IJCRR - 13(12), June, 2021
Pages: 27-33
Date of Publication: 22-Jun-2021
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
Study of Leucorrhoea in Reproductive Age Group in Patients Attending OPDs in Saraswathi Institute of Medical Sciences, Hapur, Uttar Pradesh
Author: Swati, Sarandeep Singh Puri, Seema Goel, Parul Singhal
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Background: 'Leucorrhoea', a fairly common gynaecological issue, is an abnormal vaginal discharge often associated with ir�ritation and is non-hemorrhagic. The objectives to investigate the various causes of leucorrhea among reproductive-age women. METHODS: The present study was conducted on 250 patients of adult female patients of the reproductive age group (aged 18 years to 45 years), clinically presenting with complaints of leucorrhoea during the period from October 2018 to December 2019 in the OPD Saraswathi In�stitute of Medical Sciences in Hapur, Uttar Pradesh. The PAP smear findings to establish the profile of the causative organism, presence of microorganisms done by wet mount, Gram staining and KOH mount and identify the bacterial and fungal pathogens of the indicated cases by culture identification. Results: Age-wise distribution showed most common in the age group of 26-30 years, type of discharge thin mucoid in (72.8%), followed by thick curdy discharge in (16.8%).On PAP smear subjects were Negative for intraepithelial lesion or malignancy (NILM) (88%), a minor proportion of subjects (0.8%) had a high-grade squamous intraepithelial lesion (HSIL), Atypical squamous cells-cannot exclude HSIL (ASC-H) (0.8%), and squamous cell carcinoma (0.8%). The majority of females (34%) were seen to have S. aureus as observed on the bacterial culture of leucorrhoea secretions and fungal culture majority of females (27.2%) were seen to have the presence of C. Albicans. Conclusion: A significant association of leucorrhoea with socio-demographic factors, clinical features, PAP smear, bacterial as well as fungal culture in the present study emphasizes the need for health education and preventive practices related to personal & menstrual hygiene & family planning practices in females.
Keywords: Leucorrhoea, Menstrual hygiene, Reproductive age
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION-
‘Leucorrhoea’, a fairly common gynaecological issue, is an irregular vaginal secretion frequently connected with irritation and is non?hemorrhagic. White, yellow or greenish discharges might be an indication of underlying pelvic pathology. It relates to more than an estimated 1/4th of patients’ visits to the gynaecologist.1
This may be physiological or pathological. An augment to the normal vaginal discharge develops physiologically at puberty, during pregnancy, at ovulation, sexual arousal and the premenstrual phase of the menstrual cycle. Pathological secretions may be communicable or non-infectious. Infectious secretions may be due to explicit contagion such as Gonorrhoea, Trichomoniasis, Chlamydiasis, which are sexually passed on, and commotions in the normal vaginal flora cause Moniliasis and Bacterial vaginosis.
It is measured that transformation in the vaginal epithelium; changes in the usual bacterial flora and pH of the vaginal discharge dispose to leucorrhoea. But when it turns into a pathological situation it creates connected troubles like low backache, itching and burning sensation of the vulva, poor appetite, uneasiness, common weakness, pain in both legs etc.
As there are very few similar studies in this region, and none in the Hapur area of Uttar Pradesh, this study was undertaken to investigate the various causes of leucorrhea among reproductive-age women attending OPD of a tertiary hospital (Saraswathi Institute of Medical Sciences) in Hapur, Uttar Pradesh
The study aims to investigate the causes of Leucorrhea in reproductive age group women among patients visiting the OPD of a tertiary care hospital (Saraswathi Institute of Medical Sciences) in Hapur, Uttar Pradesh. The objectives of the study are:
-
To study the PAP smear findings in the patients presenting with leucorrhoea to establish the profile of the causative organism such as bacterial, fungal, trichomonal or neoplastic.
-
To study the presence of various micro-organisms in patients resenting with leucorrhoea, identification done by wet mount, Gram staining and KOH mount.
-
To isolate and identify the bacterial and fungal pathogens of the indicated cases by culture identification.
MATERIAL AND METHODS
Study Design
The present study is an Observational, Cross-sectional, and the inferential study conducted in Saraswathi Institute of Medical Sciences, Hapur (Uttar Pradesh).
Study Area:
The study was conducted among OPD patients of SIMS Hapur (UP), India.
Study Period:
The study was conducted from October 2018 to December 2019.
SELECTION OF CASES
Inclusion Criteria:
-
Adult female patients of the reproductive age group (aged 18 years to 45 years).
