IJCRR - 13(9), May, 2021
Pages: 82-87
Date of Publication: 07-May-2021
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
Study of Renal Adverse Effects of Nsaids Used in Spondyloarthritis Patients
Author: Chaudhary GK, Das C, Dash S, Sahu S
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Introduction: Clinical history, symptoms, lab parameter along with radiological investigation help in the diagnosis and management of spondyloarthritis (SpA). However, spondyloarthritis manage mainly by NSAIDs.NSAIDs can cause subclinical renal injury which is not manifest in routine renal function tests (like serum creatinine). Published case series among ankylosing spondylitis patients have shown the prevalence of renal complication 72% higher than the general population. A limited number of studies are present on evaluating the effect of NSAIDs on changes in the level of cystatin-c. So here we studied the change in parameters of serum creatinine and cystatin-c level after the use of NSAIDs in the setting of SpA.
Objective: To study the relation of the duration of use of NSAIDs in Spondyloarthritis patients and the incidence of subclinical kidney injury by comparing serum creatinine with serum cystatin-c.
Methods: A hospital-based prospective observational study carried out over one year in IMS and SUM hospital over 31 patients on spondyloarthritis patients. Where the level of serum creatinine and cystatin-c level calculated on the baseline, four weeks and twelve-week.
Results: Patients using a different type of NSAIDs there is no significant change in serum creatinine value (p=0.546).while a significant change in serum cystatin-c level (p< 0.012) was observed over twelve weeks
Conclusion: There is no significant change in serum creatinine value after intake of NSAIDs.while significant change in serum cystatin-c value which increases two or three-fold higher than initial value and therefore it is concluded that serum cystatin-c can be used as an early biomarker for subclinical kidney injury than serum creatinine.
Keywords: Spondyloarthritis, NSAIDs, Subclinical renal injury, Ankylosing spondylitis
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION
Spondyloarthritis is a diverse group of arthritis feature by inflammation in the axial skeleton and enthesis.1 Spondyloarthritis comprises ankylosing spondylitis, reactive arthritis, arthritis, or spondylitis associated with Psoriasis, arthritis, or spondylitis related to inflammatory bowel disease.2 Spondyloarthritis may manifest with vague symptoms. Mostly present with back pain and stiffness.3 The prototype of Spondyloarthritis is ankylosing spondylitis. Ankylosing spondylitis is one of the most prevalent diseases among young adult males presenting in the outpatient department. The most common complaint is that of back pain. The most common causative factor is a genetic association with HLA B-27.4 Recent studies also reveal an association with tissue necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) and interleukin (IL-6, IL-17, and IL-23) and IL-37.5 Ankylosing spondylitis is diagnosed by clinical features, radiographic changes, and genetic analysis.6
The mainstay of treatment is a different type of NSAIDs like Aceclofenac, Indomethacin, Naproxen, Etoricoxib and biologicals, Disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs, glucocorticoids.7Although biological treatment is used frequently in western countries, NSAIDs are still the first-line treatment in our country considering the high cost of biologicals. NSAIDs can cause many side effects including renal, cardiac, gastrointestinal etc. NSAIDs can cause subclinical renal injury which is not manifested in routine renal function tests. Overt or clinical renal side effects of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) like raised serum creatinine is seen in very few cases of patients with spondyloarthritis.
