IJCRR - 13(8), April, 2021
Pages: 30-35
Date of Publication: 25-Apr-2021
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
Stress and Social Isolation- A Study of Behavioural and Attitudinal Changes among College Students During Covid-19
Author: Usha Sadasivan, Bhuvaneswari Balachander, S. Vijayalakshmi
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Introduction: Social beings need to communicate. They need to interact, they need to share. When things are going well eve�rything is smooth sailing. When there is a deviation to this, ripples are seen. Youngsters are a representative lot of this society, who are used to socializing and hanging out with their peer groups, that when they are suddenly faced with a situation of social isolation and inability to mingle with their friends, is highly unpalatable and impossible for them. With the usual stress activators such as academic tests and exams they now have to face the new stress of forced social isolation. Such situational constraints will inevitably cause psychological, physical, and behavioural problems. Objective: The authors have taken for their study the anxiety felt by a group of students who have been forced into a period of social isolation due to situational demands. Methods: The researchers have identified four clusters of parameters to test the mindset of a select group of students. The four clusters contain questions relating to their mindset regarding missing friends, their understanding of loneliness, the psychological impact resulting from this situation, and the coping strategies they employ to tackle the situation. The test-retest methodology is being followed to analyze the data. Result: The analysis of data proved that prolonged periods of peer deprivation will induce the feeling of loneliness among stu�dents. Social isolation will make students suffer unknown fears, affect the sleep patterns of students. Not being able to go out and socialize causes stress among students, however, meditation reduces levels of stress among students. When the young minds are not able to meet up with friends like they used to just a few weeks back, they need to understand their problem is a global problem. The problem has to be tackled not only by individuals but also by governments. Conclusion: We face several challenges which have to be tackled both by the government and by individuals. The authors feel that teachers who have direct contact with the student community are uniquely positioned because of their networking with students almost daily.
Keywords: Stress, College students, Social isolation, Missing friends, Covid-19, Behaviour, Relationships, Stress level, Physiological.
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION
Humans are a part of society. Society is defined as a group of individuals involved in persistent social interaction. Societies are characterized by patterns of relationships between individuals who share a distinctive culture and institutions. Social behaviour has been defined by physiologists and sociologists as the behaviour directed towards society. In a sociological hierarchy social behaviour is followed by social actions which are directed at other people and are designed to induce a response. Further along this ascending scale are social interaction and social relation.2
What differentiates man from animals is this ability to socialize and this societal bonding has become an indispensable part of his life, so much so that it is as important as breathing. So when this is removed, even though temporarily, there is an immediate feeling of loss. Those undergoing this loss begin to experience a sense of an indefinable state of panic or stress. This stress condition indicates that the situational demands exceed the personal and social resources they can mobilize. Of the members of society, a sizable chunk is the youngsters who have got so used to socializing and hanging out with their peer groups that when they are suddenly faced with a situation where even going out of the house is not something they can do now without a lot of restrictions is unpalatable for them. These adolescents are already undergoing physiological stress and experiencing a sense of role confusions. With the usual stress activators such as academic tests and exams they now have to face the new stress of forced social isolation.
Such situational constraints will inevitably cause psychological, physical, and behavioural problems. Taking these environmental and behavioural factors into account an effort has been made to understand the stress and emotional adjustments of today’s youth. The authors have undertaken this study of the anxiety and stress levels of young college students of the city, to study the effect of being socially distant from peer groups. This study it is hoped will throw light on the various factors that lead to emotional non adjustment among the student community at large. The inference of this study may lead to a better understanding of this problem of social adjustment.
Hypothesis
Hypothesis 1: Prolonged periods of peer deprivation will induce the feeling of loneliness among college students.
Hypothesis 2: Social isolation will make students suffer unknown fears.
Hypothesis 3: Social isolation will induce fear of dying among students.
Hypothesis 4: Social isolation will affect the sleep patterns of students.
Hypothesis 5: Not being able to go out and socialize causes stress among students
Hypothesis 6: Meditation reduces levels of stress among students.
