IJCRR - 13(10), May, 2021
Pages: 78-83
Date of Publication: 19-May-2021
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
Analyzing Efficiency and Slack of Tertiary Hospitals of Punjab: A Case of Data Envelopment Analysis
Author: Singh Pritpal, Angra Prikshat
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Introduction: Data envelopment analysis is an operational research-based method for estimating the efficiency of the general execution of hierarchical units of hospital considering the availability of various data sources in form of inputs and outputs. Objective: This research focuses on analyzing operational efficiency and finding slack in the input of tertiary hospitals of Punjab. Demand for health services is increasing but the availability of health services are still a big issue. In the present circumstance, it has turned out to be difficult for hospitals in Punjab to guarantee increasingly productive methods for administrations. Under the current conditions, it is fundamental to discover the fitting asset blend and its use. Methods: VRS-DEA model of data envelopment analysis is applied on data collected from 1st January 2018to 31st December 2018 for hospitals inputs and outputs to analyze efficiency and find slack of 48 tertiary hospitals of Punjab of three different sizes toward to output. Results: This research indicates that smaller hospitals have an efficiency more than large size and mid-size hospitals as smaller size hospitals average efficiency is .80. The mean efficiency of medium size hospitals is .75and large hospital is .71. Only 4hos�petals are working at the constant return to scale and working efficiently and 44 are inefficient as these 44 hospitals are suffering huge slack in Inputs. Mean Slack of 27.31%, 18.5%, 9.5%observed in large size, Medium size and small size hospitals in the number of patients attended. Conclusion: Hospital authorities must benchmark efficiency with the best performing hospitals in that area. Data envelopment analysis must be used to distinguish the hospitals on basis of efficiency and policymakers can use this as a tool to evaluate the performance of public hospitals and set key performance indicators for allocating fund to these hospitals.
Keywords: Data envelopment analysis, Input slack, Efficiency, Return to scale, Performance indicators, Operational research
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION
This research focuses on studying the operational efficiency of tertiary hospitals of Punjab. A study to find association was conducted with the help of analysis of data envelopment technique, which is used to find out the efficiency of tertiary medical hospitals considered for the study. Data envelopment analysis focuses on finding efficiency through input /output-based model which follows linear mathematical formulas.1,2 As the demand for healthcare services in India is increasing because of many reasons which include awareness for a preventive health checkup, Increasing population, Complexity of disease and availability are major contributors to this. Demand for health services is increasing but the availability of health services are still a big issue.2 Among health service providers in specialized care, the Private sector in Punjab is at the forefront and covering most of the area and population for providing health services. But still according to world health statistics report India is performing below average with 9 beds for 1000 patients which is very below the global average. Govt. hospitals in form of community health centres and civil hospitals also started improving their infrastructure to provide health services at a specialized level but still bed to patient ratio is not improving from last many years as compared to the global average which is a matter of concern.3,4 A considerable amount of money invested by government bodies and private sector to improve infrastructure to improve performance of services provided to people and to increase the availability of services to all but as a population of the country is huge that much infrastructure is not enough. In that case, it will become very important for hospitals whether private or government to optimally utilize their existing resources, Data envelopment analysis is a technique that is formulated to find operational efficiency in form of logical and scale efficiency of the organization and to decide their benchmark and operate according to benchmark or if there is no benchmark then set the benchmark.5 Health and healthcare services are too different aspect which needs to be distinguished, Health is related to person and healthcare services does not only involve providing hospital services but also to provide preventive services and post medical checkup services also. In the present circumstance, it has turned out to be difficult for hospitals in Punjab to guarantee increasingly productive methods for administrations. Under the current conditions, it is fundamental to discover the fitting asset blend and its use. So also, it is important to distinguish sources of relative cost wastefulness – specialized and allocate both.5,6 The centre point of this study is on surveying the hospitals in efficiency terms, for example, the perfect measure of inputs to deliver a given degree of output. The other inspiration driving this investigation has been to see how to address the issue of benchmarking in hospitals.