Here we have studied the change in levels of serum creatinine and change in levels of cystatin-c as sensitive biomarkers of NSAID induced kidney injury in spondyloarthritis patients.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
This is a hospital-based Prospective observational study carried in IMS & SUM Hospital Bhubaneswar after approval from the institutional committee over one year from November 2018 to October 2019. Assuming an error of 5% and considering the sample size of the thirty-one patient. A total of 31 patients aged between 22 and 54 years (all are male). All spondyloarthritis patients who came into the outpatient department and in-hospital in our tertiary care hospital over 1 year have been included in this study. Diagnose spondyloarthropathy(Axialspondyloarthropathy, Peripheral spondyloarthropathy or axial+peripheral spondyloarthropathy) based on different criteria and Radiological investigation. According to Amor criteria, every clinical feature is given a score of 1-2, and a score of 6 or more consider as “spondyloarthropathy”. A clinical feature like Lumbar pain at night or lumbar morning stiffness, Nongonococcalurethritis/cervicitis within 1 month of onset, Acute diarrhoea within 1 month of arthritis onset,
Buttock pain has a score of 1. If Clinical feature like bilateral alternating buttock pain, Asymmetric oligoarthritic, Sausage-like toe or digit(s), Heel pain or other well-defined enthesitis, Iritis, Psoriasis, balanitis or inflammatory bowel disease (Crohn’s or ulcerative colitis), Sacroiliitis (bilateral grade 2 or unilateral grade 3), human leukocyte antigen HLA-B27(+) or (+) family history of a spondyloarthropathy, Rapid less than 48 hours respond to NSAIDs having a score of 2.8 Other criteria Assessment in spondyloarthritis international society for Axial spondyloarthropathies which include sacroiliitis on imaging plus one of spondyloarthropathy feature or HLA-B27 and two other spondyloarthropathy feature.Spondyloarthropathy feature like-sausage digit (dactylitis), psoriasis-positive family history of spondyloarthropathy, inflammatory back pain ,NSAID good response, enthesitis (heel), Arthritis, Crohn’s/colitis disease-elevated C-Reactive Protein (CRP), human leukocyte antigen (HLA-B27), Eye (uveitis). How to diagnose sacroiliitis on X-ray bilateral Grades2-4 or Unilateral Grades 3-4 according to the modified new criteria, MRI Active (acute) inflammation on MRI.9 All spondyloarthritis patients included in the study except spondyloarthritis patients with psoriasis and inflammatory bowel disease, Spondyloarthritis patients using biological like sulfasalazine, methotrexate, a corticosteroid. Spondyloarthritis Patients with a known case of diabetes mellitus, hypertension, hypothyroidism, pre-existing medical renal disorder, use of NSAID for any other cause like migraine are excluded from the study. Informed consent was taken from all the patients. Based on all these criteria 31 patients have been selected and a blood sample collected at baseline, four weeks, and twelve-week for estimation of serum creatinine and serum cystatin-c level.
Statistical analysis
Statistical analysis will be carried out with the help of SPSS (version 25). The description of the data will be done in form of mean +/- SD for quantitative data while in the form of % frequency and % proportion for qualitative (categorical) data. For quantitative data Student’s t-test will be used to test the statistical significance of the difference between two independent group means. Chi-square test (or Fisher’s exact test in case of small frequencies in a cell) will be used to examine the association between patients of spondylarthritis with the use of NSAID and effect on kidney biomarkers. The univariate analysis will be done to identify the candidate variables for multiple logistic regression analysis. To determine the impact of NSAID on kidney biomarkers. Multivariate logistic regression analysis will be performed to determine risk factors associated with acute kidney injury. Analysis of Variance (ANOVA) test was performed to find out the association of quantitative variables with different NSAIDs used. The p-value was set to <0.05 for statistical significance.
RESULTS
31 patients selected all are male the mean age of the study participants was 34.26 years with a standard deviation of 11.78 years.
Basic diagnosis
Axial SpA 74.2% cases, Peripheral SpA 9.7 %cases, Axial+Peripheral SpA 16.1% cases.HLA-B27 Positive in 38.7% of cases and negative in 61.3% cases. NSAIDs use Etoricoxib use by 54.8% case, Indomethacin 19.4%, Aceclofenac 16.1% cases, Naproxen 9.7% case (Table 1).
