IJCRR - 13(7), April, 2021
Pages: 46-50
Date of Publication: 12-Apr-2021
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
Socio-Economic Factors Influencing the Diabetic Patients Choice of Healthcare Services in Vellore, Tamil Nadu
Author: P. Gokula Krishnan, Savitha N
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Introduction: Diabetes is a global health concern and also a major contributor to mortality in most developing countries. People usually choose the best available option to derive maximum satisfaction from healthcare services. Based on this the present study has been done to the factors influencing the choice of healthcare services of diabetic patients. Objective: The main aim of this study is to analyse the factors determining the diabetic patient's choice of healthcare services. Methods: To analyse the socio-economic factors determining the diabetic patient's choice of healthcare services, a binary logistic regression model was used. Results: Factors such as age, education, gender, monthly income and treatment cost were found to be the determinants. People's choice of health care services was not identical and needs to be improved. At .000 p \? valve treatment cost had a significant impact on healthcare choice. Conclusion: The study suggests that increasing formal education on patients with diabetes would help them in choosing the appropriate healthcare services and they would be able to afford healthcare charges on their own.
Keywords: Diabetes, Choice of Healthcare, Binary Logistic Regression Analysis, Health Economics, Diabetic Management, Health-care service
Full Text:
Introduction
Diabetes is a global health concern and also a major contributor to mortality in most developing countries.1 In India, the second-most populous country on earth, 50 million people suffer from type 2 diabetes. Non-communicable diseases are the major cause of death in India, with diabetes topping this list. Lack of knowledge on the disease condition and also unavailability of healthcare services worsen the health outcomes and increase the health burden in many developing countries. Timely intervention and medication are required to prevent complications, but most patients are unable to access quality healthcare to manage diseases.2
Service quality is an important factor in the choice of health centres for patients. Increased awareness of diseases and their adverse effect on health has led to patients seeking better quality healthcare services.3 Availability of specialist healthcare services makes possible the long-term management of diseases. Previous studies have shown that people prefer hospitals service based on their income, socio-economic condition, and health status. Patients choose healthcare services for diabetes depending upon the quality of care provided to them. Both public and private sector hospitals provide healthcare services in India though their service quality varies widely. However, an assessment of how parents choose healthcare services for managing diabetes is necessary.4 Location-based studies on such choices are limited and only a few periodic surveys on patient choice were done in Vellore, a historic town in Tamil Nadu in India with a population of 4.8 lakh according to the 2011 census. Therefore the present paper focuses on the socio-economic factors that determine the choice of healthcare services for diabetic patients in Vellore.
India boasts of vast public and private healthcare network. The government provides healthcare services free of cost through public hospitals in both urban and rural areas.5 Three-tier health infrastructure has been developed in rural areas where the size of the health centre depends upon the population. Mountainous areas are served by sub-centres, rural areas have primary health centres (PHC) and community health centres are present in both rural and urban areas. Tribal populations are provided by healthcare at no cost in sub-centres. PHCs operate in villages that come under the administration of village panchayat. PHCs are small clinical centres with limited infrastructure, providing basic medical aid to the rural people and focusing on creating awareness about health and healthcare promotions.6 Community health centres render services to people in rural and semi-urban regions. They have a comparatively bigger infrastructure than PHCs. Public healthcare in urban areas is provided through district hospitals and sub-division hospitals. The cost of care in privately run hospitals is high and also varies depending upon many factors.7
Materials and Methods
Several studies have been done on factors influencing a diabetic patient’s decision to choose from available healthcare services.8 Most of the studies have been conducted in developed countries, and similar studies are very few in developing countries like India. To utilise healthcare services, people look at the desired goals of efficiency, equality, good quality and responsiveness to people’s needs. Here the emphasis is on how patients value their health.
Socio-demographic factors such as age, education and gender influence the choice of patients in seeking healthcare services. In this study, the authors found male respondents to seek care in private hospitals more than in public hospitals. It was observed that females were less likely to tolerate the long waiting time in government hospitals. Older patients were seen to prefer public hospitals because the distance is a top priority, and disease pattern and being more demanding of hospital services than younger patients force them to come to public hospitals. Older patients have more experience of the available healthcare and knowledge of services rendered in hospitals.9 Mostly they tend to compare the services received between the past and the present before choosing health centres.
