IJCRR - 13(9), May, 2021
Pages: 168-173
Date of Publication: 07-May-2021
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
Attitude of MBBS Students Towards Cadaveric Dissection and their Views on Anatomy as a Subject for Career Option in Uttar Pradesh
Author: Umesh Choudhary, Priyanka Bharti, Amit Kumar Nayak
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Introduction: Anatomy is one of the important subjects taught to the MBBS first-year students. Cadaveric dissection plays an important role in the deeper understanding of three- dimensional relationship of different anatomical structures, appreciating anatomical variations which are key to practice health and medicine. First-year medical students when encountering human cadavers for the first time faces lots of emotional and mixed feelings. The exposure has both physical and psychological impact on students. Objective: This study aimed to explore the knowledge and attitude of medical students regarding cadaveric dissection and anatomy as a career option. Methods: The study was conducted at Mayo institute of medical sciences, Barabanki. A total of 300 students of MBBS batch 2016 - 2017 and 2017- 2018 participated in this study. It is a questionnaire-based study done to evaluate student's behaviour, experiences and emotions regarding cadaver dissection and also to access their views on anatomy as a career option. Results: The emotional and physical stress encountered initially was decreased gradually after 3 months of dissection. It was found that students were not much interested in pursuing Anatomy as a career option due to a lack of opportunities. Conclusion: This study concludes that anatomical dissection remains an essential part of medical education and it should not be replaced by any other modern learning methods. The emotional shock experienced by the students can be greatly reduced if they are properly counselled before the dissection class. Research and job opportunities should be encouraged in the subject to develop interest among the young medical graduates for pursuing anatomy as a career.
Keywords: Anatomy, Cadaver, Dissection, Experience, First year, Medical Students
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION
Anatomy, the study of the structure of the human body, is the first most basic and one of the most important subjects studied by medical and paramedical students when they first began their medical career.1Anatomical knowledge remains a cornerstone of medicine and related professions, despite the reduction in importance, time committed to, and status of anatomical education in modern curricula.2 Cadaveric dissection has been a regular feature in anatomy teaching since the epoch. Andreas Vesalius (1514-1564) was the first medical student to dissect the cadaver and also continued with it even as a professor.3 Dissection has been labelled as the "royal road"4 and the cadaver as the "first patient".5 Cadaver dissection has also been called the "sharp-end" of medical education.6 Surgeons advocate experience with dissection not only for learning anatomical detail but also to familiarize students with variations in anatomy. Students from their childhood are trained to emphasise scoring good marks rather than applying the knowledge practically, they enter the medical course holding the same perception. But the professional educational environment is very much different from the traditional school and junior college environment. Medical school's learning orientation has a solid scientific basis with its practical implementation on the patient in the long run.7 Anatomy is the first subject which students admitted to medical course come across. Medical students experience a lot of emotional and physical stress when they encounter a human cadaver for the first time. Working with a cadaver constitutes potential stress which includes both positive and negative experiences in this subject.8 some authors consider that cadavers may present several disadvantages. Their colour, texture, and smell are not like real life, and cadavers cannot be palpated, auscultated, or usefully asked to change position. Their use may present health hazards and ethical/legal difficulties.9
Another major concern in Anatomy is the shortage of teachers in medical colleges at the global level. The number of medically qualified teachers in preclinical subjects is continuously decreasing.10 Postgraduate seats in medical colleges are left vacant in preclinical subjects. Therefore, it is an urgent need to enhance awareness amongst students regarding available job opportunities and research possibilities in the subject of anatomy.
The present study aims to assess student's attitude towards dissection by recording their attitude thrice. First when they entered the dissection hall for the first time, second after three months of dissecting experience and third once they pass out their MBBS first year. This study also aims to evaluate the opinion of medical students regarding anatomy as a subject for a career option.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
The study was conducted at Mayo institute of medical sciences, Barabanki. It is a questionnaire-based study. A total of 300 students of MBBS batch 2016 - 2017 and 2017- 2018 was involved in this study. The objectives of the study were explained to the students. All the 150 students of MBBS batch 2016- 2017 were given 3 sets of questionnaires.
-
First - on the first day of their dissection hall experience
-
Second- after three months of dissecting experience
-
Third - after passing the first-year MBBS
The same process was repeated with the remaining 150 students of MBBS batch 2017- 2018. For each question, the students had to choose any one response - yes, no or neutral.