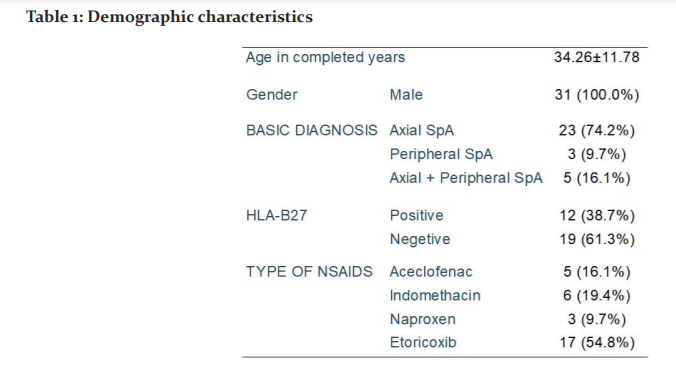
Serum creatinine changes in a different type of NSAIDs After the use of NSAIDs.At baseline Aceclofenac with a mean serum creatinine 0.73±0.13, Indomethacin with a mean serum creatinine 0.79±0.11, Naproxen 0.88±0.12, Etoricoxib with a mean serum creatinine 0.77±0.12 with p-value 0.408. After 4 weeks Aceclofenac with a mean serum creatinine 0.72±0.12, Indomethacin with a mean serum creatinine 0.78±0.06, Naproxen0.83±0.06, Etoricoxib with mean serum creatinine 0.81±0.17with p-value 0.625. After 12 weeks Aceclofenac with a mean serum creatinine 0.75±0.05, Indomethacin with a mean serum creatinine 0.78±0.04, Naproxen0.81±0.11, Etoricoxib with a mean serum creatinine 0.83±0.14 with p-value 0.546.(Table 2 and Figure 1).
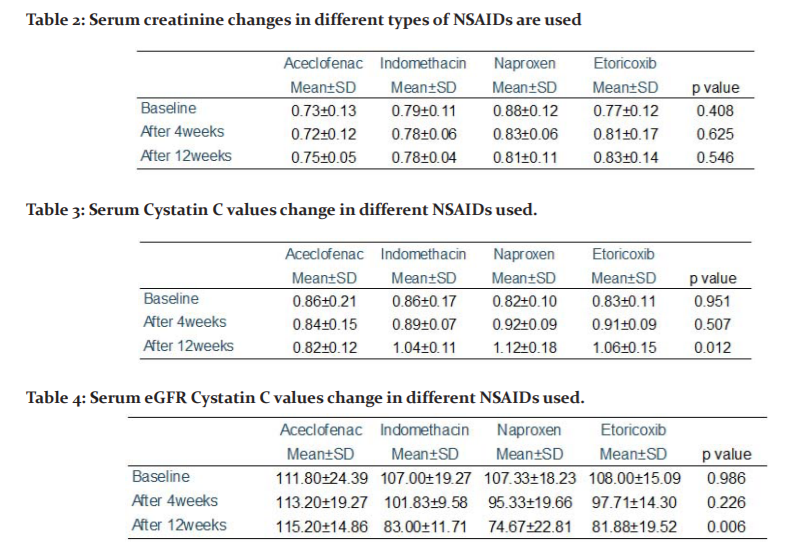
Change in serum cystatin C level after different type of NSAIDs use After use of NSAIDs. At baseline Aceclofenac with mean serum cystatin-c 0.86±0.21,Indomethacin with mean serum cystatin-c 0.86±0.17, Naproxen 0.82±0.10, Etoricoxib with mean serum cystatin-c 0.83 ±0.11 with p value 0.951. After 4 week Aceclofenac with mean serum cystatin-c 0.84±0.15, Indomethacin with mean serum cystatin-c 0.89±0.07, Naproxen 0.92±0.09, Etoricoxib with mean serum cystatin-c 0.91±0.09 with p value 0.507. After 12 weeks, Aceclofenac with mean serum cystatin-c 0.82±0.12, Indomethacin with mean serum cystatin-c 1.04±0.11, Naproxen 1.12±0.18, Etoricoxib with mean serum cystatin-c 1.06 ±0.15 with p value 0.012 (Table 3/Figure 2).
