IJCRR - 13(9), May, 2021
Pages: 130-135
Date of Publication: 07-May-2021
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
Histopathological Evaluation of Hansen's Disease in The Post Eradication Era at a Tertiary Care Hospital, South India
Author: S. G. Harish, Priyadarshini D, T. S. Kiran, D. R. Shivanand
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Background: Leprosy is a chronic, gradually progressive, granulomatous disease caused by Mycobacterium Leprae. Leprosy is difficult to diagnose due to its clinical heterogeneity and histopathological examination and sub-classification play an important diagnostic tool for the management of the cases. Objective: To study the various histomorphological spectrum of Leprosy in skin biopsies and document various patterns of diseases in the tertiary care hospital. Methods: Prospective study of 43 skin biopsy specimens suspicious of Hansen's received in histopathology laboratory. Biopsies were immediately fixed in 10% buffered formalin and stained with both haematoxylin & eosin, and Fite Faracoon. All sections were reviewed and classified according to Ridley\?Jopling classification. Clinical details of the patient were obtained like, age, sex, site, and type of lesions were obtained and clinicopathological correlation was done. Results: Out of 43 cases studied 32.5% cases showed features of Borderline Tuberculoid (BT) type of Leprosy which was the most common histological subtype, 23.2% cases showed histology of Borderlinelepromatous (BL) Leprosy, 11.6% cases were borderline (BB) case 9.3%cases demonstrated the features of Lepromatous leprosy (LL), 6.9% cases displayed Tuberculoid lep�rosy (TT), 4.6% cases were of Histoid Leprosy (HL), and 11.6% cases were reported as Indeterminate leprosy (IL). Fite Faraco stain showed positive in 28% of cases. The clinicopathological correlation was seen in 62.7% of cases studied. The disease was most common in the middle age group and was detected in the males frequently. Conclusion: Histopathological study of leprosy is very important in understanding the disease, its varied manifestation, and complications. For the correct and adequate treatment, the diagnosis must be made early and it should be accurate.
Keywords: Borderline, Indeterminate, Lepromatous, Tuberculoid, Histopathology, Chronic
Full Text:
Introduction
Leprosy is a slowly progressive, chronic granulomatous infection caused by Mycobacterium Leprae. The disease predominantly affects the skin, the peripheral nerve bundles, upper respiratory tract mucosa and eyes. The Norwegian physician, Gerhard Armauer was the first person to identify Mycobacterium Leprae in 1873. The immune status regulates the distinctive morphological patterns of Leprosy. Ridley–Jopling Classification segregates leprosy into diverse subtypes based on histology and immune statusin1966.1 Microscopic classification of leprosy is based on histomorphological criteria like the formation of granuloma, cell type and distribution of lymphocytes, bacterial load, pathologic changes in nerves, the existence or absence of the subepidermal grenz zone, and epidermal invasion.
Tuberculoid leprosy lies at one end of the spectrum presenting with few lesions and a meagreness of the organism and the other end lies Lepromatous leprosy (LL), in which there are plenty of lesions with countless bacilli and absence of cellular immune response. In between these two lies borderline-Tuberculoid (BT) and Borderline Lepromatous (BL) leprosy. The World Health Organization classification categorizes leprosy into paucibacillary and multibacillary based on skin lesions and involvement of nerve trunk. When suspected cases of Leprosy cannot be diagnosed on clinical presentation and slit skin smears, in such cases histopathology and demonstration of acid-fast bacilli usingFite Faraco stain are of paramount importance in demonstrating Leprae bacilli.2 Great diversity has been observed while interpreting the histopathological examination because of the clinical correlation of the disease. The present study is carried out in the scenario of clinical and histopathological correlation of various patterns of Leprosy. Erythema nodosum leprosum lesions present as red and tender nodules associated with systemic manifestations.
