IJCRR - 13(8), April, 2021
Pages: 143-148
Date of Publication: 25-Apr-2021
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
Does BMI affect the Academic Performance of Adolescents? A Comparative Study between the Government and Private Schools of Madurai District, Tamil Nadu, India
Author: B. Bhuvaneswari, S. Parameshwari
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Background: This study examined the prevalence of overweight, obesity and the association between BMI and Academic performance in Indian school-going adolescents. Methods: A school-based cross-sectional study was carried out in various government and private schools of Madurai District, Tamil Nadu, India to identify the prevalence rates of overweight and obesity among urban schoolgoing adolescents studying in fifth to twelfth classes of both genders. A pre-tested questionnaire was used to elicit information on family and individual characteristics. Height and weight were measured and BMI was calculated. Results: Overall prevalence of overweight and obesity was found to be 1.66 % and 5.05% respectively. The mean BMI of both genders showed a significant decrease with age. Amongst genders, girls had higher mean BMI values within each age group. Statistical results reveal that the changes in body mass index were highly related to academic performance in both of the school setups at a 1% level of significance(Private Schools - χ2 = 2.470; Government Schools - χ2 =20.051 p≤ 0.00). Conclusion: Academic performance as an adolescent has significant implications for future adult health and social well-being; therefore, understanding factors that contribute to academic achievement are vital for the future success of these adolescents.
Keywords: Prevalence, Obesity, Adolescent, School going, Academic Performance
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION
The last quarter of the twentieth century has seen childhood obesity emerging as an epidemic in developed countries and a cause of concern worldwide as it is being reported in significant numbers from nations previously considered poor or developing. Still, it is observed that 30% of obesity begins in childhood and out of that 50-80% become obese adults.1 While the prevalence and factors associated with adolescent overweight and obesity in the developed world have been well documented, the same is not true for the developing world.2 India being a country of a diverse population, it has regions still struggling with the burden of malnutrition, but at the same time, there are rapidly emerging population sub-groups that are falling into the trap of affluence related problems.3
The two areas of greatest interest in studies that have attempted to link school performance and health are diet and physical activity. Although the impact of diet and nutrition on school performance in developing countries is difficult to assess and can be confounded by socioeconomic status, school factors and other variables4, there is growing and convincing evidence for a link between diet and academic performance in countries with advanced economies. Research has shown that malnourished children or children who eat unhealthy diets, for example, manifest several behaviours that can interfere with learning and academic performance.5,6 To address these concerns, this study was designed to explore the longitudinal associations of Body Mass Index on academic performance among School going adolescents of Madurai District, Tamil Nadu, India and to the best of our knowledge, no such study has been conducted in this area earlier.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Study Area and Sample Size
Madurai District in Tamil Nadu, India is one of the major cities of Tamil Nadu and 25th most populated city in India.7Madurai has been a known academic centre for Tamil Culture, arts, Literature, music and dance for centuries. Hence, it was selected as a study area based on the author’s research direction on identifying the overweight and obesity prevalence and its association with Academic performance.
A cross-sectional study was carried out from February to April 2018 upon school children of both sexes, aged 13-18 years, from the Madurai District, Tamil Nadu, India. The sample size was statistically determined using power calculations. The sample size was calculated using the formula n = N*X / (X + N – 1), where, X = Zα/22 *p*(1-p) / MOE2. Zα/2 is the critical value of the Normal distribution at α/2 (e.g. for a confidence level of 95%, α is 0.05 and the critical value is 1.96), MOE is the margin of error, p is the sample proportion, and N is the population size. Note that a Finite Population Correction has been applied to the sample size formula.8 With Margin of Error: 1.47%, Confidence Level: 99%, Sample Proportion: 50%, the Sample Size for the above-mentioned population is 7657. For better convenience, the sample size has culminated to 7660.
