IJCRR - 13(11), June, 2021
Pages: 127-131
Date of Publication: 04-Jun-2021
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
Study of Postoperative Complications with Use of Ultrapro\? Mesh in Inguinal Hernia
Author: Nilesh Prakash Patil, SG Deshpande, Shahzad Bulsara, Vaibhav Prakash Anjankar
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Introduction: Inguinal hernia is one of the commonest surgical conditions. Various surgical procedures are in vogue since ancient times for their repair. Mesh repair is one of the promising surgical techniques though it is reported with certain complications like foreign body reaction, pain, fistula formation, infection, migration, shrinkage, and recurrence etc. Traditional \"heavyweight\" meshes (like Prolene \?) are now a day's being replaced by partially absorbable lightweight meshes, that are less dense, apparently more physiological in their flexibility, and associated with less acute and chronic postoperative pain and discomfort. Objective: The present study was formulated to study the feasibility and efficacy of ULTRAPRO\? mesh in Inguinal Hernia Repair. We also tried to study postoperative complications with the use of Ultrapro\? Mesh. Methods: A total of 90 cases of hernias were included in the study after obtaining the written consent of the patients. Various parameters were noted down. Inclusion and exclusion criteria were followed. Operative technique and mesh implantation was performed. Results: 62.00% were right-sided hernias. Direct hernias were more common (48.89%) than indirect hernias (42.22%). The commonest co-morbidity found was hypertension in about 22.22% of patients. The pain was the commonest (23.33%) acute postoperative complication followed by tightness, serosa and cord oedema. Conclusion: Type I and III are more common Nyhus type of hernia. Marginally advantageous over heavyweight mesh eg: Prolene, concerning early postoperative complications. Wound hematoma and Infection were absent with the use of Ultrapro\? mesh. Chronic pain is less commonly seen with Ultrapro\? mesh as compared to other lightweight mesh. No recurrence was seen during the study period.
Keywords: Aponeurosis, Complications, Hernia, Mesh, Subcutaneous
Full Text:
Introduction
Inguinal hernias are one of the most common conditions requiring surgery among abdominal wall hernia. Since the 19th century, when modern techniques for the repair of groin hernia were first described recurrence was a problem. At that period in the late 19th century, Bassini’s repair which was developed became revolutionary that time for low recurrence rates.1 Traditional suture repair of inguinal hernia is replaced by routine tension-free mesh repair.2 In many countries, mesh repair became more prevalent than suture repair (such as Bassini's, Darning, and Shouldice).3
In the late 19th century, Bassini’s repair was developed and became very popular at that time for low recurrence rates. It involved suturing of Bassini’s triple-layer (internal oblique, transverse abdominis, fascia transversalis) to inguinal ligament with interrupted sutures and yielded recurrence rates of 5 to 15%.4 Many tissue-based repairs were developed. Mc Vays repair involves suturing of the triple layer to Coopers ligament.1 Shouldice repair achieved a recurrence rate below 2% but lost its popularity due to its technical difficulties and inconsistent results outside Shouldice clinic.5
Lichenstein in 1986 described the tension-free inguinal hernia repair with mesh.1 It becomes one of the most popular open technique for inguinal hernia repair due to the simplicity of repair, the decreased post-operative pain and decreased recurrence rates compared to tissue-based hernia repair.1,6,7
Even so, Mesh repair is linked with complications like foreign body reaction, pain, fistula formation, infection, migration, shrinkage, and recurrence.8 Some of these complications are more commonly seen with certain types of meshes e.g. chronic pain necessitating re-operation, high recurrence and complication rate, all associated with the use of mesh plugs.2,9
Traditional “heavyweight” meshes (like Prolene ®) are now a day’s being replaced by partially absorbable lightweight meshes, that are less dense, apparently more physiological in their flexibility, and associated with less acute and chronic postoperative pain and discomfort2. Recently introduced in lightweight meshes is Ultrapro ®, a Monocryl ®Prolene ® -Composite monofilament lightweight mesh, which is designed for easier handling and better tissue integration to form a flexible “scar mesh”.2
The major objective of the present study was to study the feasibility and efficacy of ULTRAPRO® mesh in Inguinal Hernia Repair. We also tried to study postoperative complications with the use of Ultrapro® Mesh.
