IJCRR - 2nd Wave of COVID-19: Role of Social Awareness, Health and Technology Sector, June, 2021
Pages: 06-11
Date of Publication: 11-Jun-2021
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
Lifestyle in Older Adults Who Attend a Primary Health Care Facility During the COVID-19 Pandemic in North Lima
Author: Rosa PS, Hernan MS, Eduardo MS
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Background: The lifestyle of older adults due to the coronavirus pandemic has been highly affected because it restricts the daily activities they performed before the pandemic Objective: The objective is to determine the lifestyle of older adults who go to a primary health care facility during the COVID-19 pandemic in North Lima. It is a quantitative, descriptive, non-experimental cross-sectional study with a total population of 206 adults over 60 years old, who answered a questionnaire of sociodemographic data and the lifestyle instrument. Results: Their results show the lifestyle of older adults, where 82 (39.8%) of older adults have a suitable lifestyle, 41 (19.9%) have a fantastic lifestyle, 31 (15%) do a good job maintaining their lifestyle, 31 (15%) their lifestyle is in the danger zone and 21 (10.2%) have a low lifestyle although they can improve it. Conclusions: It is concluded strategies should be sought that allow the elderly to carry out their activities within the home to maintain their lifestyle.
Keywords: Lifestyle, Older adults, Care facility, COVID – 19, Vulnerable
Full Text:
Introduction
Worldwide, since 2019, the coronavirus pandemic (COVID-19) has spread in all countries, expanding throughout the population, however, the pandemic has generated fatal outcomes in the adult population, the elderly and people with comorbidities.1 Also, it has been predicted that COVID-19 considerably affects adults over 60 years old since there is a high risk that it is contagious and can contract more serious diseases from COVID-19, although older adults tend to be vulnerable to any disease since they are in a stage where their defences are weakened.2
Likewise, COVID-19 has generated a negative impact on older adults since their lifestyle changes dramatically due to isolation and quarantine3, since changes in lifestyle due to COVID-19, such as decreased physical activity, increased anxiety and decreased communication, all of this exerts a vulnerability in the elderly people, generating fragility at a physical and mental level.4,5
There are many risk factors, whether modifiable or non-modifiable, that older adults present that further compromise their health,6 since it puts them highly at risk for contracting COVID-19, factors such as smoking, alcohol, BMI (body fat), obesity, sedentary lifestyle, arterial hypertension (HBP) and diabetes mellitus,7 all this compromises the health of the same, exposing it to being infected by COVID-19.8, 9 Also, it has been predicted that in older adults factors such as physical inactivity, poor diet and comorbidities tend to influence the immune system in response to viral diseases10, which is why it is interpreted that these factors make them vulnerable to older adults to COVID – 19.11
Not only this but also the lack of sleep in older adults tends to reduce their body's immunity and increase the risk of respiratory infection, mainly COVID-19,12,13 although habits Hygiene measures are essential to prevent COVID-19 since hand hygiene has been predicted to reduce the incidence of the virus since it cannot survive long in our body.14 In the study carried out in the Netherlands,15 results were observed in 1119 older adults, between 48.3% to 54.3% of the total population had a decrease in physical activity and exercise due to the pandemic due to the COVID-19, 20.3% to 32.4% of the total population had a nutritional behaviour that superposes overnutrition, although 6.9% to 15.1% of the total population had a behaviour that predisposes to malnutrition.
In the study carried out in Brazil,16 with 1197 participants, it was observed that in older female adults with depressive symptoms and multimorbidity (various diseases), it was more associated with physical inactivity, whereas inactivity in males physical was more associated with depressive symptoms and metabolic disease such as diabetes mellitus. In the study carried out in Spain,17 they stated that social distancing due to COVID-19 has generated negative consequences at a physical and mental level, such as anxiety, depression, poor quality of sleep and physical inactivity during isolation due to COVID-19.
Therefore, the objective of the study is to determine the lifestyle of older adults who attend a primary health care facility during the COVID-19 pandemic in North Lima.
Therefore, the hypothesis in the research work is that the COVID-19 pandemic considerably affects the lifestyle of older adults, making them more susceptible to contagion.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Research Type
The present study, due to its characteristics, way of collecting data and measuring the variables involved, has a quantitative approach. Regarding the methodological design, it is a non-experimental, descriptive, cross-sectional study18.
Population
In the present study, the population is made up of 206 female and male adults older than 60 years old who attend a primary health care facility in North Lima.
Inclusion criteria
Technique and instrument
The technique used is the survey FANTASTICO questionnaire or data collection instrument whose purpose is to measure the lifestyle of older adults who attend the primary health care facility.
