IJCRR - 13(9), May, 2021
Pages: 05-12
Date of Publication: 07-May-2021
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
Food Hygiene and Nutrition Management of Nursing Homes in Korea
Author: Joo-Eun Lee
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Introduction: The elderly population is on the rise all over the world, and the importance of quality meals that affect the life of the elderly is increasing. In particular, elderly people who have been admitted to facilities such as nursing homes have a high possibility of malnutrition due to their poor appetite, and hygienic meal management is very important due to their low immunity.
Objective: To recognize the performance of meal service management in nursing homes in Korea and to provide appropriate management of meals for the elderly and the need for hygiene and nutrition education.
Methods: This study surveyed the foodservice management performance targeting a total of 300 nursing homes with no duty to hire dietitians as the number of foodservice recipients was less than 50. It calculated the mean and standard deviation of the performance score. To understand differences in mean foodservice performance following the matter of hygiene education and nutrition education, the t-test was carried out for each item and category.
Results: The questionnaires were mostly filled in by directors of facilities (n=70, 80.5%) or office managers (n=12, 13.8%). Total 57 respondents (65.5%) had experiences in hygiene education, and a total of 22 respondents(25.3%) received nutrition education. When the total of 33 items was divided into six categories and then questioned, the category showing the highest mean performance score of the six categories was foodservice facilities & environment' (4.33/5.0) while the lowest category was 'cooking process management' (3.70/5.0).The mean foodservice management performance score of the whole 33 items was3.96. In five categories and 22 items of foodservice management, the case of receiving hygiene education showed a significantly higher mean performance score than the case without it (p< 0.05, p< 0.01, p< 0.001). Regarding the items for understanding the nutrition management performance, the case of receiving nutrition education showed a significantly higher mean nutrition management performance score than the case without it (p< 0.05, p< 0.01, p< 0.001).
Conclusion: The results showed that the experiences in hygiene/nutrition education would have positive effects on food service management, and it is needed the opportunities for various education and promotion should be provided.
Keywords: Food, Hygiene, Nutrition, Education, Nursing home, the Elderly
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION
The WHO predicted that the aged population would be continuously increasing in the whole world, and the percentage of the elderly in 60 or up would be almost doubled from 12 % in 2015 to 22% in 2050.1 Even in Korea, the aged population is continuously increasing. The percentage of the elderly in 65 or up was 7.2% in 2000 as an ageing society and 14.3% in 2018 as an ageing society. It is predicted that Korea would become a super-aged society (20.3%) in 2025.2 The national problems caused by the increase of the aged population are not only a burden on healthcare costs, but also led to problems of the whole society that has to treat and support them.1,3 Thus, Korea is establishing the national system for supporting the elderly by implementing the Long-Term Care Insurance from July 2008, and the percentage of the elderly using it is gradually increasing from 5.89% in 2010 and 7.80% in 2017 to 10.02 % in 2019.4
In the aspect of pursuing the quality of life of the elderly, such a nutritionally balanced and pleasant dietary life is regarded as important because the hygiene and nutrition management of overall meals are the fundamental conditions for preventing diseases.5,6 Actually, the elderly with weak immune systems are at greater risk to be exposed to food poisoning, and some cases of food poisoning at nursing homes have been reported in reality7,8. From 1975 to 1987, a total of 115 cases of food poisoning occurred at nursing homes in 26 states of the United States, which was led to 51 deaths. The most causative organism of this food poisoning was known as Salmonella.7 Also, in 1993, a total of 119 old people were infected with food poisoning at a nursing home with 580 sickbeds in Brooklyn, New York of the United States, and the cause was revealed as cross-contamination happened in the process of grinding meat and poultry by a culinary employee infected with the disease.8 Even though the average calorie of food provided for five days to 74 old people in a nursing home of Belgium was 1,783.3 kcal per day, the actual ingested calorie was significantly low as 1,552.4 kcal, so that the risk of malnutrition was very high.9 As the malnutrition of the elderly in nursing homes could increase the outbreak of diseases and mortality risks, the actual intake which was less than half of distributed food or the cycle of checking their weight was closely related to malnutrition.10 There were significant correlations between malnutrition and specific contents of meal service such as the possibility of handling plates or lids in each meal, mass-delivery system, overall satisfaction, length of menu cycle, and the use of chinaware.11 Thus, this research was purposed to recognize the foodservice management performance of nursing homes in Korea and also the necessities of proper meal management for the elderly and hygiene/nutrition education.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Research subject and methods
From July to August 2019, this study sent the questionnaires for understanding the foodservice management performance through mail and post to the total of 300 nursing homes registered in the Ministry of Health and Welfare, with no duty to hire dietitians as the number of foodservice recipients was less than 50. And after explaining the purpose of this study by telephone, the questionnaires were collected through mail or post. As a total of 87 questionnaires of 300 were collected, the return rate was 29%. Before the survey, the respondents were explained that their replies would be confidential and anonymous, and the results not be used for purposes other than this research. And they were asked to write a consent form.
