IJCRR - 13(8), April, 2021
Pages: 132-136
Date of Publication: 30-Apr-2021
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
Histopathological Evaluation of Appendicectomy Specimens in a Teaching Institute-A Cross-Sectional Study
Author: Supreet Singh Sodhi, Samriddhi Juneja, Basanagouda K Patil, Sunita B Patil, Zuha Kadir Sange, Z N Patvegar, Nikethan B
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Introduction: Appendicitis is the most common pathological condition of the appendix. Appendectomy is a surgical procedure to remove the appendix constituting 40% of all abdominal surgeries performed in the world. Objective: The present study was conducted to analyze the histopathological profile of surgically resected appendix and create a clinical profile that may help in better diagnosis and management of appendicitis. Methods: Histopathological records of 616 resected specimens of the appendix were reviewed retrospectively to correlate clini�cal profile, histopathologic findings and unusual findings. Results: The study included 616 specimens of appendix out of which 371(60.22%) specimens were of males and 245(39.77%) specimens were of females. The most commonly affected age group was of 21 to 30 years with 285(45.96%) samples. On histopathological examination, 95 (15.3%) samples were of acute appendicitis. 314 (50.6%) samples were of chronic appen�dicitis, 155 samples (25%) had an acute on chronic impression and 52 (8.3%) samples had the acute suppurative impression. 1.1% of the samples showed perforation with slight female preponderance. 1 specimen of carcinoid tumour, 2 specimens with granulomatous lesions,1 specimen with parasitic infestation and 1 specimen of gangrenous appendicitis was found. All cases presented with pain in the abdomen clinically. Conclusion: Our study concludes that whenever young patients present with a symptom of non-specific abdominal pain, ap�pendicitis should be considered as a possibility. Histopathological analysis confirms the diagnosis of appendicitis and identifies the need for further follow-up.
Keywords: Appendicitis, Histopathology, Appendicectomy, Carcinoid tumour, Suppurative appendicitis, Enterobius vermicularis
Full Text:
Introduction
The appendix is considered to be a vestigial, small, tube-like organ placed under the ileocaecal junction. Appendicitis is the inflammation of the appendix. Its importance in surgery is due only to its propensity for inflammation which results in appendicitis. The most common mechanism is obstruction of the lumen from various etiological factors that leads to increased intraluminal pressure. Common causes of obstructive nature are: faecolith, calculi, foreign body, tumour, worms, diffuse lymphoid hyperplasia and non-obstructive causes include vascular occlusion and inappropriate diet. The lifetime risk of appendicitis in the human population is approximately 7%.1 In developing countries, the incidence of appendicitis is increasing probably due to the adoption of western diets, which include, low-fibre content, pre-processed meat and high fructose sugar.2 Even with the availability of superior technology and imaging devices, there is difficulty in the identification of appendicitis.3Histopathological examination is of vital importance for the pathological diagnosis of inflammation of the appendix. Unusual findings such as incidental tumours, granulomatous lesions or helminths noted in the appendix highlight the importance of the pathological analysis of every single resected specimen of the appendix. The present study was conducted to assess the histopathological findings and correlate with the clinical profile which may help in better diagnosis and management of appendicitis.
Materials and Methods
This cross-sectional study was conducted on 616 surgically resected specimens of appendix clinically diagnosed as appendicitis at the Department of Pathology, D. Y. Patil Medical College, Kolhapur, Maharashtra, between 2015 and 2019. The clinical profile like age, sex, clinical symptoms of the patients were recorded from the requisition forms and clinical case files which were revived from the departmental records section. All the appendix specimens and their respective blocks and slides were retrieved from departmental archives to be included in the study. Detailed microscopic evaluation was performed after recovering the slides. Statistical Analysis was done using MS excel.
Results
A total of 616 appendectomy specimens were received which included all specimens having undergone appendectomy as elective or emergency procedures. Out of the 616 specimens received 371(60.22%) were males and 245(39.77%) were females. The male: female ratio was 1.5:1. 47.1% of the male samples and 55.8% of the female samples were of chronic appendicitis. Appendicitis cases were seen ranging from 7 years to 68 years of age with a mean age of 31 years in females. Appendicitis cases were seen ranging from 8 years to 88 years of age with a mean age of 29 years in males. Clinically, all the cases presented with pain in the abdomen or localized pain in right lower abdomen.
Out of the total number of specimens, 285(45.96%) samples belonged to the age group 21-30 years. The majority of acute appendicitis (44.2%) and a majority of chronic appendicitis (49%) were also seen in the age group 21-30 years. About84% of the cases belonged to the age group of fewer than 40 years (Table 1).
