IJCRR - 13(12), June, 2021
Pages: 39-43
Date of Publication: 22-Jun-2021
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
Polypharmacy and Drug Interactions Study on Diabetic Patients of Geriatric Age Group at Rural Tertiary Care Hospital
Author: Shailesh Nagpure, Krishna Kela, Akshay C. Dahiwele
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Introduction: Polypharmacy is sometimes necessary but should be carried out with precautions when prescribing to the elderly age group. It may cause drug-drug interactions which can be dangerous and may land up into life-threatening situations. Aim: To study polypharmacy and drug-drug interactions among diabetic patients of the elderly age group at rural tertiary care hospital. Methodology: It was a cross-sectional study carried out at Acharya Vinoba Bhave Rural Hosptial, Sawangi, Wardha. Data were collected from case sheets of patients (n = 100) of either sex admitted to the hospital during the two months of study duration. Result: Patients between the age group 60\?69 years were the most common (65%) followed by 70 -79 years (26%) and 80 -89 years (9%) admitted to the hospital. The average number of drugs prescribed to 60 - 69 years, 70 \? 79 years and 80 - 89 years age group were 4.85, 4.63 and 3.09 respectively. Total 402 drugs were prescribed in 100 patients and a total of 239 drug-drug interactions was observed in the current study. Conclusion: Polypharmacy is a double-edged sword. Benefit-risk assessment always should be done before prescribing mul�tiple drugs to elderly patients.
Keywords: Diabetes, Geriatric, Polypharmacy, Drug interactions, Adverse effects, Complications
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION
Ageing is a natural and continuous process that is physiological. Due to the increasing population of elderly individuals in our country, it is very essential to develop the knowledge and understanding of appropriate and safe drugs for therapeutic purposes. Geriatric medicine is an upcoming branch of medicine that focuses on various aspects of therapeutics in an elderly population.1
The geriatric population often suffer from multiple comorbidities such as diabetes, hypertension, malignancies, heart failure, age-related pharmacokinetic variability due to liver or kidney diseases, lack of adherence (voluntary or involuntary—in psychiatric disorders), and others.2 These multiple comorbidities will lead to polypharmacy practices among the elderly. Also, elderly patients are more likely to take over-the-counter medications and herbal supplements, which can further lead to drug interactions.3
Polypharmacy is defined as the concurrent use of multiple medications, whether prescription or over-the-counter, by a single patient, to manage health problems such as diabetes, hypertension.4
Drug interactions refer to the modification of response to one drug by another when they are administered simultaneously or in sequence. The possibility of drug-drug interactions increases when more than one drug are prescribed in the same prescription. Although, the seriousness of these interactions in most of the cases is unpredictable.2
Potential drug-drug interaction after prescribing multiple drugs among the elderly must be carefully assessed.5
Polypharmacy practice in elderly patients can cause certain drug-drug interaction, which may affect the treatment provided to the patients, which ultimately increases the burden on health care providers and facilities.6
To find such potential hazards of drug interactions associated with polypharmacy in elderly diabetic patients of rural area, this study is planned.
METHODOLOGY
A cross-sectional observational study was conducted at rural tertiary care teaching hospital in Central India, Acharya Vinoba Bhave Rural Hospital (AVBRH). The ethical clearance number was DMIMS (DU) / IEC /May – 2020/8860 dated 30 June 2020. The study was conducted for 2 months, in this duration, a total of 100 patients were studied. The study was supervised based on elderly diabetic community admitted in the medicine ward of AVBRH, a rural tertiary care hospital, above 60 years of age of either sex ready to give consent were involved in this study and the patients of intensive care unit, patients with serious ailments, malignancies and other fatal, lethal, destructive issues were eliminated from the study. The study aimed to assess polypharmacy and various drug-drug interactions among geriatric diabetic patients admitted in the medicine ward at the rural tertiary care hospital. The study was designed to find out the potentially unsuitable drugs being prescribed by applying “Beers Criteria.” Data collection was done by the assessment of case sheets of the geriatric diabetic patients admitted in the medical ward. Likewise, the case sheets of all the patients were evaluated by the study investigator every day during the study time. The evaluation of case sheets was studied only once for each patient during one single admission. Comparatively to which, if any patient was admitted in the medicine ward more than once during this study time, the case sheet of such patients was considered as a separate case sheet or separate admission.