Cowling et al. (2014) found sanitary conditions, employment area and gender to have a considerable impact on the patients’ choice of healthcare services. Their evaluation of services rendered and the resulting cure determines their specific choice of healthcare services.10 The work of Abdulaziz M et al. revealed that people having health insurance visit PHCs very less than people who did not have health insurance. Health insurance had a significant effect on hospital visits.11 In their study, age and gender did not have a significant effect on hospital choice, whereas education was found to have a significant influence. The objective of Oladigboluet et al. was to assess the socio-economic factors that influence people’s healthcare utilisation. They identified three important predictors such as social class, treatment cost and educational status to influence their utilisation of healthcare services.13 The odds of paying treatment fee are twice lower in the case of people from the lower social strata with informal education. Due to their difficulty in paying, poor people are largely deprived of quality healthcare services.
According to Malik et al. people consider healthcare professionals’ efficiency, reputation and hospital effectiveness as important factors in their decision making.14 People were ready to pay the high cost and endure long waiting times for seeking care in high-quality hospitals. Islam M. state that healthcare plays an important role in keeping society in good health and helps improve public health. Social factors that determine the healthcare choices are birthplace, age, education, work and living environment.15 Most of these factors shape the quality, equality, quantity and equal distribution of resources in healthcare services.
Source of Data
Primary data was collected for the study through interviews. A meeting was arranged with respondents directly in their houses for a face-to-face interview to understand to which factors they pay attention to when choosing healthcare services. A total sample of 200 diabetic patients was selected for the study. Blocks with a high prevalence of diabetes within the Vellore municipal corporation limits were chosen for the study. A binary logistic regression model at 95.0 % CI was used for the analysis using SPSS software version 20.
Hypotheses
H01. There is no significant relationship between the choice of healthcare services and age, gender and monthly income of the respondents.16
H02. There is no significant relationship between the choice of healthcare services and the community of the respondents.17
General Linear Regression Model
Logistic regression model was applied using the following equation:
Y = β0 + β1 X1 + β2 X2 + β3 X3 + β4 X4 + β5 X5 + β6 X6 + + Ui ---------- (1)
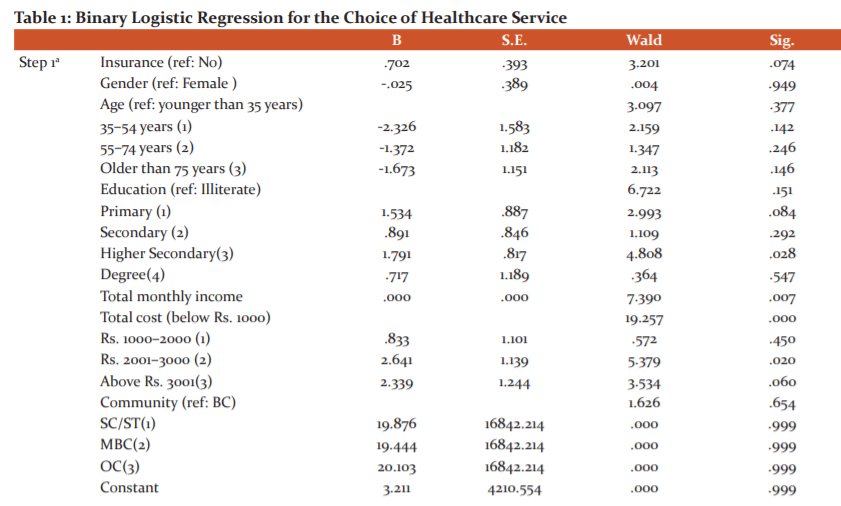
Here Choice of healthcare services as dependent variable (Y) and age, gender, monthly income of the respondents, insurance status, community as independent variables (X) as shown in Table 1.