The average length of the specimens was 5.70cm ranging from 1cm to 10cm. The length of the appendix of acute appendicitis ranged from 5cm to 10cm. The average length of the specimen of acute appendicitis was 5.9cm. The length of the appendix of acute on chronic appendicitis ranged from 2cm to 9cm. The average length of the specimen of acute on chronic appendicitis was 5.83cm. The length of the appendix of chronic appendicitis ranged from 1 cm to 10 cm. The average length of the specimen of chronic appendicitis was 5.63cm. The length of the appendix of acute suppurative appendicitis ranged from 5cm to 10cm. The average length of the specimen of acute suppurative appendicitis was 5.7 cm. About 95 (15.3%) samples were of acute appendicitis. 314 (50.6%) samples were of chronic appendicitis, 155 samples (25%) had an acute on chronic appendicitis and 52 (8.3%) samples had acute suppurative appendicitis. The perforation rate was 1.1% out of all the samples received. Perforation was more common in females as compared to males. Among chronic appendicitis, two specimens were of the granulomatous lesion and one was of Enterobius infestation. Among acute appendicitis, 1 specimen was of acute gangrenous appendicitis.
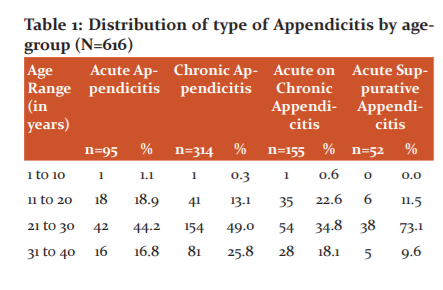
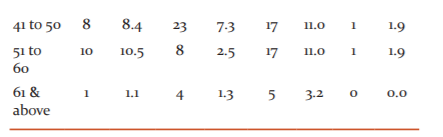
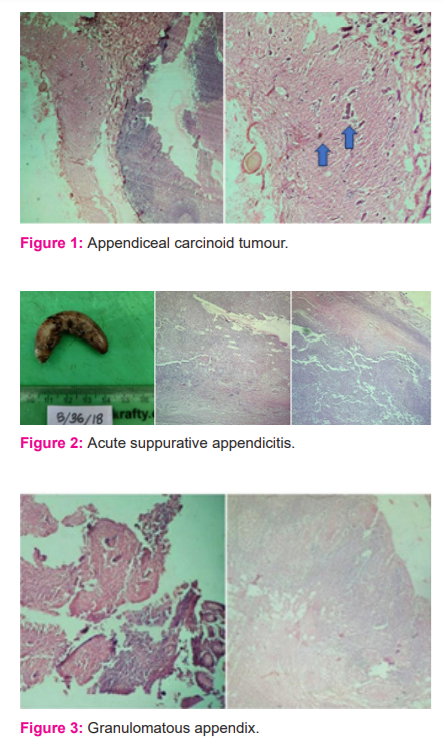
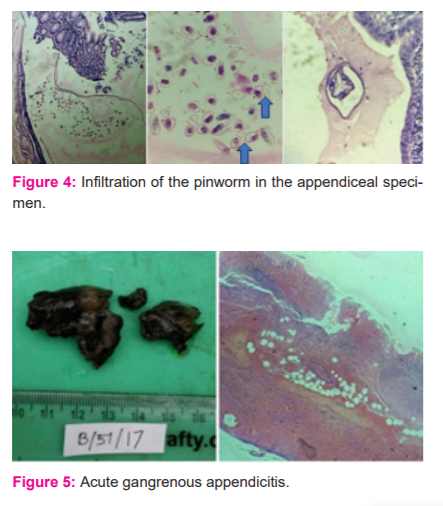
One specimen (0.1%) of the total specimens was that of a carcinoid appendix in a 40-year-old female patient diagnosed after appendectomy. The mesoappendix was 5cm long, with 0.9 cm growth located on the appendiceal tip, cut section grossly was yellow. Histopathological examination of the specimen (Figure1) revealed ulcerated mucosa, enlarged lymphoid follicles in sub-mucosa, small mononuclear cells arranged in the acinar and insular pattern seen in sub-mucosa and muscular layer, indicating carcinoid tumour. Figure 1 shows a Microscopic cross-section of appendiceal carcinoid tumour with the characteristic nested pattern. The gross specimen of acute suppurative appendicitis (figure 2) showed a tense wall and the microscopic section shows inflammatory fluid accumulation. Figure 3 shows the microscopic cross-section of the granulomatous appendix. Two cases of granulomatous lesions in the resected specimen of the appendix were observed. The section studied from the appendix showed mucosal ulceration, caseation necrosis and numerous transmural epithelioid granulomas composed of epithelioid cells, multinucleated giant cells and lymphocytes. Mononuclear infiltration is also seen in muscular and serosa. Features are suggestive of granulomatous appendicitis probably of tuberculous aetiology. On Ziehl-Neelsen staining the section was negative for acid-fast bacilli. No follow-up record was available of serological tests. A solitary case of chronic appendicitis was also confirmed with the parasitic infestation of Enterobius vermicularis. A plano-convex, D-shaped egg can be seen (Figure 4). Gangrenous appendectomy specimen with irregular and the congested external surface was received with obliterated lumen and haemorrhage. The microscopic section shows transmural necrosis along with acute inflammatory infiltrates. Figure 5 shows acute gangrenous appendicitis gross and microscopic section. None of the cases showed foreign bodies or secondaries in the appendix. Gangrenous appendectomy specimen with irregular and congested external surface was received with obliterated lumen and haemorrhage. Microscopic section shows transmural necrosis along with acute inflammatory infiltrates.