Materials and methods
The present study was carried out in the department of Surgery over 28 months (August 2009 to December 2011). The study was started after obtaining an Ethical Clearance from Institutional Ethical Committee. Total 88 patients were operated on for hernia repair. Of these 88 patients, 2 patients underwent bilateral repair of their inguinal hernias. Thus, in all 90 inguinal hernias were repaired. Ethical approval was also obtained for the study (No. KBH/AUR/ECR/009)
Inclusion criteria:
All types of adult inguinal hernias (Nyhus type I to IV) which were nonobstructive, unilateral or bilateral either primary or recurrent hernias
Exclusion Criteria
-
Patients below the age of 20 years and small children with congenital hernias were excluded from the study.
-
All patients who presented with complications of inguinal hernia like strangulation were excluded from the study.
-
Patient with associated incisional hernias was excluded from the study.
-
The patient who was not ready for adequate follow up were excluded from the study.
Written informed consent was obtained from the Patients preoperatively after explaining the procedure and advantages and disadvantages of ULTRAPRO® mesh repair. All the cases included in the study were thoroughly examined and posted for surgery. A proper preoperative procedure was followed like investigations, pre-anaesthetic check-up, physicians’ fitness etc. Preoperative antibiotics were not prescribed. All patients received a single dose of injection Cefuroxime 1.5 gm just before giving incision.
Operative Technique
Initial dissection: A standard inguinal incision was deepened down to the external oblique aponeurosis up to the superficial inguinal orifice respecting the iliohypogastric and ilioinguinal nerves to open the Inguinal canal. The spermatic cord was mobilized. In the indirect hernia, the sac was separated from the cord structures. Sac was incised and examined for its contents. Contents were reduced into the peritoneal cavity. Sac was then rotated and transfixed and ligated with a mersilk suture. Similarly, indirect hernia, sac along with its contents was reduced.
Mesh implantation: Posterior wall was prepared for mesh implantation. Thorough hemostasis was achieved. The perioperative field was cleaned. Ultrapro® mesh was rolled and placed over the posterior wall. The first suture was taken over the pubic tubercle, followed by the rest of the mesh. Vicryl 2-0 was used for the purpose. The lateral end of the mesh was split to accommodate the spermatic cord. Care was taken that the cord is not snuggly placed between the mesh. External aponeurosis was sutured with 2-0 vicryl with continuous sutures. The superficial ring was kept appropriately wide. A suction drain of appropriate size was placed over the external oblique aponeurosis layer. The subcutaneous layer was closed with vicryl 2-0 and skin was stapled.
Postoperative management: The patient was kept nil by mouth and was advised bed rest till the anaesthesia effect is worn out completely. The foleys catheter was removed once the patient is ambulatory and simultaneously he/she was urged to go about early unrestricted activities. The drain was removed either during the hospital stay or on follow up. A prophylactic antibiotic was given for 2–3 days. The patient’s pain assessment was done on day three post-operatively and on follow up at day ten, one month and six months after the procedure. Pain assessment was done based on the Visual Analogue Scale. The patient was discharged with advice not to lift or push heavyweight.
Results
The observations and results of this study are mentioned as follows-
Age-wise distribution of the patients: We divided all cases into age groups as mentioned in table 1. The youngest patient in the study was 28 years old male while the oldest was 82years old male. Maximum numbers of patients were found in the group of 51- 60 years (21 patients i.e. 23.33%). This group was followed by 61-70 years, 31-40 and 81-90 years giving a percentage of 21.11%, 20% and 16.66% respectively. The median age of patients in our study was 55 years.
Side of hernia: Out of the 88 patients 55 patients were right-sided and 31 patients had a left-sided hernia. Two patients were operated on for bilateral Ultrapro® mesh repair.
Type of hernias operated: In our study; the majority of hernias operated were direct inguinal hernias (44 i.e. 48.89%). 38 cases i.e 42.22% were of indirect type while 8 were of combined type i.e pantaloons hernia.
The extent of hernia: Out of the operated hernias 67 were incomplete and 23 were complete.
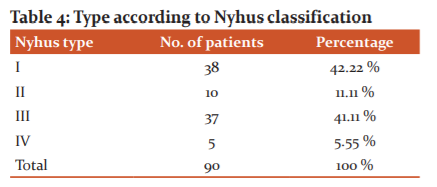
Type according to Nyhus classification: We classified the hernias by Nyhus type due to its simplicity. Maximum hernias 38 (42.22 %) were Nyhus type I hernias, whereas Nyhus type II, III and IV constituted 10 (11.11%),37(41.11%) and 5 (5.55%) hernias respectively.