Review of literature
What is this fear that is taking over young minds? What is it that is causing this narrowing down of attention span, resulting in the mental block, loss of creative thinking skills, loss of positive thinking, and less involvement in the world around them? Other stress factors that are seen are avoidance of talk with friends, and reveal reduced levels of adaptability. Normal levels of coping with adverse situations take a beating, and they are unable to think clearly that they can control the situation and not let the situation control them. Their mind has become so numbed that they think they are at the mercy of circumstances and a host of negative emotions begins to shake their otherwise stable equilibrium. The thought that they are thinking differently itself is enough to put all sorts of unnatural fears in them. Their natural self makes them act in a pseudo-natural manner but actually, they are disturbed internally. This internal stress causes eating disorders and disturbed sleep patterns.
Study on coping strategies listed restraint coping as one of the coping strategies used when the stressed person uses restraint to tackle the ‘stressor’ or the agent causing the stress.1 The social support that is sought for receiving advice, assistance, or information. This can be called problem-focused coping. Those in distress may also seek social support for emotional reasons such as moral support, sympathy, or understanding. This may also be discussed under the head of emotion-focused coping.3
Coping strategies showed that individual differences, environmental factors (social support and work demand), and situational characteristics acted as predictors of self-report measures of coping that include general coping, direct copying, and suppression.5 Studies have shown that the quality of social relationships improves physical and mental health and increases lifespan. The nine “aspects of association” of Bradford Hill which are the strength of association, consistency, specificity, temporality, biological gradient, plausibility, coherence, experiment, and analogy have been originally used to evaluate hypothesized relationships between occupational and environmental exposures and disease outcomes. This causal inference has been put to use by later researchers into the effect of social isolation on the mental state of people.6
Studies on stress and the college student have been undertaken which have reported a strong relationship between stress and college students.7-9 Stress is a mental or physical phenomenon and is a result of one’s interaction with the environment. The existence of stress depends on the existence of the stressor.10 When stressful events take control of the situation, an individual afflicted by it becomes disorganized, disoriented and as a consequence less able to cope.11 The perception of the individual determines whether or not the stressor causes physical or psychological stress symptoms in the individual.12 Extensive research have been carried out on stress and found out that, stress is associated with how an individual appraises situations and the coping strategies adopted. 13, 14
The current research aims to highlight the mental state of college students deprived of their usual peer groups and its resultant impact on their mindset, their stress levels, and the coping strategies employed by them. The methodology employed is the test-retest approach.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
A survey was conducted among the college students of the city (all girls) in April 2020 employing a self -administered questionnaire via Google forms. The students were administered the same questionnaire in July 2020, after a gap of three months. This survey aimed to check if the students missed their daily interaction with their class peers, did they feel stressed, what were the reasons they felt afraid about and what was their mindset regarding this unexpected social isolation. The study was to understand the emotional state of the students after having been socially distanced from their friends for a prolonged period. The questions were grouped under four clusters and had questions relating to their mindset regarding missing of friends, their understanding of loneliness, the psychological impact resulting from this situation, and the coping strategies they were employing to tackle the situation.
1. Cluster of questions regarding Missing friends
i) Do students feel left out and lonely when they haven’t seen their friends for a while?
ii) Do they miss their friends?
iii) Will they be able to talk with friends like before?
2. Cluster of questions on understanding Loneliness
i) Do students think their feeling of loneliness is a matter of concern?
ii) Does the thought that they may not meet friends for some time frighten them?
3. Cluster of questions regarding Psychological Impact
i) Do you often have unnatural fears like you are going to die?
ii) Do negative thoughts fill your mind?
iii) Do you feel like you’re going crazy?
iv) Do you sleep well?
4. Cluster of questions regarding coping strategies
i) How do they motivate themselves?
ii) Does meditation help in relieving stress?
iii) This also shall pass – is this a sign of positive thinking or unnatural optimism?
