IJCRR - 7(24), December, 2015
Pages: 06-12
Date of Publication: 20-Dec-2015
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
ISOLATION AND SPECIES IDENTIFICATION OF CANDIDA ISOLATED FROM PATIENTS OF VULVOVAGINAL CANDIDIASIS IN A TERTIARY CARE HOSPITAL
Author: Twinkle Gandhi, Manish G. Patel, Mannu Jain
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Introduction: An increase in the predisposing conditions in recent years has resulted in an increasing incidence of Candida infections.The accurate species identification of Candida is important for the treatment, as not all species respond to the same treatment and also because of the problem of anti-fungal resistance in certain species.Therefore, the species level identification of the Candida isolates, along with their anti-fungal susceptibility patterns can greatly influence the treatment options for the clinician. Objective: - To detect prevalence of Candida in patients with vaginal discharge. - To identify species of Candidaisolates. Methods: This study included 410 women with abnormal vaginal ischarge. Two high vaginal swabs were collected and sent immediately to the laboratory. All vaginal samples were stained with gram's stain and oval budding yeast cells were identified as Candida. Second swab was inoculated on Sabouraud's Dextrose agar and Candida isolates(n=122)were identified at species level by battery of various tests like GTT,Corn meal agar, Carbohydrate fermentation, Carbohydrate assimilation and CHROM agar inoculation. Results: Out of 410 samples Candida were isolated in 122 samples. Amongst the 122 Candida isolates highest was C.albicans 66.39%,followed by C.glabrata 15.65%,C.tropicalis 9.85%, C.parapsilosis 4.91%, C.krusei 2.4% and least wasC.guilliermondii 0.8%.In pregnancy and OCP users maximum isolates were of C.albicans(78.04% and 55.55%,respectively) were as in diabetic patients C.glabrata (47.05%) was predominant isolate,while in HIV positive patients all isolates wereC.albicans (100%). Conclusions: In our study the prevalence of VVC is 29.75%.Commonest species found was C.albicans 66.39%.VVC is more common in females with associated risk factors like pregnancy, diabetes, HIV and OCP users.Commonest species in pregnancy, OCP users and HIV patients wasC.albicans whileC.glabratawas more common in diabetic patient.
Keywords: Vulvovaginal candidiasis (VVC), Candida Spp., Germ tube test (GTT), CHROM agar
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION
Candida albicans, the most frequent cause of candidiasis, can account for up to 75% of the yeasts recovered from clinical specimens.1 Although the frequency of isolation of nonalbicans Candida (NAC) species is increasing gradually, C. albicans is the most common cause of candidiasis.1,2 Other species of Candida such as C. glabrata, C. krusei and C. tropicalis are emerging as important opportunisticpathogens and this transition had a significant clinical impact due to decreasedsusceptibility of these non-albicans yeasts to antifungal agents.4,5Identification to the species level of yeasts cultured from various clinical specimen is increasingly necessary for clinical laboratories.6,19 Generally yeast identification procedures start with a germ tube test in clinical laboratories.3 It is a rapid method to differentiate C. albicans andC. dubliniensis from other Candida species.21 Up to 5% of the strains of C. albicans may be germ tube negative, and false positive results can occur with Candida stellatoidea (now classified as C. albicans) and other yeasts that produce germ tube like structures, e.g., pseudohyphae.25,26 When the yeast cannot be identified with this method, further tests such as culturing on cornmeal agar, carbohydrate fermentation and carbohydrate assimilation tests are performed.22Detection of growth patterns on cornmeal agar takes 24-72 hours and sugar assimilation tests may take 72 hours to twoweeks.21 These procedures are labor intensive and take longer to determine the species.1 C.albicans and related species which are pathogenic for humans, become resistant to the anti-fungal agents, in particular to the azole compounds, by the expression of the efflux pumps that reduce drug accumulation, the alteration of the structure or concentration of the anti-fungal target proteins and by the alteration of the membrane sterol composition.2,20 The clinical consequences of the anti-fungal resistance can be seen as the treatment failure in the patients and as the change in the prevalence of the Candida species which causes the infection.2 Accurate species identification is important for the treatment of the Candida infections, as the non-albicans species of Candida continue to be increasingly documented and as not all the species respond to the same treatment.4 The increase in the predisposing conditions in recent years has resulted in a concurrent increase in the numberof patients who suffer from candidiasis.15,16Hence, this study was undertaken to identify species of Candida isolated from the clinical cases of VVC.
