IJCRR - 13(8), April, 2021
Pages: 36-40
Date of Publication: 25-Apr-2021
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
Prevalence of Pulmonary Mycoses Among the Clinically Suspected Cases of Pulmonary Tuberculosis in a Tertiary Care Hospital
Author: Gerard Rakesh J, Margaret Theresa J, Durga Bhavani
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Introduction: Pulmonary mycosis is a fungal infection of the lungs caused by either endemic or opportunistic fungi or a combination of both. They comprise a large group of fungal diseases, the etiologic agents are potential pathogens among the immunocompromised or debilitated patients. Objective: The study aims to identify the occurrence of pulmonary mycoses in clinically suspected cases of pulmonary tuberculosis .by isolating the fungi and identifying the various fungi causing pulmonary mycoses. Methods: Two hundred sputum samples were collected from 100 patients who were clinically suspected to have pulmonary tuberculosis. Acid Fast staining was performed to identify the presence of Acid Fast Bacilli (AFB). Potassium hydroxide (KOH) mount also performed separately to examine the presence of fungal elements. Gram stain was performed to identify the presence of bacteria and fungi elements. All the samples were cultured on Sabouraud's Dextrose Agar (SDA) slants to study the morphology of the fungal colony. A germ tube test was performed to identify Candida albicans. Lacto Phenol Cotton Blue tease mount preparations were made to identify the morphological feature of fungal components in culture. Results: The results were analyzed and various types of pathogens were detected. Out of 100 patients, 29 showed positive reports. Among the 29 cases, eight were positive for AFB, while fungus as a primary etiological agent was detected in 10 patients. Fungus as a secondary etiological agent was detected in 4 patients [AFB with fungus]. Bacteria as the primary cause of pulmonary infection were detected in 7 patients. The isolated fungi as the primary pathogen in clinically suspected cases of pulmonary tuberculosis were Candida species in 6% and Aspergillus species in 4% of patients. Conclusion: Pulmonary mycosis may be a primary infection in non-tuberculosis cases or co-infection in pulmonary tuberculosis. Therefore Pulmonary mycoses can be easily misdiagnosed and mistreated as pulmonary tuberculosis. Investigation for fungal cause in clinically suspected cases of pulmonary tuberculosis will prevent this type of misdiagnosis and management. The present study indicates that fungal aetiology should also be sought in all clinically suspected pulmonary tuberculosis patients.
Keywords: Pulmonary tuberculosis, Fungal infection, Pulmonary mycoses, Candidiasis and Aspergillosis
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION
The common fungal infection of the lung is Pulmonary mycosis which can be caused by either endemic or opportunistic fungi or a combination of both.1,2 Pulmonary mycoses are found to be cosmopolitan in distribution. Fungal organisms are highly pathogenic in immunocompromised or debilitated patients.3 Patients with tuberculosis are usually immunocompromised, hence these patients are at high risk of developing superadded fungal infections.4 Species of Candida and Aspergillus are classical examples of opportunistic pathogenic fungal organism among patients with tuberculosis. Several study reports suggested that Candida albicans be the most common fungal agent.5
Data on worldwide incidence and prevalence of pulmonary mycoses is fragmentary. Fungal infections in the lung often pose a difficult diagnostic challenge due to the lack of any pathognomonic clinical syndromes and characteristic radiological features. Mycobacterium tuberculosis (MTB) is the causative organism of pulmonary tuberculosis, which is aerobic, acid-fast bacillus and can infect one-third of the world's population.6 In recent days the incidence of people getting exposed and becoming sick is stable or gradually decreasing worldwide. Because of low socioeconomic status and overpopulation in our country, an increase in new cases is being documented every year. The incidence and prevalence of fungal infections among pulmonary tuberculosis patients in India and other developing countries hence the data remain unexplored and neglected. Therefore this neglect has to be seen as a major call for concern. A country like India has an enlarging population of patients with Pulmonary tuberculosis either Clinical or subclinical infection. It is essential to carry out the differential diagnosis since the radiological characteristics of pulmonary mycosis are very similar to that of pulmonary tuberculosis thereby making the disease easily misdiagnosed as tuberculosis. Thus, they may suffer from avoidable complications of unwarranted chemotherapy. In the present study we aimed to identify the occurrence of pulmonary mycoses and various fungal the organism causing pulmonary mycoses in clinically suspected cases of pulmonary tuberculosis.
MATERIALS AND METHODS:
Study design: Cross-sectional study
Study area: Sri Venkateshwara Medical College Hospital and Research Centre, Puducherry
Duration of study: January 2018 and September 2019.