RESULTS
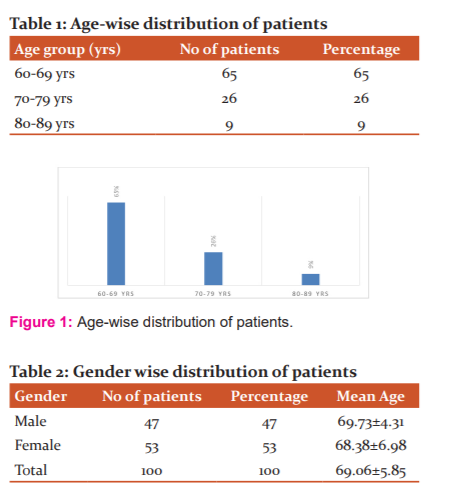
The entire study population was categorized into three age groups 60–69, 70–79, and 80–89. The age group 60–69 years were the most common geriatric diabetic patients admitted during the study time with 65% of the total study population, followed by 70–79years age group with 26% of the total study population. The third group of Geriatric patients of the 80–89years age group were admitted in fewer number and represents 7% of the total study population. The maximum age of patient admitted in the medicine ward was 89years and the minimum age of the patient was 60years [Table 1 and Figure 1]. The males were 47 in number and females were 53 in number out of the total population.
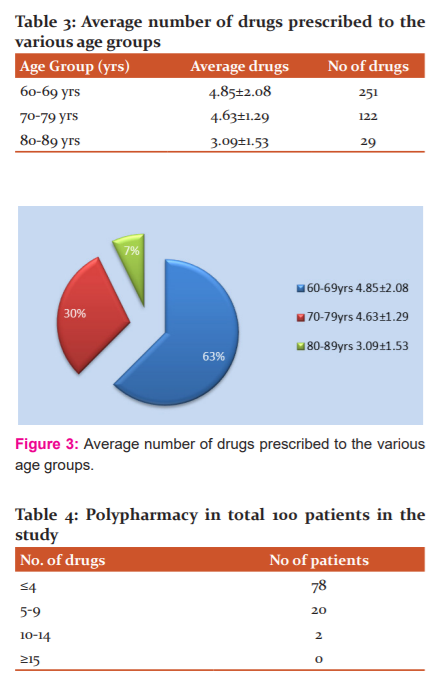
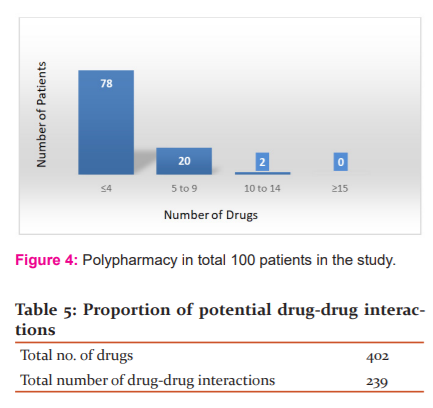
The mean age of patients was 69.06 ± 5.85 years [Table 2 and Figure 2]. Whereas, the mean number of drugs prescribed to the study population admitted in the medicine ward was (4.08 ± 1.20). Out of the total number of drugs prescribed, ≤4 number drugs were prescribed to 78% population, 5-9 number of drugs were prescribed to 20% population, and 10-14 drugs were prescribed to 2% population [Table 3 and Figure 3].
Most numbers of drugs were prescribed to 60–69 years age group with 251 number drugs in the study population, followed by 70–79 years and 80–89 years age groups which were prescribed with 122 and 9 number of drug, respectively [Table 4 and Figure 4].
Out of the total of 402 medicines prescribed to the study population, 289 potential drug-drug interactions were observed among elderly diabetic patient [Table 5 and Figure 5]. The most common drug-drug interactions observed in the study population were of moderate grade 198(2.03%), Mild drug-drug interactions were 52(7.73%) whereas severe drug-drug interactions were 39(10.30%) [Table 6 and Figure 6]. Out of 402 drugs prescribed to the study population, the total number of potentially inappropriate medicine was 8 in number [Table 7 and Figure 7].

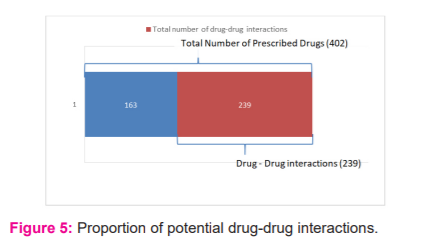
Out of the total 402 prescribed drugs, 239 drug-drug interactions were observed.
