IJCRR - 13(11), June, 2021
Pages: 122-126
Date of Publication: 04-Jun-2021
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
Effective Method of Step-by-Step Control of Haemorrhage in Obstetrics Massive Bleeding in Obstetrics
Author: Yusupbaev Rustem Bazarbaevich, Goyibov Sanjar Salimovich, Dauletova Mehriban Jarylkasynovna
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Introduction: The article describes modern approaches to the prevention of obstetric bleeding and blood-saving technologies in women who gave birth by caesarean section. It is especially important to pay attention to the timely detection of anomalies in the position of the placenta and attachment. The article analyzes the outcome of caesarean section in two groups with obstetric haemorrhage. The largest share of obstetric haemorrhage is the detachment of the normally located placenta and placental pathology. A prospective study has been conducted to assess the effectiveness of the phased control and treatment of hemorrhage during caesarean delivery. Objective: To evaluate the effectiveness of the phased control and treatment of haemorrhage during cesarean delivery. Methods: The authors divided all the patients into two groups depending on the methods of intraoperative treatment. In group I, haemorrhaging was treated by using the proposed step-by-step control and treatment tactics (cesarean section indications were haemorrhaging due to premature detachment of low or normally located placenta in the first group) and the second group were treated according to the Protocol of the treatment of haemorrhaging adopted in the hospital (indications for cesarean section was central placenta previa and uterine scar). Results: In the first group, compared to the control group, 80% (12) of type 2 and type 3 lower segmental bleeding prevailed, which indicates a high risk for the development of serious complications. In the first group, class 1 blood loss was diagnosed in 26.6% (4) cases, class 2 blood loss in 53.3% (8) cases, class 3 blood loss was diagnosed in 20.0% (3), class 4 blood loss was not present, which indicates successful treatment of bleeding. In the second control group, class 1 blood loss was diagnosed in 23.8% (5) cases, class 2 blood loss in 28.5% (6) cases, class 3 blood loss in 52.3% (11) cases, and class 4 blood loss were diagnosed in 14.2% (3) cases. Conclusion: The use of the method of step-by-step control and treatment of haemorrhage helps to reduce the number of com�plications such as hysterectomies by almost 2 times.
Keywords: Obstetric haemorrhaging, Surgical hemostasis, Detachment of the normally located placenta, Placenta previa, Uterine scar, Caesarean section
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION
Obstetric haemorrhaging is one of the pressing problems of modern obstetrics. According to WHO, obstetric haemorrhaging is the leading cause of maternal mortality in industrialized countries.8 In the occurrence of obstetric haemorrhaging, especially in its outcome, the initial state of the organism and the nature of the somatic and gynaecological diseases carried or associated with it before or during pregnancy play an enormous role. Massive haemorrhaging during pregnancy and childbirth, especially in the presence of preeclampsia and anaemia, occurs against the background of the high sensitivity of the female body to haemorrhage and, in many cases, leads to a decrease in the quality of life in women of reproductive age and disability.1,2
According to the order of the Ministry of Health of the Republic of Uzbekistan No. 185 dated May 28, 2014. on regionalization of perinatal care, a network of perinatal centres has been established in Uzbekistan, which plays a major role in providing emergency obstetric care, including for obstetric haemorrhage and the introduction of new haemorrhage control technologies in perinatal centres where obstetric pathology is centralized.1,3 Reducing maternal mortality is an urgent task of the obstetric service. The annual analysis of maternal deaths indicates that the actions of the personnel involved in emergency care in cases of haemorrhage show a deviation from the recommended procedures for the treatment of haemorrhaging, underestimation of the patient's condition, inadequate infusion - transfusion therapy, which ultimately leads to fatal consequences. The analysis of maternal mortality identified the human factor as one of the leading causes of mortality, as knowledge of protocols and algorithms is not always a guarantee that this knowledge can be activated at the right time, which is observed in many cases of maternal mortality.1,4,5
Numerous domestic and foreign studies have shown a clear causal relationship between placental anomalies and caesarean sections and the presence of scars on the uterus. Placental factors dominate in the structure of the causes of fatal haemorrhage – 20% placenta strongly attached, 10% placental Previa. Special attention should be paid to the fact that from year to year there is a steady increase in placental anomalies.6,7 According to various authors, the frequency of placenta previa ranges from 0.1% to 3%,3,8 in growth – from 0.04% to 0.2% of all births.9,10
Surgery to stop haemorrhage is a key to the successful management of many obstetric haemorrhages.8,9 However, the tactical and technical application of these methods in practice leaves much to be desired, which is associated with technical training. Therefore, the development of the most effective and technically simple methods to control haemorrhage is of great importance to reduce the manageable cause of maternal mortality.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
A prospective study was conducted in a cohort of 36 pregnant women delivered by surgery a protocol for the treatment of obstetric haemorrhaging during cesarean section. The patients were divided into 2 groups according to the methods of intraoperative treatment. In group I (n-15), treatment of haemorrhage was carried out according to the proposed step-by-step control and treatment tactic, the second group (n-18) was treated according to the treatment protocol of haemorrhage adopted in the medical institution. The study design was case-control in a cohort group with operative delivery.
