IJCRR - 13(8), April, 2021
Pages: 110-114
Date of Publication: 25-Apr-2021
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
Salivary Lead Levels in Mixed Unstimulated Saliva of Children and its Correlation with Dental Caries
Author: Aditi Mathur, Anmol Mathur, Vikram Pal Aggarwal
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Introduction: Lead is the major environmental pollutant. There is an association between dental caries with blood lead concen�trations and tooth lead content, however not much has attempted to correlate salivary lead levels with dental caries. Objective: There has been an increase in dental caries among populations across the globe, It a multifactorial disease, one of the factors could be lead content which has been correlated with a high incidence of caries but salivary lead levels have not yet been extensively tested. Hence this study was conducted to test the association of salivary lead and its effect on caries. Methods: 60 children belonging to 3-5 and 12-14 years of age groups, selected who were categorised into low caries group (deft/ DMFT less than 2) and high caries group(deft/DMFT more than 5) and 5 cc of unstimulated saliva were collected. The salivary lead levels were recorded and applied for statistical analysis, Annova test has been applied to test the association using SPSS software. Results: The high dental caries children reported with higher salivary lead concentration this difference is being reported to have a positive difference. The mean lead level is being reported to be 2.9 and 2.8 for students from 3-5 and 12-14 years students respectively. This difference is reported to be a statistically significant difference. Conclusion: Lead poisoning, particularly causing a risk to children when they live in old houses in deprived urban areas can even affect the caries susceptibility of the child. Health care professionals need to be made aware of the risk factors for caries progression beyond the traditional risk factors for caries such as this trace element.
Keywords: Dental Caries, Saliva, Lead, Children
Full Text:
Introduction
The widespread use of an organic lead compound, in the form of a tetra-alkyl derivative, as a gasoline (petrol) additive has resulted in the lead as a major environmental pollutant. Also, its use for many years in house painting has left a legacy of potential lead poisoning, particularly causing a risk to children when they live in old houses in deprived urban areas. In many developed countries efforts are being taken to reduce lead levels in the environment but lead continues to be a significant environmental pollutant in developing nations.1
Epidemiological studies have reported an association between excess of lead in the environment with an increased incidence of caries. Higher lead concentration in dentine than in enamel and the highest lead concentration was in the area of circum-pulpal dentin.2,3 A decline in the lead in caries away from the pulp.3 The equivalent levels of lead content in individual match-paired impacted and erupted third molars4 suggest that Pb enters the tooth from the bloodstream.5,6 However, higher lead content was found in surface enamel than in the enamel–dentine junction, implying that part of the lead accumulation in enamel may be acquired at the post-eruptive period from the oral environment.3,7
Many studies have been carried out to find the association between dental caries with blood lead concentrations and tooth lead content, however not much has attempted to correlate salivary lead levels with dental caries. The salivary glands represent a clearance organ for lead in the bloodstream. It has been suggested that saliva may be a significant route in the accumulation of lead on the enamel.8 More importantly, the lead concentration in saliva (PbSa) is closely related to the unbound plasma fraction and intracellular level and thus reflects the internal lead level that can exert effects on human organs.9,10
Hence there was a felt need to undertake the present study to assess the correlation between the salivary lead level and dental caries in both primary and permanent dentition among children.
Materials and Methods
This was a cross-sectional, in-vivo analytical study done on 60 children belonging to 3-5 and 12-14 years of age groups, selected from the outpatient department of Pedodontics and Preventive Dentistry of Dr R. Ahmed Dental College & Hospital. Approval from the institutional ethics committee was taken prior. Patients with no underlying medical conditions and no history of medications, which can alter the salivary flow rate, were selected for the study. Children belonging to the age group of 3-5 years and 12-14 years were selected to specifically study the effect of salivary lead on both primary and permanent dentition. Intraoral examination was done and the patients were categorised into the low caries group (deft/ DMFT less than 2) and high caries group(deft/DMFT more than 5)
The scheduled date and time of saliva collection was intimated to the subjects as well as to their parents. The subjects were advised to refrain from intake of any food or beverages (except water) one and a half hour before saliva collection on the scheduled day.11 Saliva collection was always scheduled between 9 am to 11 am to standardize saliva collection time and minimize the effect of the circadian rhythm. Within this stipulated time, it was scheduled to collect saliva from an average of six subjects per day.