Exclusion Criteria:
-
All patients below 18 years and above 45 years.
Clinical History and Examination regarding Leucorrhoea:
-
-
-
-
Gynaecological history of the patient, including parity, age at first childbirth, mass per-vaginum, history of any STD.
-
Amount, duration, colour and odour of discharge.
Visualization of Cervix: to rule out erosion, hypertrophy, suspicious growth
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
Wet Smear preparation: After a thorough vaginal examination a sample of the discharge was taken. A wet smear was prepared. For wet smear preparation, a drop of normal saline is put on a slide and mix a drop of the vaginal discharge. Placed a cover slip on the drop.
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
Then the smear was examined immediately first under low power, and later under high power for various micro-organisms like T.vaginalis (motile and flagellated), Candida (budding yeasts) along polymorphonuclear leukocytes, bacteria may be identified in wet film preparations. For further identification of various organisms, tests like the Germ Tube test were put along with various biochemicals and cultures were incubated and confirmed in the Department of Microbiology.
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
Simultaneously, the discharge was spread over another few slides for PAP staining (Papanicolau stain). Smears were immediately fixed in absolute alcohol and stained according to the PAP staining method. The cytopathological changes observed in the cervical squamous were graded according to the Bethesda system for reporting cervical cytology
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
C/S: The PAP smear showing various neutrophils or pus cells were segregated. Discharge of the cases was processed for culture/sensitivity.
Statistical Analysis:
Statistical analysis was performed using SPSS (Statistical Package for the Social Sciences) for Windows (version 24.0).
RESULTS
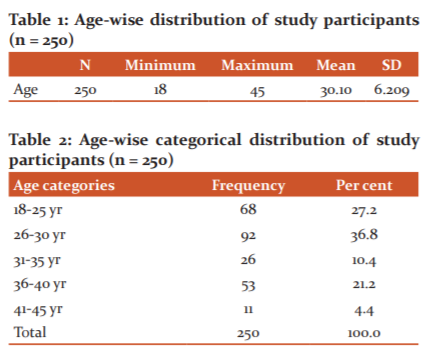
The age-wise distribution of the study participants (all females) showed that the majority of them was in the age group of 26-30 years shown in Table 1,2,3.

The type of discharge, majority of women have a thin mucoid type discharge from the vagina (72.8%), followed by less commonly reported thick curdy discharge (16.8%).
The majority of women had a ‘moderate’ amount of discharge (61.6%), followed by a less commonly ‘minimal’ amount of discharge (23.2%).
Colour of discharge, majority of women reported a greyish colour (52.8%), followed by less commonly white coloured discharge (39.2%).
More than three-fourth (76.4%) of women reported having a smell in discharge, while the rest 23.6% did not report any smell in their vaginal discharge ( Table 4,5,6).

Duration of leucorrhea, majority of women have been experiencing it since 2-4 months(54.8%), a less common reporting was of 1-2 months (33.6%) Table 6.
Pruritis was ‘absent in most of the females (64.8%) and was ‘present’ only in 35.2% of females.
Dysuria was ‘absent in 70% of the females and was ‘present’ only in 30%
Dyspareunia, where it was ‘absent in 80% of the females and was ‘present’ only in 20%.
The majority of females (88.8%) reported having no relationship of leucorrhoea occurrence with oral contraceptives (OCPs), while 11.2% said that there is a possible association between taking OCPs and occurrence of leucorrhoea.
More than half of the females were reported to have the relationship of leucorrhoea with intra-uterine devices (IUDs) (51.2%), while 48.8% of females did not have the relationship of leucorrhoea with IUDs
Only 25.2% of females face the problem of leucorrhoea who had undergone tubectomy procedures, whereas 74.8% did not have any such problem with tubectomy procedures. (Table 7)

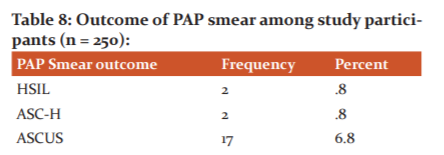
A majority of subjects were Negative for intraepithelial lesion or malignancy (NILM) (88%), followed by 6.8% subjects having atypical squamous cells of undetermined significance (ASCUS), and low-grade squamous intraepithelial lesion (LSIL) (2.8% subjects). A minor proportion of subjects (0.8%) had a high-grade squamous intraepithelial lesion (HSIL), Atypical squamous cells-cannot exclude HSIL (ASC-H) (0.8%), and squamous cell carcinoma (0.8%) ( Table 8).