Reduced prevalence of Leprosy in the present stage of eradication of the disease, there are only lean opportunities to study this ambiguous disease. A great level of expertise is vital in diagnosing this disease. The sequel of untreated or undertreated leprosy not only leads to permanent disability and deformity, by damaging the skin, nerves, limbs, and eyes leading to disfigurement. The disease also acts as a reservoir for infection in the community.3,4 With the community prevention programs and a united approach, there has been a gradual reduction in the disease burden but still, leprosy is the major public health problem in India. In 2016 Global leprosy strategy 2016– 2020 was launched by WHO which targets, accelerating towards a leprosy-free world. Before that from 2011–2015, the strategy was focused on early leprosy detection to reduce disabilities. This record states that the program of eliminating leprosy at the subnational level is still incomplete in many countries and will therefore continue to go after in the coming years.
Materials and methods
A prospective study was done in the Department of Pathology in our tertiary care center from January 2018 to December 2019.
Inclusion criteria
Skin biopsies with a clinical suspicion of Hansen’s disease, re-infected and relapse cases were also included in the study, for a period of 2 years from January 2018 to December 2019. Skin punch biopsies of all age groups and both genders were included in the study.
Exclusion criteria
Refusal to give informed consent, Cases released from treatment and follow up cases of previously confirmed Hansen disease were excluded from the study.
Data analysis
Pertinent clinical details such as age, sex, site, and type of lesions were noted.
Skin biopsies were fixed in 10% buffered formalin and then submitted to routine tissue processing and 3-4µ sections were taken and stained with Hematoxylin & eosin, and Fite Faraco stain on all the sections. All sections were reviewed and classified according to Ridley–Jopling classification(1966). Slit-skin smear was studied wherever available. The clinical diagnosis by the dermatologist was documented and clinical-histopathological correlation was observed.
Results
A total of 54 Hansen’s cases were reported from our tertiary care centre out of which 43skin biopsies were sent for histopathological study. The age group presented with Hansen’s disease was between 10-75 years, Majority of the patients were in the age group of 31-40 and 41-50 years (Figure 1). Males were affected in the majority of the cases than females accounting for 65% of cases and male to female ratio is 1.8:1 (Figure 2).
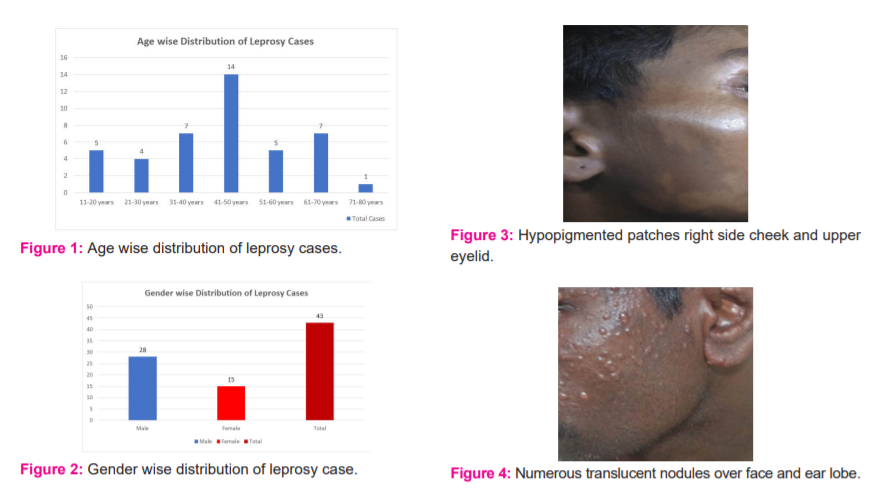
The most common clinical presentation were macules, papules, nodules and hypopigmented patches (Figures 3 and 4). Out of 43 cases studied histopathological and clinical correlation was obtained in 27cases, 62.7% were well correlated clinically and histopathologically.