Organizational Structure of health Sector in Punjab
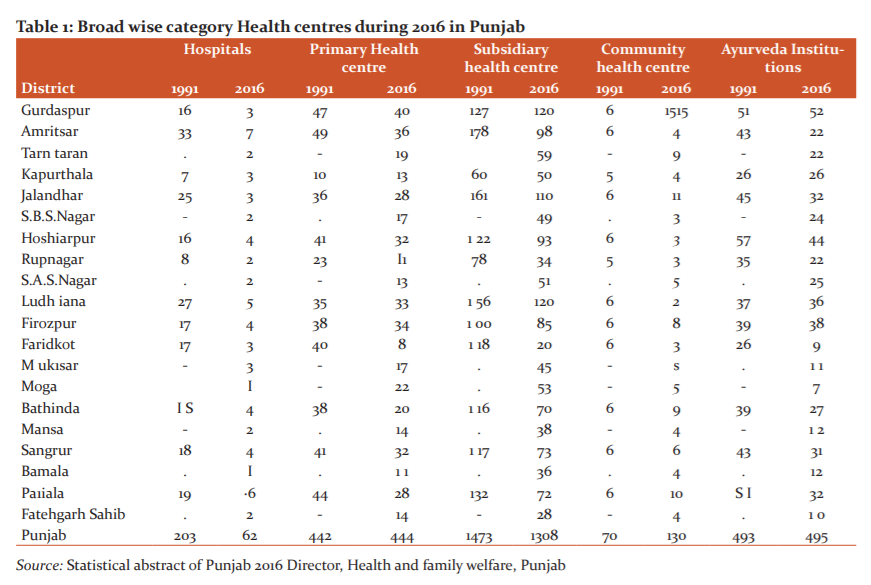
In Punjab, both the public and the private division assume a vital job in providing medicinal services administrations. It is the Department of Health and Family Welfare under the Public part which is in charge of preventive health services benefits in Punjab. There is a four-level structure of medicinal services conveyance framework in the State. This contains Sub Health Centers (SHCs)/dispensaries at the base giving the fundamental human services administrations to a population of 3000-5000 individuals. Above it, there is Primary Health Centers (PHC) serving a population of 20000-30000 individuals.6 It likewise fills in as a referral unit to six subcentres. Above Primary Health Centers there are Community Health Centers (CHC) which serves a population of 80,000 to 1.20 lac and a referral unit to four PHCs. This entire extent of SHCs, PHCs and CHCs goes under essential level healthcare where administrations are constrained. To help primary human services administration there are secondary level medicinal services.The information in Table 1 beneath demonstrates that since the 1990s, there was no impressive measure of increment in the hospital framework in Punjab.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Research Question
This research focuses on analyzing the operational efficiency of hospitals and finding slack in the input of tertiary hospitals of Punjab to set the benchmark for inputs as comparable to outputs using data envelopment analysis.
Ethical Approval
Ethical approval of this study is taken from the senior medical officer of each district for selecting their hospital data into the study and for private hospitals data is collected after taking due permission from an administrative officer of the hospital where data is not present online on their website
Study design
Data was collected from 48 hospitals in form of inputs and outputs decided for calculating efficiency from 1st January 2018 to 31st December 2018 and the selection of hospitals was made from the list of the hospitals being run by doctors registered with the Indian Medical Association. Government and private tertiary level hospitals with bed strength of more than 40 were chosen for study from the Jalandhar, Hoshiarpur, and Amritsar and Ludhiana districts of Punjab. Hospitals are selected based on quota sampling. Quota sampling is done on basis of the size of the hospital, according to the objective of this research different sized hospitals are required and three different sizes of tertiary hospitals are considered i.e. 16 Small sizes hospital having bed strength between 40 and 70, 16 medium sizes between 70 to 100 and 16 large size hospitals having bed strength more than 100.