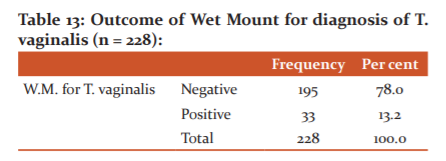
The outcome of Wet Mount for diagnosis of T. vaginalis among study participants, only 13.2% of study subjects were positive for T. vaginalis, and 78% of subjects were negative.
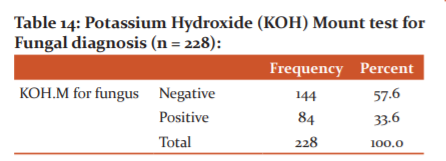
The outcome of Potassium Hydroxide (KOH) Mount for Fungal diagnosis among study participants, only 33.6% of study subjects were positive for fungal infection, and 57.6% of subjects were negative.
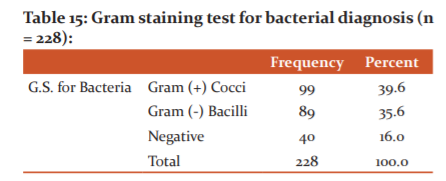
The outcome of Gram staining for Bacteria (prevalence of gram-positive/negative bacteria) among study participants, nearly 39.6% of study subjects had gram-positive cocci, and 35.6% had gram-negative bacilli, and 16% of subjects had a negative outcome. ( Table 13,14,15)
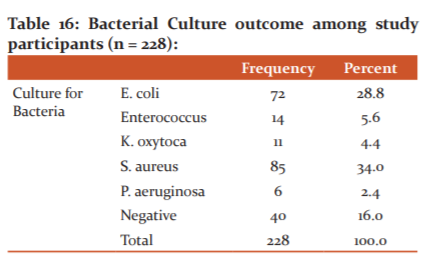
The majority of females (34%) were seen to have S. aureus as observed on the bacterial culture of leucorrhoea secretions; followed by E. coli, which was the second-highest (28.8%) observation among study participants.
A minor proportion of study subjects also presented with Enterococcus (5.6%), K. oxytoca (4.4%), and P. aeruginosa (2.4%). Around 16% of subjects had a negative outcome.
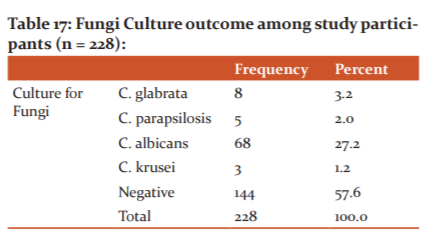
The majority of females (27.2%) were seen to have the presence of C. albicans on the culture of leucorrhoeal secretions; followed by C. glabrata (3.2%), C. parapsilosis (2%), C. krusei (1.2%). Around 57.6% of subjects had no outcome (Table 16,17)
DISCUSSION
The present study revealed that Leucorrhea is prevalent throughout life i.e. 18-45 years, but was highly prevalent in the 26-30 years age group. The findings are similar to study by Tabassum et al. in 2014 and Rudri et al. in 2017, among women 15-55 years old in Bangalore.2,3
The findings also correlate with the study by Devi U in 2013 in Nellore in which 50% of the women reporting leucorrhea belonged to the age group of 21-30 years.4
Culture for isolation of candida is a superior method in detecting vaginal candidal vaginosis. The incidence of candidiasis and TV reported in the current study were comparable to studies reported elsewhere4,5,6 Overall prevalence of TV varies from place to place, study to study and ranges from 6-14.9%.5
The chief presenting complaint in the present study was white discharge which is characteristic of leucorrhea.2 The consistency of discharge in the present study varied from thin mucoid (72.8%) to thick curdy (16.8%) and frothy (10.4%) in the current study. This is consistent with studies conducted in Banglore3, Nellore4 and Goa.7
The secretions due to noninfectious causes are non-purulent and non-offensive, nonirritant and never cause itching. Pruritis, dysuria and dyspareunia were present in 35.2%, 30% and 20% of the study participants in the present study. Itching is a common symptom in candidiasis, non-specific vaginitis and trichomoniasis. The findings correlate with the study done elsewhere.4
The mean duration of leucorrhoea in the present study was 2.89+1.32 days (Range: 1-6 days). This is in contrast to the findings reported elsewhere. In a study by Ilankoon et al in 2017 in women living in Colombo District, Sri Lanka, sought treatment at the end because the condition got worse or fear of serious disease consequences.8
Many women are not interested to discuss the symptom with their medical practitioner until matters reach such a stage that, despite their efforts at treatment, the persistence of discharge compels them to seek advice. This delay, coupled with the fact that many women regard quite a considerable amount of vaginal discharge as normal, has often the effect of making the complaint one of long duration when advice is first sought.9
Evidence indicates the minimal effect of OCP use on the vaginal epithelium and vaginal and cervical discharge, and a small effect on vaginal flora.10 The findings of our study corroborated this evidence.