Discussion
Appendectomy is the most frequently performed abdominal surgery in the western world. More than one-third of all emergency abdominal surgeries are accounted for as appendectomies.4 Its increasing rate in the developing countries can be associated with the adoption of western diet patterns of pre-processed foods, low fibre contents, high fructose sugar snacks and increased consumption of oils. A study in South Korea done by Lee et al. showed an overall incidence of appendectomy of 13.56 per 10,000 population per year, which was found to be greater than those observed in developed western countries.5 Our study showed 84% of the cases occurred in individuals less than 40 years of age in correspondence with other studies.5,6 In concordance with both developed and developing countries most affected age group was 21 to 30 years of age.5 Male to female ratio in our study is 1.5:1 which are comparable to studies of United Kingdom7 and Kemran-Iran.8 The un-equal male to female ratio may be due to the unequal access in rural healthcare setups and socio-cultural stigmas of trivialization of symptoms felt by the female population, or it may be due to females being misdiagnosed with obstetric and gynaecological abdominal pain. There is the observation of a 1.1% perforation rate with slight female preponderance. It is significantly lower from older studies9 indicating the advancement in both imaging and treatment modalities. Whereas recent contemporary studies of Saudi Arabia10 indicate similar perforation rates. The low perforation rate might be due to appropriate and early clinical diagnosis by a physician and the prompt decision to surgically resect the appendix by the surgeons indicating a better overall prognosis.10 Perforation is more common in children due to lack of self-awareness and elderly individuals with immuno-compromised comorbid conditions.
Our study indicated a higher frequency of chronic appendicitis cases (50.6%) followed by acute appendicitis (15.3%). While no cause has been established for the higher number of chronic cases, it can be associated with decreased self-awareness and education in the sample population towards non-specific abdominal pain. It can also be associated with the changing dietary habits and socioeconomic status of the population. Carcinoid tumours arise from the neuroendocrine enterochromaffin cells of the diffuse neuroendocrine system throughout the gastrointestinal tract.11 Appendiceal carcinoid tumours are rare neuroendocrine neoplasms that usually appear as benign growth, while some tumours may be able to metastasize.12In our study we found a single specimen (0.1%) of benign carcinoid appendix consistent with findings of other studies.13
Appendectomy is typically a satisfactory treatment for carcinoid tumours less than 1cm in size, and right hemicolectomy is adopted when size is more than 2 cm. Treatment of carcinoid tumours measuring 1–2 cm and/or accompanied by mesoappendiceal invasion remains controversial, with a more radical approach used in younger patients.13Granulomatous lesion in the appendix is an uncommon pathology of varied aetiology including tuberculosis, inflammatory bowel disease, sarcoidosis, parasites and fungi.14 Two specimens (0.32%) amongst the total samples showed a granuloma formation, the incidence of which is comparable to other studies.15 Variation in aetiology may differ due to differential geographical distribution. The granulomatous lesion is found to be more common in young males. The parasitic infestation was found only in one of the cases. In earlier times it was considered to be one of the most important causes of luminal obstruction but its incidence has reduced significantly indicating better sanitation of the population as well as easy availability of anti-helminthic drugs. Specimen of a 62-year-old male patient diagnosed with acute gangrenous appendicitis was received in bits of sizes ranging from 3 cm to 0.75cm with overall black discolouration. It showed features of transmural necrosis and haemorrhage microscopically. The aetiology can be traced back to untreated luminal blockage, rupture and atherosclerosis in elderly patients. It can be safely resected and followed by prophylactic use of third-generation cephalosporin antibiotic coverage.
