IJCRR - 13(12), June, 2021
Pages: 16-22
Date of Publication: 22-Jun-2021
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
Psychological Impact and Risk Factors of Sexual Abuse on Sudanese Children in Khartoum Stat
Author: Mona Isam Eldin Osman, Elsharif Ahmed Bazie, Hayat Osman, Abdalla Abdel Rahman
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Aims: This study aims to provide a review that will hopefully facilitate discussion of the children's psychological consequences of sexual abuse. Methods: Cross-sectional, descriptive study. Done in child and family protection centres in Khartoum State from September 2012 to January 2013. All children were interviewed via a questionnaire including socio-demographic characteristics, risk factors and consequences of child sexual abuse were tested using HADS & MINI scales. Results: This study summarizes what is currently known about these potential impacts of child sexual abuse. The various problems and symptoms described in the literature on child sexual abuse are reviewed in a series of broad categories. Children from all backgrounds are vulnerable to CSA but in this study younger children were more vulnerable as they constitute 53.4%. Among them 62.14% were females. Age, family status, number of household and number of rooms and low economic level were found to be associated with CSA. There is a high level of contact sexual abuse 94.17%. There is a low rate of interfamilial sexual abuse 17.48%. There is a high rate of disclosure 56.7%. Result from the high light behavioural consequence of CSA as it shows its association with posttraumatic stress disorder to be 25.2%, anxiety to be 47.57%, and depression to be 35.29%. Conclusion: Research has demonstrated that the extent to which a given individual manifests abuse-related distress is a function of an undetermined number of abuse-specific variables, as well as individual and environmental factors that existed before, or occurred after, the incidents of sexual abuse.
Keywords: Child, Sexual, Abuse, Khartoum, Sudan
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION
Child sexual abuse (CSA) defined as the engaging of a child in sexual activities that the child cannot comprehend, for which the child is developmentally unprepared and cannot give informed consent, and violate the social taboos of society .1
Before the 1970s -1980s child, sexual abuse is secretive and socially unspeakable. First studies on child molestation were done in the 1920s and the first national estimate of the number of child sexual abuse cases was published in 1948. In 1968 44 out of 50 U.S. states had enacted mandatory laws that required physicians to report cases of suspected child abuse while legal action started in the 1970s with the enactment of the Child Abuse Prevention and Treatment Act in 1974 in conjunction with the creation of the National Center for Child Abuse and Neglect. Since that time reported child abuse cases have increased dramatically. In 1979, the National Abuse Coalition was created and they create pressure in Congress to create more sexual abuse laws. Also, feminism waves brought greater awareness of child sexual abuse and violence against women and made them public, political issues. 2,3,4
By 1985, more studies that have concentrated specifically on sexually abused children started to publish. Its conceptualization is complex involving several dimensions from the medical, social, psychological, legal, ethical and moral aspect. Increasing recognition came with the women’s movement and reports by adult women survivors of CSA. 2,3,4
In Europe 10-20% of women and 3-10% of men had experienced sexual abuse before 18 years of age 11. In the United States by 2002 more than 88,000 children were confirmed to have sexual abuse with a woman ranged 15-32% depending upon definitions. 5
In a South African study, adolescent girls represented 1/3rd of the total adult rape, sexual coercion and forced sexual abuse. 6
Data from the Arab world is scarce. Only two countries (Bahrain &Palestine) have official records maintained by governmental agencies for child maltreatment cases. Hajj Yahia found the rates of sexual abuse among Palestinian students within the range of rates reported in other societies. Research participants indicated that a family member (8.6 %), a relative (36.2%), or a stranger (45.6%), had perpetrated at least one act of sexual abuse against them since early childhood. No significant differences between female and male participants, or among the sociodemographic characteristics of the sample. In addition, significantly higher levels of psychological symptoms were found among victims abused by a family member.7
Aetiology of Child Sexual Abuse:
Child sexual abuse is a social phenomenon that is linked to general attitudes and practices towards children, and ways in which social relationships are organized and regulated in a particular society 8. The occurrence of sexual abuse is affected by the following 9:
-
Motivation, which includes the abuser’s sexuality.
-
Absence of internal inhibitors (Moral values of the adult)
-
Absence of external inhibitors (Supervision of the child by others)
-
Child’s resistance towards the adult.