The inclusion criteria were: a cohort of patients at high risk of bleeding who underwent surgical intervention and performed haemorrhage during the surgery, need for additional surgical interventions to achieve hemostasis during the operation – compression sutures, ligation of the main uterine vessels and internal iliac arteries, hysterectomy.
The exclusion criteria were: medical history with planned hysterectomy of uterine fibroids, haemorrhaging linked to somatic diseases such as liver disease and malignant diseases of the blood and uterus. The proposed developed algorithm for step-by-step control and treatment of obstetric haemorrhage during delivery.
Indications for step-by-step control and treatment tactic of haemorrhage:
-
2 and 3 types of haemorrhage according to the developed method of bleeding gradation.
-
Germination or fused placenta in the uterine wall and beyond the uterus.
-
Instantaneous blood loss of more than 1500-2000 ml, or 25-35% of the volume of blood circulation.
-
Hemorrhagic shock, continuous haemorrhage of over 1500 ml and unstable hemodynamics.
-
Rupture of the uterus in the lower segment and hematoma of the retroperitoneal space and the broad ligament of the uterus and a combination of shock.
-
Relaparotomy against the background of continuing haemorrhage.
-
The absence of an experienced specialist capable of performing a complete hysterectomy and ligation of the internal iliac artery under the above conditions.
-
Need to attract related specialists – surgeons, urologists, haematologists, etc. in the event of complications. The method of step-by-step control and treatment of haemorrhage is carried out in 3 stages.
Stage 1: Primary (standard haemorrhage relief: rapid initial assessment of Ps, arterial pressure, t- body, respiratory rate, diuresis, etc.), finding the cause and the source of haemorrhage, and developing hemostasis tactics, including surgical, for this purpose, three-level gradations of the type of haemorrhage, lower median laparotomy and temporary or permanent hemostasis were used, depending on the clinical situation and the doctor’s experience. Hemostasis methods: Clamping of vessels over and pressing of the abdominal aorta. External womb tamponade for placental blocking: a tight external bind of the uterus with a sterile bandage from the lower segment to the bottom for blocking the bleeding source, manual pressing of the anterior wall of the uterus to the posterior wall. Internal uterine tamponade - the application of various elements of cylinder tamponade. Contusion of the placental bed by contracting Z with metallic and hemostatic sutures. Various compression sutures, ligation of the internal iliac artery, hysterectomy.
Stage 2: Operative pause to stabilize the patient and to relieve shock and to deal with issues such as recovery of the volume of blood circulation, blood clotting capacity, visits of highly specialized doctors if necessary. The final third stage is aimed at final hemostasis with complete stabilization of the patient and assistance of a multidisciplinary team.
To find the cause and source of hemorrhagic shock and differential diagnosis of haemorrhage, we used a three-level clinical and anatomical gradation of the bleeding source, developed during the study, depending on the blood supply to the pool of the internal and external iliac artery, which characterizes the types of obstetric haemorrhaging, which contributes to the optimal surgical technique of hemostasis.
-
Type of haemorrhage - the source of bleeding from the uterine body area is more frequent at atonia the uterus and rarely at adnation of the placenta, the blood supply from the pool of the internal iliac artery.
-
Type of haemorrhage, lower segmental haemorrhage the isthmus of the uterus, lower segment of the uterus, at low placentation and partial placenta previa, the blood supply from the pool of the internal and partially external iliac artery.
-
Type of haemorrhage - localization of the haemorrhage: the cervix, the upper third of the vagina, area of parametric and retroperitoneal space, bleeding when the uterine main vessels are injured, forming peritoneal hematomas and in cases of rupture of the uterus. Blood supply is from the pool of the internal and external iliac artery.
We used the general clinical methods of the patient’s examination and data of clinical-laboratory blood indicators, coagulation system. The methods for determining blood loss were visual in combination with the gravimetric method with the determination of the volume of blood circulation (weight X 7.7) and the table of the determination of blood loss class proposed in the national standard for the treatment of haemorrhage and hemorrhagic shock.