RESULTS
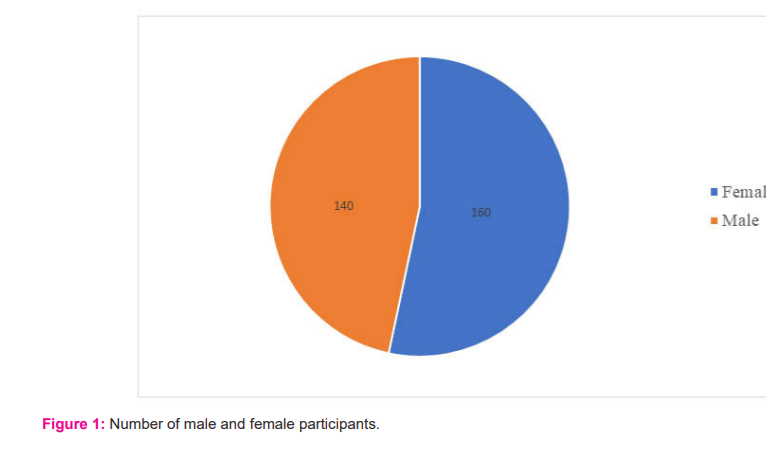
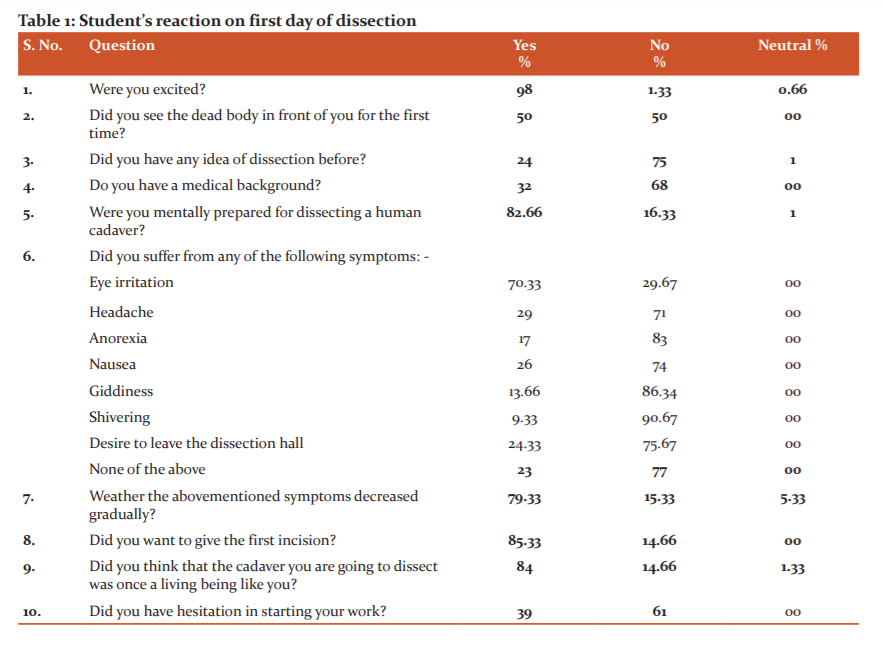
Out of the total of 300 students who participated in the study, 160 were male and 140 female (Figure 1). The age group of students who participated in this study ranges between 19- 25 years. On the first day of the dissection hall experience, 98% of the students were excited, 50% of them had not seen a dead body before. About 82.66% of the students were mentally prepared for dissecting a human cadaver. The majority of them suffered from various physical symptoms, of which eye irritation was the most commonly experienced by 70.33%, these symptoms decreased gradually with time. 85.33% wanted to give the first incision while 39% of them hesitated to start dissection as they had a thought that the cadaver which they are going to dissect was once living (Table 1).