Data analysis
Envelopment study of data is a linear mathematical programming-based method for estimating the efficiency of the general execution of hierarchical units of hospital considering the availability of various data sources in form of input and outputs. DEAOS free online \\tool was used for calculating efficiency. This study introduces the input /Output technique and uses a manual proportion of effectiveness, i.e.: how relative efficiencies can be settled around the centre on inefficient units set.7,8 Efficiency is usually considered in the range of [0, 1]. Efficiency requires a typical arrangement of loads to be applied to overall units and loads is given to each input as per the DEA model. 9,10
Inputs and outputs Variables from the hospital for data envelopment analysis
Inputs data collected is in form of number of beds, number of doctors, Nurses, Outpatient department hours per week of working, laboratory hours per week and paramedical staff supporting major staff doctors and administrative staff. Outputs for calculating efficiency are Outpatient visits, Inpatients and laboratory cases, Maternal and child healthcare all these are types of cases treated and the number of cases. Basically for efficiency calculation input and output are required. Data of some of the hospitals are collected through secondary sources and for some hospitals data is collected by visiting hospitals and meeting administrative officers of hospitals after taking due permission from SMO of the district. Outpatient and inpatient are two very important parameters to calculate efficiency in previous studies efficiency is calculated on basis of these two only, But in this study laboratory cases and maternal and child healthcare is also included which gives proper efficiency of variable return to scale which is technical efficiency. All the outputs are in form of the number of cases treated. Data is collected from hospitals from annual book release and by directly visiting the hospitals. The study includes the outputs efficiently arranged. Those can be isolated into faculty, resources, or assets and administrations.
RESULTS
In first stage efficiency of hospitals were analyzed, data envelopment analysis was utilized to analyze and evaluate the efficiency of the hospital and in the second stage, slack values were analyzed ( Taable 2).
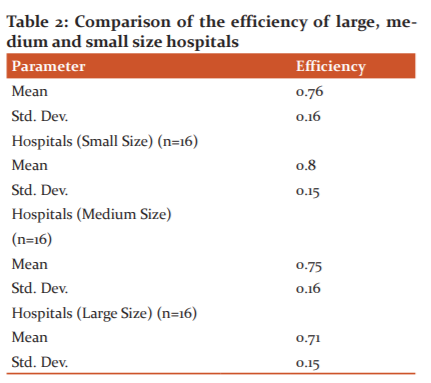
Slack Value in Large size Hospital
Slack values are value which is added to inequality constraint to convert into to equality .Slack values of large size hospitals mostly working at either increasing return to scale or diminishing return to scale all the values are derived from data envelopment analysis of data collected .hospitals can employ even 19 per cent fewer doctors to achieve the same output of outpatients. .With the same number of inputs they can cater to a large number of outpatient’s (i.e. 65000) ( Table 3).
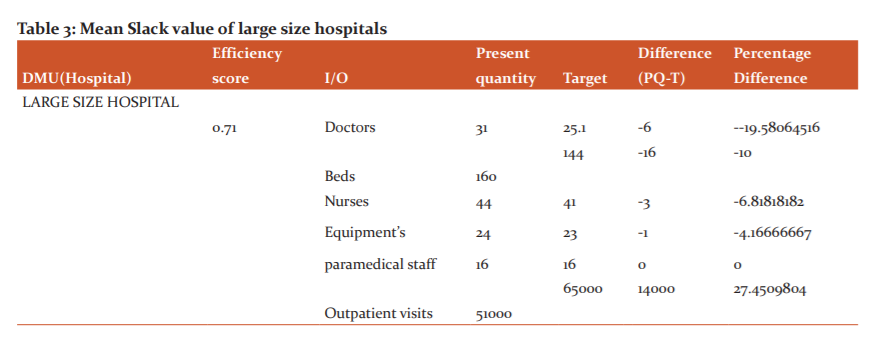
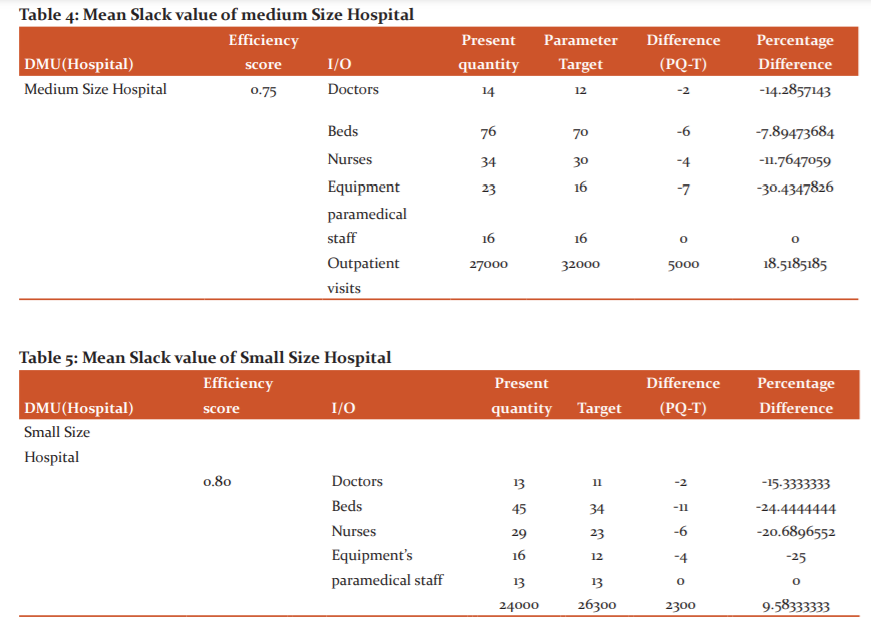
Slack Value in Medium and Small Size Hospital
Hospital administrators have three options to them for optimally utilizing wasteful assets use: Expanding network of hospital. Decreasing hospital inputs; or Hospital organization process changes in medical hospitals.11,12All together for the wasteful medical hospitals to have gotten moderately productive, as a gathering, they would have expected to build their outpatient division visits more than (18.05%) and in small size hospitals patient visits can be increased to 9.5% ( Table 4 and 5).