Survey contents and composition
The questionnaire used for this study was written by referring to the research tool used for research targeting the welfare facilities for the elderly by Seo et al.12 ‘2019 Guidelines for the Centers for Children’s Foodservice Management by the Ministry of Food and Drug Safety,13 and the hygiene & nutrition management checklist for foodservice facilities shown in ‘2019 Guidelines for Foodservice Management Support Trial Operation of Social Welfare Facilities’.14 The questionnaire was largely composed of general aspects of nursing homes, general aspects of respondents, and foodservice management performance of nursing homes. The general aspects of nursing homes and respondents suggested region, number of residents, operation period, operation type, menu writer, the place for meals, and sex, age, position, academic background, work experience, hygiene education experience, and nutrition education experience of recipients as nominal scale. Regarding the foodservice management performance, a total of 33 items were divided into six categories and then questioned like six items of ‘foodservice facilities & environment’, six items of ‘personal hygiene’, seven items of ‘cooking process management’, three items of ‘food ingredients management’, two items of ‘washing & disinfection management’, and nine items of ‘nutrition management’. The Likert 5-Point Scale(1: very bad∼ 5: very good) was used for food service management performance.
Data analysis
The SPSS ver. 20.0 for Windows(Statistical Package for Social Science, SPSS Inc, Chicago, IL, USA)was used for statistical analysis. On top of calculating the frequency and percentage of general aspects of nursing homes and respondents, this study also calculated the standard deviation and the mean of each item of foodservice management performance. Also, to understand differences of mean foodservice performance following the matter of hygiene education and nutrition education, the t-test was conducted for each item and category.
results
General aspects of nursing homes and respondents.
The general aspects of nursing homes as the research subjects are shown inTable 1. In the number of residents in nursing homes, there were 21 nursing homeswith less than ten residents (24.1%), and 66 nursing homes with10-49 residents (75.9%). In the operation period of facilities, the nursing homes for 5-10 years were the most (32 places, 36.8%). In the operation type, the direct management (77 places, 88.5%)was more than consignment(10 places, 11.5%). Regarding the menus in use, most cases received them from the association of long-term care centres (31 places, 35.6%). There were 30 places (34.5%) using the menus written by dietitians in their own or other institutions, and also 24 places (27.6%) using the menus of local health centres. Regarding the place for meals, most cases (43 places, 49.4%) used a cafeteria mixed with the bed. In the case of drinking water, most nursing homes (67 places, 77.0%) used water purifiers.
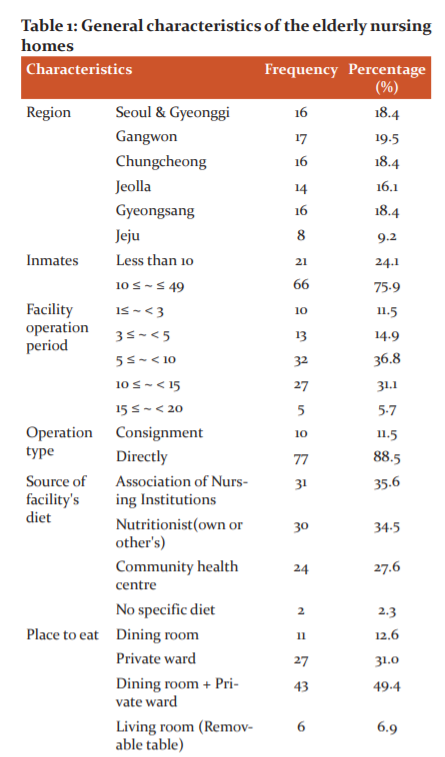

The general aspects of respondents to the questionnaires sent to nursing homes are shown in Table 2. The questionnaires were mostly filled in by directors of facilities(n=70, 80.5%) or office managers (n=12, 13.8%). In the sex ratio of respondents, there were a bit more women (n=46, 52.9%) than men (n=41, 47.1%). In their age, the respondents in their 50s (n=31, 35.6%) were the most, which was followed by the 60s and 40s (n=20, 23.0%). In the academic background, the college graduates (n=39,44.8%)were the most. Regarding the work experience, the respondents with experiences for 5-10 years (n=27,31.0%)were the most. There were 57 respondents (65.5%) with hygiene education experience and 22 respondents (25.3%) with nutrition education experience.