The FANTASTICO instrument is administered to assess how good its lifestyle is, consists of 30 items that are indicated in 10 dimensions, F: family and friends, A: associativity and physical activity, N: nutrition, T: toxicity, A: alcohol, S: sleep and stress, T: personality type and activities, I: inner image, C: control of health and sexuality, finally, O: order; which are evaluated with a Likert-type scale where “0 = Never”, “1 = Sometimes”, “2 = Always”. The final score is multiplied by 2, to obtain a final range from 0 to 120, where the ranges are quantitatively appreciated where “0 to 46 = is in the danger zone”, “47 to 72 = some low, you could improve”,“ 73 to 84 = adequate, you're fine”, “85 to 102 = good job, you're on the right track”, “103 to 120 = congratulations, you have a fantastic lifestyle”19.
Place and application of the instrument
The survey was applied to the elderly population of the San Martín de Porres district of the Ex-Fundo Naranjal Health Center, which is in North Lima.
First, the coordination with the Health Center was carried out so that they authorize us to carry out the surveys to the elderly at the time they come for care, and then the permission of the elderly, explaining about the survey and why the work is done the research so that they understand what is going to be done.
The survey was carried out during the mornings with a time of approximately 15 minutes for each older adult in the research work, concluding with satisfaction since it could be carried out with the support of the elderly for the research.
It is important to emphasize the presence of health workers at the time of filling in the survey, since they may benefit from the research since it will allow them to know what the lifestyle of the elderly adult at home is like and what strategies to use to maintain a healthy lifestyle of themselves.
Results
Below is a summary table of the surveys carried out following the guidelines corresponding to the research work:
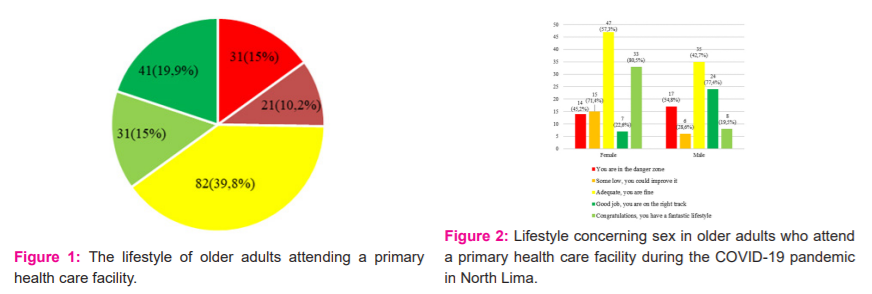
In Figure 1, the lifestyle of the elderly is observed, where 82 (39.8%) of the elderly have a suitable lifestyle, 41 (19.9%) have a fantastic lifestyle, 31 (15%) do a good job maintaining their lifestyle, 31 (15%) their lifestyle is in the danger zone, and 21 (10.2%) have a low lifestyle although they can improve it.
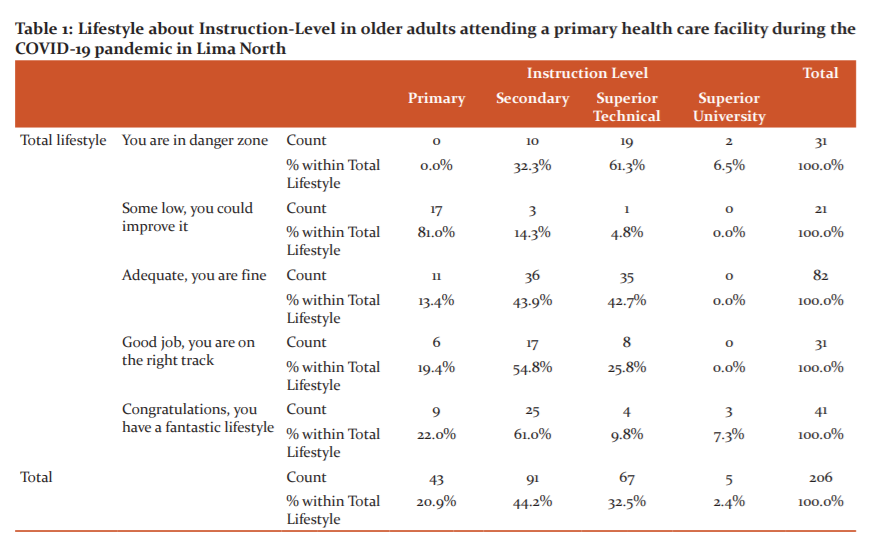
In Figure 2, the lifestyle is observed concerning sex, where we can see that in the female sex 14 (45.2%) their lifestyle is in a danger zone and male sex 17 (54, 8%), in some low lifestyle, 15 (71.4%) are female and 6 (28.6%) are male, in an appropriate lifestyle, 47 (57.3%) are female and 35 (42.7%) male, those who do a good job in their lifestyle 7 (22.6%) are female and 24 (77.4%) are male and those who have a fantastic lifestyle, 33 (80.5%) are female and 8 (19.5%) are male.
