IJCRR - 13(8), April, 2021
Pages: 115-119
Date of Publication: 25-Apr-2021
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
Co-relation between Hip Axis Length and Femoral Neck-Shaft Angle with Body Mass Index of Indian Population: A Radiological Study
Author: Lopamudra Nayak, Pratima Baisakh, Sitansu Kumar Panda, Prafulla Kumar Chinara
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Introduction: Proximal femoral geometry plays an important role in the prediction of hip fractures as it provides mechanical strength to the femur. Objective: To find out the relationship between body mass index (BMI) and femoral morphometry in the study population. Methods: This is an observational cross-sectional study in 168 patients where parameters such as hip axis length(HAL) and femoral neck-shaft angle(FNSA) were measured by using a dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry scan. BMI was calculated by taking the weight and height of the patients. The relationship of proximal femoral morphometry with different groups of BMI (Normal, Pre-obese and Obese group)has been studied by using the Karl Pearson correlation coefficient (r). Results: The mean age, height, weight, HAL, FNSA, and BMI of the study population were found to be 58.72 years, 160.15 cm, 64.38 kg, 104.14 mm, 128.51\?, and 26.89 kg/mt2 respectively. In the normal group, the BMI has a low level of positive correlation with HAL (r=0.484) and a moderate level of correlation with FNSA (r=0.413). In the pre-obese group, the BMI has a low level of positive correlation with HAL and FNSA (r=0.404 & 0.473 respectively). In the obese group, BMI has a moderate level of positive correlation with HAL and FNSA (r=0.501 & 0.507 respectively). Conclusion: The present study established a positive correlation between proximal femoral morphometry and BMI.
Keywords: Proximal femur morphometry, Hip axis length, Femoral neck-shaft angle, Body mass index
Full Text:
Introduction
Fractures particularly hip fractures are major health problem in terms of disability, death, and medical cost. This morphology of the proximal femur is one of the important risk factors regardless of bone mass and bone strength.1 Since middle of the 19th century the morphology of the proximal femur, specifically the relationship between its different parts with the proximal shaft is a subject of interest and debate in literatures.2 There are lots of differences in skeletal components among populations and these variations are related to genetic and environmental factors (geography, diet, lifestyle). There are variations in human skeletal measurements that determine the racial characteristics of the populations. The shape of bones and different skeletal measurements, both anatomically and radiologically, can offer a guide to clinicians for the determination of fracture risks. The risk of hip fracture can be predicted by different factors like body mass index (BMI), bone mineral density (BMD), the direction and severity of the fall, muscle strength, femoral morphometry, family history, body habitus and lifestyle factors.
As the femoral head supports the entire weight of the body and is involved in different activities, it shows that morphometry of the proximal femur has a great contribution to femoral neck strength. The biomechanical properties of the proximal femur depend on the length and width of the femoral neck.3 The typical morphology of the proximal femur and the muscle balance around the hip joint are important factors that help in weight-bearing.4 Different morphometric parameters like hip axis length (HAL), femoral neck axis length (FAL), femoral neck-shaft angle (Q angle), femoral neck width (FW), femoral head width (HW) and intertrochanteric width (TW) provide mechanical strength to the proximal femur. These parameters provide resistance of bone to impact and higher values are being found in races with a high incidence of hip fracture.5 Previously many studies have been carried out to find different risk factors of hip fracture and that helps to identify those at risk and accordingly preventive measures are taken.6,7 The present study was carried out to find out the correlation of hip axis length and femoral neck-shaft angle with the bone mass index of the study population.