The prevalence of leucorrhoea among IUD users and tubectomized women was 51.2% and 25.2% respectively in the present study. This was much higher than reported by Devi in 2013 and Kulkarni et al in 2005 in Nagpur.4,11
The findings corroborated with the study done by Nwankwo et al in 2010 among women of the reproductive age group in Nigeria.12 The IUCD has been reported to produce inflammation and changes in cervical cytopathology.
In the study done by Ocak et al in 2007 among women in Turkey, 20.7% of UD users were reported to have leucorrhoea as against 8.8% OCP users.13 Leucorrhea among IUD users is most strongly related to the insertion process and the background risk of STI.14
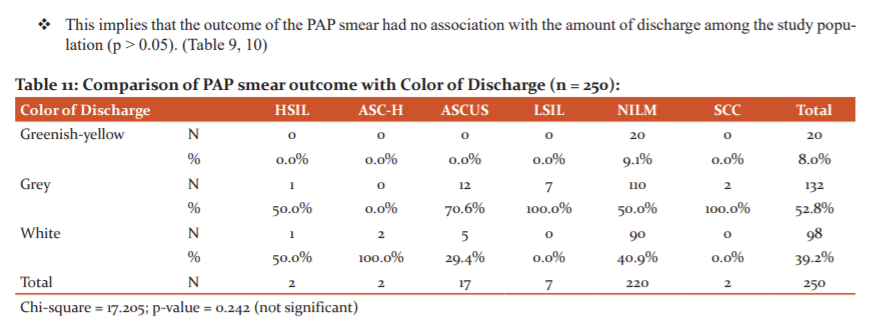
The PAP smear findings among patients in our study were similar to those reported by Sujatha et al in 2016, Yogita et al in 2014 and Karuna et al in 2003.15-17 Thin mucoid discharge was associated with most PAP smear changes in the present study. This is consistent with findings by Parate et al in 2017.18 Atypical squamous cells of undetermined significance (ASCUS) was associated with greyish discharge. The findings corroborated with studies done elsewhere.15-19
Patients diagnosed with TV infection reported varied colour discharge (greenish-yellow to white). Usually, TV infection among women results in a clear, white, greenish, yellow discharge with an unusual fishy smell.20 In the current study too, one-third of the patients reported foul-smelling discharge.
CONCLUSION
The present study revealed that Leucorrhea is prevalent throughout life i.e. 18-45 years, but was highly prevalent in the 26-30 years age group. Married females are at a greater risk for leucorrhoea as they are exposed to sexual activity and frequent childbearing which may lead to vaginal infections, cervicitis, cervical erosion, pelvic inflammatory disease etc. that could lead to leucorrhoea in these women.
Infection of vaginal mucosa by Trichomonas vaginalis and Candida is the most common cause of leucorrhoea. The most common causes of Leucorrhea in our study were: Gram-positive cocci (39.6%), Gram-negative bacilli (35.6%), Fungal/candidiasis (33.6%) and Trichomonas vaginalis (TV) (13.2%).
The chief presenting complaint in the present study was white discharge which is characteristic of leucorrhea.1 The consistency of discharge in the present study varied from thin mucoid (72.8%) to thick curdy (16.8%) and frothy (10.4%) in the current study.
Pruritis, dysuria and dyspareunia were present in 35.2%, 30% and 20% of the study participants in the present study. Itching is a common symptom in candidiasis, non-specific vaginitis and trichomoniasis. The mean duration of leucorrhoea in the present study was 2.89+1.32 days (Range: 1-6 days). The prevalence of leucorrhoea among IUD users and tubectomised women was 51.2% and 25.2% respectively in the present study.
Patients diagnosed with TV infection reported varied colour discharge (greenish-yellow to white). Usually, TV infection among women results in a clear, white, greenish, yellow discharge with an unusual fishy smell.19 In the current study too, one-third of the patients reported foul-smelling discharge. Patients with fungal infection in the present study reported white and grey discharge. The foul smell was present in 17.9% of the patients with a candida infection.