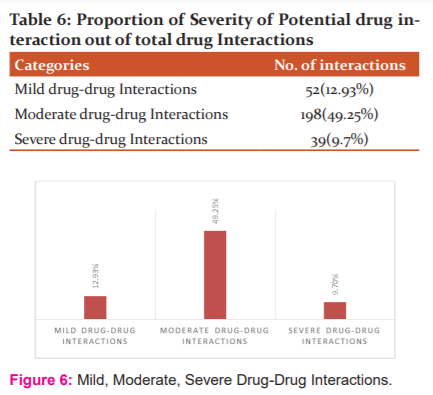
Out of the total drugs administered in 100 patients, mild, moderate and severe type of drug-drug interactions observed were 12.93%, 49.25% and 9.7% respectively.
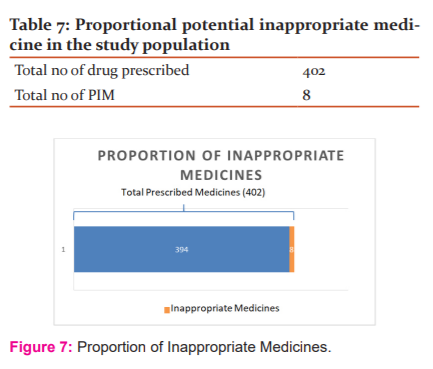
402 medicines were prescribed in 100 patients out of which 8 medication were found to be potential inappropriate medicine.
DISCUSSION
According to the study, the maximum number of patients were between the age group 60-69 years admitted in the medical ward and the number of patients admitted declined with age. Similarly, the maximum number of drugs were prescribed to the patients between the age group 60-69 years. The findings of our study are analogous to the study findings by Armugam A. In this study, a large number of drugs were advised to the age group ≥75 years of age. Although, the results of our study were different from the study by David Baumgartner. In this study, there was an increase in the mean number of drugs advised to elderly patients.
The mean number of drugs prescribed to geriatric patients admitted in the medicine ward was 402. Among this, 78% of the population were prescribed with ≤4 number drugs, 20% of the population were prescribed with 5-9 number of drugs and 2% of the population were prescribed with 10-14 number of drugs. The findings of our study were similar to Armugam et al. and Schuler et al study findings. In both of the above-mentioned study, the polypharmacy observed in elderly patients was >55%. Corresponding to which the polypharmacy in Kaufman and Zaveri HG study was considered when more than 5 drugs were prescribed to a patient. Since our study findings resulted in higher polypharmacy than that of international reports, it might be due to patients not responding to the medication, so more options of drugs were used by doctors to treat the elderly patient admitted in the medicine ward. Along with this, the study results indicated several drug-drug interactions. Online drugs interaction checker of drugs.com was reported interaction in the extensive majority of patients. In a study conducted by Gosney M, 33% of potential drug-drug interactions in all prescriptions in admitted elderly patients were seen. The 71.89% (289) of drugs caused potential drug-drug interactions out of the 402 drugs prescribed to the geriatric population. According to our study, 49.25% of potential drug interaction were most common in the population of the elderly. When compared to a study conducted by Björkman et al. in the year 2002, drug interactions were present in 46% of patients. Moreover, Gosney M’s study revealed 33% of potential drug-drug interaction, prescribed to elderly patients admitted in the medical ward.
To find out the drug interaction, different computerized drug-drug interaction programs were used in various studies. The studies showing potential drug-drug interaction should be differentiated from those studies determining the actual drug interaction with the adverse patient outcome as a result of a drug interaction. The probability of drug-drug interactions increases exponentially with the number of drugs prescribed as there are an additional couple of drugs to interact. The ubiquity of clinically appropriate drug interactions in patients taking 2-4 medication is about 6%, those taking 5 medication is 50% and those taking 10 medication is around 100%. Accordingly, we noticed potential drug-drug interaction in >50% of patients in our study also. Various studies noticed low levels of sensitivity and specificity while testing the functioning of drug interaction software, however recent studies specified that sensitivity and specificity have been upgraded.
For evaluating the appropriateness of prescribing medications in the geriatric population, beer’s criteria is a very constant method used. It was recently updated by the American Geriatric Society in 2012 and was developed in 1999. 1.98% potentially inappropriate medicines were prescribed of total prescribed drugs in elderly patients in our study. Similarly, a study showed potentially appropriate medicines in 22.1% of patient at admission conducted in South India by Harugeri which is much higher than our study findings. Our study findings are alike to a study in which she observed 4.33% of patients by Veena et al. in 2012. Although, our study findings are different from the study conducted by Rothberg et al. in 2008 in which he noticed at least 1 potential appropriate medicine in 49% of patients. The reason for the contradiction may be that our study was conducted in a limited population in tertiary care hospital whereas a study done by Harugeri and Rothburg was conducted on a large population. An increased number of medications may benefit to few patients, but it can be dangerous for other patients. Therefore it is necessary to find out about the inappropriate medicines and their possible drug-drug interactions.