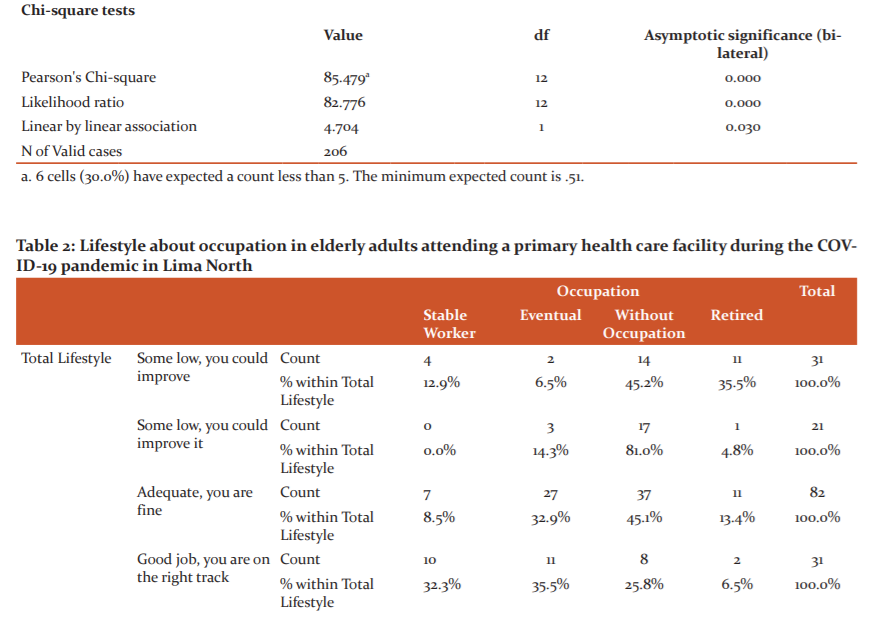
In Table 1, the lifestyle is related to the level of education of the elderly who attend a primary health care facility during the COVID-19 pandemic in North Lima, which was determined with the test of Pearson's chi-square (X2). The level of significance of the test obtained a value of 0.51 (p> 0.05) (X2 = 85.479; d.f = 12). Therefore, a hypothesis of an association between variables is not rejected, for which there is statistical data that verify the relationship between the lifestyle and the educational level of the elderly. So, we interpret that the lifestyle that is in a danger zone, 19 (61.3%) of the elderly have a higher technical level of instruction, in some low lifestyle, 17 (81%) of the elderly have a primary level of education, inadequate lifestyle, 36 (43.9%) of older adults have a secondary level of education, in good lifestyle, 17 (54.8%) of older adults have a level of secondary education and a fantastic lifestyle 25 (61%) of older adults have a secondary level of education.
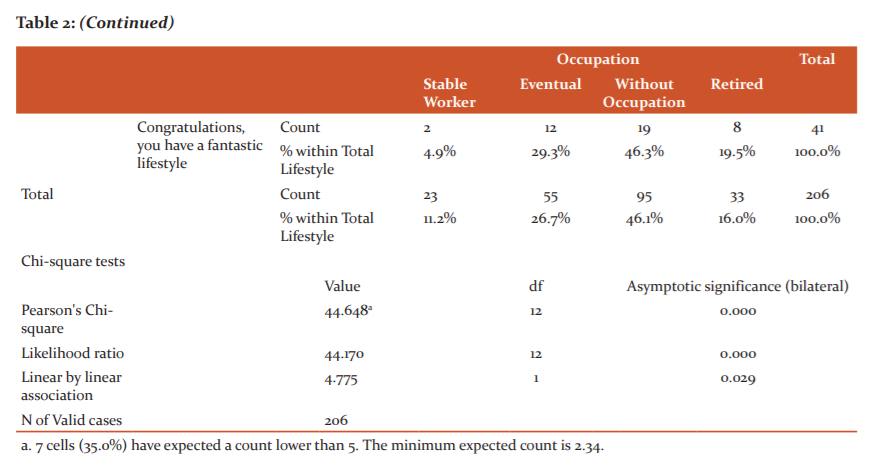
In Table II, the lifestyle is related to the occupation of the elderly who attend a primary health care facility during the COVID-19 pandemic in North Lima, which was determined with the chi-square test of Pearson (X2). The level of significance of the test obtained a value of 2.34 (p> 0.05) (X2 = 44.648; d.f = 12). Therefore, a hypothesis of an association between variables is not rejected, for which there is statistical data that verify the relationship between the lifestyle and occupation of the elderly. Therefore, we can interpret that in a good lifestyle 10 (32.3%) of the elderly have a stable occupation, in an adequate lifestyle, 27 (32.9%) of the elderly have a temporary occupation, in Adequate lifestyle 37 (45.1%) of the elderly do not have an occupation, in a lifestyle that is in a danger zone, 11 (3.5%) of the elderly are retired.
