IJCRR - 7(24), December, 2015
Pages: 24-29
Date of Publication: 20-Dec-2015
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
IMMUNOTHERAPEUTIC TREATMENT OF HIV-1: REVIEW OF SAFETY AND EFFICACY
Author: Kariuki, SM, Musyoki, SK and Kemoi, EK
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Background: For over two decades, the treatment of HIV-1 patients has relied on antiretroviral (ART). These drugs have had a great deal of achievement in not only controlling the viral load but also partly reconstituting the immune system in HIV-1 infected persons. However, the misfortune is that ART is a lifelong treatment because it cannot achieve complete eradication of HIV-1 virus, yet with its side effects like many other drugs. Scientists have hence introduced immunotherapy in an effort toward complete eradication of HIV-1 in HIV/AIDS patients.
Objective: The aim of this paper was to determine the effectiveness and safety of the various immunotherapy formats used in the treatment of HIV-1 infection.
Method: We reviewed a number of peer-reviewed published articles to determine the effectiveness and safety of the different immunotherapy formats tested in randomized clinical trials and animal model experiments.
Results: Majority of immunotherapy regimens used in combination with ART to treat HIV-1 positive human or animals were found to be effective in boosting the cell-mediated immune responses in HIV-1 infection but achieved insignificant results in controlling the viral load in these experiments. Most of the immunotherapy formats were also well tolerated recording minimal to no adverse effects on HIV-1 patients.
Conclusion: Most immunotherapy agents are relatively effective and safe when used in combination with ART in modulating immune response to HIV-1. These immunotherapy agents do not significantly reduce the viral load and hence cannot eliminate HIV-1.
Keywords: Immunotherapy, HIV-1, ART, HIV/AIDS, Effectiveness, Efficacy, Safety
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION
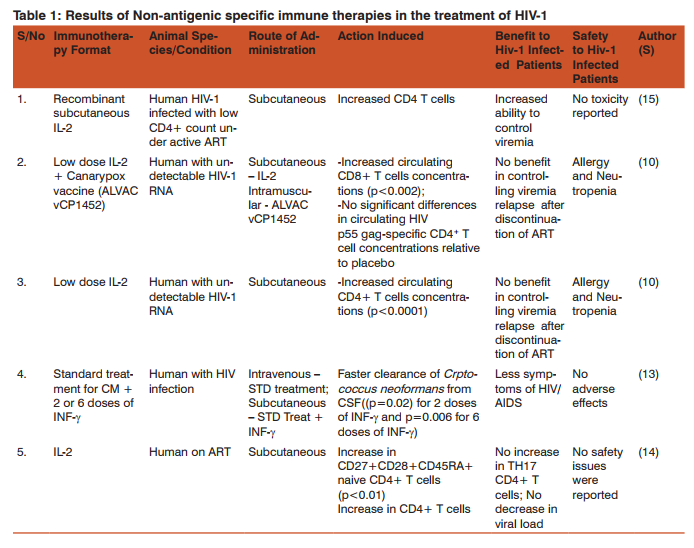
The traditional treatment of HIV/AIDS patients for the past two decades has been anti-retroviral drugs (ART). While these drugs have performed relatively well in dramatically keeping the viral load down and partly reconstituting the HIV-specific CD4+ T cells (1), anti-retroviral have been unable to completely clear the virus in its reservoir tissues in the body (2) and little is known about the effect of ART outside the peripheral blood circulation (3). As such these drugs are taken for life which means the patients suffer from their side effects as long as they live using them. Immunotherapy is the alternative that has emerged in the recent past years where significant amount of research is ongoing to determine its effectiveness and safety in the treatment of HIV/AIDS. Immunotherapy assists the natural immune system to control HIV infection (4). Two types of immunotherapy are being pursued by researchers i.e. “a sterilizing cure” where there is elimination of HIV-1 infected cells from the body and “functional cure” an effective human host immunity modulation which achieves a lifelong suppression of the virus replication (4). Some of the challenges that make it difficult to achieve complete control of HIV replication is the inability by the vaccines to sufficiently activate the immune system (5) and inability to eliminate the latent state of the virus (6). Several approaches have been employed to make various formats of immunotherapy. Some are non-antigenic approaches like the administration of