Materials and Methods
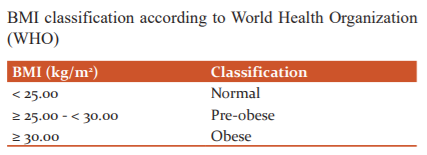
The present study was an observational cross-sectional study carried out on 168 patients irrespective of sex, attending various outpatient department of a tertiary care hospital and coming to the Department of Radiology for radiography. The sample size was calculated by using the formula n = NX/[(n-1)E2+X], taking a 95% confidence interval and 5% standard error. The subjects were selected after written informed consent was obtained from the participants. The samples were collected by the non-probability sampling method using haphazard (convenience) samples. The total study population was divided into three groups by using WHO classification criteria (Table-1). This study design was approved by the institutional ethical committee (IEC letter number:235/09/01/2013). The exclusion criteria for the study population were, patients with metabolic bone diseases, bilateral hip fracture, having a history of fracture due to osteoporosis, malignancy, renal failure, terminal illness, psychiatric illness, and severe dementia Age, sex, height, and weight were measured for all the patients. Morphometric indices of the upper end of the femur such as HAL and FNSA were measured by dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DEXA) scan by using LUNAR XR 1000 scanner. The equipment used for the study were being updated regularly for standardization of reading. The BMI was calculated as per WHO guideline, by using the formula.

Using the above equation, BMI was calculated until the second decimal value.
Radiographic assessment
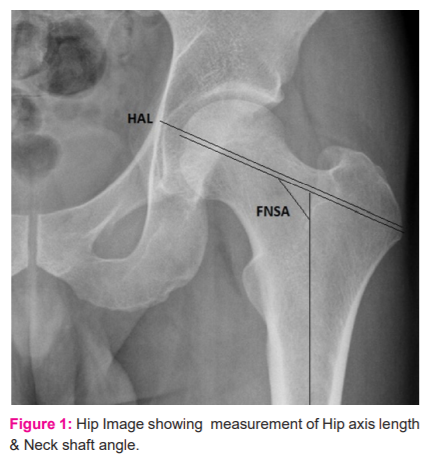
The radiography of the proximal femur was taken in a supine position with 15–30° of internal rotation of hips. With a film focus distance of 100cm, the beams were centred in the symphysis pubis. To measure different morphometric parameters 15 inch×12inch size films were used. A longitudinal line was drawn over the film, and few perpendicular lines 1 cm apart were drawn on that longitudinal line. The film was placed over radiograms to facilitate accuracy and consistency of measurements and points of desired measurements were marked over lines. For uniformity of sample, in all patients skiagrams of the left femur were taken. Following parameters were taken for measurement in all patients (Figure 1).
-
Hip Axis Length in mm (HAL): From the base of the lateral part of the greater trochanter up to the inner pelvic brim.
-
Femoral Neck-Shaft Angle in degree (FNSA): Angle between neck and shaft of the femur.
Statistical analysis
The data collected in the process were analysed through statistical tools and techniques as explained in the methodology using IBM SPSS 24.0 statistics, SPSS South Asia private limited. The correlation of BMI with femoral morphometric parameters has been studied by using Kal Pearson’s correlation coefficient (r). The level of correlation depends upon ‘r’ value which lies between -1 to +1. If r<0.5, the correlation is of low level; if r>0.5 but <0.7, the correlation is of moderate level; if r>0.7 but <0.8, the correlation is of high level; if r> 0.8, the correlation is of very high level.