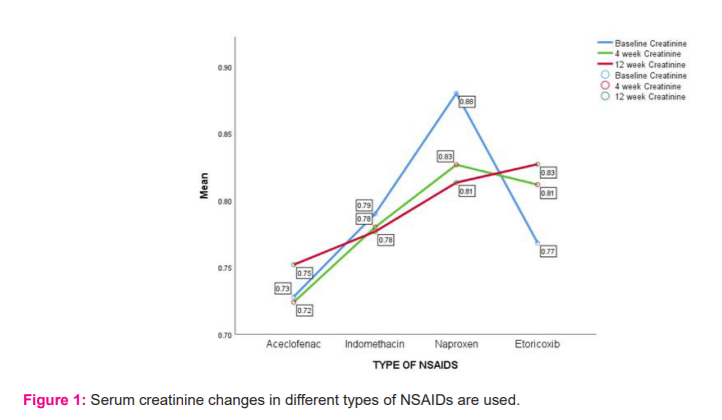
Serum e-Glomerular filtration rate (GFR) cystatin C values change in a different type of NSAID used After the use of NSAIDs at baseline Aceclofenac with eGFR111.80±24.39, Indomethacin with 107.33±19.27, Naproxen with eGFR 107.33±18.23, Etoricoxib eGFR 108.00±15.09 with p-value 0.986. After 4 weeks Aceclofenac with eGFR 113.20±19.27, Indomethacin eGFR101.83±9.58, Naproxen e-GFR 95.33±19.66, Etoricoxib with eGFR97.71 ±14.30 with p-value 0.226. After 12 weeks, Aceclofenac with eGFR 115.20±14.86, Indomethacin with eGFR 83.00±11.71, Naproxen with e-GFR 74.67±22.81, Etoricoxib with e-GFR 81.88 ±19.52 with p-value 0.006 (Table 4/figure 3).
DISCUSSION
The mean age of the study participants was 34.26 years with a standard deviation of 11.78 years. Gender is male. Malakar et al. in a cross-sectional study in 2020. In India observed that the male to female ratio was 3.2:1. Mean age of the patients was 45 ± 20.2 years.10 Axial SpA 74.2% cases, Peripheral SpA 9.7% cases, Axial+Peripheral SpA16.1% cases. HLA-B27 positive in 38.7% of case and negative in 61.3% of cases. NSAIDs use Etoricoxib use by 54.8% case, Indomethacin 19.4%, Aceclofenac 16.1% cases, Naproxen 9.7% case. The most common type is Ankylosing spondylitis (AS) (56%), second most common is reactive arthritis (ReA) (15%), undifferentiated (UdSpA) (15%). Psoriatic arthritis (PsA) (12%) and juvenile SpA (3%). Fan et al done randomized controlled trials concentrating on six NSAIDs (etoricoxib, celecoxib, meloxicam, diclofenac, naproxen, beta?D?mannuronic acid) find that all NSAIDs decrease pain more than placebo. Etoricoxib is better to control pain than others while the adverse effect of all is the same.11 The risk of kidney injury more with naproxen or non-selective than selective NSAIDs.12
In our study after the use of the different types of NSAIDs serum creatinine value was collected at baseline, after 4 weeks, after 12 weeks. At baseline serum, creatinine value was collected and the p-value was calculated by using Fisher’s exact test which was 0.408. After 4-week use of NSAIDs serum creatinine value was collected and the p-value was calculated by using Fisher’s exact test which was 0.625 which is statistically insignificant. After 12 weeks of use of NSAIDs serum creatinine value was collected and the p-value was calculated by using Fisher’s exact test which was 0.546 which is statistically insignificant. Total intake of twenty-five hundred NSAIDs tablets no significant changes in serum creatinine and e GFR value.13
In our study after the use of a different type of NSAIDs serum CystatinC value was collected at baseline, after 4 weeks, after 12 weeks. At baseline serum, cystatin C value was collected and the p-value was calculated by using Fisher’s exact test which was 0.986. After 4-week use of NSAIDs, serum cystatin c value was collected and the p-value was calculated by using Fisher’s exact test which was 0.507which is statistically insignificant. After 12 weeks of use of NSAIDs, the serum cystatin c value was collected and the p-value was calculated by using Fisher’s exact test which was 0.012 which is statistically significant.