Informants
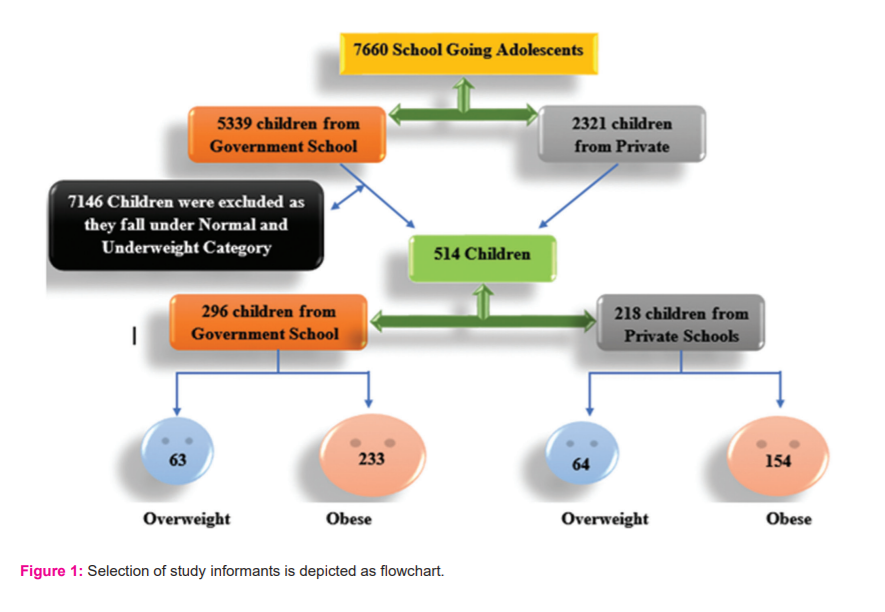
Six Government & Government-aided schools and five private schools have been chosen for the study. In all eleven schools, 7660 subjects were screened for the prevalence of overweight and obesity, which included 5339 school children from Government and Government aided schools, 2321 school children from private schools. 6.71 % (514) of children fall under the overweight and obesity category, whereas the rest of them falls either in the normal or underweight category. Out of 5339, 63 (1.17%) children were overweight and 233 (4.36 %) were obese in Government and Government aided Schools (5.53 %) whereas 64 (2.75 %) were overweight and 154 (6.63 %) were obese out of 2321 children from private schools (9.38 %). These 514 school going children were considered as respondents to elicit further information (Figure 1).
Questionnaire
A pre-tested, Semi-Structured and validated questionnaire was provided in both English and local language-Tamil. The required information was elicited through the direct interview method. Socio-Demographic data were collected in the form of gender, age, educational qualification, monthly household income and occupation of the informant. Socioeconomic status was assessed using the Kuppuswamy scale, a standardized scoring system for the urban Indian population.9The people interviewed were representing both urban and rural lifestyles.
The questionnaire included both the open and closed questions, which inquired about the informant’s individual characteristics like residence, type of school, religion, type of family, family history and dietary habits. Students were asked to self-report their average grades (%) obtained in their previous examination. Children were interviewed about the father’s occupation in the presence of the school teacher. The help of the school teacher was also taken if the child had any problem in explaining the father’s occupation. During data collection, the school authorities were asked to accompany us to the respective classes. An initial pilot study was undertaken with 10 informants; the questionnaire and its components were discussed with the informants to determine whether they found any aspect of the questionnaire difficult. After minor revisions, the final questionnaire was used for the survey.
Measures
Body Mass Index
Since BMI values are sensitive to changes in fat distribution and the development of muscle during puberty, we calculated and used a BMI z-score for each student’s age within the 2- year spread in the age of our study population.10
A child was labelled as underweight when BMI was less than or equal to the fifth percentile; labelled as overweight when BMI exceeded the eighty-fifth percentile and labelled as obese when BMI exceeded the ninety-fifth percentile for that age and sex.