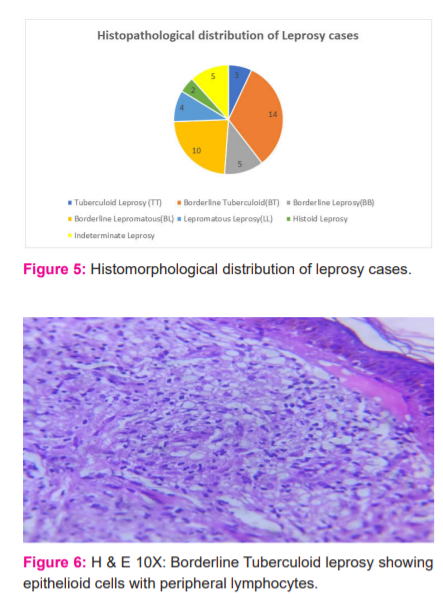
Out of 43 cases (Figure 5) studied 32.5% cases showed features of (Figure 6) Borderline Tuberculoid (BT) type of Leprosy which was the most common histological subtype, 23.2% cases showed histology of Borderline lepromatous (BL) Leprosy,11.6% cases were borderline (BB) cases, 9.3% cases demonstrated the features of (Figure 7) Lepromatous leprosy (LL) (Figure 7), 6.9% cases displayed Tuberculoid leprosy(TT), 4.6% cases were of
(Figure 8) Histoid Leprosy (HL) and 11.6% cases were reported as Indeterminate leprosy(IL).
Fite Faraco stain showed positive in 28% cases (Figure 9), in borderline tuberculoid and all cases of lepromatous leprosy. Slit skin smears were available for 18cases and showed positive in 38.8% of cases.
Discussion
Hansen’s disease is a chronic granulomatous disease that mainly affects the skin and peripheral nerves.3 In the absence of the standard involvement of the peripheral nerves, the divergent clinical presentations of leprosy can imitate other dermatological disorders.
Histopathological features of leprosy subtypes: The Grenz zone was the prevailing feature highlighted in all the biopsies of LL.14 In our study, only 23% of the Lepromatous leprosy cases displayed the Grenz zone. It was rare in BT and completely absent in TT. It is universally recognized as a distinctive feature of nontuberculous leprosy. It is not considered as the diagnostic feature of leprosy, but aids in considering the diagnosis of leprosy and its variants.
Tuberculoid Leprosy (TT): Epithelioid cells aggregate, numerous lymphocytes at the periphery of the granuloma and a few Langhan’s giant cells, nerve with intact perineurium, and caseation in the centre. Clinically presents as one or few asymmetrical distributed hypopigmented or erythematous, anaesthetic lesions with or without nerve thickening. In the present study, clinicopathological findings were better correlated BT and LL when compared to TT similar to Manandharetal.5
Borderline Tuberculoid (BT): Diffuse epithelioid cell granuloma with a moderate number of lymphocytes and few small giant cells within the granuloma. Presence of many asymmetrically arranged hypopigmented/erythematous/anaesthetic lesions with or without thickened nerves. Our study showed the majority of cases of BT followed by BL similar to the study done by Shivamurthy Vet. al and Kumar et al.6,7
Borderline Leprosy (BB): Shows both the characteristics of TT and LL.
Borderline lepromatous (BL): Borderline Lepromatous Leprosy patients were clinically present with multiple lesions which are ill-defined, shiny and asymmetrically arranged, with or without anaesthetic patches and thickened nerves. Histomorphological features display diffuse infiltrates of macrophages, foamy macrophages and few lymphocytes were seen involving nerves and skin appendages.8
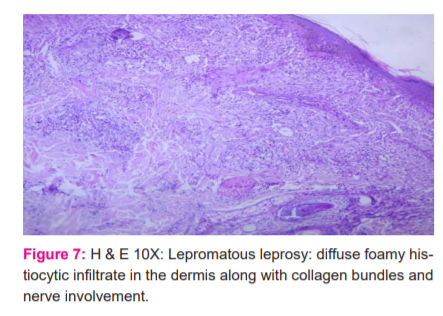
Lepromatous leprosy (LL): The prevailing histologic feature of Lepromatous leprosy is Diffuse infiltrates of histiocytes with vacuolated cytoplasm because of the globe of leprosy bacilli in the dermis. Lymphocytes may be scarce or absent.
Grenz zone is usually seen in the papillary dermis and absence of granulomas. Most patients presented with multiple- defined, shiny, symmetrical anaesthetic skin lesions with or without thickened nerves.9,10
Histoid Leprosy (HL): The multibacillary clinical type of Leprosy is Histoid leprosy (HL), which has been in the check constantly since its birth. It clinically presents as a firm, reddish dome or oval-shaped nodules or papules and shiny stretched on the overlying skin and rarely manifests as sharply demarcated plaques. The lesions are commonly seen over the lower back, face, extremities, and bony prominences. Subcutaneous histoid leprosy has to be differentiated from subcutaneous rheumatoid nodules.