specific cytokines which stimulate the immune system or down regulate viral replication (7). Another approach involves administration of antibodies meant to block the entry of HIV into the host cells (8). Other formats of immunotherapy against HIV virus are induction of effective CD8 T cells and harnessing dendritic cells (DC) function in order to improve the quality of T cell immune responses (4). There are a number of success stories that have been published in relation to immunotherapy in the treatment of HIV1 but the most interesting one is that of the HIV-1 patient in Berlin with acute myelogenous leukemia who received graft from a donor with polymorphism that confers resistance to HIV-1 infection. As a result, this patient remained negative for over 3 years without using anti-retroviral therapy (9). This article reviews published peer-reviewed articles on different formats of immunotherapy against HIV-1 virus to determine the effectiveness and safety of this kind of treatment. (1) says that despite some positive immunomodulation results that have been reported in animal models, there is potential for toxicity of these immunomodulators in human. Data from both randomized clinical trials (RCT) and experiments on animal models of HIV-1 will be reviewed. In the principles of immunotherapy, there are three approaches mainly used (10). These are: Non-specific enhancement of antiviral immune response by various immune stimulating cytokines including type-1 IFNs, IFN-γ, IL-12, and γ–chain signalling cytokines related to IL-2 (10). Blocking antibodies against immune suppressive receptors such as PD-1 and CTLA-4 could also provide beneficial immune stimulation (11). Antigenic formats to induce HIV-specific T cell response in order to elicit more effective CD8 T Cell-mediated immune surveillance (10). DISCUSSION FOR REVIEW a) Cytokine therapies Interferon-gamma (IFN-γ) Serum IFN-γ in the acute phase of HIV-1 infection has been shown to reduce the replication of the virus in both CD4+ and monocytes-macrophage cells (4). However, according to this article the role of IFN-γ in the chronic phase of HIV-1 is not clear since the increased activity of IFN-γ markers like β2 –microglobulin and neopterin lead to poor HIV-1 infection prognosis. Therefore IFN-γ might be helpful in the initial stages of HIV-1 infection but not in the full-blown AIDS. Of the many opportunistic infections in HIV positive patients is the cryptococcal meningitis caused by Cryptococcus neoformans. In some studies, Interferon gamma (INF-γ) monotherapy as opposed to type 1 IFNs (which have antiviral activity) is said to have no direct antiviral activity against HIV-1 as demonstrated in primary cultures, in invitro studies and ex vivo studies (12). These studies have in fact showed a possible negative role where INF-γ increases HIV-1 replication and hence their safety and efficacy cannot be guaranteed. However, the use of INF-γ in combination with the standard therapy in HIV-associated cryptococcal meningitis has been suggested in the past, to reap its benefits. In a randomized clinical trial, (13) demonstrated that treatment of HIV-positive patients with standard treatment (Amphotericin-B 1mg/kg/day plus 5-FC 100mg/kg/day for 2-weeks) in combination with 2 or 6 doses of INF-γ cleared Cryptococcus neoformans from cerebral spinal fluid (CSF) faster than the standard therapy alone (p=0.02 for 2 doses of INF-γ and p=0.006 for 6 doses of INF-γ) (Table 1). This immunotherapy treatment was well tolerated raising no additional adverse effects compared to standard therapy only.