MATERIAL AND METHODS
The present study was carried out in the Department of Microbiology, SMIMER medical college, Surat during the period of July 2010 to October 2011. Total 410 OPD patients who were attending department of Obstetrics and Gynaecology with complain of abnormal vaginal discharge were included in the study.A detailed history of patients was taken. All procedures were done under aseptic precautions and with standard protocol.
1 Collection of sample
The amount, colour, character and smell of vaginal discharge were noted. The discharge was then collected by two sterile swabs from upper part of the posterior fornix and lateral vaginal walls.
2 Processing of Specimen
First swab was used for preparation of smear for direct Gram’s staining. Second swab was inoculatedonto Sabouraud’s dextrose agar supplemented with 0.05g/L Chloramphenicol. Culture plate was incubated at 37?C for 48 hours, cultures were examined for pasty, creamy and smooth white colonies of yeasts.Colonies were confirmed by gram’s stain examination for oval budding yeast cells and further species identification done by battery of test.
3 Tests for Identification of Candida Species
A) Germ Tube Test (GTT)-
The suspected Candida colonies were inoculated into 0.5 ml human serum in a small test tube.Reading were taken after 2 -3 hrs of incubation at 37º C.A drop of suspension was examined on slide under microscope for germ tube productiontrue hyphal structure.
B) Test for Chlamydospore formation –
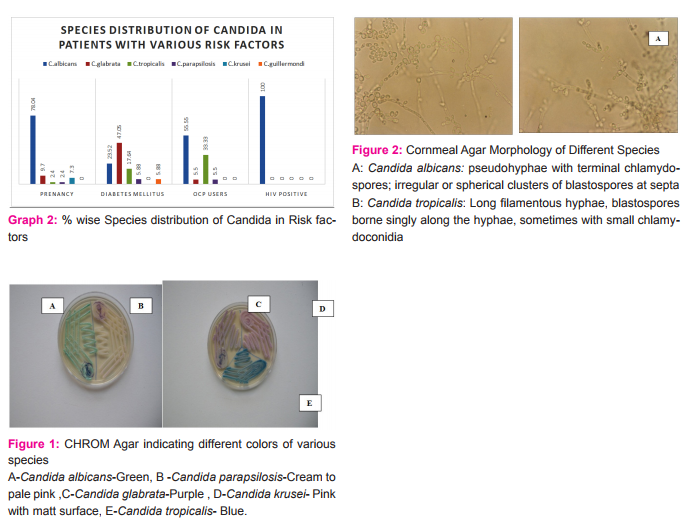
Pure culture of Candida species was inoculated on CornMeal agar and Dalmau plate culture was done.Inoculated plateswere incubated at 30°C for 24-48 hrs.At the end of incubation, examined microscopically through the cover slip and observe for the presence of chlamydospore.
C) Carbohydrate Assimilation testsSugar
Assimilation test was performed using following sugars. Glucose, Sucrose, Maltose, Lactose, Cellobiose, Raffinose and Trehalose.
Procedure
2-3 colonies were taken and suspension was prepared in normal saline.Lawn culture was done on Yeast Nitrogen Base (YNB, Sugar free medium).Carbohydrate discswere placed onto the surface of plateand incubated at 37°C. Results were read after 20-24 hours.In case of insufficient growth plates were further incubated till 48hours.Utilization of particular carbohydrate was determined by presence of growth around the disk.
D) Carbohydrate fermentation tests
Carbohydrate fermentation was performed for glucose, sucrose, maltose and lactose.