For labelling a child as underweight, normal, overweight or obese, the frequencies of BMI cutoffs relative to the National Centre for Health Statistics (NCHS)/World Health Organization (WHO) reference data (CDC Charts) 11 were used.
Academic Performance
Academic performance was measured as the aggregate percentage of marks scored in subjects such as Language, Mathematics, Science, and Social Studies. All students took the same tests in school and the scores which ranged from 0 to 100 were extracted from the school records at the end of each grade.
Statistical Analysis
The data obtained through the questionnaire were coded, classified and entered into MS Excel sheets for further statistical analysis. Data recorded were analyzed using SPSS version 21.0. Descriptive statistical techniques were used to provide a summary of data in the form of mean, median and standard deviation for almost all the quantitative data. The Association between the Socio-demographic characteristics across the BMI and Academic Performance were performed using cross-tabulation: Chi-square test. Descriptive statistical analysis was used to present the general details and responses.
RESULTS
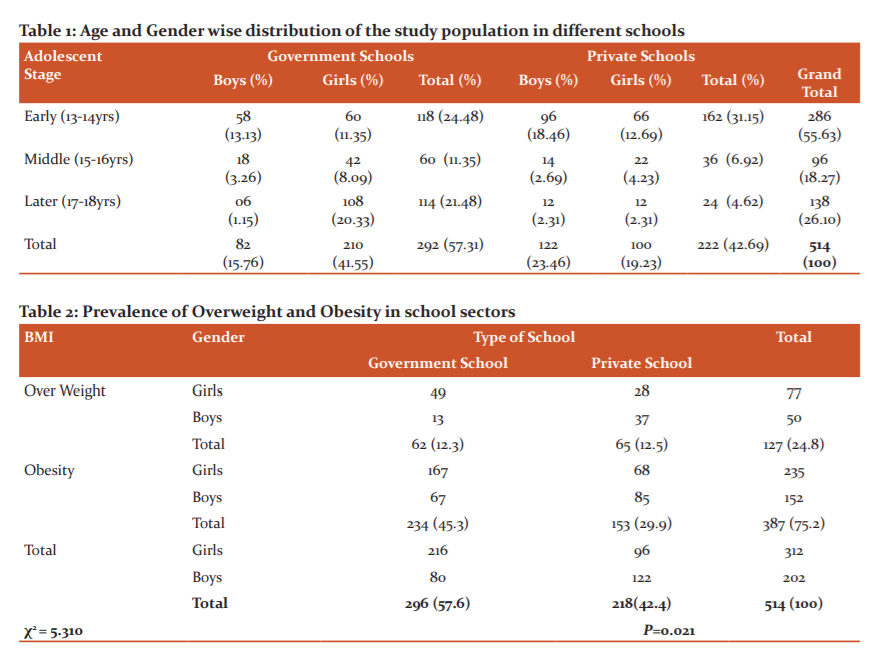
Table 1 represents the sample of 514 students comprising 310 females and 204 males. There were more girls than boys (60.78 vs. 39.22 %) in the total sample. Of the total 310 females, 210 (41.55 % of total students) and 100 (19.23% of total students) were from government and private schools, respectively. Similarly, of a total of 204 males, 82 (15.76 % of total students) and 122 (23.46% of total students) were from government and private schools respectively. In Government Schools, the largest group (24.48%) comprised of 13-14 years old and the smallest (11.35%) of 15-16 years old. Similarly, in private schools, the largest group (31.15%) comprised of 13-14 years old and the smallest (4.62%) of 17-18 years old.