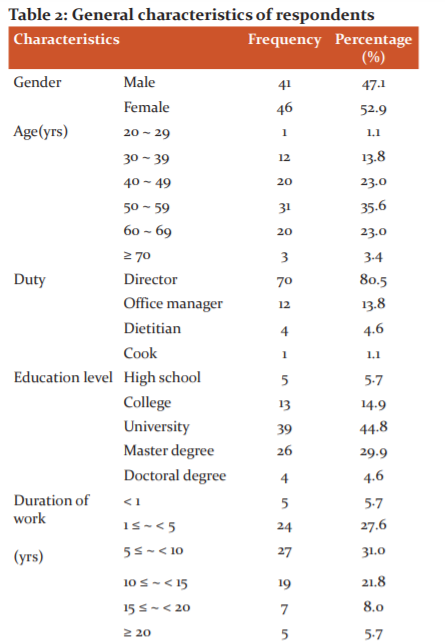

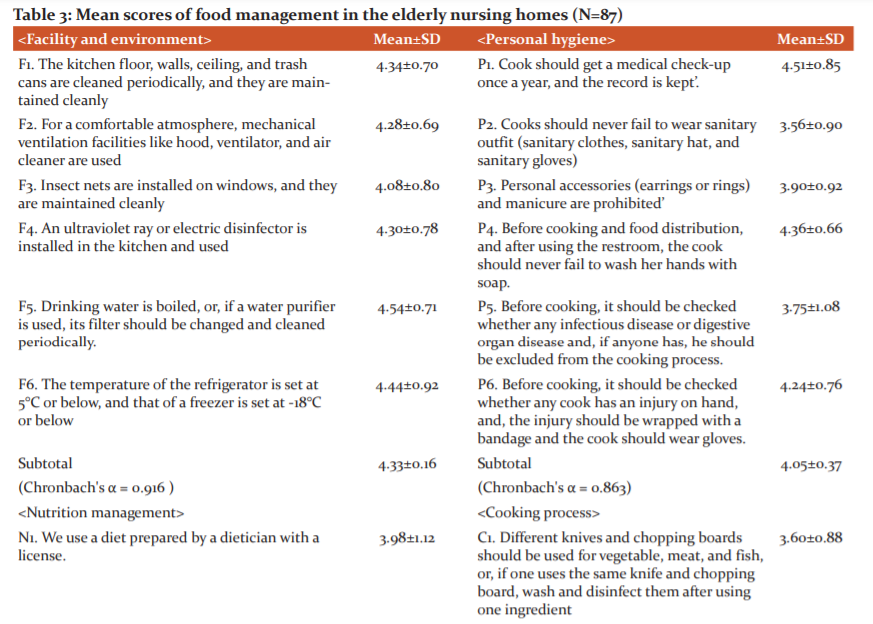
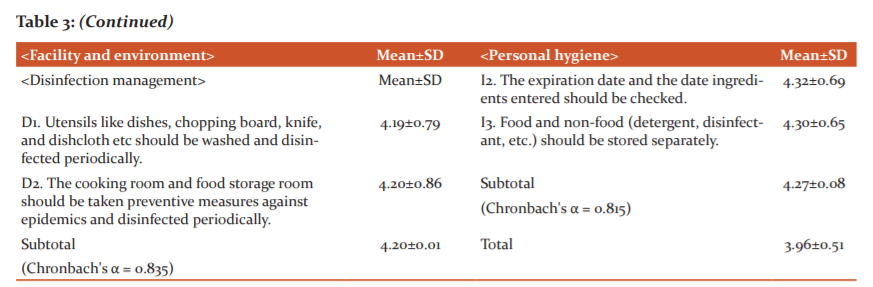
Mean score of food management performance of nursing homes
Understanding the foodservice management performance of nursing homes in each category, the mean and standard deviation were shown inTable 3. The category showing the highest mean performance score of the total six categories was ‘foodservice facilities & environment’(4.33/5.0) while the category showing the lowest score was ‘cooking process management’(3.70/5.0). The mean foodservice management performance of the whole 33 items was 3.96.