Rosenthal et al. studied in intensive care units (ICU) patients both surgical and medical at the University Hospital Essen with normal GFR (calculated by serum creatinine which is below 115 micromol/L) which is measured two times repeatedly and it indicates that serum cystatin C achieves fine marker to detect Acute Kidney Injury (AKI). Cystatin C may also help to detect the progress of AKI one to two days before serum creatinine, which is a standard marker to detect AKI and studied also shows that cystatin C detected AKI earlier with more sensitivity (increase≥50%) and to more specificity (increase ≥100% or ≥200%), which are equivalent to the R-, I-, and F-criteria of the recently proposed RIFLE (Risk, Injury, Failure, Loss of kidney function) and End-stage kidney disease classification and a supplementary major finding is that serum cystatin C increase ≥50% was established to expect that requirement of renal replacement therapy (RRT) in course of acute renal failure (ARF) ascetically well and hence serum cystatin C may be a valid marker in the early and later stages of ARF.14 These findings have great clinical importance because early detection of ARF can provide a spell to avoid the progression of ARF.15-17 Initial starting of preventive measures may prevent the consequence of ARF and prevent markedly from any ailment that noticeably increases mortality.18-21
Serum cystatin C has a higher prediction and prognostic value in the case of AKI than the old biomarker.22 Paola Lagos-Arevalo et al. Done a prospective cohort study in PICU in Canada and published in 2015 and observed that Cystatin C may be used for early predicting progression of AKI in ICU patients.23 Carlo Briguori et al. measured Cystatin C and serum creatinine in chronic kidney disease patients investigating for coronary or peripheral angiography or angioplasty and concluded that in chronic kidney disease, cystatin c is a better marker for early diagnosis and prognosis of contrast-induced acute kidney injury.24 Vaidya et al. in the USA studied a biomarker of AKI in the USA observed that cystatin c sensitive serum marker of GFR and a stronger predictor than serum creatinine of risk of death and cardiovascular events in an older patient.25 Frans J. Hoek et al. in 2003 in the Netherlands and concluded that Cystatin C gives a decent evaluation of GFR which has better accuracy than the Cockcroft-Gault formula. (cystatin c have low biological variability.26
There is no such equation as Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) – Exocrine pancreatic insufficiency (EPI) cystatin to calculate e GFR value in AKI patients. No classification based one-GFR for AKI like KDIGO for CKD. Here we study only a small sample size, hence a large sample size should be studied. Here we follow only up to 12 weeks, there is a need for a longer duration of follow up. Subclinical injury on chronic kidney outcome after prolonged NSAIDs use should be studied. In the study, we took only normal serum creatinine value and this type of patient is given less priority and may be left unnoticed until they develop AKI and hence measuring cystatin C level is more useful, and hence more attention is given to these patients to prevent the progression of AKI.
CONCLUSION
We tackle the study of the incidence of Kidney injury in spondylarthritis patients using NSAIDs and earliest detection by using serum cystatin-c. In our study, we concluded:
There is no significant increase in serum creatinine value after intake of NSAIDs and there is a significant change in serum cystatin C value which two to three-fold higher than the initial value, and that it concluded that serum cystatin c can be used as an early biomarker for subclinical kidney injury than serum creatinine. When e GFR is calculated by using chronic kidney disease-exocrine pancreatic insufficiency (CKD- EPI cystatin C it shows a progressive decrease in Glomerular filtration rate GFR value.
Conflict of interest: There is no conflict of interest among the authors.
Funding: Nil
Author contribution
Chandan Das and Samir Sahu conceived, planned, designed, guided the study and wrote the manuscript. Shree Dash and Gautam Kumar Chaudhary did the data collection.
References:
-
Shukla A, Rai MK, Prasad N, Agarwal V. Short-term non-steroid anti-inflammatory drug use in spondyloarthritis patients induces subclinical acute kidney injury: biomarkers study. Nephrologist 2017;135(4):277-286.
-
Akgul O, Ozgocmen S. Classification criteria for spondyloarthropathies. World J Orthop 2011;2(12):107.
-
Terenzi R, Monti S, Tesei G, Carli L. One year in review 2017: spondyloarthritis. Clin Exp Rheumatol 2018;36(1):1-4.
-
Tam LS, Gu J, Yu D. Pathogenesis of ankylosing spondylitis. Nat Rev Rheumat 2010 Jul;6(7):399-405.
-
Chen B, Huang K, Ye L, Li Y, Zhang J, Zhang J, Fan X, Liu X, Li L, Sun J, Du J. Interleukin-37 is increased in ankylosing spondylitis patients and associated with disease activity. J Trans Med 2015;13(1):36.
-
McVeigh CM, Cairns AP. Diagnosis and management of ankylosing spondylitis. Br Med J 2006;333(7568):581-585.