Procedure
1-2colonies of 1 mm diameter was inoculated into sugar fermentation tubes containing the appropriate sugars and Durham’s tubes. Inoculated tubes were incubated at 24°C for up to 1 week. Tubes were examined at 48 hours intervals for acid production (yellow colour) and gas formation (in Durham’s tubes).Production of gas indicates fermentation while only acid formation may indicate that the sugar has been assimilated. The reactions were read as A/G for each sugar separately.
E) CHROM agar Candida Differential Medium
Suspected Candida colonies from SDA agar was inoculated onto CHROMagar. The plates were incubated at 30°C for 48-72 hrs. The different Candida species shows following colours of colonies:
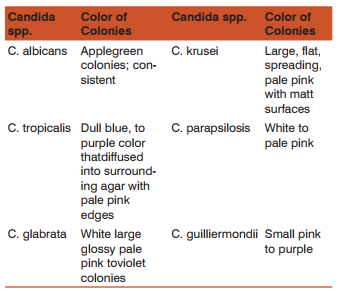
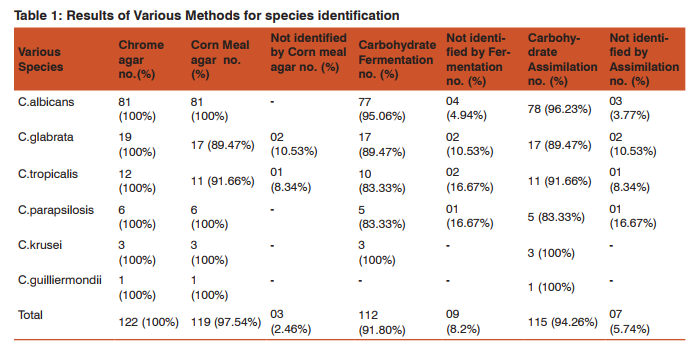
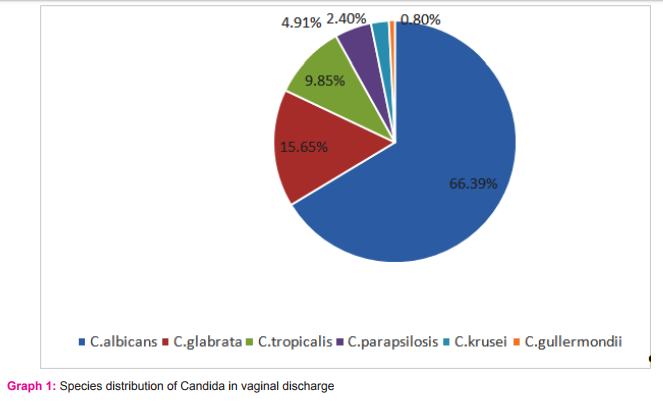
Results: Total 122Candida species were isolated out of 410 vaginal swab specimens. Out of 122 isolates 78were germ tube test positive while 44 isolates showed negative germ tube test. Inoculation on CHROMagar shows following results: C.albicans 81/122(66.39%), C.glabrata19/122(15.65%), C.tropicalis 12/122(9.85%), C.parapsilosis 6/122(4.91%), C.krusei 3/122(2.40%),C.guilliermondii 1/122(0.80%) (Table-1,Graph-1,Fig-1). We have considered CHROM agar as gold standard test. Inoculation on Corn meal agar had shown following results: C.albicans 81/122, C.glabrata17/122, C.tropicalis 11/122, C. parapsilosis 6/122, C.krusei 3/122, C.guilliermondii 1/122. Carbohydrate fermentation test results: C.albicans77/122, C.glabrata 17/122, C.tropicalis 10/122, C. parapsilosis 5/122, C. krusei 3/122,C.guilliermondii 0/122. Carbohydrate assimilation test had shown following results: C.albicans 78/122, C.glabrata 17/122, C.tropicalis 11/122, C. parapsilosis 5/122, C. krusei 3/122, C.guilliermondii1/122 (Table-1,Fig-2). The species isolates amongst the pregnant patients were:C.albicans 78.04% (n=32), C.glabrata 9.70% (n=4), C.tropicalis 2.4% (n=1), C.parapsilosis 2.4% (n=1), C.krusei 7.3% (n=3), C.guilliermondii 0 % (n=0) (Graph-2). The species isolates amongst the diabetic patients were:C.albicans 23.52% (n=4), C.glabrata 47.05% (n=8), C.tropicalis 17.64% (n=3), C. parapsilosis 5.88 %( n=1), C. krusei 0 % (n=0), C.guilliermondii 5.88 % (n=1) (Graph-2). The species isolates amongst the OCP users were:C.albicans 55.55% (n=10), C.glabrata 5.50% (n=1), C.tropicalis 33.33% (n=6), C. parapsilosis 5.5 %( n=1), C. krusei 0 % (n=0), C.guilliermondii 0 % (n=0) (Graph-2). The species isolated from PLWH patients were allC.albicans100 % (n=7)(Graph-2).