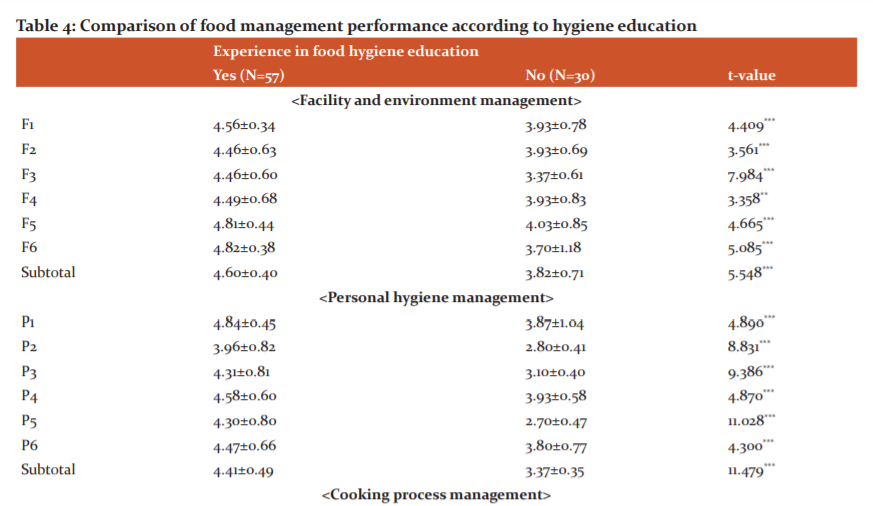
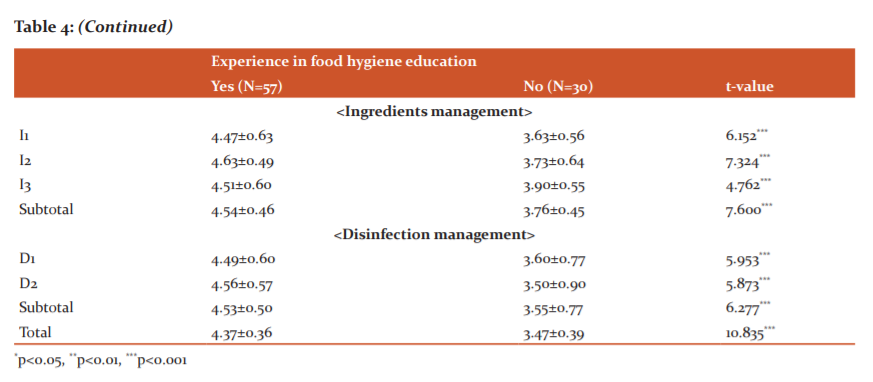
Comparison of food management performance following the matter of hygiene education
The results of comparing the food management performance of nursing homes through t-test to see if there would be differences in mean score following the matter of hygiene education are shown in Table 4. In total five categories and 22 items of foodservice management, the case of receiving hygiene education showed a significantly higher mean performance score than the case without it (p<0.05, p<0.01, p<0.001).

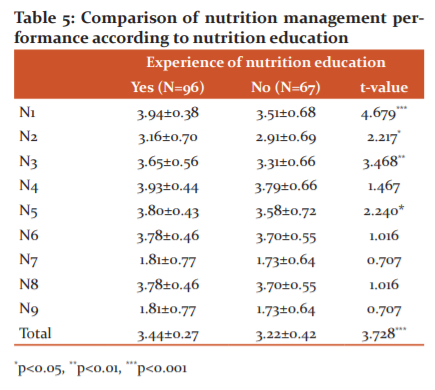
Comparison of nutrition management performance following the matter of nutrition education
The results of comparing the mean nutrition management performance score following the matter of nutrition education were shown inTable 5. In the four items for understanding the nutrition management performance such as the menus written by a licensed dietitian are used’, ‘The menus suitable for the elderly foodservice recipients in facilities are used’, ‘On top of furnishing the monthly menus, the menu list is open to the recipients(homepage, bulletin board, etc.)’, and ‘Every meal is cooked by checking the standard recipe of each menu’, the case of receiving nutrition education showed significantly higher mean nutrition management performance score than the case without it(p<0.05, p<0.01, p<0.001).
discussion
This research was purposed to recognize the necessities of proper meal management for the elderly and hygiene/nutrition education by understanding the foodservice management performance of nursing homes in Korea and then comparing differences following the matter of hygiene education and nutrition education.