Interleukin-2 (IL-2)
Many immunotherapy formats target to stabilize the immune system and suppress the viral load permanently, while at the same time eliminating the need to continue with the use of highly active antiretroviral drugs (HAART). Interleukin-2 (IL-2) combination with ART is known to increase CD4+ T cell responses in HIV infection and has been approved in some European Countries for use as an immunotherapy agent (14). A phase II randomized, partially blinded 2x2 factorial study found administration low dose of IL-2 to chronically infected HIV-1 patients not helpful in controlling viremia relapse after discontinuation of HAART, but induced significant levels of CD4+ T cells (10). The therapy had been administered to patients with undetectable HIV-1 RNA and CD4 T-cells count of >400 cells/µl and compared to placebo. In that study even when the low-dose of IL-2 was combined with a ALVAC vCP1452 (Canarypox) vaccine it was still found not effective in preventing replication of HIV-1 once HAART had been discontinued but was in this case found to significantly increase the concentration of circulating CD8+ T cells (Table 1). In a another study, (15) who administered a subcutaneous recombinant of human IL-2 to HIV-1 patients with low baseline CD4 count (50-299cells/mm3 ) found that IL-2 increased CD4 T cells count compared to antiretroviral therapy alone. However, a combination of antiretroviral with IL-2 therapy in this study added no value in terms of immune response. In contrast, (16) found a significant increase of CD4+ T cells count among HIV-1 patients that were treated with ART+IL-2 relative to those who received ART only, compared to the baseline CD4+ T cells count. In addition, ART + IL-2 treated patients showed an increase in CD27+CD28+CD45RA+ on naive CD4+ T cells compared to those treated with ART alone (p<0.01). There was however a change of pattern in this trend where the group treated with ART + IL-2 showed a decline in TH17 CD4+ T cells while the ART-only treated group did not show any change in the TH17 cells population compared to the baseline data. This data suggests that a combination of IL-2 with ART increases HIV-1 specific cell-mediate immune responses but has an insignificant effect in reducing the viral load in HIV patients in the long run.
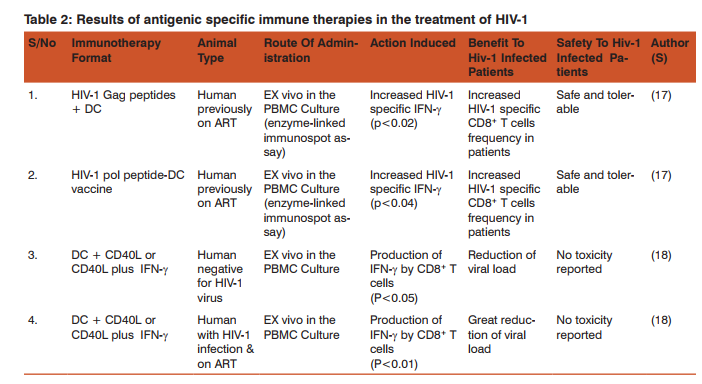
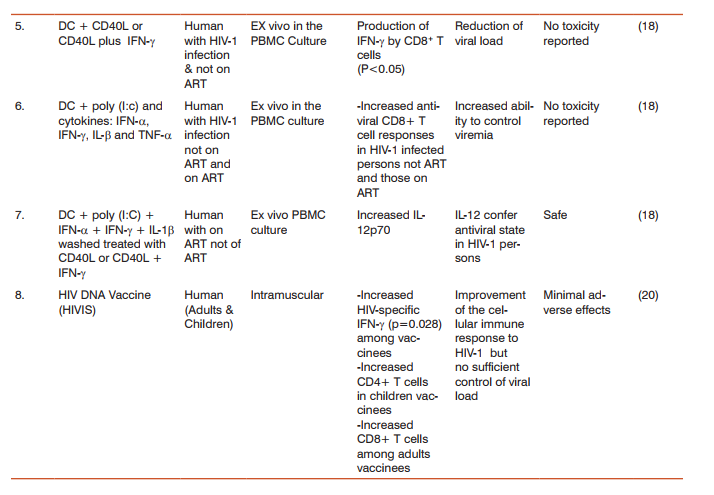
b) Antigenic specific immune therapies
Antigenic specific immune therapies have proven potential in the treatment of HIV-1 infection. In a phase 1 clinical safety trial, (17) found that the HIV-1 HLA*A0201, Env, Gag and pol peptides loaded to mature dendritic cells (DC) were safe and tolerable in the primary end point. In the secondary end point, these vaccines were found to induce HIV-1 specific IFN-γ responses in enzyme-linked immunospot assay, as well as clinical correlates of an immune response consistent with those expected in vaccination. Specifically, there was significant increase in CD8+ T cells in response to HIV-1gag peptide DC (p<0.02) as well as HIV-1 pol peptide-DC vaccine (p<0.04), in HIV-1 patients previously on ART. In another study, (18) demonstrated that mature DC treated with CD40L or CD40L plus IFN-γ compared with immature DC in HIV-1 negative patients, HIV-1 positive patients on ART and those not on ART, induced significant HIV-1 specific IFN-γ produced by CD8+ T cells in these patients (Table 2). This study also demonstrated that maturation of DC stimulated with TLR3 ligand polyinosinic:polycytidylic acid – cytokine combination produces significant amount of HIV-1 specific IFN-γ by CD8+ T cells (Table 2). In the same study, Huang et al., showed that the highest levels of IL-12p70 which enhances the activity of CD8+ T cells was produced by DC treated with CD40L plus IFN-γ, and DC treated with a combination of CD40L plus poly (I:C) (Table 2). In this study, it was found that DC stimulation of protective anti-viral CD8+ T cells reactivity was greatly enhanced by activated CD4+ T cells in low concentration but