Results
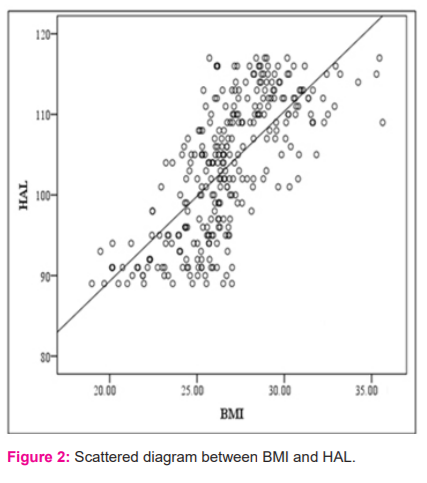
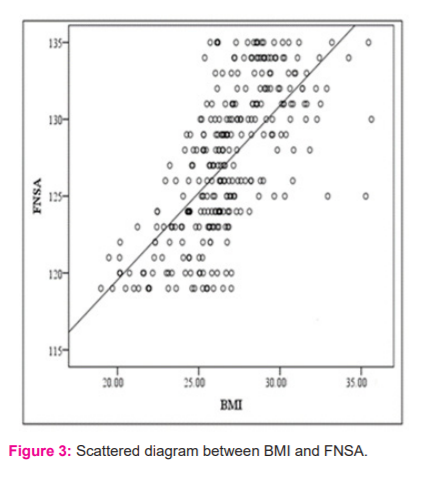
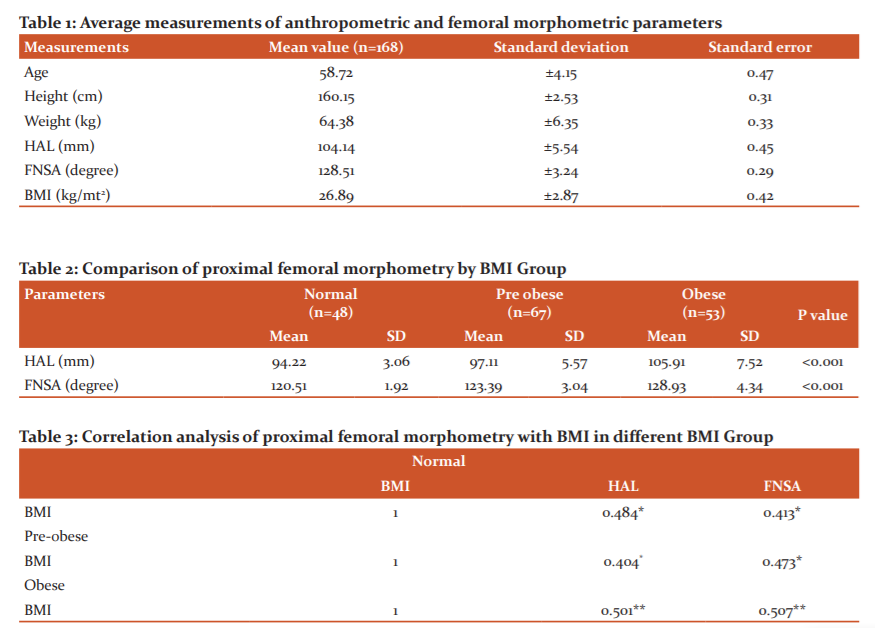
The mean age, height, weight, HAL, FNSA and BMI of the study population were found to be 58.72, 160.15cm, 64.38 kg, 104.14mm, 128.51 degrees and 26.89 kg/m² respectively (Table-1). In the sampled population 39.8% of subjects were in the pre-obese group, 28.5% in the normal BMI group and 31.5% were in the obese group (Table 2). The comparison of proximal femoral morphometry in different BMI group was represented in Table 2. In the obese and pre-obese group, there was a significant increase in mean values of all parameters as compared with the normal BMI group (P<0.001). The relationship of proximal femoral morphometry with different groups of BMI has been studied (Normal, Pre-obese and Obese group). The correlation coefficient (r) values are presented in table- 3. In the normal group, the BMI has a low level of positive correlation with HAL (r=0.484) and a moderate level of correlation with FNSA (r=0.413). In the pre-obese group, the BMI has a low level of positive correlation with HAL and FNSA (r=0.404 & 0.473 respectively) (Table-3). In the obese group, BMI has a moderate level of positive correlation with HAL and FNSA (r=0.501 & 0.507 respectively). The study of the bivariate correlation between proximal femoral morphometry and BMI can be visualized from the scattered diagram presented below (Figures 2 and 3).