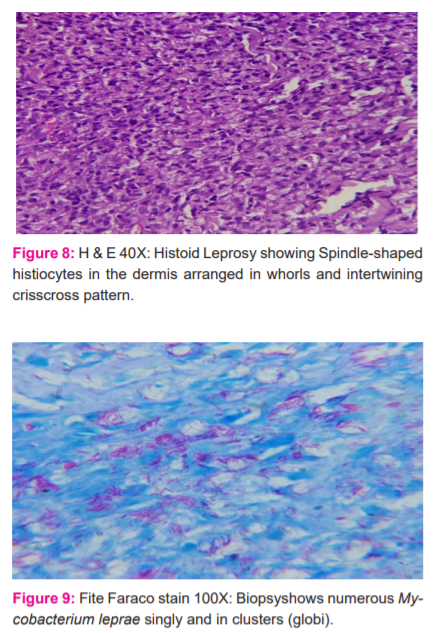
In Histoid Leprosy the histiocytes are spindle-shaped and arranged in the storiform pattern mimicking spindle cell lesions described by Virendra N.Setal11our study showed similar histopathological features of Histoid Leprosy. A single case report describes Sacroidosis, atypical mycobacterial infection, and secondary syphilis as mimickers of HL.
Histoid leprosy (HL) is first defined by Wade in 1960 which a rare variant of lepromatous leprosy. Wade portrayed the histopathological view of Histoid Leprosy as bacillary rich leproma displaying spindle-shaped cells and the absence of the globe. Even though Histoid leprosy is a variant of LL it is recognized by distinct ultrastructural, immunological, clinical, and histopathological features.12
Indeterminate Leprosy (IL): Shows mild non-specific perivascular and periadnexal lymphocytic and histiocytic infiltrate in the dermis or thickened deep dermal nerve showing intraneural lymphocytic infiltration. In IL there are only minor histopathological changes that can be easily missed unless there is an adequate biopsy. In our study, the most common type of Leprosy we come across is borderline tuberculoid leprosy, succeeded by borderline lepromatous and others. Histoid leprosy and tuberculoid leprosy were the least confronted subtypes of leprosy.13,14
Few cases may show both the features of tuberculoid and lepromatous leprosy. In borderline cases, the Immunological uncertainty in these borderline cases may shift in either direction onwards the borderline spectrum. Patients who receive treatment change towards the tuberculoid pole and who do not receive treatment turn towards the lepromatous pole.
Bacillary index: Bacillary indices are maximal in lepromatous leprosy types and minimal in borderline tuberculoid types. Jopling also recognized that the bacilli are scanty or absent in borderline tuberculoid leprosy, always present in borderline leprosy, and plentiful in borderline lepromatous leprosy and lepromatous leprosy. In both clinical and histopathological evaluation, Tuberculoid leprosy shows slight variation from borderline tuberculoid leprosy often with an overlapping line of demarcation. The ample number of Leprosy cases continually shows altering immunological patterns. If a biopsy is taken in the initial stages there are more confrontations between the clinical and histopathological observation.
Indeterminate leprosy cases are ambiguous because of nonspecific histopathological changes and clinical and histopathological inter-observer discrepancy.15-17 The decisive diagnosis of IL depends on illustrating the nerve lesions and acid-fast bacilli or confirmed without any bacilli if clinical and histopathological features are reminiscent particularly in endemic areas. Immunological status is not yet known in IL which is an early and transitory stage of leprosy. Diagnosis of Leprosy clinically in the early stages is difficult which may be achievable by histomorphological examination. Histomorphological features demonstrate the exact tissue response, while the clinical features are due to underlying pathology which shows only the gross morphology of the lesions.
Significance of histopathology in determining Leprosy
In Paucibacillary Leprosy: Treatment for Leprosy kills the organisms by halting the multiplication of M. Leprae and releasing antigens into the tissues. The granulomatous inflammation disintegrates the antigens which lead to the resolution and disappearance of the granuloma. Fibro collagenous tissue is not seen during healing leading to atrophied and wrinkled lesions. Perineural and intraneural fibrosis may be seen, these sites become a nidus for bacilli causing relapse.