To assess the extent of the effects detected and the benefits of the tested method, the following basic parameters of evidence-based medicine are applied:
1. Relative reduction of the frequency of adverse outcomes (reduction of relative risk);
2. Absolute reduction of the frequency of adverse outcomes (reduction of absolute risk);
3. Risk ratio;
4. The number of patients who need to be treated for a certain time to prevent one adverse outcome or achieve a beneficial effect in one patient;
5. Odds ratio. They are calculated based on a standard "study connection table” using several formulas.14 Statistical processing of research results was carried out by the program "STATISTICA6.0" with the calculation of the student's criterion. The confidence criterion is p<0, 05.
Results
The age of women ranged from 19 to 35. The median age was 24±0.5 years. First-time births accounted for 33.3% (5) in the first group, repeat births 40.0% (6), and three or more births were also observed in 26.6% (4) cases. First-time births in the second group were 28.5% (6), second-time births were 19.0% (4), and three or more births were also observed in 52.0% (11) cases.
Haemorrhaging during pregnancy was observed in 58.3% (21) (the first group 66.6% (10), in the second group 73.3% (11) of patients, indicating a cesarean section. Haemorrhaging during cesarean section operation developed in 36.0% (13) of patients (the first group 46.6% (7), in the second group28.5% (6), haemorrhaging after delivery was observed in 4 (19.0%) patients in the second group only. Pre- and post-operation blood tests indicate that there was a reliable decrease in overall haemoglobin in the control group compared to the study group. Before the operation, the Ng in the first group was 104.1±11.2, and in the second group 101.1± 12.6. After surgery on day 2 in the first group, Ng was 92±10.3, in the second group 71± 11.8 at P<0.05 (Table 1).
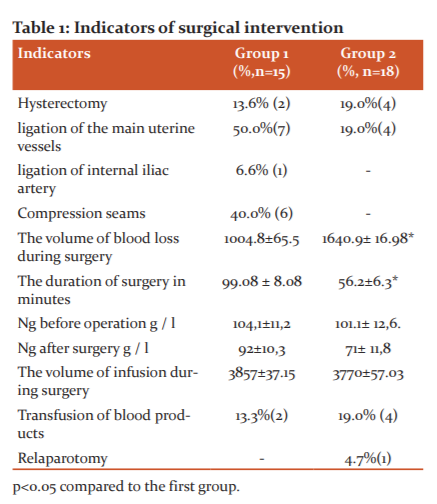
The main indications for surgical delivery by cesarean section were haemorrhaging due to premature detachment of normal or low located placenta in the first group of 33.3%(5) cases, in the second group of 28.5%(6) cases, central placenta previa was the indication in the first group of 26.6%(2) cases, in the second group of 19.0%(4) cases, uterine scar after the cesarean section was in the first group of 20.0% (3) cases, in the second group was 14.2% (3) cases.
The results showed that the indications for cesarean section, such as preterm detachment of a normal placenta and placenta previa and uterine scarring dominated in the cohorts studied. The majority of women were between 28 and 42 weeks pregnant. In a full-term pregnancy, 58.3%(21) of women were delivered, 36.0%(13) of women were delivered at 28-36 weeks, and 6.7%(2) of women were delivered at 22-27 weeks of pregnancy. Operations were carried out on an emergency basis in the first group in 80% (12), the second group in 66.6% (14), as planned in 20%(3) and 33% (7) cases. Haemorrhage of the first type according to the proposed method of bleeding gradation was diagnosed in the first group 50%(7) in the second group in 71.4%(15) cases. Level 2 haemorrhaging was diagnosed in the first group of 20.0% (3) and the second group in 19.0% (4) cases. Level 3 haemorrhaging was diagnosed in the first group at 35.7% (5), in the second group only in 9.5% (2) cases.
The results of the study showed that the first group was dominated by the first and third levels of haemorrhage, which was an indication of the tactic of treating and controlling haemorrhage. In the first group, compared to the control group, lower segmental haemorrhaging prevailed 80% (12) of type 2 and 3, indicating a high risk of developing serious complications. In the first group, blood loss category I was diagnosed in 26.6% (4) cases, blood loss category II in 53.3% (8) cases, blood loss category III was diagnosed in 20.0% (3), category IV of blood loss was not diagnosed, indicating successful treatment of haemorrhaging. In the second control group, category I of blood loss was diagnosed in 23.8% (5) cases, category II of blood loss in 28.5% (6) cases, category III of blood loss in 52.3% (11) cases, and category IV of blood loss was diagnosed in 14.2% (3) cases.