On the day of saliva collection, the children were asked to perform regular oral hygiene procedure after breakfast (1.5 hours before collection) and during this period children were not allowed to eat or drink. Children were seated on dental chairs and 5 cc of unstimulated saliva was collected in special tubes using the method described previously.12 In this method, the child was asked to pool the saliva in the floor of the oral cavity and asked to spit intermittently. No exogenous stimulation was used and every effort was made to obtain as nearly as possible the resting secretion of a salivary gland. The salivary samples were transported within an hour in a Thermo insulated box. Estimation of salivary lead was done by Atomic Absorption Spectrophotometer (Model: Analyst 200, Perkin Elmer) using the air acetylene flame.
Statistical Analysis
Student t test is being used using the SPSS software version 22 IBM Corp. Released 2013. IBM SPSS Solutions for Windows, Version 22.0. Armonk, NY: IBM Corp. p values is being calculated to test any association between the low and high caries groups among different age groups.
Results
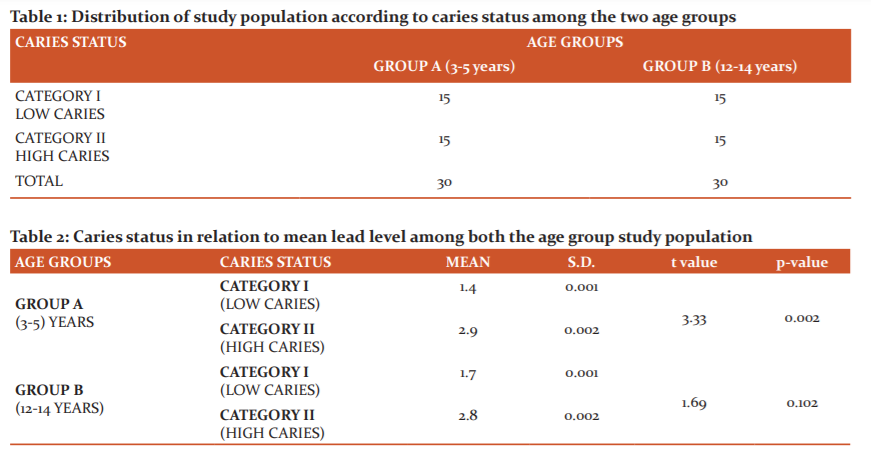
The study sample according to table 1 consisted of 60 children selected randomly from the outpatient department, according to the inclusion criteria. These children selected comprised of two age groups 3-5 years and 12-14 years, which represented the two dentitions, they were further classified into two categories according to their caries status but in equal numbers [n=15] to allow a valid comparison. The two groups were formulated as follows.
1) Group A: Consisted of samples with age group 3-5 years.
Category I): deft score less than 2 and Category II): deft score more than 5.
2) Group B: Consisted of samples with age groups 12 -14 years
Category I): DMFT score less than 2. and Category II): DMFT scores more than 5.
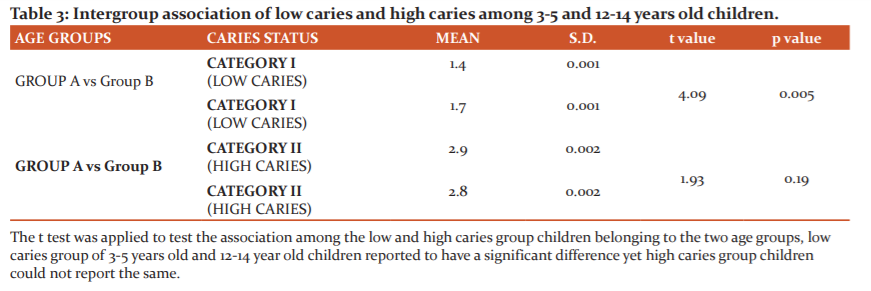
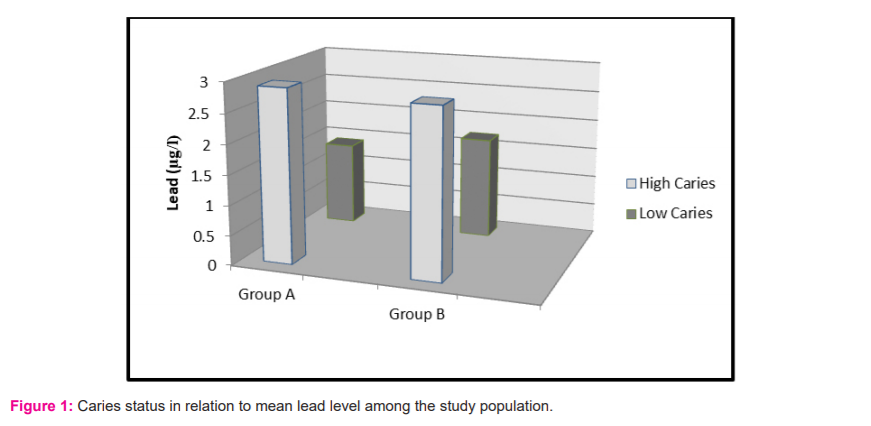
The mean salivary lead concentration in table 2 computed for Group A is 1.4 µg/l for low caries and 2.9 µg/l for high caries category. Among Group B, the values computed are 1.7 µg/l and 2.8 µg/l for the low and high caries category respectively. The values for mean salivary lead concentration are higher in the high caries category of both the age groups, but a statistically significant difference is achieved only in Group A.