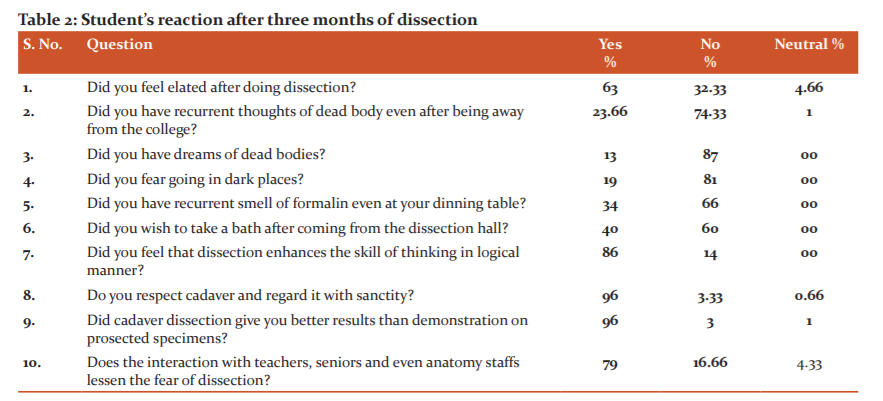
After three months of dissection, 63% felt elated. 23. 66% of students had recurrent thoughts of the dead body even being away from the college, while 13% even dreamt of dead bodies. About 34% had the recurrent smell of formalin even at their dining table. 40% wished to take a bath after coming from the dissection hall. The majority of students felt that dissection logically enhances the skill of thinking. 96% of them had respect for cadaver and regard it with sanctity. 79% think that teachers and anatomy staff plays an important role in reducing their fear and stress and creating a comfortable environment in the dissection hall (Table 2).
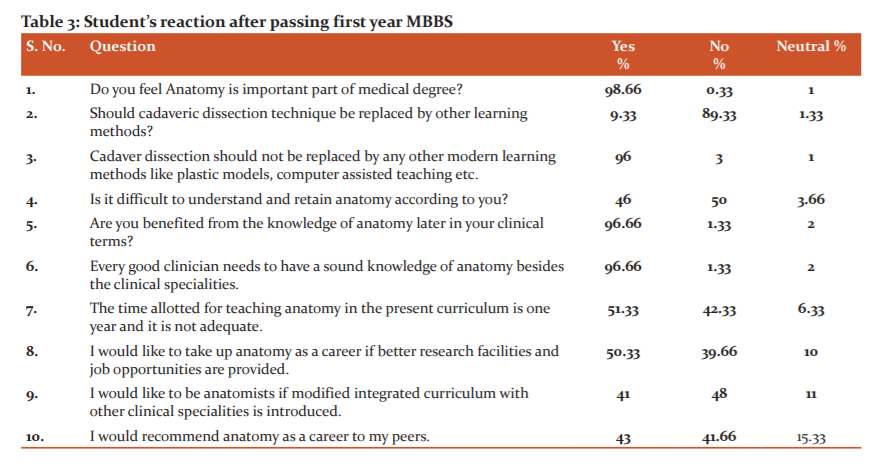
The majority of students after passing first-year MBBS felt anatomy dissection as an important part of a medical degree and participating in cadaver dissection provides more opportunities to develop professional skills, therefore they consider themselves benefited from the knowledge of anatomy later in clinical terms. 50% of them accepted that anatomy is not difficult to understand and retain while 51.33% of them felt that one year time allotted to teach anatomy is not sufficient. 96% do not want cadaver dissection to be replaced by any other modern learning methods such as plastic models, computer-assisted training etc in the near future.96.66% think that every good clinician needs to have a sound knowledge of anatomy besides the clinical specialties.50.33% of students would like to take up anatomy as a career if better research facilities and job opportunities are made available while 41% would like to be an anatomist if modified integrated curriculum with other clinical specialities is introduced. Only 43% of the students participating in the study would recommend anatomy as a career to their peers (Table 3).
DISCUSSION
In the present study, dissection was considered important for gross anatomy learning particularly the three-dimensional aspect of human anatomy. It enhanced the student’s skill of logical thinking which helped them in better understating other medical subjects. This is in concordance with the previous studies.11-24
Furthermore, the majority of the students agreed that actual hands-on training on cadaver dissection gave better results than the demonstration of the protected specimen and it should not be replaced by any other learning methods. This finding is consistent with the findings from previous studies.25 It is at variance with the observations made by some other authors.26-29
It was found that the physical and emotional symptoms suffered by the students decreased gradually. This finding is similar to the previous observations made.30-32 It has been reported that sometimes the urge and strong interest in medicine career motivates students and lowers the level of mental stress while increasing their preparedness.17 We observed that most of the students were excited after visiting the dissection hall on the first day. This is in agreement with the previous studies done.34-36 It is also suggested that the majority of the students were upset at the beginning of the dissection.29 In the present study most of the students felt elated after dissection, which is similar to the previous finding done by Cahill KC et al. on Irish medical students.37 Most of the students considered that cadavers were once living humans and had sympathy and respect for them. This finding is in concordance with studies done.19,22,34 There is a need to emphasize the sanctity of the cadaver as a human specimen, to inculcate into students carefulness and empathy, which is important in the subsequent medical practice.