DISCUSSION
Present research indicates that smaller hospitals have an efficiency more than the larger size and mid-size medical hospitals as demonstrated in the above table smaller size hospitals average efficiency is .80. The mean efficiency of medium size hospitals is .75 and the large hospital is .71. As per our outcomes, small size medical hospitals are generally more efficient. The objective of small, medium and big size hospitals are different as some concentrate more on care and quality some on quantity. Big size hospitals will in general increment their physical, innovative and medicinal work limit in request to understand the requirement of far-reaching care. Nature of care may essentially increment in parallel with the addition of these limits. Strangely, huge size medical hospitals are not performing like small and medium-size medical hospitals as far as scale effectiveness. As results estimate large size hospitals don‘t work at an ideal scale size. , big size hospitals may frame smaller patient consideration units inside their association. Along these lines, large size medical hospitals not just take out the negative impact of their non-ideal scale size, yet besides they make explicit treatment units for patients.
Other than efficiency estimation this DEA model also provided important information about return to scale of hospitals, Outcomes uncovered that all hospitals understudy would result in:
The constant return to scale in 4 (8.33%) medical hospitals, suggesting that their healthcare administration outputs would increment to a similar extent. This implies hospitals were working at their most gainful scale sizes.14,15
Increasing return to scale in 23 (47.9%) medical hospitals, suggesting that their healthcare administration outputs would increment by a more prominent extent. These medical hospitals subsequently expected to expand their size to accomplish ideal scale, for example, the scale at which there is a steady return to scale in the connection among inputs and outputs.16,17
Decreasing return to scale in 21(43.7%) hospitals, inferring that their healthcare administration outputs would increment by a small extent. medical hospitals would have expected to decrease their size to accomplish ideal scale.18,19
Slack values are valued which is added to inequality constraint to convert into equality. The present study uncovers immense slack in the utilization of assets, for example, specialists, Beds. With better observing, medical hospitals will have the option to serve more patients with existing assets and in the current situation in the healthcare area in India, the ideal use of assets in the segment is vital. in the first stage efficiency of hospitals are calculated and only 4 % of hospitals are working at an efficient scale and 44 % of hospitals are inefficient and now in this stage research is to find out the cause of inefficiency that will cause input slack in Hospitals. In this stage, analysis is applied to find whether these medical hospitals ideally use contributions for human services to give out-persistent and good administrations to the overall population if not what is the actual reason for inefficiency and how much each hospital can contribute to out to reach efficiency.