DISCUSSION
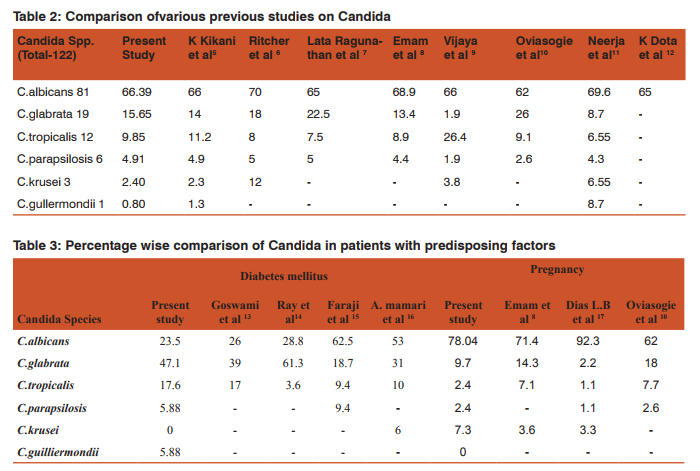
Despite therapeutic advances, vulvovaginal Candidiasis remains a common problem worldwide, affecting all strata of society.5 Candidial infections are more dynamic than other diseases prevailing in the community.11Their epidemiological profile varies from country to country and from one region to another within a country depending upon demographic, socio-economic and health factors.23 There is always a need of a medium whichhelps not only in the isolation but also in the identification of the agent at the species level.1 CHROMagar is a differential medium being widely used to differentiate Candida species.2 It facilitates the detection and identification of yeasts from mixed cultures and can provide results in24 to 48 hrs sooner than standard isolation and identification procedures.24It is superior to SDA in terms of suppressing the bacterial growth.A major advantage ofCHROMagar is the ability to detect mixed cultures of yeasts in clinical specimens.1,3Although CHROMagar appears to be quite accurate in identifying the most common Candida species, it is not proposed as a substitute for standard identification protocols.24 Sensitivity of GTT in our study is 96.2% which is quite comparable with J.E. Hoppe et al25(98.9%) and Arthur E. Crist et al26(94.7%). As shown in table 2 Candida albicans was the major pathogen causing VVC in various studies. Candidaalbicans produces protease, phosphates and carbohydrates which enhance its attachment to human epithelium7 .So, C. albicans is more adhesive than other non-C.albicans species (This could be considered as one of the likely reasons that this species are predominant rather than non-C. albicans species) 5 . In present study the incidence of C. albicanswas 66.39% which is quite comparable with the studies of K.kikani et al (66%)5, Vijaya et al (66%)9 ,Latha Ragunathanet al(65%),7 K Dota et al (65%)12and Emam et al8 (68.9%) (Table-2). As per Table 2 the incidence of non-albicans species is very similar to findings of Ritcher et al6 , Latha Ragunathan et al7 and Emam et al. 8 C. glabrata found second common spp. after C. albicans in most of the studies. In this study the incidence of C.glabrata is 47.1% in diabetic patientswhile it was 39%in Goswami et al13 and 61.3% in Ray et al14in diabetic patients(Table-3). Incidence of vaginal candidiasis is remarkably higher during pregnancy due to physiological changes.10Various study has reported incidence of symptomatic vaginal candidiasis high in pregnancy and increases during the course of gestation.18C.albicans was most frequently isolated also in pregnancy 78.04 % in this study. Oviasogie F.E et al10 has reported 61.5% and Dias L.B et al17 has reported 92.3% C.albicans in pregnant patients (Table-3).