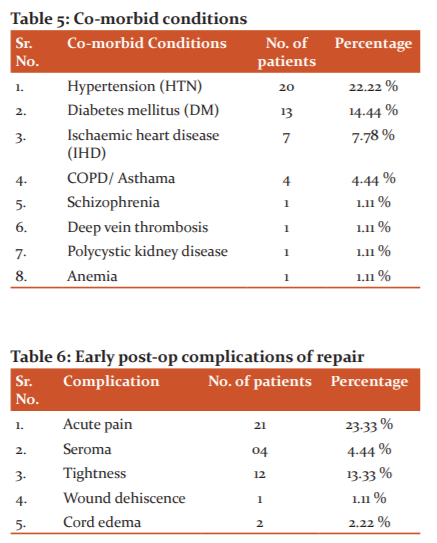
Co-morbidities found in the patients: It was noticed that patients having associated comorbid conditions had increased hospital stay and were more prone to develop complications.
Early (<1 month) postoperative complications: Out of the 90 hernia repair, 21 patients noticed pain at the operative site. All patients had VAS score less than 6 except for one who had a VAS score of 8. The pain was dealt with nonsteroidal analgesic satisfactorily in all of them. Four patients had seroma at the wound site, out of which one needed needle aspiration. Twelve complained of a sense of tightness at the operative site, more during walking. Out of these two had mild restriction in their routine daily activities which persisted up to a maximum period of two months. There was one case of minor wound dehiscence which healed with dressing only and did not require resuturing. Two patients had cord oedema in an early postoperative period which subsided with anti-inflammatory drugs. There were no other complications seen in the immediate postoperative period. There were no cases of infection of the wound or discharging sinuses.
Late (>1 month) postoperative complication: Out of 90 hernia repairs in 88 patients, only two patients in our series had pain in the operative region that lasted for more than one month. Only non-steroidal analgesics sufficed to deal with this problem. No patient in our series developed a late infection or testicular atrophy. No recurrence was noted during the period of follow-up. This was consistent with the result of other series performed worldwide. The pain was noted in 2 patients (2.22%)
Discussion
Inguinal hernias are one of the most common cases encountered in surgical practice. In our study, we operated on 90 inguinal hernias on 88 patients.
The mean age of the patient was 48.11years (range 28 – 82 years). Holzheimer et al10 found the mean age of 48.4 years similar to our study. Similarly, Khan et al11, 12 had 48.78 years as mean age. The most common age group affected in our study was “51-60 years” affecting 23.33% of patients. This shows that middle-aged patients are more in the number who present to the hospital with an inguinal hernia irrespective of the duration that they were having a hernia.
Inguinal hernia can present as direct, indirect or combined i.e Pantaloon’s hernia. In our study, 42.22% of patients had the indirect type of hernia, 48.89% of the direct type hernia. George H Sakorafas et al13 from Athens had 55% as indirect hernia cases, 30% as direct ones and 15% as combined type. In the study by M. Smietanski et al.14 56% had indirect hernia while 39% had direct and 7% had the combined type of hernia. In our study direct type of hernia was more common rather than the indirect type, differing from other studies. This was because most of the patients belonged to age above 50 years at which abdominal wall weakness is found commoner than that in younger patients.
In our study there were more number of right sided inguinal hernia i.e. 55 out of 90 operated cases while 31 of left side and 2 bilateral cases. Study by Nadim Khan et al also had more cases (53.6%) of right-sided hernia, left-sided in 41.1% and 5.4% as bilateral. The cause of preponderance of the right side is not known. It is postulated that as the right testis descends later than the left testis so right-sided processus vaginalis is patent for a longer time. Appendectomies were reported to be the cause of right-sided hernias which does not stand true in our study as only four patients had undergone previous appendectomies and all did not have the right sided presentation.
Postoperative pain was assessed on day third, tenth, and one, six months after surgery. Visual Analogue Scale was used to assess the pain. In a study conducted by Holzheimer et al10, the majority i.e. 96% of patients had mild to moderate pain after hernia repair while only 4% of patients complained of severe pain. M. Smietanski et al also shows that with the use of Ultrapro® mesh complaints of mild pain with slight discomfort, feeling of tightness (Visual Analogue Score VAS score less than 2) were found in only 8.2% of patients. Usoro et al2 studied on twelve patients, all were pain-free at the time of discharge. This shows that with the use of Ultrapro® mesh and proper technique postoperative pain is minimum. Another randomized clinical trial by Smietanski et al showed that post-operative pain is less with lightweight mesh as compared to heavyweight mesh.
Another complication, i.e seroma formation was seen in 4 (4.44%) patients in our study. Holzheimer et al.10 did not note a single case of seroma formation in their study. Nadim Khan et al had 3.6% patients with seroma in the lightweight mesh group and 3.5% patients in the heavy weight mesh group. Overall it seems that the occurrence of seroma formation is technique dependent and its incidence does not significantly change with the use of lightweight mesh.