It is very despondent to notice that very few students are interested to pursue anatomy as a career option similar to the previous findings.32,38 This issue needs immediate intervention measures to be taken to develop career interest in this subject by increasing research and job opportunities. Financial consideration is a major criterion for career selection and preclinical subjects as a career option are associated with low financial returns, which may be one of the major reasons for low interest in anatomy as a career. This is also agreed in the previous studies done.39-43
CONCLUSION
Anatomical dissection is still valued as one of the most effective and indispensable teaching tool for human anatomy, which help students in every walk of their medical career. However, to make the dissection hall experience more pleasant, there is a need to address the students physical, mental and emotional problems repeatedly through proper counselling. Furthermore, interest in anatomy as a career option can be increased by better remuneration, increased research opportunities and career guidance. Research opportunities can be increased by linking clinical embryology and andrology labs, cytogenetic labs, radiological labs and neurobiology labs to the department of anatomy.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
We are grateful to all the students of batch 2016- 2017 and 2017- 2018 of Mayo Institute of Medical Sciences, Barabanki, Uttar Pradesh for their punctual assistance in responding to the questionnaire. The authors acknowledge the immense help received from the scholars whose articles are cited and included in references of this manuscript. The authors are also grateful to authors/editors/publishers of all those articles, journals and books from where the literature for this article has been reviewed and discussed.
CONFLICT OF INTEREST – NIL
SOURCE OF FUNDING – NIL
AUTHOR’S CONTRIBUTION –
UC: Designed the analysis and collected the data.
PB: Contributed to data analysis and interpretation of the result.
AKN: Wrote the paper.
References:
-
Rajkumari AB, Singh YI. Body donation and its relevance in anatomy learning – a review. J Anat Soc India 2007;56:1-6.
-
Gillingwater TH. The importance of exposure to human material in anatomical education: a philosophical perspective. Nat Sci Educ 2008;1(6):264-6.
-
Gayatri R, Krishna G . Inception of cadaver dissection and its relevance in present-day scenario of medical education. J Indian Med Assoc 2006;104(6):331-333.
-
Newell RLM. Follow the royal road: the case for dissection. Clin Anat 1995:8:124-127.
-
Coulehan JL, Williams PC, Landis DD, Naser C. The first patient, reflections and stories about the anatomy cadaver. Teach LearnMed 1995;7:61-66.
-
Dubhashi S, Dubhashi U. Medical students react to cadaveric dissections. Rece Res Sci Technol 2011;3(1):135-138.
-
Teunissen PW, Westerman M. Junior doctors caught in the clash: The transition from learning to working explored. Med Educ. 2011;45: 968-970.
-
Dinsmore CE, Daugherty S, Zeitz HJ. Students responses to the gross anatomy laboratory in a medical curriculum. Clin Anat 2001;14(3):231-236.
-
McLachlan JC. New path for teaching anatomy: living anatomy and medical imaging vs. dissection. Anat Rec B New Anat 2004;281(1):4-5.
-
Schockley DG. In quest of profound courtesy: Chaplin enters the anatomy lab. Christ Cent 1986;24:808-10.
-
Weeks SE, Harris EE, Kinzey WG, Human gross anatomy: A crucial time to encourage respect and compassion in students. Clin. Anat 1995;8:69-79.
-
Mutyala S, Cahill DR. Catching up. Clin Anat 1996;9:53-56.
-
Cahill DR, Leonard RJ, The role of computers and dissection in teaching anatomy: A comment (Editorial). Clin Anat 1997;10:140-141.
-
Parker LM. What’s wrong with the dead body? Use of the human cadaver in medical education. Med J Aust 2002;176(2):74-76.
-
Johnson JH. Importance of dissection in learning anatomy: Personal versus peer teaching. Clin Anat 2002:15:38-44.
-
McLachlan JC, Bligh J, Bradley P, Searle J. Teaching anatomy without cadavers. Med Educ 2004;38:418-24.
-
Rajkumari A, Das BK, Sangma GTN, Singh YI. Attitudes and views of first-year medical students towards cadaver dissection in anatomy learning. Calicut Med J 2008;6(4):550-554.
-
Mullu A, Muche A, Tegabu D. Assessment of the attitude and views of second-year medical students towards cadaver dissection in the anatomy course. Ethiop J Health Biomed Sci 2007;2:111-117.