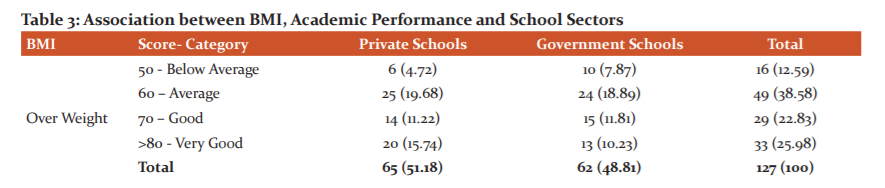
Table 2 shows the prevalence of overweight and obesity among school-going adolescents. In Government Schools, 49 girls were overweight and 167 girls were obese when compared with 28 overweight and 68 obese girls from Private schools. Similarly, In Government Schools, 13 Boys were overweight, 67 boys were obese when compared to 37 overweight and 85 obese boys from Private schools. An association of BMI with both gender and schools (Government and Private) was statistically significant (p<0.00). Girls from Government schools were found to be overweight and obese than girls from Private schools. On the contrary, Boys from Private schools were overweight and obese than boys from Government schools.
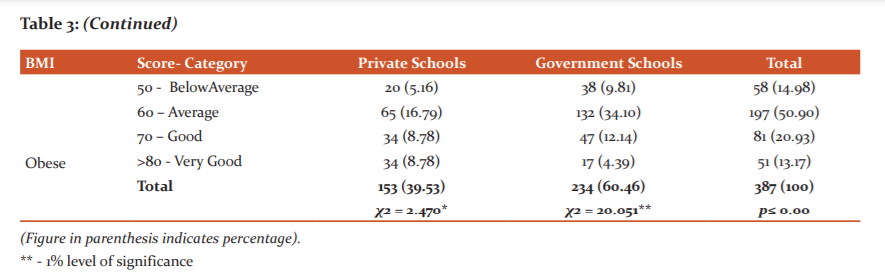
Table 3 shows the frequency distribution of obese and overweight adolescent children from different school sectors and grades of academic performance (‘Very good’; ‘Good’; ‘Average’ and ‘Below average’). In Private Schools, majority of overweight students fall under the Average (19.68) and very good marks (15.74) category, whereas in Government Schools, most of the overweight students were of Average marks (18.89) category and Good marks (11.81) category. With respect to Obese Students, the majority of them performed averagely (16.79 & 34.10) in both Private and Government Schools. Statistical results reveal that the changes in body mass index were highly related to academic performance in both of the school setups at 1% level of significance which is also consistent with previous cross-sectional studies.
DISCUSSION
Obesity among children in India has become a public health problem (prevalence >5%). In the present study, overweight and obesity were found to be 1.66% and 5.05%, respectively, together constituting 6.71% for overweight/obesity. Furthermore, it is higher than that of studies found in various parts of India such as Lucknow city, Delhi, and Wardha.12,13,14This might be because of the inclusion of children from both rural and urban areas studying in government and private schools in contrast to other studies where they have included only rural areas or Government schools.
In the present study, the mean body mass index (BMI) of both genders showed a significant decrease with age. Between genders, females had higher mean BMI values within each age group. The reason for this finding may be attributed to the fact that in children, BMI changes physiologically (substantially) with age and sex. Mahajan et al. reported that the mean BMI of both genders showed a significant increase with age in Shimla city which is in contrast to the results of the present study. This may also be due to the difference in age group and the place of the study. But, the similarity was found in the gender description, as females had higher mean BMI Values than Males.15 Similar findings have also been reported by Misra et al.16 and Kunwar et al.17 Higher prevalence of obesity among adolescent girls may be linked to early attainment of puberty as compared to boys. Post pubertal adolescent girls in the socio-cultural milieu of developing countries like ours have very low levels of physical activity that is mainly restricted to household chores. Their participation in outdoor games and other health-enhancing physical activities are much less as compared to boys.