CONCLUSION
In our study most common species was Candida albicans in cases of VVC. Candida glabrata was the most common species in diabetic patients and Candida albicans was the most common in HIV. In India there is an increase in prevalence of non-albicans Candida spp.due to increase in immunocompromised patients. This also specifies the need of species identification and antifungal susceptibility as a part of the laboratory diagnosis of vaginal candidiasis. CHROM agar is very good medium for species identification of Candida isolates, which give result in short time compared to other methods of species differentiation.This will ultimately help clinician to choose appropriate antifungal in cases of VVC.
Abbreviations:
VVC-Vulvovaginal Candidiasis SDA-Sabouraud’s Dextrose agar NAC-Non albicans Candida DM-Diabetes Mellitus HIV-Human Immunodeficiency Virus PLWH-Patient Living With HIV AG-acid,gas production GTT-Germ Tube Test CHROM Agar- Chromogenic agar OCP –Oral Contraceptive Pill
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
Authors would like to thank Dean and Medical Superintendent,SMIMER Medical College and hospital for allowingus to carry out this study and for providing thefacilities and help. We are also thankful to the Head of Department Obstetrics and Gynecology, SMIMER Medical College and hospital for allowing us to collect the specimens from their patients. Weacknowledge the immense help received from the scholars whose articles are cited and included in references of this manuscript. We are also grateful to authors/editors/publishers of all those articles, journals and books from where the literature for this article has been reviewed and discussed.
References:
1. V. P. Baradkar, M. Mathur, S. KumarHichrom. Candida agar for identification of Candida Species.Indian Journal of Pathology and Microbiology-53(1)January-March 2010.
2. Shivanand Dharwad, Saldanha Dominic R.M.Species Identification of Candida Isolates in Various Clinical Specimens with Their Antifungal Susceptibility Patterns Journal of Clinical and Diagnostic Research. 2011 November (Suppl-1), Vol-5(6): 1177-1181.
3. Sayyada Ghufrana Nadeem, Shazia Tabassum Hakim,Shahana Urooj Kazmi.Use of CHROMagar Candida for the presumptive identification of Candida species directly from clinical specimens in resource-limited settings Libyan J Med 2010, 5: 2144 - DOI: 10.3402/ljm.v5i0.2144
4. Kelen F. D. Dota, Alessandra R. Freitas, Marcia E. L. Consolaro, Terezinha I. E. Svidzinski.A Challenge for Clinical Laboratories: Detection of Antifungal Resistance in Candida Species Causing Vulvovaginal Candidiasis. Journal of Lab medicine February 2011 Volume 42 Number 2.
5. Sandra S. Richter, Rudolph P. Galask,Shawn A.et al.Antifungal Susceptibilities of Candida Species Causing Vulvovaginitisand Epidemiology of Recurrent Cases Journal Of Clinical Microbiology, May 2005, p. 2155–2162.
6. Kikani K M. Species Distribution And Antifungal Susceptibility Pattern In The Cases Of Vaginal Candidiasis In Saurashtra Region Of Gujarat. Electronic Journal of Pharmacology and Therapy.January 1,2010.
7. Latha Ragunathan, Poongothai G.K, Annie Rofeena Sinazer et al Characterization and Antifungal Susceptibility Pattern to Fluconazole in Candida species Isolated from Vulvovaginal Candidiasis in a Tertiary Care HospitalJournal of Clinical and Diagnostic Research. 2014 May, Vol-8(5): DC01-DC04.
8. Sherin M Emam, Abeer A Abo Elazm and Ahmed Walid A.Exoenzymes Production and Antifungal Susceptibility of Candida Species Isolated from Pregnant Women with Vulvovaginitis. Journal of American Science 2012;8(12).
9. Doddaiah Vijaya, Tumkur Anjaneya Dhanalakshmi, Sunanda Kulkarni.Changing Trends of Vulvovaginal Candidiasis Journal of Laboratory Physicians / Jan-Jun 2014 / Vol-6 / Issue-1.