Data Analysis
The test- and retest responses were analyzed to check if there were any significant changes in
the behaviour and attitude of the respondents from the time the first questionnaire was carried
out, to the time the second questionnaire was administered. The questionnaire was
conducted to the same set of respondents after a gap of eight weeks. Comparative Analysis
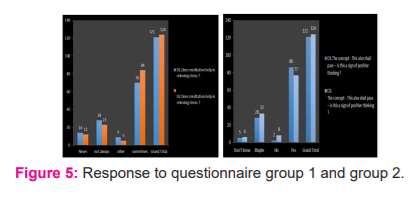
of two sets of data is represented in fig 1.
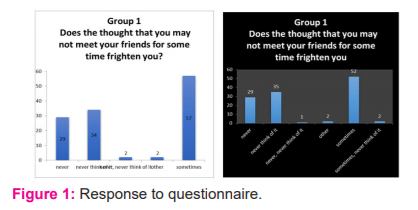
From the given graphs in fig 1, we can see that nearly 50% of the students are not frightened and on the other hand there is an increase of 3% in the bar ‘sometimes’ which shows an increase in the number of students who are frightened when they have the thought of not being able to meet their friends. Similarly from the questionnaire, we could also see that feeling of loneliness is gradually increasing from the responses received which indicate that nearly 70% of the students are worried and concerned about being alone.
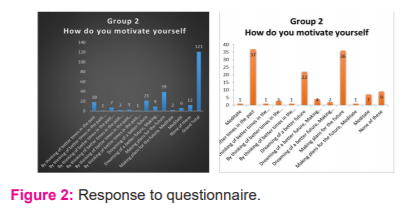
These graphs show that, although at times of difficulties students interest in making plans for their future haven’t reduced, which means students are highly motivated when they positively think about their future. And in graph 2 we can notice that there is a drastic increase in the bar” better times in the past “which shows students are trying to motivate themselves by also thinking about their past. Nearly 60% of the students have said sometimes they feel relieved when they do meditation as per the responses received from the questionnaire, we can also notice the increase in the number of students in the column “sometimes” from the responses, which shows that the students are gradually becoming stress-free and it’s a kind of positive development. Many have agreed with “yes”, but still if we have a deeper look at the responses we can notice that at first, nearly 70% of the students are positive about the concept of “THIS ALSO SHALL PASS” and in graph 2 we can see that only 60% of the students have agreed “yes”, this shows the decrease in their level of positivity and hope. Almost 60% of the students have said that they haven’t experienced unnatural fears like they are going to die and Some students have preferred not to answer this question which can also be considered in either way that they were ignorant of their fears or they were trying to suppress their fears.
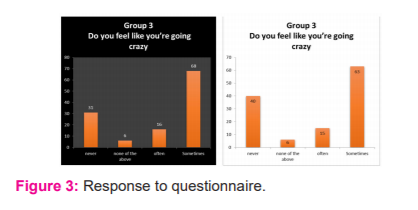
In both, the graphs, For almost 60% of the students have said that they haven’t experienced unnatural fears like they are going to die and Some students have preferred not to answer this question which can also be considered in either way that they were ignorant of their fears or they were trying to suppress their fears. We can also see from the responses received that only 30% of the students have said “no”, which shows remaining 70% of them are feeling crazy more often and sometimes. But if we have a deeper look at these graphs we can also see that there is a slight increase in the number of people who have said “never”, which shows the moderate increase in the behaviour of students. From the first set of data, it is shown that nearly 50% of the students have agreed to “sometimes” that is sometimes they do have their minds filled with negative thoughts but if we look at the second set of data, it’s nearly 86% of the students have agreed to “sometimes” and “never” with this we can say that the students are changing progressively by occupying themselves with positivity. On comparing the responses received, we can easily find out the stress level of students since it deals with lack of sleep, unfortunately, we can see that nearly 80% of the students are suffering from lack of sleep and if we notice we can see that it has a steady increase in the rate of 3%.