Study sample: Two hundred sputum samples were collected from 100 patients who were clinically suspected to have pulmonary tuberculosis.
Inclusion criteria: Patients presented with signs and symptoms of pulmonary tuberculosis
Exclusion criteria: Pediatric age group (who are not able to produce sputum) and patients with extra pulmonary diseases.
Ethical clearance: We have taken institutional ethics committee learance before the commencement of the study.IEC Ref: SVMCH/IEC/2016/4.
Procedure: A total number of 100 patients clinically suspected of pulmonary tuberculosis attending Sri Venkateshwara Medical College Hospital and Research Centre, Puducherry were included in this study.
Specimen collection: Two sputum samples, from the patients (early morning and spot) were collected into sterile wide neck universal containers as per the RNTCP guidelines. A total of 200 samples were collected from 100 patients who were clinically suspected to have pulmonary tuberculosis. None of the participants had been placed on antifungal therapy.
Microscopic Examinations
Acid Fast staining was carried out. A smear was made from each of the sputum samples and was stained by the Ziehl-Neelsen technique as per the Revised National TB control programme (RNTCP) guidelines. The stained slide was examined under oil immersion objective for the presence of Acid Fast Bacilli. The results were recorded and grading was done as per the grading system for AFB.
Potassium hydroxide (KOH) mount: With the use of Pasteur’s pipette, a large drop of 10% KOH was placed on the centre of a clean glass slide. A small portion of the sputum is transferred into the KOH drop with a sterile wire loop and mixed well. The preparation is flattened under a coverslip, placed in a moist chamber and kept at room temperature for 30 minutes. The slide is then examined under low power and high power (10x and 40x objectives) for the presence of fungal elements. The presence of any filament, pseudohyphae or fungal elements were documented.
Gram stain: Smears were made from the most purulent or mucopurulent part of each sputum samples and Gram stain was performed. Stained smears were examined for the presence of any bacteria or fungi. The size, shape and arrangement of fungal elements were documented. In the case of any Gram-positive yeast like-cells, the presence or absence of pseudohyphae were also noted. The Grams reaction on bacteria was also recorded.
Culture on Sabouraud’s Dextrose Agar (SDA): Irrespective of the outcome of the sputum microscopy, all sputum samples were cultured for the characterization of mycotic agents. Sputum samples were streaked on to SDA slants and placed in a BOD incubator. Following incubation, the tubes were examined every day for a week and twice a week from the second week onwards for the growth of fungus.
Cultural identification: After appropriate incubation, the colony morphology, the rate of growth, surface, the texture of the colony and any pigmentation on the surface and reverse of the colony on SDA tubes were observed macroscopically and recorded. The isolates were subjected to Gram stain and lactophenol cotton blue mount (LPCB) tease mounts were studied microscopically. The significant fungal isolates recovered on culture were identified to the species level using standard mycological procedures. For Candida species, a Germ tube test was performed to identify the Candida albicans. Aspergillus species were identified with the various morphological features observed on Lacto Phenol Cotton Blue tease mount, the colony characters and pigment productions on culture. No fungal growth until 6 weeks were reported as negative for fungal growth.
RESULTS
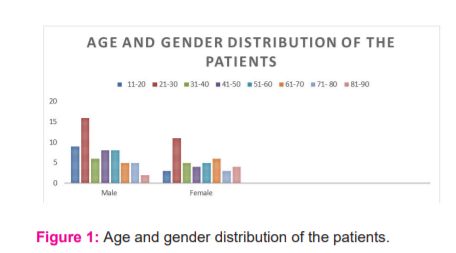
A series of 200 Sputum samples were collected from100 patients who were clinically suspected to have pulmonary tuberculosis. The age and sex-wise distributions showed 59 of them were males and the remaining 41 of them were females. Details of distributions were shown in Figure 1.
On analysis of the results, different types of pathogens were detected. Among the 100 patients, 29 were positive for microbial infections. Eight patients showed positive for AFB alone, while fungus was isolated as the etiological agent in another 10 patients. In yet another group, Fungus was isolated as a secondary etiological agent in 4 wherein both AFB and fungus were detected shown in Figure 2.