CONCLUSION
As indicated by research outcomes and findings, small size hospitals are generally more efficient and have higher patient satisfaction as compared to other hospitals. Medical hospital likewise concentrates on the reasons for low efficiency before reconfiguring their entire hospital structure. The organization through decentralized set-up and the small zone level authorities screens these associations and study slack of every hospital. The activity of government is essential in ensuring that finding slack is used effectively. This will require making execution based pointers to screen the slack in the input of hospitals and plan to manage to particularly work on which area. In this research also many slacks are identified in each hospital infrastructure use which can be regulated to other paces if it is surplus. Moreover when an organization is big then management must ensure efficiency consideration. The health care industry can adopt Benchmarking scheme of their services with the best one in the same field to improve efficiency. The reason for benchmarking in medicinal services is to improve effectiveness, nature of care, understanding healthcare and patient satisfaction.
RECOMMENDATIONS
DEA data envelopment analysis can be applied in the organization to solve the proper staffing problem. Utilizing information to examine staff distribution can prompt operational productivity. Information on patient volume can be recorded and medical hospital staff can be suitably designated dependent on the equivalent. The present research demonstrates that smaller medical hospitals have a more significant level of effectiveness than bigger and medium-size emergency hospitals as appeared in the above table smaller size hospitals normal efficiency is .80. So two hundred bed hospitals are more efficient than one 200 bed hospitals. In a country like India here Population is very high small hospitals with more outreach is required. Healthcare operations management is urgent for the effective working of healthcare administrations, particularly when the medicinal services segment is experiencing a lot of changes.
FUTURE SCOPE OF STUDY
This study provides the idea about how to evaluate the efficiency of tertiary hospitals. This methodology can act as a tool to benchmark efficiency for hospital authorities for best in that area. The technique utilized right now i.e. Data envelopment analysis to distinguish the hospitals on basis of efficiency, which can improve their administration. In past, the checking and assessment of these foundations have stayed a significant issue. The administration through decentralized set-up and the area level healthcare specialists can screen these foundations. The job of the government is very basic in guaranteeing that hospital infrastructure is utilized optimally. This will require creating execution based pointers to screen these awards using data envelopment analysis. The procedure recommended right now help healthcare agencies to recognize moderately less efficient medical hospitals. The methodology suggested in this research can be used by the Department of Health and Family Welfare to develop benchmarks for monitoring and evaluating the performance of both public and private hospitals. Based on the findings the steps can be initiated to improve the efficiency of resource use in hospitals. DEA can be applied to compare hospital performance after Electronic Medical record system implementation
Acknowledgement: Authors acknowledge the immense help received from the scholars whose articles are cited and included in references of this manuscript. The authors are also grateful to authors/editors/publishers of all those articles, journals and books from where the literature for this article has been reviewed and discussed
Financial Support and sponsorship: Nil
Conflict of interest: No conflict of interest.
Author Contribution:
Dr Pritpal Singh and Prikshat Kumar conceived the idea. Dr Pritpal Singh developed the theory and performed the computations. Prikshat Kumar verified the analytical methods and encouraged Dr Pritpal Singh to investigate and supervised the findings of this work. Both authors discussed the results and contributed to the final manuscript. Dr Pritpal Singh and Prikshat Kumar wrote the manuscript.