The abuser’s sexuality and sexual development which includes paedophilia, fear or avoidance of peer sexual relationship, sadism and interpersonal motivators such as the need to overpower more vulnerable persons, arising as a result of one’s past abuse and low self-esteem all are acts as motivators. However, the rates of CSA is lower than rates of expressed sexual interest as the inhibiting factors overcome for CSA to occur. Occasions, where the perpetrator’s internal inhibitions (e.g. moral values) may be overcome, are the use of alcohol and the presence of stress. Cognitive distortions including rationalization, minimization of the harmful effect of abuse and conceptualization of abuse as ‘love’ or ‘education’ may be motivators for abuse. On the other hand, a protective family, secure attachment to the primary caregiver, good monitoring of child’s whereabouts and a confiding relationship with the child prevent or decrease the chances of abuse.
In ‘Family Systems Theory’ the basic problem is that of a father-daughter incestuous relationship due to a dysfunctional family arrangement where parents suffer from an ‘emotion-sexual’ conflict. When the child comes to the parent(s) seeking emotional relief/care and the child gets a sexual response this a CSA. There are two forms of family pathology viz. conflict avoidance and conflict regulation. In the former type, the family is too insecure to cope with acknowledging the abuse and in the latter, though they hide the abuse from the outside world, they openly recognize the abuse, which leads to frequent arguments amongst the members 9.
Disclosure
Most time Child sexual abuse is silent and witness-free that had no physical signs. The delay between the onset of abuse and disclosure is common. Adults usually did not tell anyone about their abuse during childhood. 10
Medical Indicators of Child Sexual Abuse
Significant development has been in the medical field to diagnose sexual abuse. In the medical diagnosis of CSA, the presence or absence of a hymen was no longer the only indicator of possible sexual abuse and the same progress occurs in genital findings. It is also observed that in the majority of sexually abused children there are no physical findings. These findings, particularly vaginal ones, are most useful with pre-pubertal victims. As children become older, the possibility of consensual sexual activity needs to be considered. Further, changes that occur with puberty render insignificant some symptoms that have great significance in young children. 11
Two High-Probability Physical Indicators
the highest probability indicators of child sexual abuse are: 11
DIAGNOSTIC CONSIDERATIONS
The diagnosis of child sexual abuse is made on the basis of a child’s history and rarely diagnosed based on only physical examination or laboratory findings. Physical findings are often absent even when the perpetrator admits to penetration of the child’s genitalia. 12, 13 Most cases of abuse leave no physical evidence, and mucosal injuries often heal rapidly and completely. In a recent study of pregnant adolescents, only 2 of 36 had evidence of penetration. Occasionally, a child presents with clear evidence of anogenital trauma without an adequate history. Abused children may deny the abuse. Findings in child abuse include:12,13
-
-
Abrasions or bruising of the genitalia;
-
An acute or healed tear in the posterior aspect of the hymen that extends to or nearly to the base of the hymen;
-
A markedly decreased amount of hymenal tissue or absent hymenal tissue in the posterior aspect;
-
Injury to or scarring of the posterior fourchette, fossa navicularis, or hymen; and
-
Anal bruising or lacerations.
Consequences of Child Sexual Abuse
The consequences of child sexual abuse are both psychological and physical. Damaged tissue can heal without scarring but psychological consequences persist 14. Pregnancy and sexually transmitted diseases may result in lifelong effects, some of which can be life-threatening. Serious psychological consequences such as suicide attempts and posttraumatic stress occur in most the abused children. Thus all children with suspicion of being sexually abused should be referred for psychological testing and treatment 14,15.
METHODOLOGY
Study design:
This is a descriptive cross-sectional facility-based study.
Study area:
The research took place in Khartoum state, in three police centres that belong to the child and family protection unit-Khartoum (Khartoum, Omdurman and Sharg Alneel) with staff working three shifts. Those centres are receiving direct reporting from victims and their families or indirect reporting through hotlines 24 hours a day. Family and Child Protection Unit became operational in Khartoum in January 2007, operating 24 hours. The unit focuses on providing a child and family-friendly environment, which lessens the trauma of child survivors of crimes and reduces secondary victimization.
Study period:
This study was conducted during the period from September 2012 to January 2013
RESULT
A total of 103 children who had been sexually abused were studied from the three police centres that are serving family and child protection unit in Khartoum during the study period.
