IJCRR - 13(9), May, 2021
Pages: 35-39
Date of Publication: 07-May-2021
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
Outcome of Induction of Labour: A Prospective Study in a Tertiary Care Centre from Aurangabad, Maharashtra
Author: Lakshmi Rachakonda, Savita Kadam, Kritika Agrawal, Harshini T
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Introduction: Induction of labour is an intervention carried out to artificially initiate uterine contractions causing progressive dilatation and effacement of the cervix leading to vaginal delivery. There should be a clear medical indication for induction of labour. Induction of labour is a challenge to obstetricians, patients and fetuses.
Objectives: To evaluate the causes of induction of labour and its neonatal outcome
Material and Methods: The prospective observational study was conducted from July 2019 to December 2019 in the Department of Obstetrics and gynaecology, Mahatma Gandhi Mission Medical College and Hospital, Aurangabad, Maharashtra. During this period 1504 patients delivered to our hospital, out of which 174 were induced (11.56%). Foley's catheter with Dinoprostone gel, only Dinoprostone gel, oral Mifepristone and sweeping of membrane were methods of induction. Written consent was taken of each patient after explaining the procedure in detail to the patient and her relatives.
Results: In our study, the rate of induction in our hospital was 11.56%. 84.48% of patients were between the ages of 19-29 years. We have induced 48.28% booked patients. In our study 44.25% of patients were primigravida. Most of them were between the gestational ages of 37-40 weeks. Most of the patients were induced for postdatism (35.05%) and PROM (28.73%). The average induction delivery interval was 10-20 hours.83.34% of patients delivered vaginally. Only 14.97% of babies required NICU.
Conclusion: Induction of labour is safe and beneficial in high-risk pregnancy. In our study, postdatism and PROM were common indicators of induction with good perinatal outcome. It has to be monitored carefully to avoid complications.
Keywords: Induction of labour, Bishop score, Maternal outcome, Perinatal outcome
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION
Induction of labour is an intervention carried out to artificially initiate uterine contractions causing progressive dilatation and effacement of the cervix leading to vaginal delivery of baby.1It is generally done when benefits to mother and fetus will outweigh benefits if pregnancy is continued.1 The World Health Organization recommends that there should be a clear medical indication of induction and it should be practised when benefits outweigh potential harms.2 There is a trend towards rising inductions in the USA and Europe which may lead to increased cesarean delivery.1,3-6 The rate in the U.S ranges from 9.5-33.7%.2 It is seen that elective induction which are inductions in absence of medical or obstetric indications are becoming common and contribute to the overall increasing induction rate.3 This is because of an improved ability to plan the timing of delivery by the patient, her family and obstetrician. Few studies have shown that delivery before 39 weeks of gestation without medical indication is associated with worse perinatal outcomes than delivery at full term.7 Other studies have also concluded that induction of labour beyond 41 weeks varies from country to country.8 There are various methods of induction including pharmacological and mechanical methods. Misoprostol (PGE1) as an inducing agent is less expensive, more stable and easier to store than PGE2.1 Another inducing agent is PGE2 (Dinoprostone) gel which increases hyaluronidase and collagenase levels in the cervix which will cause cervical softening.1
This study was conducted to analyze the various indicators of induction in our hospital along with understanding maternal and neonatal outcomes.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
This study was conducted in MGM Medical College & Hospital, Aurangabad, Maharashtra after obtaining permission from the ethical committee.
The study period was from July 2019 to December 2019. It was a prospective observational study of 6 months duration. Out of 1504 deliveries during that period 174 were induced. Written consent was taken after explaining the details to patients and relatives. Basic requirements and contraindications for induction were assessed. The inclusion and exclusion criteria were pre-decided and accordingly patients were selected. The various methods of induction were Dinoprostone gel, Foley’s catheter with gel and oral Mifepristone. Sweeping and stretching of the membrane was also carried out in some patients. Induction of labour was done using Dinoprostone gel in 163 patients and 5 patients gel was combined with intracervical Foley’s catheter as Bishop Score was less.
The inclusion criteria in our study were post-dated pregnancy, pre-eclampsia, fetal growth restriction, oligohydramnios, PROM, IUFD and others. The patient excluded were patients not willing to give consent and all contraindications for induction.
A detailed proforma was made and details filled out. All patients were monitored in the labour room as per the protocol of labour room monitoring. The patients were monitored in the labour room with NST, auscultation and CTG. Mifepristone was given orally and Dinoprostone gel was inserted in the posterior fornix.
