, Kumar A, TVS Arya. To study the association of high sensitivity c-reactive protein with newly diagnosed DM type 2. J Int Ame Med; 2015:16(1):12-15.
-
Bugiardini R, Manfrini O, Pizzi C, Fontana F, Morgagni G. Endothelial function predicts future development of coronary artery disease: A study of women with chest pain and normal coronary angiograms. Circulation. 2004 Jun 1;109(21):2518-23.
-
Halcox JP, Schenke WH, Zalos G, Mincemoyer M, Prasad A, Waclawiw MA, et al. Prognostic value of coronary vascular endothelial dysfunction. Circulat. 2002 Aug 6;106(6):653-8
-
Konukoglu D, Serin O, Turhan MS. Plasma total homocysteine concentrations in obese and non-obese female patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus; its relations with plasma oxidative stress and nitric oxide levels. Clin Hemorheol Microcirc. 2005; 33(1):41–6.
-
M Cassone Faldetta, O Laurenti, G Desideri, M C Bravi, O De Luca, M C Marinucci, G De Mattia, C Ferri. L-arginine infusion decrease plasma total homocysteine concentration through increased nitric oxide production and decreased oxidative status in Type II diabetic patients. Diabetol. 2002 Aug;45(8):1120-7.
-
Yugar-Toledo JC, Tanus-Santos JE, Sabha M, Sousa MG, Cittadino M, Tácito LHB, Moreno H Jr. Uncontrolled hypertention, uncompensated type 2 diabetics and smoking have different pattern of vascular dysfunction.Chest.2004 Mar;125(3):823-30.
-
Ghosh A, Sherpa ML, Bhutia Y, Pal R, and Dahal S. Serum nitric oxide status in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus in Sikkim. Int J Appl Basic Med Res. 2011 Jan-Jun; 1(1): 31–35.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License