-
Braun JV, Van Den Berg R, Baraliakos X, Boehm H, Burgos-Vargas R, Collantes-Estevez E, et al. 2010 update of the ASAS/EULAR recommendations for the management of ankylosing spondylitis. Ann Rheumat Dis 2011;70(6):896-904.
-
Amor B, Dougados M, Mijiyawa M. Criteria of the classification of spondylarthropathies. Revue du rhumatisme et des maladies osteo-articulaires. 1990;57(2):85-89.
-
Lipton S, Deodhar A. The new ASAS classification criteria for axial and peripheral spondyloarthritis: promises and pitfalls. Int J Clin Rheumat 2012;7(6):675.
-
Malakar A, Kakati S, Barman B, Dutta A. Clinical presentation and subtypes of spondyloarthritis patients in North East India. Egyp Rheum 2020;23(6):721-724.
-
Fan M, Liu J, Zhao B, Wu X, Li X, Gu J. Indirect comparison of NSAIDs for ankylosing spondylitis: Network meta-analysis of randomized, double-blinded, controlled trials. Exp Therap Med 2020;19(4):3031-3041.
-
Lafrance JP, Miller DR. Selective and non?selective non?steroidal anti?inflammatory drugs and the risk of acute kidney injury. Pharmacopoeia. Drug Safety 2009;18(10):923-931.
-
Rexrode KM, Buring JE, Glynn RJ, Stampfer MJ, Youngman LD, Gaziano JM. Analgesic use and renal function in men. JAMA 2001;286(3):315-321.
-
Herget-Rosenthal S, Marggraf G, Hüsing J, Göring F, Pietruck F, Janssen O, et al. Early detection of acute renal failure by serum cystatin C. Kidney Int 2004;66(3):1115-1122.
-
Esson ML, Schrier RW. Diagnosis and treatment of acute tubular necrosis. Ann Int Med 2002;137(9):744-752.
-
Ronco C, Bellomo R. Prevention of acute renal failure in the critically ill. Nephr Clin Pract 2003;93(1):c13-20.
-
Molitoris BA. Transitioning to therapy in ischemic acute renal failure. Journal of the Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 2003;14(1):265-267.
-
Chertow GM, Levy EM, Hammermeister KE, Grover F, Daley J. Independent association between acute renal failure and mortality following cardiac surgery. Am J Med 1998;104(4):343-348.
-
Joannidis M, Metnitz PG. Epidemiology and natural history of acute renal failure in the ICU. Crit Care Clin 2005;21(2):239-249.
-
Clermont G, Acker CG, Angus DC, Sirio CA, Pinsky MR, Johnson JP. Renal failure in the ICU: comparison of the impact of acute renal failure and end-stage renal disease on ICU outcomes. Kidney Int 2002;62(3):986-996.
-
Levy EM, Viscoli CM, Horwitz RI. The effect of acute renal failure on mortality: a cohort analysis. J Am Med Ass 1996 May 15;275(19):1489-1494.
-
Haase-Fielitz A, Bellomo R, Devarajan P, Story D, Matalanis G, Dragun D, et al. Novel and conventional serum biomarkers predicting acute kidney injury in adult cardiac surgery—a prospective cohort study. Crit Care Clin 2009;37(2):553-560.
-
Lagos-Arevalo P, Palijan A, Vertullo L, Devarajan P, Bennett MR, Sabbisetti V, et al. Cystatin C in acute kidney injury diagnosis: early biomarker or alternative to serum creatinine. Pediatr Nephrol 2015;30(4):665-676.
-
Briguori C, Visconti G, Rivera NV, Focaccio A, Golia B, Giannone R, et al. Cystatin C and contrast-induced acute kidney injury. Circulation 2010;121(19):2117.
-
Vaidya VS, Ferguson MA, Bonventre JV. Biomarkers of acute kidney injury. Ann Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 2008;48:463-493.
-
Hoek FJ, Kemperman FA, Krediet RT. A comparison between cystatin C, plasma creatinine and the Cockcroft and Gault formula for the estimation of glomerular filtration rate. Nephrol Dial Transplant 2003;18(10):2024-2031.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License