RESULTS
During our study of 6 months, out of the 1504 patients who delivered in that period, 174 patients were induced. The rate of induction in our hospital was 11.56%.
Demographic factors in the study population
Table 1 shows that around 84.48% of patients were in the age group between 19 - 29 years as this is the commonest reproductive age group seen in our hospital.

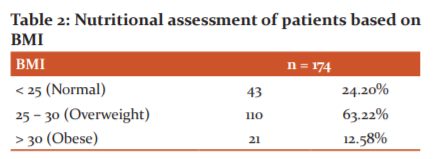
Table 2 shows that majority of the patients had a BMI in the range of 25 – 30 kg/m2. BMI of >30 kg/m2 also did not influence the route of delivery to much extent. In patients with BMI more > 30 kg/m2, 69.9% underwent LSCS and 38.09% delivered vaginally.
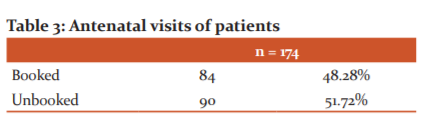
Patients maintaining follow-up in the institute till the time of delivery were considered as booked patients and patients with irregular visits or presented at time of delivery were considered as unbooked patients. As is evidenced by Table 3, the booking status did not influence the induction of labour in our study.
Variables affecting Induction of Labour
Table 4 shows that 44.25% of patients were primigravida. Out of all the primigravida delivered in our study period 15.2% were induced. In 2nd/ 3rdgravida only 7.75% required induction. Nearly 39.3% of patients with 4thgravida and above required induction. This could indicate that more primigravida requires induction as compared to multigravida.
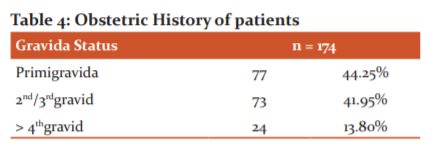
Table 5 shows that 56.33% of the patients were between 37 – 40 weeks of gestation. Though postdatism is a common indication for induction, 76% required induction for a different obstetric indication. As 23.56% of patients were above 40 weeks gestational age, naturally postdatism became the commonest indication of induction. The common reasons for induction in patients with <37 weeks of gestation were PROM, IUFD and preeclampsia.
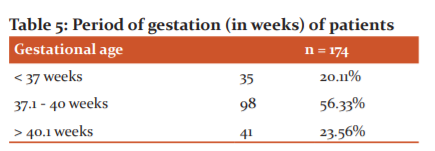
Table 6 shows that the commonest indication for induction in our hospital was postdatism (35.05%) followed by PROM (28.73%) and oligohydramnios (22.98%). 14.79% of the patients had preeclampsia and underwent induction of labour. Induction was the preferred mode of delivery in 7 patients presenting with IUFD.
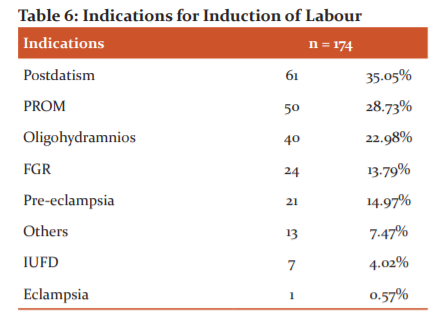
Method of Induction of Labour
Table 7 shows the majority i.e. 93.68% (163) of the patients were induced using Dinoprostone gel. This was followed by Foley’s catheterisation with gel as Bishop’s score was less. Mifepristone was used only in 3 patients and the indication was intrauterine fetal death. Misoprostol was not used in our hospital in that period.
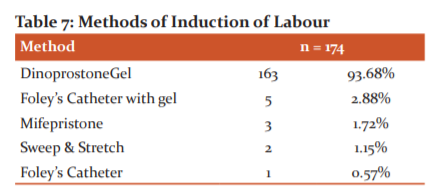
Table 8 shows that majority of the patients delivered with 1 induction gel and most of these patients had a favourable Bishop’s score on examination while instillation of the gel. 15.48% required 3 gels as the Bishop score in those patients was poor.