In multibacillary leprosy: Amid anti-leprosy treatment lepromatous lesions resolve with increased macrophages which finally converts into foam cells. Few cases show lymphoplasmacytic infiltrate in the granuloma. Invariably granuloma resolve with no residual fibrosis and scar. The Schwann cells of dermal nerves may also undergo foamy change and perineurium undergoes hyalinization. AFB (Acid-fast bacilli) in granulomas becomes fragmented and granular within two to three months of competent treatment and AFB in nerves and wall of blood vessels may survive for a longer time. Even after years of treatment few foam cells may be seen in skin biopsies. Healed lesions may show mild nonspecific chronic inflammation around the adnexa. To conclude, the present study emphasizes the importance of histopathological examination and bacillary index in the management of Leprosy. Accurate diagnosis is important as under-diagnosed cases may lead to the continuous transmission of disease. Histopathological examination remains the gold standard and continues to be a crucial diagnostic tool for accurate diagnosis and classification of leprosy.18-20
Sexual distribution: In general, leprosy is believed to be more common in males than females similar to a previous studies.5,10 It is more predominant in males due to industrialization, urbanization, and more contact opportunities and due to social customs and taboos, fewer females report to the clinic.
Clinical presentation
Loss of sensation is the most common clinical finding, nerve thickening predominant in ulnar, lateral popliteal, and radial nerve and Hypopigmented and rarely trophic ulcers.
Leprosy is healable with multidrug therapy, definitive diagnosis is required for proper management and limiting the deformities and drug resistance. Histomorphological diagnosis is also considered useful for monitoring treatment response. The preponderance of the borderline spectrum and multibacillary leprosy is due to lower socioeconomic status, poor sanitary conditions, overcrowding, and illiteracy rate in rural areas of Karnataka state.
The findings of this study might help the government authorities to develop more effective treatment strategies for rightly achieving the target of eradicating leprosy. Expanded understanding of the people to national programs makes them attend the leprosy clinic at the initial stages which commit towards the early diagnosis and treatment The bacteriological index alone does not form the basis for diagnosing various types of leprosy. Many specifications impact histopathological diagnoses like duration of the presenting lesion, biopsy depth, histopathological section quality, and Ziehl–Neelsen stain. Divergent criteria are used to select the cases, immune status of the patient, and any previous treatment taken by the patient. Clinical, histopathological, and immunological concurrence is often observed among various subtypes of leprosy. Clinical and histopathological correlation along with bacteriological index will be more precise than considering a single parameter to increase the efficiency for leprosy subtyping In our study, the clinicopathological correlation was seen in 62.7% similar to Kumar et al.7
Conclusion
Leprosy is a slowly progressive chronic infectious disease caused by a bacillus, Mycobacterium leprae which multiplies slowly and the symptoms of the disease appear after a long incubation period average of 5 years. The disease predominantly affects the skin, the peripheral nerves, upper respiratory tract mucosa, and eyes. The most commonly affected age group affected was 10 to 75 years with male predominance. The disease is classified into paucibacillary (PB) if lesions are few appearing reddish or pale, and multibacillary associated with multiple skin lesions, nodules, plaques, thickened dermis, or skin infiltration. In 2005, though the elimination of leprosy at the national level has been achieved; but still there is an incidence of this disease is reported from our region affected by this chronic debilitating disease. For eliminating Leprosy, early case detection and treatment is very important in reducing the source of infection and interrupt transmission in the community. There can be many overlapping features between different types of leprosy, both clinically and morphologically. So clinicopathological correlation along with bacteriological index will lead to more accurate typing of leprosy. Histopathology also helps in monitoring the treatment response. Leprosy is a healable disease if a proper diagnosis is made which can prevent drug resistance and deformity.
Acknowledgement
The authors are thankful to the management of the Shridevi institute of Medical sciences for their constant support and encouragement. The authors acknowledge the immense help received from the scholars whose articles are cited and included in references of this manuscript. The authors are also grateful to authors/editors/publishers of all those articles, journals and books from where the literature for this article has been reviewed and discussed.