In this study, only 2.22% of patients complained of pain at the operative site that lasted for more than one month. There was no recurrence of hernia or testicular atrophy seen. R. Holzheimer et al10 noted mild pain at the site in 2% of patients after three months. Smietanski et al14,15 documented chronic pain in 10.3% of patients but only 2.8% were affected by their daily activities. The recurrent hernia was found in 1.6%. Recurrence was within one year.
Conclusion
Inguinal hernia is a common problem seen during surgical practice. Inguinal hernias are more common in the middle ages than in young adults. The right side is more commonly affected than the left side. The incomplete hernia is more common than the complete type. Type I and III are more common Nyhus type of hernia. Acute pain was the most common early postoperative complaint followed by “Sense of Tightness”. Marginally advantageous over heavyweight mesh eg: Prolene, concerning early postoperative complications. Wound hematoma and Infection were absent with the use of Ultrapro® mesh. Chronic pain is less commonly seen with Ultrapro® mesh as compared to other lightweight mesh. No recurrence was seen during the study period.
Inguinal hernias have only surgical treatment so patients should be advised to undergo surgery to avoid future complications like obstruction and strangulation. Mesh hernioplasty is the ‘GOLD STANDARD’ for inguinal hernia as treatment and should be advised. Proper techniques and skilful surgery have shown good results with fewer complications so surgeons should learn them and teach effectively as well. Associated illness adversely affects the overall outcome of the patient so they should be given special attention. The latest guidelines and recommendations issued should be followed as they are based on studies of specialized centres managing a large number of patients. Postoperative counselling with instructions should be given to patients to avoid delayed complications at home. Ultrapro ® mesh has promising results concerning acute and chronic complications but its higher cost remains a restraining factor for its use.
Conflicts of Interest: Nil
Source of funding: None
Acknowledgement: We would like to acknowledge the support received from all the patients. We also acknowledge the support and dedication of nursing and support staff without whom this project would not be possible.

References:
-
Mukthinath G, Shankar K and Bhaskaran A. A comparative study of postoperative complications of lightweight mesh and conventional prolene mesh in Lichtenstein hernia repair. Int J Res Med Sci. 2016;4:2130-4.
-
Usoro N, Agbor C, Emelike K and Bamidele A. Early Outcome of Inguinal Hernia Repair Using Ultrapro® Mesh in University of Calabar Teaching Hospital, Nigeria. Int J Third World Med. 2007;6(2):1-7.
-
Schumpelick V and Klinge U. Prosthetic implants for hernia repair. Br J Surg 2003;90:1457-8.
-
Woods B and Neumayer L. Open repair of inguinal hernia: Evidence-based review. Surg Clin North Am. 2008;88:144-6.
-
Stephen HG, Mary TH, Kamal MFI. Surgical progress in inguinal and ventral incisional hernia repair. Surg Clin North Am. 2008;88:18.
-
Schofield PF. Inguinal Hernia: Medico-legal Implications. Ann R Coll Surg Engl. 2000;82:109-10.
-
Madden JL, Hakim S, Agrorogianuis AB. The anatomy and repair of inguinal hernias. Surg Clin North Am. 1971;51(6):1269-92.
-
Schumpelick V and Klinge U. The properties and clinical effects of various types of mesh used in hernia repair. Association of Great Britain and Ireland (Yearbook) 2001.
-
LeBlanc KA. Complications associated with the plug-and patch method of inguinal herniorrhaphy. Hernia 2001;5:135-8.
-
Holzhiemer RG. First results of Lichtenstein hernia repair with ultrapro mesh. 2004;9: 323-7.
-
Khan N. Early outcome of Lichtenstein technique of tension-free mesh repair for inguinal hernia. J Ayub Med Coll Abbottabad. 2008;20(4):50.
-
Khan N. comparative study b/w vypro and prolene mesh using Lichtenstein technique. Saudi J Gastroenterol. 2010;16(1):8-13.
-
Sakorafas GH. Open tension-free repair of inguinal hernias; the Lichtenstein technique. BMC Surg. 2001;1:3.
-
Smietanski M. Five-year results of a randomised controlled multi-centre study comparing heavy-weight knitted versus low-weight, non-woven polypropylene implants in Lichtenstein hernioplasty. Hernia. 2011;15:495–501.
-
Smietanski M. Prospective cohort study to evaluate ultrapro mesh for lichtenstein inguinal mesh repair. Hernia. 2009;13:239-42.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License