-
Izunya, AM, Oaikhena GA, Nwaopara AO. Attitudes to cadaver dissection in a Nigeria medical school. Asian J Med Res 2010;2:89-95.
-
Agnihotri G, Sagoo MS. Reactions of first-year Indian medical students to the dissection hall experience. Nat J Res Med 2010;1(4):4-9.
-
Patel B, Jadav J, Parmar A and Trivedi B. Attitude of medical students to cadaver dissection in Ahmedabad city. Int J Cur Res Rev 2012;4:54-58.
-
Paul BK, Alex W, Kevin N, Joseph M, Peter N. Perception to cadaver dissection and views on anatomy as a subject between two pioneer cohorts in a Kenyan medical school. Anat J Africa 2014;3(2):318-323.
-
Rajeh NA, Badroun LE, Alqarni AK, Alzhrani BA, Alallah BS, Almghrabi SA, et al. Cadaver dissection: A positive experience among Saudi female students. J Taib Univ Med Sci 2016;13:1-5.
-
Nitasha S, Subedi S, Pandit R. Medical students attitude towards anatomy dissection: A study in Nepal. J Univ Coll Med Sci 2017;5(16):12-17.
-
Jones LS, Paulman R. Thadhani L. Terracio. Medical student dissection of cadavers improves performance on practical exams but not on NBME anatomy subject exam. Med Educ Online 2001;6:2.
-
Jones LS, Welsh MG, Terrace L. First-year medical students’ views on computer programs: Give us our teaching assistants. FASEB J 1998;12:5635.
-
Bernard GR. Prosection demonstrations as substitutes for the conventional human gross anatomy laboratory. J Med Educ 1972;47:724-728.
-
Peppler RD, Kwasigroch TE, Hougland DW. Evaluation of simultaneous teaching of extremities in a gross anatomy program. Acad Med 1985:60(8):635-639.
-
Nnodim JO, Ohnaka EC, Osuji OC. A follow up a comparative study of the two modes of learning human anatomy: By dissection and from prosections. Clin Anat 1996;9:258-262.
-
McGarvey MA, Farrell T, Conroy RM, Kandiah S, Monkhouse WS. Dissection: a positive experience. Clin Anant 2001;14(3):227-230.
-
Evans EJ, Fitzgibbon GH. The dissecting room: Reactions of first-year medical students. Clin Anat 1992;5:311-320.
-
Ajao MS, Alimi TA, Yahya WB, Eweoya OO, Jimoh OR, Olawepo A. Gender effects on physical reactions of health science students at the first encounter with cadaver using Pearson chi-square test. Res J Med Sci 2008;2:100-103.
-
Arora L, Sharma B. Assessment of the role of dissection in anatomy teaching from the perspective of undergraduate students: A qualitative study. Ibnosina J Med Biomed Sci 2011;3(2):59-65.
-
Oyeyipo IP, Falana BA. The attitude of preclinical students to cadaver dissection in a South-West Nigerian Medical School. Int J Trop Med 2012;7(1):1-5.
-
Kemerer MA. Attitudes and views of medical students toward anatomy learnt in the preclinical phase at King Khalid University. J Fam Community Med 2012;19:190-3.
-
Khan HM, Mirza TM. Physical and psychological effects of cadaveric dissection on undergraduate medical students. J Pak Med Assoc 2013;63:831-834.
-
Cahill KC, Ettarh RR. Attitudes to anatomy dissection in an Irish medical school. Clin Anat. 2009 Apr; 22(3):386-91.
-
Anand MK, Raibagkar CJ, Ghediya SV, Singh O. Anatomy as a subject and career option because of medical students in India. J Anat Soc India 2004;53(1):10-14.
-
Anand BK. Manpower recruitment of medical teacher, measures for meeting the requirements. Indian J Med Edu 1992;31:50-54.
-
Soufi HE. The attitude of the medical student towards psychiatry. Med Educ 1992;26:38-41.
-
Sim GS, George KE, Stephen Z. Method of recruiting and selecting resident for US family practice residencies. Acad Med 1994;4(69):1-4.
-
Anantraman V, Kanya R. MBBS students observations on pre and paraclinical subjects. J Anat Sci 1995;14(1):31-33.
-
Koivusilla L, Rimpela A, Rimpela L. Health Status, does it predict choice in future education. J Epid Comm Health 1995;49(2):131-38.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License