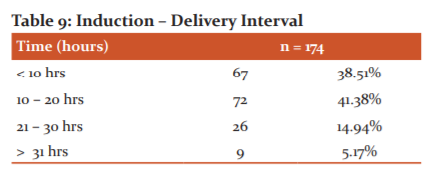
Table 9 shows that practically equal number of patients i.e. 38.50% and 41.38% delivered before 10 hours or between 10 – 20 hours of induction. Less duration was required when the Bishop score was good. Only 9 patients took more than 31 hours for delivery and the highest time taken was 38 hours. These patients who required more time were having preterm PROM, preeclampsia along with a low Bishop’s score.
Maternal and neonatal outcome of Induction of Labour
Table 10 shows that vaginal delivery was the commonest mode of delivery, observed in 83.34% of the patients. Only 16.66% required lower segment cesarean section(LSCS). Application of forceps or vacuum for delivering the baby was not required in any of the patients.

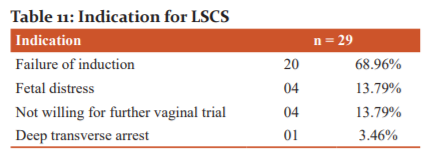
Table 11 shows that out of the 29 patients who underwent LSCS, failure of induction was the commonest reason, noted in 20 patients. 70% of these patients were primigravida and 30% were multigravida. The next common indication for LSCS was fetal distress and non-compliance of the patient for further vaginal trial.
Seven patients had IUFD so they were excluded from the neonatal outcome. Table 12 shows that out of 25 babies who required NICU admission, 28% of the mothers had PROM as a reason for induction. They additionally were preterm pregnancies. 16% of the mothers had preeclampsia as a reason for induction, so chronic hypoxia could be the reason for NICU admission.

DISCUSSION
Induction of labour is done when there is a benefit to the health of the fetus or mother or both. Induction is justified when benefits outweigh those of continuing pregnancy.1It is generally said that induction may be associated with complications as compared to spontaneous labour.1 The purpose of our study was for a better understanding of this concept.
In our study, 174 patients out of 1504 delivered from July 2019 to December 2019 were induced. The rate of induction was 1.86%. In the study carried out by Lamichhane et al in December 2014 – 2015 in Nepal, the induction rate was 9.92%.1 In a similar study by Soni et al in Berhampur – Odisha, over 2 years from August 2014 to July 2016, the induction rate was 13.6%.2 The lower rate in our study could be due to our being a tertiary care centre with the availability of trained staff for the entire 24 hours.
In our study, 84.48% of patients were in the age group of 19 – 29 years. In the study by Lamichhane et al., 78% were between 20 – 30 years.1 In a similar study by Ethiraj et al in 2016, 79.2% of patients were between 21 – 30 years of age.6 This could be due to this being the reproductive age group. In our study, 63.22% of patients were having BMI of between 25 - 30 Kg/m. In the studies conducted by Soni et al and Dogl et al, the BMI between 21-25 Kg/m2 was 53.1% and 53% respectively.2,3 Higher BMI is associated with an increased risk of undergoing cesarean section. In our study, around 44.25% were primigravida and 41.95% were 2nd or 3rd gravida. In a similar study by Chawla et al, 52.8% were primigravida and 41.1% were 2nd or 3rd gravida. There is a significant correlation between multiparity and normal vaginal delivery. In the study by Lamichhane et al, and Ethiraj et al. most patients, that is around 62% were primigravida.1,6
In our study, 56.33% had a gestational age between 37.1 - 40 weeks during induction. In the study by Dogl et al., 75% had gestational age below 40 weeks.3 In the study by Chawla et al, 54.7 % had a gestational age between 37 - 40 weeks.5 Also in the study by Ethiraj et al, 68.9% had a gestational age between 37 - 40 weeks.6 This could be due to good awareness and regular antenatal checkup. In our study, the common indicators for induction of labour were post-dated pregnancy in 35.05%, PROM in 28.73%, oligohydramnios in 22.98% and preeclampsia in 12.06% and FGR in 13.79%. The commonest cause in our study was postdated as we have more patients being referred from periphery hospitals and patients take longer time to make decisions. In the study by Lamichhane et al, indications of post-dated pregnancy were seen in 44.5% of the patients, PROM in 21.3%, oligohydramnios in 11.5% and preeclampsia in 12%.1 In the study by Soni et al, indications were PROM in 39.8%, HDP in 15.4%, postdated in 10.8%, FGR in 8.59%.2 In the study by Chawla et al, indications for induction were post-dated pregnancy (35.8%), heart disease in pregnancy (17.81%), PROM (6.2%) and IUFD (6.6%).5 In our study, 93.68% were induced by Dinoprostone gel and 1.72% by Mifepristone. In the study by Dogl et al., 70% were induced with Prostaglandins (misoprostol tablet, Dinoprostone gel).3 In our study, the induction delivery interval (IDI) was less than 10 hours in 38.51% and up to 20 hours in 41.3%. In the study by Soni et al, IDI was 6 - 12 hours in 15.5% and 12-18 hours in 45.8%. It could be due to the judicious selection of patients for induction of labour.