not in higher concentration. This data suggests that targeting DC maturation with the appropriate stimulation in HIV-1 patients on ART can be a helpful strategy in HIV-1 immunotherapy. Among structural components of HIV-1 that have been targeted for vaccines, is the DNA of the virus. For more than two decades scientists have been testing HIV DNA vaccines on non-human primates and human subjects and the vaccine has been found to have the potential for eliciting T cell-mediated immunity (19). Immunotherapy research by (20) found that a multi-gene multi-subtype A, B, C HIV DNA vaccines induced HIV-1 specific cellular immune responses in both HIV-positive children and adults on ART. In adults, vaccines were found to significantly increase HIV-1 specific IFN-γ responses (p=0.028) at week 10 from the baseline, relative to the placebo group of adults (Table 2). There was also an increase in HIV-specific, MHC class 1 restricted CD8+ T cell response among the adults vaccinated and an increase in CD4+ T cell response among the HIV DNA vaccinated children. HIV DNA vaccine was well tolerated with minimal adverse effects. Though there were no good results on viral load reduction, in the study by Palma et al., (2014) this data shows that a combination of ART and HIV DNA vaccines should be considered as a strategy in the treatment of HIV infection because it is both safe and relatively immunogenic. The efficacy results by (20) in that study were contradicted the work by (21) who found efficacy of HIV DNA vaccine among HIV-Positive patients was as low as 0.1% showing no benefit to HIV-1 patients as far as disease progression is concerned.
c) Antibody Therapies
Antibody therapy is one of the immunotherapy strategies that have been studied by scientists in the recent past years in an effort toward reinforcing the antiretroviral therapy currently in use in the treatment of HIV infection. (22) have documented that accumulating data on antibody responses shows no role in containing HIV-1 replication in patients. However, some studies have demonstrated that a combination of ART and broadly neutralizing antibodies raised against the gp120 portion of HIV-1 have a long-term control of the viral load in hu-mice (23). The hu-mice were immunized with three proteins of gp120 subcutaneously twice every week for six weeks. The antibodies administered were 3BNC117, PG16 and 10-1074 of gp120. After six weeks there a significant drop in HIV-1 plasma RNA as well as cell-associated DNA in hu-mice treated with a combined therapy of antibody and ART compared with those treated with ART only. It was further demonstrated that the antibody therapy could control viral load even after ART is stopped and the viral load goes to the pre-treatment state. This data suggests that a combination therapy of antibody and ART can overcome the challenge of inability of ART to control viral load on long-term basis without continued permanent mandatory use of the ART.
 CONCLUSION
CONCLUSION
Most immunotherapy agents are relatively effective and safe when used in combination with ART in modulating immune response to HIV-1. However, more studies are needed to determine the ability of immunotherapy to reduce the viral load and ultimately eradicate HIV-1 from the patients suffering from HIV/AIDS.
Funding and Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the funding for this work was by the authors’ own contributions. There is therefore no conflict of interest of any form. All people who made significant contribution in writing this paper are included as authors while the scholars whose work was cited and referenced were acknowledged in this manuscript.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
The authors of this work acknowledge the immense help received from the scholars whose articles are cited and included in references of this manuscript. The authors are also grateful to authors/editors/publishers of all those articles, journals and books from where the literature for this article has been reviewed and discussed.