DISCUSSION
Intraoperative interventions after fetal removal in the first group in half of the cases 50.0% (7) performed ligation of the main uterine vessels as the first stage of the step-by-step control of haemorrhage, compression seams were applied in 33.3% (5) cases and 9.5% (2) B-Lynch sutures, hysterectomy was performed in 13.6% (2) cases, and ligation of the internal iliac artery was performed in 6.6% (1) cases, mainly in patients with level 3 haemorrhage. Intraoperative interventions in the second group included, after fetal removal, only in 19.0% (7) cases of ligation of the main uterine vessels, in 19% (4) cases hysterectomy was performed, indications were atonia and increased blood loss of more than 1500 ml. The duration of the operation was 68.08 ± 18.08 minutes in the first group, taking into account the intraoperative pause, and 56.2 ±26.3 minutes in the second group. The volume of blood loss during surgery in the first group was 1004.8±65.5, in the second group 1640.9± 16.8 at P<0.05.
When using adjoint tables to calculate the basic data on evidence-based medicine, the following is observed compared to the control group in the group using control and treatment of haemorrhage tactics:
1. Relative reduction of the frequency of adverse outcomes = 3.5
2. Absolute reduction of the frequency of adverse outcomes = 0.06
3. Risk ratio = 0.68
4. The number of patients who need to be treated for a certain time to prevent one adverse outcome or achieve a beneficial effect in one patient, at a confidence interval of 95% of the results obtained, are (the number patients needing treatment)=17.
Conclusion
Thus, the third level of haemorrhage, according to the proposed gradation method, in almost all cases leads to massive blood loss and requires the assistance of a multidisciplinary team with the possibility for experienced staff to perform staff the ligation of the internal iliac artery and total hysterectomy. The use of step-by-step control and haemorrhage treatment techniques reduces the number of complications such as hysterectomies by almost 2 times. Prevention of hysterectomy, as well as a reduction in the frequency of use of blood products from 19.0% to 13.3%, the absence of the development of complications such as relaparotomy, demonstrates the effectiveness of the proposed method of controlling and treating haemorrhage during operative abdominal delivery.
Conflict of interest: No
Authors contributions: This work was carried out in collaboration among all authors. Yusupbaev Rustem conducted operations and wrote the first draft of the manuscript. Goyibov Sanjar designed the study, performed the statistical analysis, wrote the protocol, and Dauletova Mehriban managed the analyses of the study and the literature searches. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Source of funding: The research was carried out in the Republican specialized scientific-practice medical centre of Obstetrics and Gynecology within the framework of the applied research project: “Development of a new step-by-step technology for the treatment and control of obstetric bleeding, taking into account the main pathological determinants of haemorrhage”.
References:
-
Voronin VK, Kozlov SV. Ligation of the main vessels of the uterus in obstetric bleedings taking into account anatomical and topographic variants of its blood supply. J Nau Obraz. 2002;3:162.
-
Golyanovsky AV, Mekhedko V, Kulchitsky DV. Complex prevention of complications in the case of repeated cesarean section. Ped Obstet Gynec. 2011;73(6):88-91.
-
Gorin VS, Zaitseva RK, Serebrennikova ES.Placental abnormalities: obstetric and perinatal aspects. Russ Bull Obst Gynec. 2010;6:26-31.
-
Ishchenko AA. Modern organ-preserving operations on the uterus during cesarean section. Moscow: Fed state Univ. 2010; 30.
-
Kulakov VI, Chernukha EA, Komissarova L. Cesarean section. Russ Bull Obstet Gynec. 2011;4: 36-38.
-
Kurzer MA, Lukashina MV, Panin AV. Kurtser is an ingrowth of the placenta. Organ-preserving operations. Quest Gynec Obst Perinat. 2009; 8(5): 31-35.
-
Latyshkevich OA. Placenta regrowth in patients with a scar on the uterus after cesarean section: Organ-preserving operations. Dis Moscow. 2015; 23(6): 133.
-
Makarov OV, Aleshkina VA, Savchenko TN. Problems of reproductive health. Obst Gynec. 2007;15(30):31-39.
-
Oppenheimer L. Clinical practical guide of the Association of obstetricians and gynaecologists of Canada: diagnosis and management of placenta previa. Obst Gynec. 2014;67:76-83.
-
World Health Organization. WHO recommendations for the prevention of postpartum haemorrhage. Geneva: WHO. 2007.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License