References:
1. Bowlin F. Measuring performance: An introduction to data envelopment analysis (DEA). J Cost Anal 1998;7(2):3-27.
2. Bhat R, Verma BB, Reuben E. An empirical analysis of district hospitals and grant-in-aid hospitals in Gujarat state of India. Health Policy Development Network (HELPONET), 2001;13(2):1-40.
3. Hassan M, Tuckman HP, Patrick RH. Hospital length of stay and probability of acquiring infection. Int J Pharm Health Mark 2010;4(3):24?38.
4. Ghosh B, Bhadia U. A study on the inpatient system in a state hospital of Calcutta. Indian J Commu Med 1990;15(1):135?149.
5. Mogha SK, Yadav SP, Singh SP. Performance evaluation of Indian private hospitals using DEA approach with sensitivity analysis. Int J Manag Eco 2012;11(2):1-2.
6. Singh PP, Farhan M, Asif M. An Empirical Study on Association of Operational Efficiency and Customer Satisfaction in Tertiary Hospitals in Punjab. Int J Manag Eco 2019;10(9):295-301.
7. Oussofiane A, Dyson RG, Thanassoulis E. Applied data envelopment analysis. Eur J Oper Res 1991;5(2):1-15.
8. Jat TR, Sebastian MS. Technical efficiency of public district hospitals in Madhya Pradesh, India: A data envelopment analysis. Glob Health Act 2013;(6:2):17-42.
9. Kirigia JM, Emrouznejad A, Sambo LG, Munguti N. Using data envelopment analysis to measure the technical efficiency of public health centers in Kenya. J Med Syst 2004;2(8):155-66.
10. Sheikhzadehl Y, Roudsari AV, Vahidi RG .Public and private hospital services reform using data envelopment analysis to measure technical, scale, allocative, and cost efficiencies. Health Promot Perspect 2012;2(2);28-41.
11. Singh Z. Aging: The triumph of humanity-are we prepared to face the challenge? Indian J Public Health 2012;5(6):189-195.
12. Davey S, Raghav SK, Muzammil K, Singh JV, Davey A, Study on the role of rural health training centre (RHTC) as a supporting component to a primary health care system for NRHM programme in district Muzaffarnagar (UP). Int J Res Med Sci 2014;2(6):53-61.
13. Austin MJ, Shawcross DL. The outcome of patients with cirrhosis admitted to intensive care. Curr Opin Crit Care 2008;14(2):202-7.
14. Charif I, Saada K, Benajah D, Abkari ML. Predictors of Intra-Hospital Mortality in Patients with Cirrhosis. J Gastroenterol 2014;14(4):141-8.
15. Wong F, Bernardi M, Balk R, Christman B, Moreau R, Garcia-Tsao G, et al. Sepsis in cirrhosis: report on the 7th meeting of the International Ascites Club. Gut 2005;54(5):718-25.
16. Viasus D, Garcia-Vidal C, Castellote J, Adamus J, Verdaguer R, Dorca J, et al. Community-acquired pneumonia in patients with liver cirrhosis: clinical features, outcomes, and usefulness of severity scores. Med. 2011;90(2):110-8.
17. Alsherif A, Darwesh H, Badr M, Eldamarawy M, Shawky A, Emam A. SOFA Score as a Predictor of Mortality in Critically Ill Cirrhotic Patients. Life Sci J 2013;10(2):178-181.
18. Hamza RE, Villyoth MP, Peter G, Joseph D, Govindaraju C, Tank DC, et al. Risk factors of cellulitis in cirrhosis and antibiotic prophylaxis in preventing recurrence. Anna Gastroent 2014;2:28.
19. Jalan R, Fernandez J, Wiest R, Schnabl B, Moreau R, Angeli P, et al. Bacterial infections in cirrhosis: a position statement based on the EASL Special Conference 2013. J Hepatol 2014;60(6):1310-24.
20. Maiwall R, Kumar S, Chaudhary AK, Maras J, Wani Z, Kumar C, et al. Serum ferritin predicts early mortality in patients with decompensated cirrhosis. J Hepatol 2014;61(1):43-50.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License