The present study results revealed a strong association between the Body Mass Index and Academic Performance in both the school sectors. Literature regarding the BMI-academic performance, the relationship remains equivocal. BMI or obesity is negatively associated with academic performance among schoolchildren in some studies.2,19Others (adjusted with other forms of fitness) have indicated no significant association.18,20 Some studies have demonstrated that cognitive ability is influenced by obesity and the likelihood of being obese is influenced by the quality of nutrition.21 Obesity has also proven to lead to mental and emotional problems, such as anxiety and depression.22 There is some potential explanation for reveres association between student grades average and BMI: firstly, as proven in previous studies, there is a significant correlation between high BMI and depression that could strongly affect student performance.23,24 Noting that, a study in North Korea on 405 students confirmed that, psychological problems in overweight and obese student are the major cause of poor school performance rather than their body image.25 Besides, obese students are mostly less physically activated which lead them to experience lower school performance compared with normal BMI students.26-29 Numerous studies have been performed across the United States on whether or not physical fitness levels have a significant positive correlation with academic achievement.30-33
Conclusion
Obesity continues to be the most important preventable risk factor for lifestyle diseases. The prevalence of overweight and obesity among school-going adolescents has increased when compared with the previous studies. To mitigate the risk of overweight and obesity, adequate physical activity and Healthy dietary practices should be promoted not only among school-going children but also teachers and parents who motivate and help to implement behavioural changes among adolescents. It is highly recommended to allocate regular class hours on healthy food habits and lifestyle which will, in turn, help them to understand health-related problems and diseases. Parents should be educated on overweight and obesity problems not only for their children but also for themselves. Children should also be encouraged to play outdoor games and sports irrespective of their gender to maintain a healthy lifestyle.
Acknowledgements: The authors gratefully acknowledge the generosity of those who responded to the questionnaire for this study.
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Author Contribution: We declare that all of the authors mentioned in the article have contributed equal efforts in this research and also for the submission of the article.
Funding support: The authors declare that they have no funding support for this study.
References:
-
Obesity: preventing and managing the global epidemic. Report of a WHO consultation. (WHO Technical Report Series, No.894). Geneva, World Health Organization 2000.
-
Manyanga T, El-Sayed H, Doku DT . The prevalence of underweight, overweight, obesity and associated risk factors among school-going adolescents in seven African countries. BMC Public Health 2014;4:887.
-
Chhatwal J, Verma M, Riar SK. Obesity among pre?adolescent and adolescents of a developing country (India). Asia Pac J Clin Nutr 2004;13:231?235.
-
Glewwe P. The impact of child health and nutrition on education in developing countries: theory, econometric issues, and recent empirical evidence. Food Nutr Bull 2005; 26(Suppl. 2): S235–250.
-
American School Food Service Association. Impact of hunger and malnutrition on student achievement. Sch Food Serv Res Rev 1989; 13: 17–21.
-
Parker L. The relationship between nutrition & learning. In: A School Employee’s Guide to Information and Action. Washington, DC: National Education Association of the United States, 1989.
-
Surendran U, Kumar V, Ramasubramoniam S, Raja P. Development of Drought Indices for Semi-Arid Region Using Drought Indices Calculator (DrinC) – A Case Study from Madurai District, a Semi-Arid Region in India. Water Resou Mgmt 2017;31(11):3593-3605.
-
Daniel WW. Biostatistics: A Foundation for Analysis in the Health Sciences. 7th ed. New York: John Wiley & Sons 1999;141-142.
-
Kuppuswamy, B. Manual of Socio-Economic Status Scale. Manasayan Publications 1962 Delhi.
-
Sigfusdottir ID, Kristjansson AL, Allegrante JP. Health behaviour and academic achievement in Icelandic school children. Health Educ Res 2007;22(1):70-80.
-
Mohan B, Kumar N, Aslam N, Rangbulla A, Kumbkarni S, Sood NK, et al. Prevalence of sustained hypertension and obesity in urban and rural school-going children in Ludhiana. Indian Heart J 2004;56:310?314.
-
Vohra R, Bhardwaj P, Srivastava JP, Srivastava S, Vohra A. Overweight and obesity among school-going children of Lucknow city. J Fam Community Med 2011;18:59-62.