Discussion
The role of trace elements as an indirect or contributing factor in the dental caries process has been a subject of interest. The null hypothesis was rejected which stated no effect of salivary lead on dental caries. Lead has shown a direct effect on the mineral phase of calcifying tissues.13 The proposed mechanism for this effect is that lead interferes with the enzymes for extracellular matrix proteinases involved with amelogenesis.14 It has been postulated that lead is first adsorbed to hydroxyapatite crystals and later take positions within the structure.15 Levels of lead as high as 4,000 ppm have been found in the outer layers of enamel.7 In the oral cavity, high levels of lead can damage the acinar cells of the parotid gland, resulting in altered salivary secretion of protein, calcium and lysosomal enzyme N- acetyl-b-D-glucosaminidase (NAG).16 Lead poisoning can impair normal salivary function with xerostomia (dry mouth) being one of the first recognized clinical symptoms of lead poisoning. 17
In the present study, lead could not be detected in six of our samples for those detected salivary lead levels were in the range of 1- 5 µg/l. Lead in the concentration of 2.4 ± 0.13 µg/l in whole saliva samples of the adult population of Detroit, Michigan.8 The mean salivary lead levels in lead-exposed workers and reported the mean value of 7.7µg/l.18 A mean concentration of 1.07 ± 1.31 µg/l in children of age 7-9 years.19 Much higher levels are reported by some authors, 44 µg/l by Brudevold in 1977 7 34 µg/l for parotid samples by DiGregorio et al.20 and 55µg/l for the whole saliva by P’an.21 It has been proposed that earlier studies carried the risk of being compromised by contamination artefacts. 22 A mean salivary lead concentration in the range of 0.0014 mg/l for the low caries group and 0.0029 mg/l for the high caries group was detected among the children of age group 3-5 years. In children of age 12-14 years mean values were 0.0017 mg/l and 0.0028 mg/l for the low and dental caries group respectively.
A significant difference was obtained in salivary lead concentrations in 3-5 year age group children but not among the children of 12-14 years. In both age groups, the mean lead concentration was higher in children with high caries index. Our results are following the study conducted by Nriagu J et al. 8 in the year 2006. They found a weak but significant association with salivary lead as well as blood lead concentrations with dental caries. Caries promoting the effect of lead is also supported by a study from Brudevold.7 They found that a group of children with high enamel lead content had higher caries scores than children with low lead enamel content. Gil et al.23 demonstrated that tooth lead concentration was an independent risk factor for caries. In the Third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES III), Moss et al.24 reported a significant association between blood lead exposure and caries prevalence on both primary and permanent teeth in children aged 5–17 years.
Youravong 25 correlated blood lead levels with DMFS and defs of children aged 6-11 years. In their study defs but not DMFS correlated with blood lead levels. On the contrary, any association between caries and childhood lead exposure in their retrospective cohort study conducted in the year 2000 is not detected.26 Similar results were found in a study where the average values of lead in the low caries group and high caries group were found to be 2.84 mcg/l and 8.0 mcg/l, respectively.27
Conclusion
Oral health caregivers should be made aware of the risk factors for caries progression beyond the traditional risk factors for caries and consider those risks in caries risk assessment. Lead possibly plays a role in the development of caries by modifying host susceptibility and hence there is a wide scope to conduct further research to understand the exact mechanism.
Conflict of interest: No conflict of interest to report.
Source of Funding : Nil
References:
1. Anderson RJ, Davies BE, James PM. Dental caries prevalence in a heavy metal contaminated area of the west of England. Br Dent J 1976;141:311-314.