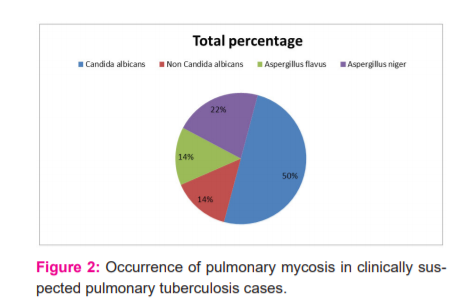
 Bacteria as the primary cause of pulmonary infection were observed in 7 cases. The fungi isolated as the primary pathogen in clinically suspected cases of pulmonary tuberculosis included were Candida species and Aspergillus species. Candida species were isolated in 6 patients, whereas Aspergillus species were isolated in 4 patients. Aspergillus species comprised of Aspergillus flavus in 2 cases and Aspergillus niger in 2 cases. Whereas Candida albicans were isolated in 4 patients and Non-Candida Albicans species were seen in 2 cases. It was found that patients in whom sputum sample with AFB was detected and fungi were recovered in culture as a secondary pathogen, included Candida species. Candida albicans was isolated in 3 cases and Aspergillus niger in1 patient. As shown in Table: 2
Bacteria as the primary cause of pulmonary infection were observed in 7 cases. The fungi isolated as the primary pathogen in clinically suspected cases of pulmonary tuberculosis included were Candida species and Aspergillus species. Candida species were isolated in 6 patients, whereas Aspergillus species were isolated in 4 patients. Aspergillus species comprised of Aspergillus flavus in 2 cases and Aspergillus niger in 2 cases. Whereas Candida albicans were isolated in 4 patients and Non-Candida Albicans species were seen in 2 cases. It was found that patients in whom sputum sample with AFB was detected and fungi were recovered in culture as a secondary pathogen, included Candida species. Candida albicans was isolated in 3 cases and Aspergillus niger in1 patient. As shown in Table: 2
DISCUSSION
Fungal infections of the lungs are important infective processes that are being encountered more and more often in day today’s practice. Data on worldwide incidence and prevalence of Pulmonary mycoses is fragmentary. Aspergillus and Candida's species are more common pathogens causing pulmonary mycoses in clinically suspected cases of pulmonary tuberculosis.7
Shadzi and Chadeganipour in their study reported that among the 43 patients with tuberculosis, the patients were predisposed with 7.3% yeast infections and 0.4% Aspergillosis infection.8Fortunately, we only encounter a few of these pathogenic fungi. With extensive usage of various broad-spectrum antibiotics, chemotherapy agents, immunosuppressive drugs and with increased incidence of several respiratory diseases including chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, lung cancer and tuberculosis, the chances of encountering these diseases are steadily increasing.9
Though treatment is difficult, nevertheless, the results are encouraging. Hence, it is all the more important today to know these diseases well so that we can manage them scientifically. Diseases like opportunistic fungal infections, if diagnosed early can be treated effectively to prevent progression to the fibrotic stage and reduce the number of respiratory cripples. Gemoets et al in his study suggested that a tendency for pulmonary tuberculosis to develop a more devastating course when it was associated with an invasion of fungi which increased the virulence of tuberculosis.10
Out of 100 clinically suspected pulmonary tuberculosis patients, pulmonary mycoses was noted in 14 patients (14%). Pulmonary mycoses were more likely in female patients (9%) when compared to male patients (5%). It was observed that fungal infections were commonly seen in elderly patients aged more than 50 years of age. Further, it was also noted the Primary pulmonary mycosis was significantly higher (10%) in the age group above 50 years when compared to secondary pulmonary mycosis which was only( 4%).
The present study demonstrated that Candida and Aspergillus species constitute the main fungi causing pulmonary mycosis and these findings are consistent with reports of Biswas et al and Khalidi et al.11,12 As per the present study, Candida albicans seems to be the frequent isolate. Among the fungal isolates in clinically suspected pulmonary tuberculosis patients. This finding related to the occurrence following previously published reports by Njunda et al and Jha et al.13,14 Tuberculosis infection manifest with a wide spectrum of clinical conditions resulting from multisystem involvement producing varied clinical features due to opportunistic infections. Mycotic infection is an important co-infection in such patients. Active mycosis is an independent marker of advanced immunosuppressive patients, which can accelerate the clinical course of tuberculosis.
The occurrence of pulmonary tuberculosis in the present study was 12% in the study population, of which the occurrence of pulmonary tuberculosis as primary pathogen seen in 8% of patients and the remaining 4% of patients was as the combination of pulmonary tuberculosis along with pulmonary mycosis. The relationship between fungus and tuberculosis infection has been studied earlier. It was reported that 24% of cases of opportunistic fungal infections were present in tuberculosis patients.15 This was strongly proved by the study of Shome et al.16 and Bansod et al.17 who reported 18% and 40%.