Sources of Funding – Nil
Authors contribution:
Design and data collection: Dr Harish S.G, Dr Shivanand D.R
Data analysis and interpretation, drafting the article: Dr Priyadarshini D, Dr Kiran T.S
Conflict of Interest - Nil
References:
-
Ridley DS, Jopling WH. Classification of leprosy according to immunity. A five-group system. Int J Lepr Other Mycobact Dis 1966;34:255-273.
-
Parajuli S, Shah M, Sushma S. Clinico-histopathological correlation of leprosy in the western region of Nepal-A pioneer pilot study. Ind J of Clin Exp Dermatol 2016;2(3):93-97.
-
Prerana R, Reeta D, Prabhakar P. Histopathological Study of Leprosy Patients in a Tertiary Care Hospital in Navi Mumbai. Int J Health Sci Res 2019;9(2):6-12.
-
Suri SK, Iyer RR, Patel DU, Bandil S . Histopathology and Clinico-histopathological correlation in Hansen’s disease: J Res Med Dent Sci 2014;2(1):23-28.
-
Manandhar U, Adhikari RC, Sayami G. Clinico-histopathological correlation of skin biopsies in leprosy. J Path Nepal 2013;3:452-458.
-
Shiva Murthy V, Gurubasavaraj H, Shashikala PS, Kumar P. Histomorphological study of leprosy. Afr J Med Health Sci 2013;12:68-73.
-
Kumar A, Negi SR, Vaishnav K. A study of clinic histopathological correlation of leprosy in a tertiary care hospital in the Western district of Rajasthan. J Res Med Dent Sci 2017;2:43-48.
-
Narasimha PR, Sujai S. Current situation of Leprosy in India and its future implications. Ind Dermatol J 2018;9(2):83-89.
-
Anuja S, Rajesh KS, Goswami KC, Subash B. ClinicoHistopathological Correlation in Leprosy. J Korean Sci 2008;10(3).
-
Nitesh M, Nitin M. clinicohistopathological correlation within the spectrum of Hansen's disease: a multicentric study in north India. Int J Med Res Health Sci 2013;2(4):887-892.
-
Virendra NS, Govind S, Navjeevan S. Histoid Leprosy: Histopathological Connotations’ Relevance in Contemporary Context. Am J Dermatopathol 2009;31(3).
-
Mathur MC, Ghimire RB, Shrestha P, Kedia SK. Clinicohistopathological correlation in leprosy. Kathmandu Univ Med J 2011;9:248-51.
-
Banushree CS, Ramachandra VB, Udayashankar C: Clinicopathological correlation of Hansen’s disease: a retrospective study of skin biopsies. Ind J Path Oncol 2016;3(3):491-495.
-
Shubhangi TK, Sunita W, Pratibha D. Recent trend in leprosy: Histopathological study aspect in a tertiary care hospital: Ind J Basic Appl Med Res 2016;5(2):481-486.
-
Shivani S, Nilesh S, Jignasa B. Clinicopathological correlation in leprosy. Int J Med Sci Public Health 2019;8(6);459-464.
-
Tiwari M, Ranabhat S, Maharjan S. Clinico-histopathological correlation of leprosy: A retrospective study of skin biopsy specimens in Chitwan medical college. Int J Med Sci Res Pract 2015;2:8-11.
-
Nadia S, Rashmi J, Sohaib A. Clinicopathological correlation of leprosy: A 4 years retrospective study from a tertiary referral centre in north India. Int J Med Res Health Sci 2015;4:350-4.
-
Taviyad S, Gandhi S, Purohit M, Purohit T, Dhruva G. A study of leprosy cases: Correlation of clinical features, histopathology and demonstration of lepra bacilli. BJ Kines. Natl J Basic Appl Sci 2017;9:1-7.
-
Sindhushree N, Vernekar SS. A study of clinico-histopathological correlation of leprosy in a tertiary care hospital, KIMS, Hubbali, Karnataka. Int J Curr Res Biol Med 2018; 3:29-39.
-
Ruchi S, Mamta K, Punam P.B. Histopathological Panorama of Leprosy in a Tertiary Care Hospital of Bihar. J Clin Diagn Res 2019;13(4):12-15.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License