2. Grobler SR, Rossouw RJ, Kotze TJ, Stander IA. The effect of airborne lead on lead levels of blood, incisors and alveolar bone of rats. Arch Oral Biol 1991; 36:357-360.
3. Purchase NG, Fergusson JE. Lead in teeth: the influence of the tooth type and the sample within a tooth on lead levels. Sci Total Environ 1986; 52:239-250.
4. Bercovitz K, Laufer D. Systemic lead absorption in human tooth roots. Arch Oral Biol 1992;37:385-387.
5. Anderson RJ, Davies BE, Nunn JH, James PM. The dental health of children from five villages in North Somerset concerning environmental cadmium and lead. Br Dent J 1979;147:159-61.
6. Davies BE, Anderson RJ. The epidemiology of dental caries concerning environmental trace elements. Experientia 1987;43:87-92.
7. Brudevold F, Aasenden R, Srinivasan BN, Bakhos Y. Lead in Enamel and Saliva, Dental Caries and the Use of Enamel Biopsies for Measuring Past Exposure to Lead. J Dent Res 1977; 56:1165-1171.
8. Nriagu J, Burt B, Linder A, Ismail A, Sohn W. Lead levels in blood and saliva in a low-income population of Detroit, Michigan. Int J Hyg Environ Health 2006;209:109-121.
9. Mandel ID. The diagnostic uses of saliva. J Oral Pathol Med 1990;19:119-125.
10. Giannobile WV, McDevitt JT, Niedbala RS, Malamud D. Translational and clinical
applications of salivary diagnostics. Adv Dent Res 2011;23(4):375-380.
11. Jorma O. Tenovu O. Human saliva: Clinical chemistry and microbiology. CRC Press; 1989;2(4):23-26.
12. Collins LMC, Dawes C. The Surface Area of the Adult Human Mouth and Thickness of the Salivary Film Covering the Teeth and Oral Mucosa. J Dent Res 1987;66:648-653.
13. Kato Y, Takimoto S, Ogura H. Mechanism of induction of hypercalcemia and hyperphosphatemia by lead acetate in the rat. Calcif Tissue Res 1977;24:41-61.
14. Kim YS, Ha M, Kwon HJ, Kim HY, Choi YH. Association between Low blood lead levels and increased risk of dental caries in children: a cross-sectional study. BMC Oral Health 2017;17(1):42.
15. Bhatnagar VM. The preparation, x-ray and infra-red spectra of lead apatites. Arch Oral Biol 1970;15:469-480.
16. Abdollahi M. Dehpour AR. Fooladgar M. Alterations of rat submandibular gland secretion of proteins, calcium and N-acetyl-b-D-glucosaminidase activity by lead. Gen Pharmacol 2001;29:675–680.
17. Nriagu JO. Lead and Lead Poisoning in Antiquity. 1983 Wiley, New York.
18. Koh D, Ng V, Chua LH, Yang Y, Ong HY, Chia SE. Can salivary lead be used for biological monitoring of lead-exposed individuals? Occup Environ Med 2003;60:696–698.
19. Ogboko B. Cadmium and Lead Concentration in Saliva of Children in Ceres District of South Africa. J Basic Appl Sci Res 2011;1(8):825-831.
20. DiGregorio GJ, Ferko AP, Sample RG, Bobycock E, McMichael R, Chernick WS. Lead and daminodeluvinic acid concentrations in human parotid saliva. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 1974;27:491-493.
21. Pan AYS. Lead levels in saliva and blood. J Toxicol Environ Health 1981;7:273-280.
22. Settle DM, Patterson CC. Lead in albacore: guide to lead pollution in Americans. Science 1980;207:1167-1176.
23. Gill F, Facio A, Villanueva E, Perez ML, Tozo R, Gill A. The association of tooth lead content with dental health factors. Sci Total Environ 1996;192:183-191.
24. Moss ME, Lanphear BP, Auinger P. Association of dental caries and blood lead levels. JAMA 1999;281:2294-2298.
25. Youravonga N, Chongsuvivatwong V, Geater AF, Dahlen G, Teanpaisan R. Lead associated caries development in children living in a lead-contaminated area, Thailand. Sci Total Environ 2006;361:88-96.
26. Campbell JR, Moss ME, Raubertas RF. The association between caries and childhood lead exposure. Environ Health Perspect 2000;108(11):1099-1102.
27. Choudhari S, Parmar G. Salivary Lead Level As A Biomarker For Dental Caries -A Cross-Sectional Clinical Study. Int J Rec Sci Res 2018;9(1):23644-23648.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License