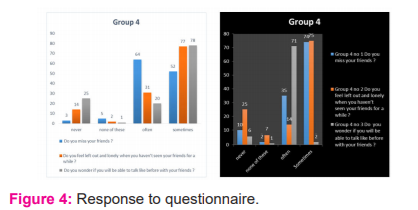
These graphs show the feel of loneliness faced by the students when they are not around their friends. When we compare these graphs we can see that their” fear of not being able to talk with their friends like before” and “their feeling of loneliness “have increased from graph 1 to graph 2 as shown in fig 4. Both the graphs are similar, we can see that the fear of not being able to go outside haunts nearly 40% of the students than any of the other stress factors. But still, some of them have said parental pressures and not being able to see their friend’s causes more stress.
This graph shows the comparison of group 2 from both the datasets, in this we can see that students have said sometimes they do feel relieved from stress when they meditate. From this we can say that before the students were more positive about the concept of “this shall also pass” and now they are slowly losing their positive hope in this concept.
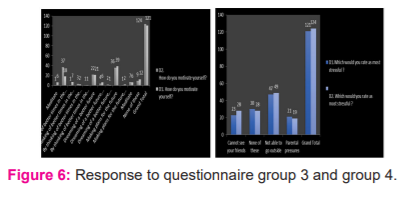
This shows that students feel motivated by thinking about their future in a progressive way which also makes them plan their future instead of feeling sick and trapped. In this graph, the most stressful factor according to students is not being able to move outside, which is quite unfair for students since their lifestyle is designed that way, it can be considered to be a natural thinking process of students to be wanting to go out and explore things.
Comparing these two datasets, we can say that there is a slight deviation in data_2 compared to data_1. Respective deviations in the following parameters, there is a negative increase in the parameter ”feeling of loneliness is a matter of concern”. There is a positive attitude among students in the parameter “meditation helps in relieving stress“. There is a negative impact in the parameter “The concept – This also shall pass “ among students. There is a Positive increase in the variable “ feeling crazy”. The parameter “ negative thoughts “ has a positive increase. The parameter “ Do you sleep well “ shows a negative increase. The group of variables that deals with “missing friends “is increased negatively.
The following hypotheses are proven:-
-
Prolonged periods of peer deprivation will induce the feeling of loneliness among students.
-
Social isolation will make students suffer unknown fears.
-
Social isolation will affect the sleep patterns of students.
-
Not being able to go out and socialize causes stress among students
-
Meditation reduces levels of stress among students.
The hypothesis that ‘Social isolation will induce fear of dying among students.’ has not been proven from the analysis of the two sets of data.
The insights obtained from a comparison of the two sets of data collected will provide a framework to understand the mental state of these young minds and also see what kind of remedies can be suggested for alleviating their stress levels. It will also suggest recommendations for the authorities and those in power to make decisions to take corrective and alleviative measures so that the future leaders will benefit from any positive social changes that may arise.
Recommendations
Some measures that could be possible remedies:
-
They could use the technique of mindfulness. Being mindful makes it easier to become fully engaged in activities, and creates a greater capacity to deal with adverse events. By focusing on the here and now, many people who practise mindfulness find that they are less likely to get caught up in worries about the future or regrets over the past, are less preoccupied with concerns about success and self-esteem. Mindfulness means acceptance of their experiences and not avoidance.
2. Peer group interaction and laughter sessions will greatly alleviate the feeling of social isolation. Good friends are good for health, friends prevent loneliness and increase your sense of belonging and purpose. Improve your self-confidence and self-worth and reduce stress levels.
3. They could be encouraged to involve in physical activity. Exercise of any kind that encourages some physical activity has beneficial effects. Exercise and physical activity are associated with better quality of life and health outcomes. Medical evidence suggests that the human brain produces a variety of chemicals such as dopamine (reward), endorphins (pain relief)and serotonin (relaxation). Moderate exercise increases attention and academic performance Studies show that endorphins released may help in overcoming social anxiety.