Hence, polypharmacy in the geriatric population causes many problems like the use of potentially inappropriate medicines and increased probability of drug-drug interactions, but on the other hand, we cannot ignore it as this population suffered from numerous chronic diseases. For ensuring the safety of the geriatric population and curbing irrational prescriptions, awareness should be created by physicians about life-threatening drug-drug interactions and polypharmacy.
Conclusion
The conclusion from the present study suggests that polypharmacy is a vital risk factor for secondary morbidity in geriatric patients. The use of various drugs to treat various diseases is necessary, but the unnecessary overload of drugs to the patient will increase the safety problems. Polypharmacy leads to potentially inappropriate medicine use and potential drug-drug interactions. Also, it can be avoided by proper planning and treatment goals. Appropriate prescribing is more important than decreasing the number of prescribed drugs to ensure safety in this high-risk population. Small population and restriction to one speciality are the limitations of the study. To perceive this important problem and to make the prescriptions more rational, larger studies including geriatric patients in the different department was mandatory.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
We would like to thank to the staff from the Department of Medicine of Acharya Vinoba Bhave Rural Hospital, Sawangi (Meghe).
FINANCIAL SUPPORT AND SPONSORSHIP
None
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST
There are no conflicts of interest.
Authors contribution
Dr Shailesh Nagpure – Synopsis preparation and conduction of the study
Krishna Kela - Data collection
Corresponding author: Dr Akshay Dahiwele – Manuscript preparation
References:
-
Varma S, Sareen H, Trivedi JK. The geriatric population and psychiatric medication. Men's Sana Monogr 2010;8:30-51.
-
Salwe KJ, Kalyanasundaram D, Bahurupi Y.A Study on Polypharmacy and Potential Drug-Drug Interactions among Elderly Patients Admitted in the department of medicine of a tertiary care hospital in Puducherry. J Clin Diagn Res. 2016 Feb;10(2): FC06-10.
-
Dobric? EC. Polypharmacy in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Insights from an Internal Medicine Department. Medicine. 2019;55(8):436.
-
Stawicki A, Stanislaw D, Gerlach H, Anthony J. Polypharmacy and medication errors: Stop, Listen, Look, and Analyze. OPUS Sci. 2009; 3(1):6-10.
-
Chester B. Good Polypharmacy in Elderly Patients With Diabetes Oct 2002, 15 (4) 240-248.
-
TurnheimK.Drug therapy in elderly .Exp Gerontol. 2004 Nov-Dec;39(11-12):1731-8.
-
Antonelli Incalzi R, Corsonello A, Pedone C, Corica F, Carbonin P. Depression and drug utilization in an elderly population. Ther Clin Risk Manag. 2005 Mar ;1(1):55-60.
-
Marengoni A. Aging with multimorbidity: A systematic review of the literature. Ageing Res Rev. 2011;10:430?9.
-
Sousa RM. Contribution of chronic diseases to disability in elderly people in countries with low and middle incomes: A 10/66 dementia research group population?based survey. Lancet. 2009;374:1821?30.
-
Harugeri A, Joseph J, Parthasarathi G, Ramesh M, Guido S. Prescribing patterns and predictors of high-level polypharmacy in the elderly population: A prospective surveillance study from two teaching hospitals in India. Am J Geriatr Pharmacother. 2010;8:271?80.
-
Armugam A, Leon TS, Kugap P, Dhamraj SA. Polypharmacy in elderly patients at discharge medication. Int J Pharm Res Dev. 2011;3:1?9.
-
Sharma HL, Sharma KK. Principles of Pharmacology. 2nd ed. Hyserabad: Paras Medical Publishers. 2011. p. 906?7.
-
Agrawal RK, Nagpure S. A study on polypharmacy and drug interactions among elderly hypertensive patients admitted in a tertiary care hospital. Int J Health Allied Sci. 2018;7:222-7.
-
Baumgartner D. Polypharmacy and drug interactions in elderly in? and outpatients. Int J Pharm Pract. 2010;1:34?6.
-
Zaveri HG, Mansuri SM, Patel VJ. Use of potentially inappropriate medicines in elderly: A prospective study in medicine outpatient department of a tertiary care teaching hospital. Indian J Pharmacol. 2010;42:95?8.
-
Srivastava SK. A Complete Textbook of Medical Pharmacology. 1st ed. New Delhi: A vishal Publishing Company; 2013:1322?3.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License