CONCLUSION
Pulmonary mycosis can be a primary infection in non-tuberculosis cases or co-infection in pulmonary tuberculosis cases. It can be caused by either endemic or opportunistic fungi or a combination of both pulmonary mycoses can be easily misdiagnosed and mistreated as pulmonary tuberculosis. Investigation for fungal cause in clinically suspected cases of pulmonary tuberculosis will prevent misdiagnosis and mismanagement of cases. Of late emergence of various types of drug resistance strains among the Mycobacterium tuberculosis (MDR–TB, XDR–TB, XXDR–TB) is documented. Hence the unwarranted chemotherapy in non-tuberculosis cases will curtain the emergence of drug-resistant strains. The present study indicates that fungal aetiology should also be sought in all clinically suspected pulmonary tuberculosis patients.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT: Authors acknowledge greatly the scholars whose articles are cited and included in references of this manuscript and also to authors, editors and publishers of all those articles, journals and books from where the literature for this article has been reviewed and discussed. We are sincerely indebted to all the patients who made this study possible.
Informed Consent: The patient was informed and taken written consent was obtained before the initiation of the study.
Sources of funding: No funding
Conflict of interest: There is no conflict of interest from our side for this study.
AUTHOR’S CONTRIBUTIONS
Dr. J. Gerard Rakesh: Designed the study, protocol writing and manuscript preparation
Dr. J. Margaret Theresa: Manuscript review and guided the research work.
Ms. Durga Bhavani: Sample documentation and protocol writin
References:
1. Meersseman W, Lagrou K, Maertens J, Wijngaerden EV. Invasive aspergillosis in the intensive care unit. Clin Infect Dis 2007;45(2):205-16.
2. Bulpa P, Dive A, Sibille Y. Invasive pulmonary aspergillosis in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Eur Resp J 2007;30(4):782-800.
3. Jasmer RM, Nahid P, Hopewell PC. Latent tuberculosis infection. New Engl J Med 2002;347(23):1860-6.
4. Babita SS, Prabhat K. Prevalence of mycotic flora with pulmonary tuberculosis patient in a tertiary care hospital. Int J Contemp Med Res 2016;3(9):2563-4.
5. Kali A, Charles MP, Noyal MJ, Sivaraman U, Kumar S, Easow JM. Prevalence of Candida co-infection in patients with pulmonary tuberculosis. Aus Med J 2013;6(8):387.
6. Chadeganipour M, Shadzi S, Dehghan P, Bijary J. The incidence of opportunistic fungi in patients suspected of tuberculosis. Mycoses 2000;43(7?8):269-72.
7. Buthia T, Adhikari L. Pulmonary mycoses among the clinically suspected cases of pulmonary tuberculosis. Int J Res Med Sci 2015;3(1):260-268.
8. Shadzi S, Chadeganipour M. Isolation of opportunistic fungi from bronchoalveolar lavage of compromised hosts in Isfahan, Iran. Mycopathologia 1996;133(2):79-83.
9 Latha R, Sasikala R, Muruganandam N, Babu RV. Study on the shifting patterns of Non-Candida Albicans Candida in lower respiratory tract infections and evaluation of the CHROMagar in the identification of the Candida species. J Microbiol Biotechnol Res 2011;1(3):113-119.
10. Greer AE, Gemoets HN. The coexistence of pathogenic fungi in certain chronic pulmonary diseases: with especial reference to pulmonary tuberculosis (a preliminary report). Dis Chest 1943;9(3).
11. Biswas D, Agarwal S, Sindhwani G, Rawat J. Fungal colonization in patients with chronic respiratory diseases from the Himalayan region of India. Ann Clin Microbiol Antimicrob 2010;9(1):28.
12. Buthia T, Adhikari L. Pulmonary mycoses among the clinically suspected cases of pulmonary tuberculosis. Int J Res Med Sci 2015;3(1):260-268.
13. Njunda AL, Ewang AA, Kamga LH, Nsagha DS, Assob JC, Ndah DA, Kwenti TE. Respiratory tract Aspergillosis in the sputum of patients suspected of tuberculosis in Fako division-Cameroon. J Microbiol Res 2012;2(4):68-72.
14. Jha BJ, Dey S, Tamang MD, Joshy ME, Shivananda PG, Brahmadatan KN. Characterization of Candida species isolated from cases of lower respiratory tract infection. Kathm Univ Med J 2006;4(3):290-294.
15. Babita SS, Prabhat K. Prevalence of mycotic flora with pulmonary tuberculosis patient in a tertiary care hospital. Int J Contemp Med Res 2016;3(9):2563-2564.
16. Shome SK, Upreti HB, Singh MM, Pamra SP. Mycosis associated with Pulmonary Tuberculosis. Ind J Tub 1976;23:64-68.
17. Bansod S, Rai M. Emerging of Mycotic infection in patients infected with Mycobacterium tuberculosis. World J Med Sci 2008;3(2):74-80.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License