4. Help them identify stressors
Training the students to identify stressors it will give them the ability to eliminate causes of stress and thus alleviate its effects to some extent. The survey highlighted some of these factors that caused them stress. Ways of handling stressful situations differ from person to person. Coping strategies differ according to situational demands and situational environmental situations. The survey respondents seemed to have some idea of their stressful situations and also managed to control their mood swings from developing into extreme mood disorders.
Limitations of the study
The survey was limited to college students of a particular city and only female students. There could be differences in the attitudes of the respondents had been male students. Another limitation could be recall bias as the same set of questions were given within a gap of some few weeks. Familiarity with the questions may have coloured their thinking. Similarly, some students may have deliberately hidden their real thoughts or given exaggerated details regarding their stress levels or they may have underrated or over rated their handling of coping strategies. Further research may be conducted on male students or how students outside the city viewed the similar situation.
CONCLUSION
The phenomenon of stress continues to receive increasing attention from various fields such as medicine, counselling, psychologists and educational managers. When young minds are not able to meet up with friends as they used to just a few weeks back, they need to understand their problems on a larger scale. It is a not narrow problem affecting only a small circle of people. It is a global problem. The world is facing many allied challenges that include poverty, hunger, deprivation of education, and climate change. These issues have to be tackled both by the government and by individuals.
The authors feel that teachers who have direct contact with the student community are uniquely positioned because of their networking with students almost daily. They can help by providing the necessary emotional support by just being there and offering support when needed.
Compliance with Ethical Standards
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Authors’ contributions
The author(s) read and approved the final manuscript.
Funding
Not applicable.
Research involving human participants and/or animals
The datasets used and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Competing interests
All authors certify that they have no affiliations with or involvement in any organization or entity with any financial interest or non-financial interest in the subject matter or materials discussed in this manuscript.
Informed consent
Verbal informed consent was obtained before the collection of data.
References:
-
-
-
-
Carver C, Scheier M, Weintraub J. Assessing coping strategies: A theoretically based approach. J PersSoc Psychol 1989; 56:267–83.
-
Shields N. Stress, active coping, and academic performance among persisting and non-persisting college students. Journal of Applied Biobehavioral Research 2001; 6(2): 65–81.
-
Cooley E, Toray T. Coping in women college students: the influence of experience. Journal of College Student Development 1998; 39(3):291–295.
-
Aldwin C M & Revenson, T. A. Does coping help? A reexamination of the relation between coping and mental health. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology 1987; 53(2): 337–348.
-
Parkes K R. Coping in stressful episodes: The role of individual differences, environmental factors, and situational characteristics. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology 1996; 51: 1277-1292.
-
Hill AB. The environment and disease: association or causation? Proceedings of the Royal Society of Medicine 1965; 58: 295–300.
-
Altmaier E M. Helping students manage stress. San Francisco. Jossey Boss Inc, 1983.
-
Fisher S. Stress in academic life. New York: Open University Press, 1994.
-
Greenberg S F & Valletutti P J. Stress & helping professions. Baltimore: Paul H. Brookes 1980.
-
Lazarus R S. & Folkman S. Stress, appraisal, and coping. New York: Springer, USA, 1984.
-
Erkutlu HV, Chafra J. Relationship between leadership power bases and job stress of subordinates: example from boutique hotels, Manage. Res. News 2006; 29(5): 285-297.
-
Stevenson A, Harper S. Workplace stress and the student learning experience, Qual. Assur. Educ. 2006; 14(2): 167-178.
-
Gibbons RM, Gibbons B. Occupational stress in chef professional, Int. J. Contemp. Hospitality Management 2007; (19): 32-42.
-
McCarty WP, Zhao JS, Garland BE. Occupational stress and burnout between male and female police officers. Are there any gender differences? Policing: Int. J. Police Strateg. Manage. 2007; 30(4): 672-691.
-
James A. Haley V. The Impact of COVID-19 on Residents of Skilled Care Facilities Throughout the United States. International Journal of Current Research and Review 2020; 12(16): 1.
-
Kariv D. and Heiman T. Task-oriented versus-oriented coping strategies: the case of college students. College Student Journal 2005; 39(1):72–84.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License