Age of the patients ranged between 7 years and 18 years, with a mean of 10.58 ± 3.1 years (95% confidence interval, CI = 9.97 to 11.19). The age group 7-10 years of age represent 53.4% (n=55) of the sample, 31.07% (n=32) were between 11-14years and 15.53% (n=16) were between 15-<18years .Among them, 62.14% (n=64) of cases were females and 37.86% (n=39) were males .
Regarding family status 56.31% (n=58) of children are living with their parents together, 26.21% (n=27) are living with their parents separated, 11.65% (n=12) are living with a single parent as they lost either their father 9.71% (n=10) or their mother 1.94% (n=2) and the rest 5.83% (n=6) their fathers are abroad ,
Most of the children fathers are characterized by low level of education as 6.8% (n=7) are illiterate, 10.68% (n=11) attended Khalwa, 30.1% (n=31) achieved primary level of education, and 20.39% (n=21) achieved intermediate level of education, while only 18.45% (n=19) and 13.59% (n=14) achieved secondary and university level of education respectively.Most of the children mothers are either illiterate 28.2% (n=29) or characterized by low level of education: 12.6% (n=13) attended only khalwa, 32% (n=33) achieved primary level of education, 5.8% (n=6) achieved intermediate level of education and the rest 21.4% (n=22) attended secondary & university level of education in an equal percentage 10.7% (n
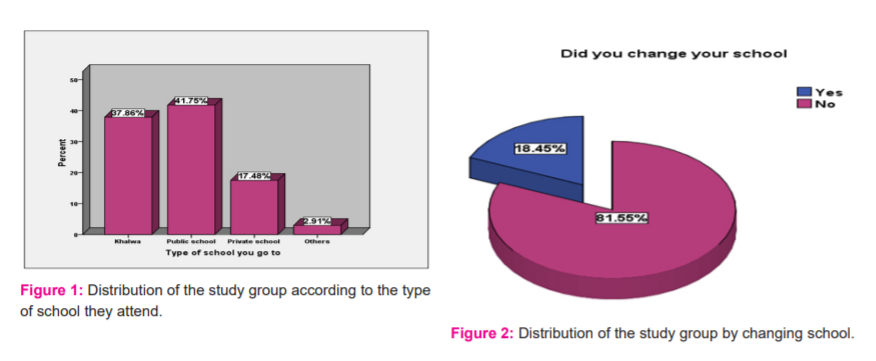
Most children are of low social economic status 51.46% (n=53). Most of the children are attending khalwa 37.86% (n=39) and public schools 41.75% ( n=43) as shown in figure(1). Most of the children didn’t change their schools 18.45 %( n=19) as shown in figure (2).
Most of the children have no mental illness 98.1% (n=101), while those who have mental disabilities represents 1.9% (n=2).
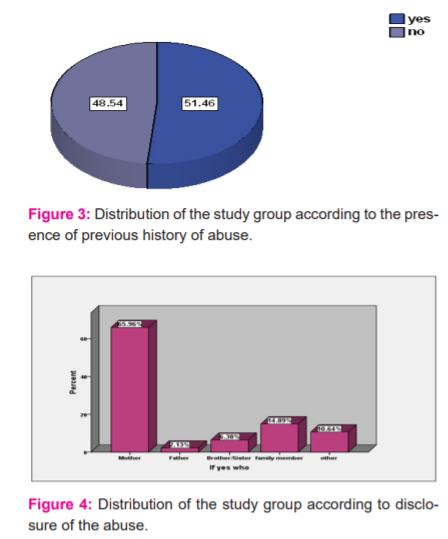