Imaging can minimize delay in surgical treatment and also reduce the risk of appendiceal perforation.16 Imaging techniques have been used to study the association between the gross length of the specimen and its propensity for perforation. In our study, we equate the length and the histological diagnosis. The average length of the specimens was 5.70 cm ranging from 1cm to 10cm. Establishing a correlation between an enlarged appendix with appendicitis will not aid in an accurate diagnosis and may jeopardize optimal care of patients presenting with non-specific acute abdominal pain.17 C reactive protein is a contributory marker in acute appendicitis but comes with the drawback of being nonspecific.18
Conclusion
It is inadvisable to use length as a diagnostic aid for the prospective treatment of appendicitis. Histopathological examination of a resected appendix specimen confirms the type of appendicitis as well as identifies aetiology, while also revealing any other incidental pathology that may include a carcinoid tumour, granulomatous lesion or parasitic infestation which may require specific medications, surgical interventions or follow-ups.
Acknowledgement: "Authors acknowledge the immense help received from the scholars whose articles are cited and included in references of this manuscript. The authors are also grateful to authors/editors/publishers of all those articles, journals and books from where the literature for this article has been reviewed and discussed."
Conflict of interest: NIL.
Source of funding: NIL.
Authors contributions: Supreet Singh Sodhi: Data collection and preparing the draft.
Samriddhi Juneja: Data collection and preparing the draft.
Basanagouda K Patil: Data analysis and preparation of tables.
Sunita B Patil*: Conceived the presented idea, writing of the manuscript and interpretation.
Zuha Kadir Sange: Data collection.
Z N Patvegar: Conceived the presented idea and critical revision of the draft.
Nikethan B: Critical review of the draft
References:
1. Kumar V, Abbas A, Aster J, Turner JR. The Gastrointestinal tract, In Kumar, Abbas, Fausto (eds). Robbins and Cotran Pathologic basis of disease. 8th Edn. Saunders: Philadelphia; 2010;870-871.
2. Walker ARP, Segal I. Appendicitis: an African perspective. J Res Soc Med 1995; 88:616-619.
3. Shreshta R, SR Ranabhat SR, Tiwari M. Histopathological Analysis of Appendectomy specimens. J Pathol Nepal 2012;215-216.
4. Edino ST, Mohammed AZ, Ochicha O and Anumah M; Appendicitis in Kano, Nigeria: a 5-year review of the pattern, morbidity and mortality. Ann Afr Med 2004; 3:38-41.
5. Lee JH, Park YS, and Choi JS; The Epidemiology of Appendicitis and Appendectomy in South Korea: National Registry Data. J Epidemiol 2010;97.
6. Noudeh YJ, Sadigh N, Ahmadnia AY. Epidemiologic features, seasonal variations and false positive rate of acute appendicitis in Shahr-e-Rey, Tehran. Int J Surg 2017;97.
7. Omiyale AO, Adjepong S. Histopathological correlations of appendectomies: a clinical audit of a single centre. Ann Transl Med 2015.
8. Nabipour F. Histopathological Feature of Acute Appendicitis in Kerman-Iran from 1997 to 2003. Am J Environ Sci 2005;1(2):131.
9. Rao PM, Rhea JT, Rattner DW, Venus LG, and Novelline RA. Introduction of appendiceal CT: impact on negative appendectomy and appendiceal perforation rates. Ann Surg 1999;344.
10. Jat MA, Al-Swailmi FK, Mehmood Y, Alrowaili M, Alanazi S. Histopathological examination of appendicectomy specimens at a district hospital of Saudi Arabia. Pak J Med Sci. 2015;893.
11. Pinchot SN, Holen K, Sippel RS, and Chen H; Carcinoid Tumours. Oncologist 2008 Dec;13(12):1255-69.
12. Parks SK, Muir KR, Al Sheyyab M, Cameron AH, Pincott JR, Raafat FR, et al. Carcinoid tumours of the appendix in children 1957–1986: Incidence, treatment and outcome. BJS Society 1993.502-504.
13. Goldblum JR. Rosai and Ackerman's Surgical Pathology. 2012;Vol2;11thEd. Cambridge, MA. Elsevier.
14. Tucker ON, Healy V, Jeffers M, Keane FBV. Granulomatous appendicitis. Surgeon 2003;1(5):286-9.
15. Gaffar BA.Granulomatous diseases and granulomas of the appendix. Int J Surg 2010 Feb;18(1):14-20.
16. Wise SW, Labuski MR, Kasales CJ, Blebea JS, Meilstrup JW, Holley GP, et al. Comparative assessment of CT and sonographic techniques for appendiceal imaging. Am J Roentgenol 2001 Apr;176(4):933-41.
17. Gwynn LK. Appendiceal enlargement as a criterion for clinical diagnosis of acute appendicitis: is it reliable and valid? J. Emerg. Med 2002;9.
18. Ramrao LY, Gajbhiye V, Vaidya VP, Akther MJ, Mangesh Padmawar M. Role of C Reactive Protein in Acute Appendicitis: A Cross-Sectional Study. Int J Cur Res Rev 2020;12 (20):66-69.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License