10. Oviasogie FE, Okungbowa FI. Candida species amongst pregnant women in Benin city, Nigeria: Effect of predisposing factors. Afr J Clin Exper Microbiol 2009;10:92-8.
11. Neerja J,Aruna A,Paramjeet G. Significance of Candida culture in women with vulvovaginal symptoms. J Obstet Gynecol India 2006;56:139-41.
12. Kelen F. D. Dota, Alessandra R. Freitas, Marcia E. L. Consolaro, Terezinha I. E. Svidzinski.A Challenge for Clinical Laboratories: Detection of Antifungal Resistance in Candida Species Causing Vulvovaginal Candidiasis. Journal of Lab medicine February 2011 Volume 42 Number 2.
13. R.Goswami,V Dadhwal,S.Tejaswi et al.Species-specific prevalence of vaginal Candidiasis among patients with Diabetes mellitus and its relation to their glycemic status Journal of infection (2000)41,162-166 .
14. Debarti Ray ,Ravinder Goswami, Uma Banerjee et al. Prevalence of Candida glabrata and Its Response to Boric Acid Vaginal Suppositories in Comparison With Oral Fluconazole in Patients With Diabetes and Vulvovaginal Candidiasis;Diabetes and vulvovaginal candidiasis;Diabetes Care, volume 30, number 2, february 2007.
15. Reza Faraji, Mehr Ali Rahimi, Fatemeh Rezvanmadani and Masoud Hashemi: Faraji et al.Prevalence of vaginal candidiasis infection in diabetic women10 January, 2012.
16. Abdullah Al-mamari, Mahmoud Mahyoob Al-buryhi and Sadeq Al-hag.Species-specific prevalence of vaginal candidiasis with type 1 and type 2 diabetes mellitus among women in Sana’a city Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research, 2013, 5(8): 217-224.
17. Luciana Basili Dias, Márcia de Souza Carvalho Melhem, Maria Walderez Szeszs et al.
18. Vulvovaginal Candidiasis In Mato Grosso, Brazil: Pregnancy Status, Causative Species And Drugs Tests. Brazilian Journal of Microbiology (2011) 42: 1300-1307.
19. Rui Fernandes Ana Viegas Fatima CerqueiraCandida Species distribution in clinical samples Revista da Faculdade de Ciencias da Saude.ISSN 1646-0480. 6 (2009) 264-271.
20. Patrick Williams Narkwa B.Sc (Hons) ;Antifungal Susceptibility Of Candida Species And Cryptococcus Neoformans Isolated From Patients At The Komfo Anokye Teaching Hospital In Kumasi;February, 2010.
21. Chander J. Candidiasis. In: A textbook of Medical Mycology, 3rd ed. Mehta Publishers, New Delhi, 2009; 266-90.
22. Fran Fisher,Norma cook,Fundamentals of diagnostic mycology,Philadelphia.W.B saunders company 1998;197-222.
23. Deepa Babin, Subbannayya Kotigadde, P.Sunil Rao et al. Clinico-mycological profile of vaginal candidiasis in a tertiary care hospital in Kerala International Journal of Research in Biological Sciences 2013; 3(1): 55-59.
24. Veena Manjunath , Vidya GS, Archana Sharma, Mridula Raj Prakash et al. Speciation of Candida by Hicrome agar and Sugar assimilation test in both HIVinfected and non infected patients. Int J Biol Med Res. 2012; 3(2):1778-1782.
25. J.E. Hoppe, P. Frey;Hoppe et al;Evaluation of Six Commercial Tests and the Germ-Tube Test for Presumptive Identification of Candida albicans ;Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis (1999) 18 :188–191.
26. Arthur E. Crist, Theresa J. Dietz, And Kristin Kampschroer; Comparison of the MUREX C. albicans, Albicans-Sure, and BactiCard Candida Test Kits with the Germ Tube Test for Presumptive Identification of Candida albicans; Journal Of Clinical Microbiology, Oct. 1996, p. 2616–2618, Vol. 34, No.10
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License