In the results of self-evaluation on the foodservice management performance of nursing homes in this study, the mean score was 3.96 of 5.0, which was higher than the average. When questioning about a total of 33 items in six categories, the scores of cooking process management (3.70) and nutrition management (3.71) were lower than the mean score of the whole (3.96). Especially, the item ‘The vegetables and fruits eaten raw are soaked in disinfection fluids and then rinsed with the running water before use of cooking process showed the lowest performance score (3.03). Also, in the research on the actual state of foodservice operation in food service facilities for the elderly by Choi et al.,15 the items like ‘Chlorination (100 ppm) of fresh vegetables and ‘Measurement of central temperature when heating food showed the lowest management score. In this study, the item of fully heating up, so that the central temperature would reach 74?, and checking the temperature was lower than the average. According to Lee,16 the dietitians of nursing homes had a low perception of the importance of ‘Checking the central temperature of food that should be heated up. In the research on the actual foodservice management state of welfare facilities for the elderly by Seo et al.,13 even when there was a dietitian, the disinfection of unheated food ingredients showed the performance rate (64.8%) which was lower than the mean performance of the whole (90.5%). In the case of facilities with no dietitian, the performance rate was very low (37.5%). In the case of the elderly with weak immune systems, on top of the high risk to be infected with food poisoning, the prevalence rate could be also increased by malnutrition or lack of exercise, so that the hygienic management of food service for the elderly is very important.17, in the results of analyzing microorganisms like E.coli in salad eaten raw at food service facilities for the elderly, there were very close correlations between correct food handling of culinary employees and cleanliness of cooking utensils/environment.18 Thus, it would be necessary to perform thorough hygiene management of food service for the elderly, and also to provide hygiene education to culinary employees.
In this study, the category showing the low performance together with cooking process management was ‘nutrition management’, and the items every meal is cooked by checking the standard recipe of each menu’ and ‘Checking and managing the salinity of soup as 0.6~ 0.8%’ showed the lowest performance. The standard recipe is an important guideline that could decide the taste of food by correctly delivering the number of ingredients and seasoning. In case when it is not observed, the satisfaction with meals of the elderly and the actual intake could be affected.12,19,20 In the results of researching the actual meal intake at nursing homes, about 60% of the whole elderly were lacking in intake of recommended energy, calcium, and Vitamin D, and in the case when this intake is continued, malnutrition could be caused.21
In the results of this study, the salinity management showing the low-performance level of nutrition management’ is the aspect that should be essentially considered for the prevention of cardiovascular diseases like high blood pressure of the elderly, and actually, the dietary habit of eating salty food is closely related to the occurrence of adult diseases.22,23 Especially, in the meal pattern of Korean people, the salt intake is high because of soup, which could be improved through the management of dietary habit.24,25 Thus, the nursing homes that continuously provide meals to the elderly should importantly perceive salinity management, and also correctly practice it.
conclusion
This study understood the self-evaluated foodservice management performance by conducting a survey targeting nursing homes in Korea. In the results of this study, in the case of receiving hygiene education and nutrition education, the mean performance score was highly shown in most of the items, which showed the necessities of proper hygiene education and nutrition education for desirable food service management for the elderly. Especially, to inform the importance of the items showing the score lower than the mean performance score of the whole, the opportunities of various education and promotion should be provided.
acknowledgement
The author acknowledges the help received from the scholars whose articles are cited and included in references of this manuscript. The author is also grateful to authors / editors / publishers of all those articles, journals and books from where the literature for this article has been reviewed and discussed.
Financial Support: Nil.
Conflict of Interest: Nil.
References:
-
World Health Organization. Ageing and health. 2018 [cited 2021 Jan 12]. Available from: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/ageing-and-health.
-
Statistics Korea. Major population index. [updated 2019 Mar 28; cited 2021 Jan 12]. http://kosis.kr/statHtml/statHtml.do?orgId=101&tblId=DT_1BPA002&checkFlag=N. Korean.
-
Koohsari MJ, Nakaya T, Oka K. Activity-friendly built environments in a super-aged society, Japan: current challenges and toward a research agenda. Int J Environ Res Public Health 2018 Sep;15(9):1-9.