These results are important to be able to observe if the lifestyle of the elderly changes due to the COVID-19 pandemic, so that solution strategies are carried out to maintain the appropriate lifestyle.
Discussions
This study focused on the physical and mental health of older adults who are cared for in a primary care facility since elderly people who cannot perform their basic activities due to the COVID-19 pandemic have drastically changed their lifestyle since they cannot go outside the home since they are people with a high rate of contagion to COVID – 19.
In the results on the lifestyle in older adults, they demonstrated an adequate lifestyle, this is because at home older adults tend to spend more time with their families, also, they carry out the routine activities that they did before the pandemic, such as passive physical activities, adequate food, good quality of sleep, and social interaction with the family, all of this exerts emotional support since older adults, being alone, negatively affects them and therefore they are depressed or worried about interrupting routines they can do at home. The authors argue that older adults with physical inactivity, poor sleep quality and a poor diet increase their chances of contracting COVID-19 even though they are vulnerable people with age to any disease12. Similarly, the authors maintain that older adults who present some comorbidity and who do not perform any routine activity are potentially people at risk of contracting COVID-19, since comorbidities such as hypertension, overweight or obesity are both mainly make the elderly more susceptible to being able to have it quickly.11
In the results of lifestyle about sex, we have obtained that those of the female sex have an adequate lifestyle better than men, this is due to factors such as levels of education and that are involved in Domestic and care activities allow them to maintain their lifestyle, on the other hand, men have responsibilities at home, thus obstructing their routine activities. They argue that the female sex had less lifestyle since there were factors that made their participation in activities less, such as physical limitations, lack of confidence, they lived alone and had no company, therefore this made their style life was not adequate.16 They argued that women have a better lifestyle than men since they argue that they have a healthier life index due to habits and their state, whereas men present inappropriate habits and their state with the Age tends to be complicated since they can present some disease either due to high cholesterol.20 The limitation in the research work is access to each of the older adults since not all of them reported being participants in the research since they only wanted to be treated at the health center and access to the health center to be able to carry out the research work.
Conclusions
For older adults to have a good lifestyle during the COVID-19 pandemic, they need emotional and social support from their family, as it will allow them the confidence to carry out their daily activities. Strategies should be sought that allow the elderly to carry out their activities within the home to maintain their lifestyle. The COVID-19 pandemic has affected the nutritional behaviour of older adults since they are more susceptible to eating less and losing weight due to activities that they cannot perform. This research work will be beneficial for future work, since it details the lifestyle that older adults have followed during the COVID-19 pandemic and how it will be after the pandemic has ended.
Conflict of Interest: The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Funding Source: This research work doesn’t have Funding Source
Acknowledgement: The authors acknowledge the immense help received from the scholars whose articles are cited and included in references of this manuscript. The authors are also grateful to authors/editors/publishers of all those articles, journals, and books from where the literature for this article has been reviewed and discussed.
Author’s Contributions: Rosa PS: Conceived and designed the analysis, wrote the paper, contributed data and translation. Hernan MS: Collected the data, Performed the analysis.
Eduardo MS: Contact the people for the survey-taking.
References:
1. Ferrante G, Camussi E, Piccinelli C, Senore C, Armaroli P, Ortale A, et al. Did social isolation during the SARS-CoV-2 epidemic have an impact on the lifestyles of citizens? Epidemiol Prev. 2020;44(5–6):353–362.
2. Yamada M, Kimura Y, Ishiyama D, Otobe Y, Suzuki M, Koyama S, et al. Effect of the COVID-19 Epidemic on Physical Activity in Community-Dwelling Older Adults in Japan: A Cross-Sectional Online Survey. J Nutr Heal Aging. 2020;24(9):948–950.