-
Bharati DR, Deshmukh PR, Garg BS. Correlates of overweight and obesity among school-going children of Wardha city, Central India. Indian J Med Res 2008;127:539-543.
-
Sethi M, Kapoor P. Obesity. New Delhi: Voluntary Health Association of India; 2003.
-
Mahajan A, Negi PC. Prevalence of overweight and obesity in urban school-going adolescents in Shimla city. Int J Nutr Pharmacol Neurol Dis 2014;4:23-28.
-
Misra A, Shah P, Goel K, Hazra DK, Gupta R, Seth P, et al. The high burden of obesity and abdominal obesity in urban Indian school children: A multicentric study of 38,296 children. Ann Nutr Metab 2011;58:203?211.
-
Kunwar R, Minhas S, Mangla V. Is obesity a problem among school children? Indian J Public Health 2018; 62:153-155.
-
Eveland-Sayers BM, Farley RS, Fuller DK, Morgan DW, CaputoJL. Physical fitness and academic achievement in elementary school children. J Phys Act Health. 2009; 6(1):99-104.
-
Sabia JJ. The effect of body weight on adolescent academic performance. South Econ J. 2007;73(4):871-900.
-
Van Dusen DP, Kelder SH, Kohl HW, Ranjit N, Perry CL. Associations of physical fitness and academic performance among schoolchildren. J Sch Health 2011; 81(12):733-740.
-
Alswat KA, Al-shehri AD, Aljuaid TA, Alzaidi BA, Alasmari HD. The association between body mass index and academic performance. Saudi Med J 2017; 38(2):186-191.
-
Pine DS, Goldstein RB, Wolk S, Weissman MM. The association between childhood depression and adulthood body mass index. Paediatrics 2001;107(5):1049–1056.
-
Wehigaldeniya WGDS, Oshani PAL, Kumara IMNS. Height, Weight, Body Mass Index (BMI) and Academic Performance (AP) of University Students in Sri Lanka: With Special Reference to the University of Kelaniya. Int J Sci Res 2017; 7(2):217-219.
-
Sjöberg RL, Nilsson KW, Leppert J. Obesity, shame, and depression in school-aged children: a population-based study. Paediatrics 2005;116(3):389–392.
-
Kim B, Park MJ. The influence of weight and height status on psychological problems of elementary school children through child behaviour checklist analysis. Yonsei Med J 2009; 50(3):340–344.
-
Hernandez B, Gortmaker S, Colditz G, Peterson K, Laird N, Parra-Cabrera S. Association of obesity with physical activity, television programs and other forms of video viewing among children in Mexico City. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 1999;23(8):845.
-
Freedman DS, Wang J, Maynard LM, Thornton JC, Mei Z, Pierson R, et al. Relation of BMI to fat and fat-free mass among children and adolescents. Int J Obes (Lond). 2004; 29(1):1–8.
-
Tremblay MS, Inman JW, Willms JD. The relationship between physical activity, self-esteem, and academic achievement in 12-year-old children. Pediatr Exerc Sci. 2000; 12(3):312–323.
-
Coe DP, Pivarnik JM, Womack CJ, Reeves MJ, Malina RM. Effect of physical education and activity levels on academic achievement in children. Med Sci Sports Exerc 2006; 38(8):1515.
-
Fox CK, Barr-Anderson D, Neumark-Sztainer D, Wall M. Physical activity and sports team participation: Associations with academic outcomes in middle school and high school students. J School Health 2010;80(1):31-37.
-
Wittberg RA, Northrup KL, Cottrell LA. Children's aerobic fitness and academic achievement: A longitudinal examination of students during their fifth and seventh-grade years. Am J Public Health 2012;102(12):2303-2307.
-
Grissom JB. Physical fitness and academic achievement. J Exercise Physiol 2005;8(1):11-25.
-
Todd FA, Shults J, Stettler N. Perception of Overweight Is Associated With Poor Academic Performance in US Adolescents. J School Health 2011;81(11):663-670.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License