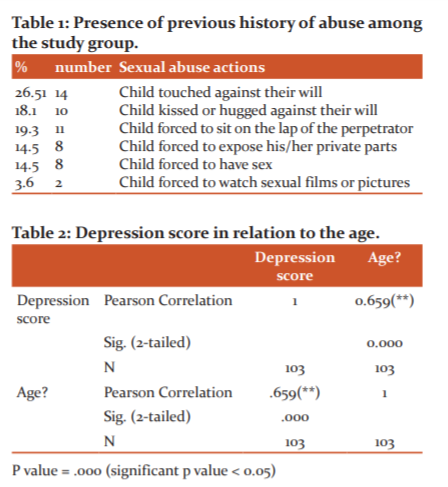
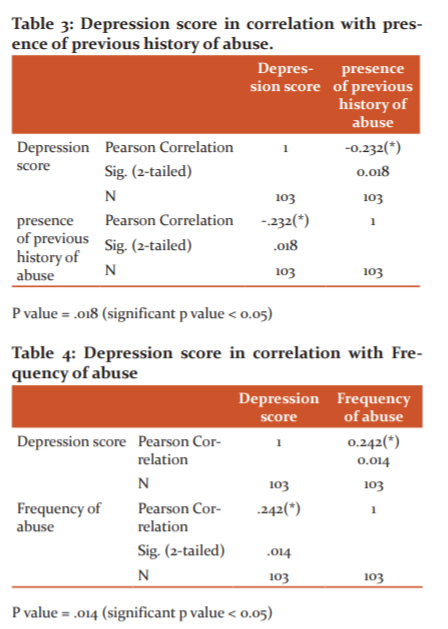
It also shows that the presence of disability was found to be 3.9% (n=4) of the sexually abused children, while most of the children haven’t 96.1% (n=99). Figure (3) shows that 51.46% (n=53) have a previous history of abuse, while 48.54% (n=50) have no history of previous abuse, and those are represented in table (1) as follows:
Children who had been touch against their will represents 26.51% (n=14), while those not represent 73.49%
Children who had a hug or kissed in an upsetting way represents 18.1% (n=10), while those not, represents 81.93%.
Children who had been pressed to sit on others lab represents 19.3% (n=11), while those not, represents 80.72%.
Children who had been forced to expose their private parts represents 14.5% (n=8), while those not, represents 85.5%.
Children who had sex against their will represents 14.5 %( n=8), while the majority 85.5% have no previous history.
Children who had been forced to look at sexual films represents 3.6% (n=2), while the majority of children 96% mentioned that there is no one made them look at sexual films or pictures against their will.
Figure (4) demonstrate that 65.96% (n=20) of those having a previous history of abuse disclose to their mothers, 14.89% (n=5) disclose to a family member, 10.64% (n=3) disclose to others, 6.38% (n=2) disclose to brothers or sisters and only 2.13% (n=1) disclose to their fathers.
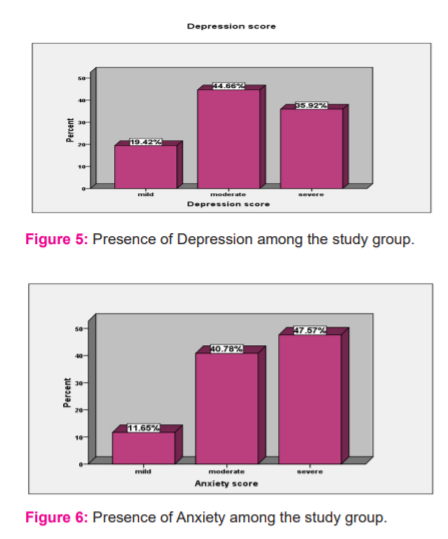
The majority of sample size in figure (5) shows that most of the children have a moderate degree of depression 44.66% (n=46), while those with mild degree represent 19.42% (n=20) and those with severe degree represents 35.92% (n=37). The depression score was significantly correlated to age, previous history of abuse, and frequency of abuse as shown in table (2, 3, and 4).