In our study, 16.66% required cesarean section out of which 68.9% underwent LSCS as a failure of induction. In 13.79% of patients underwent LSCS for fetal distress. In the study by Lamichhane et al, 44% underwent LSCS for failed induction.1 Their rate of caesarean section was 32.3%. In a study by Soni et al., 31.1% underwent LSCS for failed induction and 27.3% were for fetal distress.2 In the study by Chawla et al, 27.1% delivered by cesarean section and 69.6% vaginally.5 In the study by Ethiraj et al, 71.39% delivered vaginally.6 Vigilant monitoring will lead to a better outcome in the form of vaginal delivery. In our study, 14.97% of babies were admitted to NICU. In the study by Dogl et al, 12.5% of babies were admitted to NICU.3 Vigilant monitoring will lead to a better outcome in the form of vaginal delivery.
CONCLUSION
Induction of labour is safe and beneficial in high-risk pregnancy when the benefits of early delivery outweigh the risk of continuation of pregnancy. But, this has to be monitored carefully to avoid complications. In our study, postdatism and PROM were common indicators of induction of labour. Dinoprostone was the most commonly used inducing agent. The number of cesarean sections was also less and the neonatal outcome was good. Those babies who went to NICU were also recovered fast. So, induction of labour is to be performed when there is a clear indication and benefits are more. At the same time, we should be aware of its complications too. The rate of vaginal deliveries was more in our study and the neonatal outcome was also good.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
The authors acknowledge the immense help received from all the patients who participated in this study. The authors also acknowledge the help received from all scholars whose articles are cited in the manuscript. The authors are also grateful to all the editors and publishers of those articles and journals from where the literature has been reviewed.
Source of funding: NA
Conflict of interest: Nil
Abbreviations: CTG – Cardiotocography
FGR – Fetal Growth Restriction
IUFD – Intrauterine Fetal Demise
LSCS – Lower Segment Cesarean Section
NICU – Neonatal Intensive Care Unit
NST – Non-Stress Test
PROM – Premature Rupture Of Membranes
References:
-
Lamichhane S, Subedi S, Banerjee B, Bhattarai R, Outcome of induction of labour: A prospective study. Ann Int Med Dent Res 2016;2(6):1-5.
-
Soni, Kavita, K. Subudhi, B. Misra, B. Gouda and S. Chaudhary. Maternal and perinatal outcome in the induction of labour: A comparative study. Sch J App Med Sci 2017;5(1D):273-281.
-
Dögl M, Romundstad P, Berntzen LD, Fremgaarden OC, Kirial K, Kjøllesdal AM, et al. Elective induction of labor: A prospective observational study. PLoS One. 2018;13(11): e0208098.
-
Wood S, Cooper S, Ross S. Does induction of labour increase the risk of caesarean section? A systematic review and meta-analysis of trials in women with intact membranes. Bri J Opth 2014;121:674-685.
-
Chawla S, Singh SK, Saraswat M, Vardhan S, Induction of labour: Our experience. J Marine Med Soc 2017;19:96-98.
-
Gomathy E, Ramachandra A, Rajan S. Induction of Labor and Risk for Emergency Cesarean Section in Women at Term Pregnancy. J Clin Gynecol Obstet 2019;8:17-20.
-
Grobman WA, Rice MM, Reddy UM, Alan TN, Yasser Y.Labor Induction versus Expectant Management in Low-Risk Nulliparous Women. N Engl J Med 2018;379:513-523.
-
Keulen J, Bruinsma A, Kortekaas JC, Dillen J, Bossuyt P, Oudijk M, et al, Induction of labour at 41 weeks versus expectant management until 42 weeks (INDEX): multicentre, randomised non-inferiority trial. Bri Med J 2019;364:1344.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License