Abbreviation
AIDS – Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome
ART – Anti Retroviral Therapy
CD – Cluster of Differentiation
CSF – Cerebral Spinal Fluid
CTLA-4 – Cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-associated protein 4
DC – Dendritic Cells
DNA – De-oxy ribonucleic acid
HAART – Highly Active Antiretroviral Treatment
HIV-1 – Human Immune Virus
IFN - Interferon IL – Interleukin
MHC – Major Histocompatibility Complex
PD-1 - Programmed cell death protein 1
RCT - Randomized Clinical Trials
RNA – Ribonucleic Acid
TH – T-helper Cell
TLR3 – Toll-like Receptor 3
References:
1. Haes W De, Pollard C, Vanham G, Rejman J. “ Wrapped Up ” Vaccines in the Context of HIV-1 Immunotherapy. 2012;41.
2. Poonia B. Infectious Diseases and Therapy Immunotherapy in HIV Infection. 2013;1(1):1–5.
3. Denton PW, Long JM, Wietgrefe SW, Sykes C, Spagnuolo RA, Snyder OD, et al. Targeted cytotoxic therapy kills persisting HIV infected cells during ART. PLoS pathogens [Internet]. 2014 Jan [cited 2014 Nov 2];10(1):e1003872. Available from: http:// www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?artid=3887103 andtool=pmcentrezandrendertype=abstract
4. Vanham G, Van Gulck E. Can immunotherapy be useful as a “functional cure” for infection with Human Immunodeficiency Virus-1 Retrovirology [Internet]. Retrovirology; 2012 Jan [cited 2014 Nov 16];9(1):72. Available from: http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?artid=3472319andtool=pmcent rezandrendertype=abstract
5. Luban J. Innate immune sensing of HIV-1 by dendritic cells. Cell host and microbe [Internet]. Elsevier Inc.; 2012 Oct 18 [cited 2014 Nov 16];12(4):408–18. Available from: http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?artid=3619430andtool=pm centrezandrendertype=abstract
6. Chun T-W, Fauci AS. HIV reservoirs: pathogenesis and obstacles to viral eradication and cure. AIDS (London, England) [Internet]. 2012 Jun 19 [cited 2014 Nov 5];26(10):1261–8. Available from: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22472858
7. Pett SL, Kelleher AD. Cytokine therapies in HIV-1 infection: Present and future [Internet]. Expert Review of Anti-Infective Therapy. 2003. p. 83–96. Available from: http://www.scopus.com/inward/record.url?eid=2-s2.0-2942557197andpartnerID=tZOtx3y1
8. Kwong PD, Mascola JR, Nabel GJ. Broadly neutralizing antibodies and the search for an HIV-1 vaccine: the end of the beginning. Nature Reviews Immunology [Internet]. Nature Publishing Group, a division of Macmillan Publishers Limited. All Rights Reserved.; 2013 Aug 23 [cited 2015 Sep 28];13(9):693–701. Available from: http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/nri3516
9. Nanotechnology in Diagnosis, Treatment and Prophylaxis of Infectious Diseases [Internet]. Nanotechnology in Diagnosis, Treatment and Prophylaxis of Infectious Diseases. Elsevier; 2015 [cited 2015 Sep 23]. 39-49 p. Available from: http://www. sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/B9780128013175000037
10. Smith K a, Andjelic S, Popmihajlov Z, Kelly-Rossini L, Sass A, Lesser M, et al. Immunotherapy with canarypox vaccine and interleukin-2 for HIV-1 infection: termination of a randomized trial. PLoS clinical trials [Internet]. 2007 Jan [cited 2014 Nov 16];2(1):e5. Available from: http://www.pubmedcentral.nih. gov/articlerender.fcgi?artid=1783674andtool=pmcentrezandrender type=abstract
11. Velu V, Shetty RD, Larsson M, Shankar EM. Role of PD-1 coinhibitory pathway in HIV infection and potential therapeutic options. 2015;1–17.