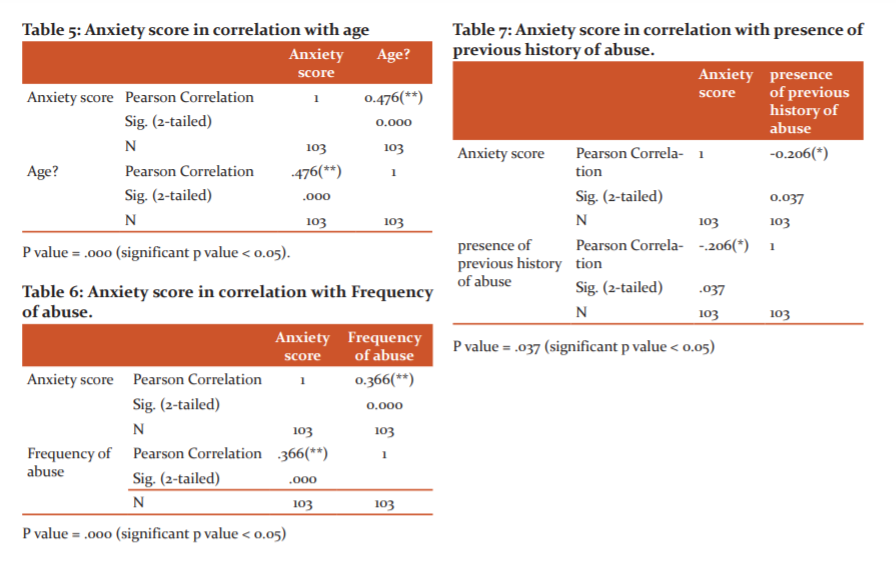
Figure (6) shows that most of the children have a moderate degree of anxiety 40.74% (n=42), while those with mild degree represent 11.65% (n=12) and those with severe degree represents 47.57% (n=49). The anxiety score was significantly correlated to age, previous history of abuse, and frequency of abuse as shown in table (5, 6, and 7).
DISCUSSION
This study attempts to shed light on sexual abuse in Sudan.103 children were involved in this study, their age range between 7 and 18 years. CSA rate was found to be higher among younger age groups 53.4% were between 7 and 10 years. This finding is consistent with another study conducted by Nahid in Sudan and with the international literature where some authors believe that as a risk factor, age operates differentially for girl and boys with a high risk starting earlier and lasting longer. 16 The mean age in this study was found to be 10.5 which coincide with pubertal changes.
CSA abuse was found to be in higher rates among females (62.4%), this result is consistent with the international literature and what had been mentioned by Sedlak, A. J. et al and Lab D. But this against what been mentioned by Nahid and Haj Yahii that there are no significant gender differences.
Absent father, mother or both parents wasn’t consistent with CSA, this is consistent with Nahid results, but against the international literature where family constellation, particularly the absence of one or both parents is a significant factor of child sexual abuse,16 also what had been mentioned by Finkelhor D. that children who live with only one parent are at elevated risk of child sexual abuse, particularly by males who are sexually involved with the mothers but not fully part of the household.
Economic status: Low family income was associated with CSA as 51.4 % of children families were living with a monthly income of < 500 SD. Socioeconomic status is an area of disparity in international research that found low socioeconomic status to be a powerful risk factor for physical abuse and neglect and has less impact on child sexual abuse. There is a community survey that found almost no socio-economic effects, but a disproportionate number of child sexual abuse reported to child protection services come from lower socio-economic classes. 8 Most of the children in this study are not working resembling 88.35%. This difference is because children in poor families go to work to help their families as stated by national research in Sudan that 7-10% of Sudanese children are economically active. 17
The result of this study shows that the low educational level of parents was found to be associated with child sexual abuse and this finding was consistent with what had been stated by Nahid.
Regarding the history of previous abuse although most of the children had been abused once 83.5% and 51.46% have a previous history of abuse in form of touching, kissing, attempted intercourse..etc, this finding is consistent with Nahid as she stated 81.9% had been abused once.
Although the abuse may continue for months or years before someone discovers it or the child disclose it, in this study 65.96% of those who had a previous history of abuse disclose the incidence. This finding was consistent with what had been mentioned by Nahid that 61% disclose the incidence to their parents. Internationally in a research done by Tine Jensen and others, the result indicated that disclosure is a fundamentally dialogical process that becomes less difficult if the child perceives that there is an opportunity to talk, and a purpose for speaking, and a connection has been established to what they are talking about.18 Also what had been mentioned in the international literature that in low-income families dependent on a sole breadwinner, such as a single mother, child victims as well as adult witnesses may be reluctant to disclose sexual abuse for fear that the sole earner of income will be removed from the household.19, 20
Child sexual abuse psychological consequences studied in this research were PTSD, depression and anxiety. Post-traumatic stress disorder was found in 25.2% of the studied cases and this is consistent with the international research reports that show 20 -70% of children with substantiated child sexual abuse suffer from PTSD.11 Other study stated that older age of onset is associated with higher rates of Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD) and lower general psychological functioning.
The anxiety score was found to be 47.57% and it was significantly related to age, frequency of abuse and number of abusers.