Discussion
In fracture of hip, morphometry of proximal femur is an important factor. When a bone is subjected to stress more than its bearable strength it can undergo fracture.1 The strength of a bone is determined by its composition, geometric arrangement and amount of force subjected to it.8,9 Different factors that influence the hip fracture risks are body mass index, bone mineral density, body habitus, muscle strength, femoral geometry, family history of bone diseases and lifestyle factors.10,11 The mean HAL & NSA in the present study was found as 104.11 mm and 128.51 degrees respectively. In comparison to a study by Bhattacharya et al. the findings were 96.9mm and 125.53 degrees, respectively.12 Another study have reported 104.8 mm and 131.52 degrees respectively.13 This variation may be due to difference in race, different body habitus or different level of physical activity. The present study represents the correlation of proximal femoral morphometry with BMI in different BMI groups. In normal, pre-obese and obese group BMI had a low to moderate level of positive correlation with femoral parameters; In other words, as the values of BMI increase, the values of HAL and FNSA will increase accordingly. In this respect, it may be considered as BMI influences the length and angulations of the femoral neck positively. Felson DT et al reported body weight and body mass index increases the fracture risk due to osteoarthritis.14 According to some previous studies, there is a relationship between hip fracture risk and hip axis length, femoral neck axis length, femoral neck-shaft angle.15-17 Longer in hip axis length, wider femoral neck-shaft angle and larger femoral neck width is associated with an increased risk of fracture.15-19 Longer hip axis length may cause a high impact on the greater trochanter and decreases impact absorption after a fall and that may increase the fracture risk.5,20 Femoral neck strength is higher in normal BMI individual than higher BMI individuals. Increased BMI in older males causes smaller cortical area and reduced bone strength in the femoral neck relative to younger males, thus making the femoral neck more susceptible to fracture in obese individuals.21 There is a positive correlation between hip axis length, femoral neck width, neck-shaft angle and head radius with body weight. In females, the neck-shaft angle was positively related to body height and negatively to body weight.22 Another study stated that short individuals have a lower risk of hip fracture compared to tall individuals.23 There is a positive correlation between BMI and femoral neck width. But they don’t report any correlation between BMI and hip axis length, femoral neck axis length and femoral neck-shaft angle.13 A negative correlation and BMI in a higher age group (age>65yrs) is also reported.24,25 As BMI is associated with body weight & BMD, decreased body weight may be associated with decreased bone mass and increases the fracture risk.6,7,9 But in the present study osteoporotic patients were excluded from the study population. The present study coincides with the study by Bhattacharya et al on the Indian population that demonstrates a moderate to the high level of correlation between BMI and femoral neck axis length, hip axis length, head width, femoral neck width, neck-shaft angle in normal and obese BMI individuals. Femoral morphometric measurements related to different races are worth obtaining the validity of risk factors for a fractured hip.
Conclusion
The present cross-sectional study found a significant correlation between BMI and proximal femoral morphometry, hip axis length and femoral neck-shaft angle. Both the parameters should be evaluated together for better prediction of fracture risk in an individual and can help clinicians in choosing the proper size prosthesis during hip arthroplasty.
Acknowledgement: Authors are grateful to all the patients, doctors and persons those who helped, with the collection of the data for the study. The authors also acknowledge the help of the institute for permitting to carry out the study. We are also grateful to the researchers and publishers whose articles are referred to in the present article.
Conflicts of interest: Authors have no conflicts of interest
Source of funding: nil
References:
-
Gregory JS, Testi D, Stewart A, Undrill PE, Reid DM, Aspden RM. A method for assessment of the shape of the proximal femur and its relationship to osteoporotic hip fracture. Osteoporosis Int 2004;15:5-11.
-
Cooper AA, Boston MA, Lilly and Wait. Treatise on Dislocations and Fractures of the joints. Philadelphia : Blanchard and Lea, 1851.
-
Cheng XG, Lowest G, Boonen S, Nicholson PHF, Brys P, Nijs J, et al. Assessment of the strength of proximal femur in vitro: relationship to femoral bone mineral density and femoral geometry. Bone 1997;20:213-218.
-
Canto RS, Silveira MA, Rosa AS, Gomide LC, Baraúna MA. Morphological and radiological features of the proximal femur in fractured people. Ortop Int J 2003;38:12-20.
-
Faulkner KG. Letter to the editor: Hip axis length and osteoporotic fractures. J Bone Miner Res 1995;10: 506-508.
-
Hawker GA, Jamal SA, Ridout R, Chase C. A clinical prediction rule to identify premenopausal women with low bone mass. Osteoporos Int 2002;13:400-40
-
Munaisinghe RL, Rotea V and Edelson GW. Association among age, height, weight, and body mass index with discordant regional bone mineral density. J Clin Densitom 2002;5:369-373.