-
National Health Insurance Service. Homepage of Long-term Care Insurance for the Elderly. 2020. http://www.longtermcare.or.kr/npbs/index.jsp. Korean.
-
Hoffmann AT. Quality of life, food choice and meal patterns - field report of a practitioner. Ann Nutr Metab 2008;52:20–24.
-
Buccheri C, Mammina C, Giammanco S, Giammanco M, La Guardia M, Casuccio A, et al. Knowledge, attitudes and self-reported practices of food service staff in nursing homes and long-term care facilities. Food Control 2010 Oct;21(10):1367-73.
-
Levine WC, Smart JF, Archer DL, Bean NH, Tauxe RV. Foodborne disease outbreaks in nursing homes, 1975 through 1987. JAMA. 1991 Oct;266(15):2105–9.
-
Layton MC, Calliste SG, Gomez TM, Patton C, Brooks S. A mixed foodborne outbreak with Salmonella heidelberg and Campylobacter jejuni in a nursing home. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol 1997 Feb;8(2):115–21.
-
Buckinx F, Allepaerts S, Paquot N, Reginster JY, de Cock C, Petermans J, et al. Energy and nutrient content of food served and consumed by nursing home residents. J Nutr Health Aging 2017;21(6):727-32.
-
Papparotto C, Bidoli E, Palese A. Risk factors associated with malnutrition in older adults living in Italian nursing homes: a cross-sectional study. Res Gerontol Nurs 2013;6(3):187-97.
-
Carrier N, Ouellet D, West GE. Nursing home food services linked with risk of malnutrition. Can J Diet Pract Res. 2007;68(1):14-20.
-
Seo JE, Kwon KI, Kim GH. Study on the actual conditions of institution foodservice management in the elderly welfare facilities by the employment of dietitians. Korean J Food Cook Sci 2019;35(2):216~25.
-
Korean Ministry of Food and Drug Safety. Guideline of Center For Children’s Foodservice Management. Cheongju: Korean Ministry of Food and Drug Safety Press; 2019. p.123-30. Korean.
-
Korean Ministry of Food and Drug Safety. Guidelines for trial operation of food management support for social welfare facilities. Cheongju: Korean Ministry of Food and Drug Safety Press; 2019. p.77-86. Korean.
-
Choi JH, Kim DH, Choi EH, Chung MJ, Lee HS, Lee MJ, et al. Assessment of foodservice management practices according to types of elderly foodservice facilities. J Korean Soc Food Sci Nutr 2019;48(4): 469-81.
-
Lee JE. Dietitians’ perception of importance about standards of foodservice management associated with long-term care hospital accreditation. J Korean Soc Food Sci Nutr 2015; 44(10):1558-66.
-
McCabe-Sellers BJ, Beattie SE. Food safety: emerging trends in foodborne illness surveillance and prevention. J Am Diet Assoc 2004;104(11):1708-17.
-
Rodríguez M, Valero A, Posada-Izquierdo GD, Carrasco E, Zurera G. Evaluation of food handler practices and microbiological status of ready-to-eat foods in long-term care facilities in the Andalusia region of Spain. J Food Prot 2011;74(9);1504-1512.
-
Church SM. The importance of food composition data in recipe analysis. Nutr Bull 2015;40(1):40–4.
-
Crogan N, Dupler AE, Short R, Heaton G. Food choice can improve nursing home resident meal service satisfaction and nutritional status. J Gerontol Nurs 2013;39(5):38-45.
-
Grieger JA, Nowson CA. Nutrient intake and plate waste from an Australian residential care facility. Eur J Clin Nutr 2007;61(5):655-63.
-
Schoner W. Salt abuse: the path to hypertension. Nat Med 2008;14(1):16-7.
-
Cummins RO. Recent changes in salt use and stroke mortality in England and Wales. Any help for the salt-hypertension debate? J Epidemiol Community Health 1983;37(1):25-8.
-
Kim JN, Park SY, Ahn SH, Kim HK. A Survey on the salt content of kindergarten lunch meals and meal providers` dietary attitude to sodium intake in Gyeonggi-do area. Korean J Community Nutr 2013;18(5):478-90.
-
Jung EJ, Kwon JS, Ahn SH, Son SM. Blood pressure, sodium intake and dietary behavior changes by session attendance on salt reduction education program for pre-hypertensive adults in a public health center. Korean J Community Nutr 2013;18(6):626-43.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License