3. Sepúlveda W, Rodríguez I, Pérez P, Ganz F, Torralba R, Oliveira D, et al. Impact of Social Isolation Due to COVID-19 on Health in Older People: Mental and Physical Effects and Recommendations. J Nutr Heal Aging. 2020;24(9):938–947.
4. Somekawa Y, Miura T, Katsumata S, Nishida Y, Shimada M, Umeki H. The relationships among frailty index, various physical, psychological, lifestyle-related factors, and social connections in Japanese elderly women. Maturitas. 2019;124(2019):151–189.
5. Shinohara T, Saida K, Tanaka S, Murayama A. Association between frailty and changes in lifestyle and physical or psychological conditions among older adults affected by the coronavirus disease 2019 countermeasures in Japan. Geriatr Gerontol Int. 2021;21(1):39–42.
6. Türkmeno?lu C, Etaner A, Kiraz B. Recommending healthy meal plans by optimising nature-inspired many-objective diet problem. Health Informatics J. 2021;27(1):146045822097671.
7. Zhu H, Chen X, Zhang B, Yang W, Xing X. Family History of Diabetes and the Effectiveness of Lifestyle Intervention on Insulin Secretion and Insulin Resistance in Chinese Individuals with Metabolic Syndrome. J Diabetes Res. 2021;2021:1–9.
8. Ruissen M, Regier H, Landstra C, Schroijen M, Jazet I, Nijhoff M, et al. Increased stress, weight gain and less exercise in relation to glycemic control in people with type 1 and type 2 diabetes during the COVID-19 pandemic. BMJ Open Diabetes Res Care. 2021;9(1):1–7.
9. Ho F, Celis C, Gray S, Katikireddi S, Niedzwiedz C, Hastie C, et al. Modifiable and non-modifiable risk factors for COVID-19, and comparison to risk factors for influenza and pneumonia: Results from a UK Biobank prospective cohort study. BMJ Open. 2020;10(11):40402.
10. Jia L, Du Y, Chu L, Zhang Z, Li F, Lyu D, et al. Prevalence, risk factors, and management of dementia and mild cognitive impairment in adults aged 60 years or older in China: a cross-sectional study. Lancet Public Health. 2020;5(12):661–671.
11. Sacco V, Rauch B, Gar C, Haschka S, Potzel A, Kern S, et al. Overweight/obesity as the potentially most important lifestyle factor associated with signs of pneumonia in COVID-19. PLoS One. 2020;15(11):1–9.
12. Gao C, Zhao Z, Li F, Liu J, Xu H, Zeng Y, et al. The impact of individual lifestyle and status on the acquisition of COVID-19: A case-Control study. PLoS One. 2020;15(11):1–9.
13. Janssen X, Fleming L, Kirk A, Rollins L, Young D, Grealy M, et al. Changes in physical activity, sitting and sleep across the COVID-19 national lockdown period in Scotland. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020;17:9362.
14. Kilani H. Healthy lifestyle behaviours are major predictors of mental wellbeing during COVID-19 pandemic confinement: A study on adult Arabs in higher educational institutions. PLoS One. 2020;15(12):1–15.
15. Visser M, Schaap L, Wijnhoven H. Self-reported impact of the covid-19 pandemic on nutrition and physical activity behaviour in dutch older adults living independently. Nutrients. 2020;12(12):1–11.
16. Gomes R. Association between chronic diseases, multimorbidity and insufficient physical activity among older adults in southern brazil: A cross-sectional study. Sao Paulo Med J. 2020;138(6):545–553.
17. Sepúlveda W, Rodríguez I, Pérez P, Ganz F, Torralba R, Oliveira D, et al. Impact of Social Isolation Due to COVID-19 on Health in Older People: Mental and Physical Effects and Recommendations. J Nutr Heal Aging. 2020;(27):1–10.
18. Fernández C, Baptista P. Metodología de la Investigación. 6ta ed. México: Mc Graw-Hill/Interamericana.. 2015. 1–634 .
19. Villar M, Ballinas Y, Gutierrez C, Abgulo Y. Análisis de la Confiabilidad del Test Fantástico para medir Estilos de Vida saludables en trabajadores evaluados por el programa “Reforma de Vida” del Seguro Social de Salud (Essalud). Rev Peru Med Integr. 2016;1(2):17–26.
20. Yu J, de Antonio A, Villalba E. Older adult segmentation according to residentially-based lifestyles and analysis of their needs for smart home functions. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020;17(22):1–21.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License