A significant association of leucorrhoea with socio-demographic factors, clinical features, PAP smear, bacterial as well as fungal culture in the present study emphasizes the need for health education and preventive practices related to personal & menstrual hygiene & family planning practices in females.
Acknowledgement: Nil
Conflict of interest: Nil
Source of funding: Nil
References:
1. Sabaratnum, Drukumaran, Sivanesa VR, Alokananda C. Textbook of Adolescent gynaecology, a sexually active adolescent. 1999; 46(2):733.
2. Tabassum K, Begum S, Rais N, Zulkifle. Analysis of Leucorrhoea manifestations an observational case study. Int J Herb Med. 2014;2(2):23-26.
3.Rudri Bai IM, Deepthi M, Dharmavijaya MN. Analysis of leucorrhoea in tertiary care hospital in rural Bangalore. Int J Clin Obstet Gynec. 2018;2(4)76-9.
4. Devi SU. A study on the prevalence of leucorrhoea in women attending in OPD of gynaecology and obstetrics department in a tertiary hospital. Int J Res Heal Sci. 2013;1(3):230-4.
5. Lavanya D, Venkatarao B, Kamala P, Sivamma BV, Subhalakshmi N. Microbiological profile of leucorrhea in reproductive age group. Int J Res Heal Sci. 2014; 3(5):503-09.
6. Rani UY, Sarada D, Varalakshmi D, Rajeshwari MR, Padmaja Y. Microbiological study of leucorrhea with special reference to Gardnerella Vaginalis. Int J Adv Res. 2015;3(7):1192-97.
7. Tanksale VS, Sahasrabhojanee, Patel V, Nevreker P, Menezes S, Mabey D. the reliability of a structured examination protocol and self-administered vaginal swab: a pilot study of gynaecological outpatient in Goa, India. Sex Transm Infect. 2003; 79:251-53.
8. Sharman A. The significance of leucorrhoea. Brit Med J. 1935;12:1199-1200.
9. Ilankoon MPS, Goonewardena GSE, Fernandopulle RS, Perera PPR. Women’s Knowledge and Experience of Abnormal Vaginal Discharge Living in Estates in Colombo District, Sri Lanka. Int J Women’s Healt Reprod Sci. 2017;5(2):90–6.
10.Eschenbach DA, Patton DL, Meier A, Thwin SS, Aura J, Stapleton A, Hooton TM. Effects of oral contraceptive pill use on vaginal flora and vaginal epithelium. J Contrac. 2000;62(3):107-12. doi: 10.1016/s0010-7824(00)00155-4. PMID: 11124356.
11.Kulkarni RN, Durge PM. A Study of Leucorrhoea in Reproductive Age Group Women of Nagpur City. Ind J Pub Hea. 2005; 49(4):238-9.
12. Nwankwo EOK, Kandakai Olukemi YT, Shuaibu SA. Aetiologic agents of abnormal vaginal discharge among females of reproductive age in Kano, Nigeria. J Med Biomed Sci. 2010; 12:12-16.
13.Ocak S, Cetin M, Hakverdi S, Dolapcioglu K, Gungoren A, Hakverdi AU. Effects of intrauterine device and oral contraceptive on vaginal flora and epithelium. Saudi Med J 2007;28(5):727-31.
14.Martinez F, Lopez-Arregui E. Infection risk and intrauterine devices. Acta Obstet Gynec. 2009; 88: 246-50.
15. Sujatha P, Indira V, Kumar KM. Study of PAP smear examination in patients complaining of leucorrhoea - A 2 years prospective study in a teaching hospital. Int J Med 2016; 3(5):106-12.
16. Yogita M. Patil, R.N. Consai. Pap smear study of cervical cytology. Int J Scientific Research 2014; 3(11): 425- 426
17.Karuna, gaspanal V, Van Dan Brule R. The clinical profile and cervical cytomorphology. Ind J Pathol Microbiol. 2003; 46(2): 78.
18.Parate SN, Gupta A, Wadadekar A. Cytological Pattern of Cervical Smears in Leukorrhea. Int J Sci Stud 2017;4(10):85-89.
19. Nair RV, Seetha PM, Sowbharnika CP. A study on cervical Pap smears among women with leucorrhoea in a tertiary care centre. Int J Clin Obst Gyn. 2019;3(2):135-37.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License