Depression score was founded to be 35.29% and it was significantly related to age, frequency of abuse and number of abusers. These findings are consistent with the international literature that mental health conditions such as depression, anxiety, post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), insomnia, and lack of trust in others are reported more often by people who have experienced child sexual abuse. 21,17
CONCLUSION
Children from all backgrounds are vulnerable to CSA but in this study younger children were more vulnerable as they constitute 53.4%.
Small Age and low economic level are more associated with CSA but parental characteristics were not associated with child sexual abuse.
Also, the study showed CSA was significantly a single event.
Our result high-light the behavioural consequence of CSA as it shows its association with PTSD, anxiety, depression.
Acknowledge
We would like to acknowledge all the police teams for their great effort in investigations and support to the children and their families.
References:
-
Kendall-Tackett KA, Williams LM, Finkelhor D. Impact of sexual abuse on children: a review and synthesis of recent empirical studies. Psych Bull. 1993 Jan;113(1):164.
-
Hall RC, Hall RC. A profile of paedophilia: definition, characteristics of offenders, recidivism, treatment outcomes, and forensic issues. In Mayo Clinic Proc. 2007 Apr; 82(4):457-471. Elsevier.
-
Behrman RE, Vaughan III VC. Nelson textbook of paediatrics. WB Saunders Company; 1983.
-
Rhind N, Leung T, Choi F. Child sexual abuse in Hong Kong: Double victimization?. Child abuse Neglect. 1999;23(5):511-7.
-
Vogeltanz ND, Wilsnack SC, Harris TR, Wilsnack RW, Wonderlich SA, Kristjanson AF. Prevalence and risk factors for childhood sexual abuse in women: National survey findings. Child abus neglect. 1999 Jun 1;23(6):579-92.
-
Jewkes R, Abrahams N. The epidemiology of rape and sexual coercion in South Africa: an overview. Soc Sci Med. 2002 Oct 1;55(7):1231-44.
-
Haj-Yahia MM, Tamish S. The rates of child sexual abuse and its psychological consequences as revealed by a study among Palestinian university students. Child abus neglect. 2001 Oct 1;25(10):1303-27.
-
Glaser D, Wiseman M. Child sexual abuse. Principles of Medical Biology. 2000 Jan 1;14:357-78.
-
Svedin CG, Back C, Söderback SB. Family relations, family climate and sexual abuse. Nordic J Psych. 2002 Jan 1;56(5):355-62.
-
Fluke J, Harden BJ, Jenkins M, Ruehrdanz A. Research synthesis on child welfare: Disproportionality and disparities. Disparities and disproportionality in child welfare: Analy the Res. 2011 Dec;1.
-
Kerns DL, Ritter ML. Medical findings in child sexual abuse cases with perpetrator confessions. Am J Dis Child. 1992;146:494.
-
Heger A, Ticson L, Velasquez O, Bernier R. Children referred for possible sexual abuse: medical findings in 2384 children. Child Ab Neglect. 2002 Jun 1;26(6-7):645-59.
-
Glaser D. Child abuse and neglect and the brain—a review. J child Psychol Psychiatry. 2000 Jan;41(1):97-116.
-
Malhotra S, Biswas P. Behavioral and psychological assessment of child sexual abuse in clinical practice. Int J Behav Consul Ther. 2006;2(1):17.
-
Putnam FW. Ten-year research update review: Child sexual abuse. Journal of the American Acad Child Adolescent Psych. 2003 Mar 1;42(3):269-78.
-
Walsh T, Douglas H. Legal responses to child protection, poverty and homelessness. J Soc Wel Family Law. 2009 Jun 1;31(2):133-46.
-
Mossige S, Jensen TK, Gulbrandsen W, Reichelt S, Tjersland OA. Children's narratives of sexual abuse: What characterizes them and how do they contribute to meaning-making. Narrat Inq. 2005 Jan 1;15(2):377-404.
-
Tabachnick J, Klein A. A reasoned approach: Reshaping sex offender policy to prevent child sexual abuse. Beaverton. Ass Treat Sexual Abus. 2011 Apr.
-
Arreola SG, Neilands TB, Diaz R. Childhood sexual abuse and the socio-cultural context of sexual risk among adult Latino gay and bisexual men. Am J public health. 2009 Oct;99(S2): S432-8.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License