12. Roff SR, Noon-Song EN, Yamamoto JK. The Significance of Interferon-γ in HIV-1 Pathogenesis, Therapy, and Prophylaxis. Frontiers in immunology [Internet]. 2014 Jan 13 [cited 2014 Nov 10];4(January):498. Available from: http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?artid=3888948andtool=pmcent rezandrendertype=abstract
13. Jarvis JN, Meintjes G, Rebe K, Ntombomzi G, Bicanic T, Williams A, et al. Europe PMC Funders Group Adjunctive Interferon- γ Immunotherapy for the Treatment of HIV- associated Cryptococcal Meningitis : A Randomized Controlled. 2013;26(9):1105–13.
14. Ndhlovu LC, Sinclair E, Epling L, Tan QX, Ho T, Jha AR, et al. IL-2 immunotherapy to recently HIV-1 infected adults maintains the numbers of IL-17 expressing CD4+ T (T(H)17) cells in the periphery. Journal of clinical immunology [Internet]. 2010;30(5):681–92. Available from: http://www.scopus.com/inward/record.url?eid=2-s2.0- 77957571862andpartnerID=tZOtx3y1
15. Abrams D, Levy Y, Losso MH, Babiker A, Collins G, Cooper DA, et al. Interleukin-2 therapy in patients with HIV infection. N Engl J Med. 2009;361(16):1548–59.
16. Ndhlovu LC, Sinclair E, Epling L, Tan QX, Ho T, Jha AR, et al. IL-2 immunotherapy to recently HIV-1 infected adults maintains the numbers of IL-17 expressing CD4+ T (T(H)17) cells in the periphery. Journal of clinical immunology [Internet]. 2010 Sep [cited 2014 Nov 16];30(5):681–92. Available from: http://www. pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?artid=2935971andtool= pmcentrezandrendertype=abstract
17. Connolly NC, Whiteside TL, Wilson C, Kondragunta V, Rinaldo CR, Riddler S a. Therapeutic immunization with human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) peptide-loaded dendritic cells is safe and induces immunogenicity in HIV-1-infected individuals. Clinical and vaccine immunology : CVI [Internet]. 2008 Feb [cited 2014 Nov 16];15(2):284–92. Available from: http://www. pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgiartid=2238066andtool= pmcentrezandrendertype=abstract
18. Huang X-L, Fan Z, Borowski L, Rinaldo CR. Maturation of dendritic cells for enhanced activation of anti-HIV-1 CD8(+) T cell immunity. Journal of leukocyte biology [Internet]. 2008 Jun [cited 2014 Nov 16];83(6):1530–40. Available from: http:// www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18364435
19. Chen Y, Wang S, Lu S. DNA Immunization for HIV Vaccine Development. Vaccines [Internet]. 2014 Feb 25 [cited 2014 Nov 16];2(1):138–59. Available from: http://www.mdpi.com/2076- 393X/2/1/138/
20. Palma P, Gudmundsdotter L, Finocchi A, Eriksson L, Mora N, Santilli V, et al. Immunotherapy with an HIV-DNA Vaccine in Children and Adults. Vaccines [Internet]. 2014 Jul 17 [cited 2014 Nov 16];2(3):563–80. Available from: http://www.mdpi. com/2076-393X/2/3/563/
21. Pitisuttithum P, Gilbert P, Gurwith M, Heyward W, Martin M, van Griensven F, et al. Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled efficacy trial of a bivalent recombinant glycoprotein 120 HIV-1 vaccine among injection drug users in Bangkok, Thailand. The Journal of infectious diseases. 2006;194(12):1661–71.
22. Letvin NL, Walker BD. Immunopathogenesis and immunotherapy in AIDS virus infections. Nature medicine [Internet]. 2003 Jul;9(7):861–6. Available from: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/ pubmed/12835706
23. Horwitz JA, Halper-Stromberg A, Mouquet H, Gitlin AD, Tretiakova A, Eisenreich TR, et al. HIV-1 suppression and durable control by combining single broadly neutralizing antibodies and antiretroviral drugs in humanized mice. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America [Internet]. 2013;110(41):16538–43. Available from: http://www. pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?artid=3799352andtool= pmcentrezandrendertype=abstract
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License