-
Testi D, Cappello A, Chiari L, Viceconti M, Gnudi S. Comparison of logistic and bayesian classifiers for evaluating the risk of femoral neck fracture in osteoporotic patients. Med Biol Eng 2001;39:633-7.
-
Liu JM, Zhao HY, Ning G, Zhao YJ, Zhang LZ, Sun LH, et al. Relationship between body composition and bone mineral density in healthy young and premenopausal Chinese women. Osteoporos Int 2004;15:238-42.
-
Gluer CC, Cummings SR, Pressman A, Li J, Gluer K, Faulkner KG, et al. Prediction of hip fractures from pelvic radiographs: the study of osteoporotic fractures. J Bone Miner Res 1994;9:671-7.
-
Calis HV, Eryavuz M, Calis M. Comparison of femoral geometry among cases with and without hip fractures. Yonsei Med J 2004; 45: 901-7.
-
Bhattacharya S, Chakraborty P, Mukherjee. A Study of Proximal femoral Morphometry By Radiography and its correlation with Body Mass Index. JASI 2012; 61(2):183-188.
-
Irdesel J, Ari I. The proximal femoral morphometry of Turkish women on radiographs. Eur J Anat 2006;10(1):21-26.
-
Felson DT, Zhang Y, Hannan MT, Anderson JJ. Effects of weight and body mass index on bone mineral density in men and women. Framingham study. J Bone Miner Res 1993;8:567-573.
-
Faulkner KG, Cummings SR, Black D, Palermo L, Gluer CC, Genant HK. Simple measurements of femoral geometry predict hip fracture: the study of osteoporotic fracture. J Bone Miner Res 1993;8:1211-7.
-
Boonen S, Koutri R, Dequeker J, Aerssens J, Lowest G, Nijs J et al. Measurements of femoral geometry in type I and type II osteoporosis: differences in hip axis length consistent with heterogeneity in the pathogenesis of osteoporotic fractures. J Bone Miner Res 1995;12:1908-1912.
-
Alonso CG, Curiel MD, Carranza FH, R. Cano RP, Pérez AD: Femoral Bone Mineral Density, Neck-Shaft Angle and Mean Femoral Neck Width as Predictors of Hip Fracture in Men and Women. Osteoporosis Int 2000:11:714–720.
-
Faulkner KG, Mc Clung M and Cummings SR. Automated evaluation of hip axis length for predicting hip fracture. J Bone Miner Res 1994;9:1065-70.
-
Gnudi S, Ripamonti C, Lisi L, Fini M, Giardino R, Giavaresi G. Proximal femur geometry to detect and distinguish femoral neck fractures from trochanteric fractures in postmenopausal women. Osteoporos Int 2002;13: 69-73.
-
Rosso R, Minisola S. Hip axis length in an Italian osteoporotic population. Br J Radiol 2000;73:969-972.
-
Wheeler RL, Hampton AD, Langley NR. The effects of body mass index and age on cross-sectional properties of the femoral neck. Clin Anat. 2015; 28(8):1048-57.
-
Nissen N, Hauge EM, Abrahamsen B, Jensen JEB, Mosekilde L, Brixen K. Geometry of the Proximal Femur concerning Age and Sex: a Cross-Sectional Study in Healthy Adult Danes. Acta Radiologica 2005;46(5):514-518.
-
Hemenway D, Feskanich D, Coldits GA. Body height and hip fracture: a cohort study of 90000 women. Int J Epidemiol 1995;24:783-786.
-
Folsom AR, Kushi LH, Anderson KE, Mink PJ, Olson JE, Hong CP, et al. Associations of general and abdominal obesity with multiple health outcomes in older women: the Iowa Women's Health Study. Arch Intern Med 2000;160(14):2117-28
-
Young Y, Myers AH, Provenzano G. Factors associated with time to first hip fracture. J Aging Health 2001;13(4):511-526.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License