Binary Logistic Regression Model
Logistic regression is one of the most significant models used for binary classification type variables.18 Logistic regression is mainly used for assigning discrete values like 0 and 1. In the present study, we assigned the value of 0 to a government hospital and 1 to a private hospital. The data should be linear. If it is a non-linear function, it is converted into a linear function by applying the following equation.22
ln(P1-P)= β0+ β1 X1 + β2 X2 + β3 X3 + β4 X4 +β5 X5+ Ui ---(2)
The term P/ 1 – P is called an odd ratio. Values β0,β1,β2,β3and β4are coefficients of the independent variables.
Results and Analysis
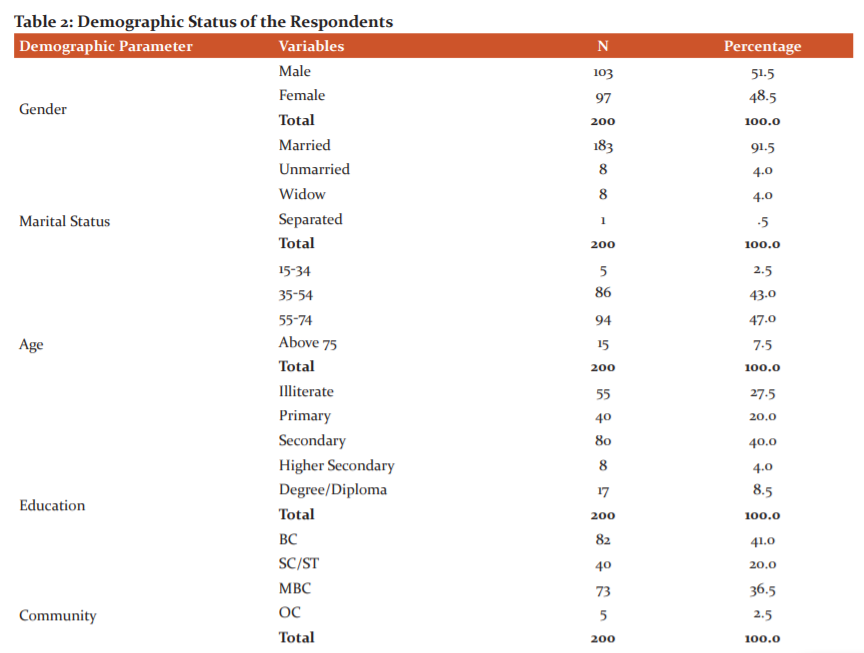
The results of the logistic regression analysis revealed that age, education, gender, marital status as well as a direct cost and indirect cost of care were significant determinants for patients in choosing healthcare services. Patients primarily consider cost and at times pay attention to quality as well. These factors had a strong effect on the choice of hospital for seeking diabetes treatment. Table 2 shows the demographic characteristics of the respondents of the study. 51% of the respondents were male and 49% were female. 30% of the respondents choose a government hospital and 70% choose a private hospital for the treatment. Table 1 shows the results of the binary logistic regression model. The variable ‘monthly income’ was found to be significant at .007. Variables having a significant value have an impact on choosing healthcare services. The unstandardized regression coefficient is expressed as the change in standard error.18
Discussion
Table 1 shows the goodness of fit in the logistic regression model. B represents the values for the logistic regression equation for predicting the dependent variable from the independent variable22. They are identified as log-odds units. The prediction equation is
Log (p/1 – p) = b0 + b1*× 1 + b2*×2 + b3*×3 + b4*×4 +ui - - - - (3)
In Table 2 the least square regression coefficient value of 0.84 for education implies the predicted amount of the change in the dependent variable (choice of health care), for every variable, alters the value of independent variables. Therefore the logistic regression equation is written as
log(p/1 – p) = 3.211 + 0.702 *Insurance + -.025*gender + -2.326*age (1) -1.372*age (2) – 1.673*age (3) + 1.534*education (3) + 19.8* community - - - - (4)
The reference group ‘Insurance’ is assigned a value of 0 and 1. So this coefficient represents the difference between Insurance 1 and Insurance 0. For every one-unit increase in monthly income, we expect a 0.000 increase in the log-odds of choice of health care, holding all other independent variables constant. A constant value is the expected value of the log-odds of choice of health care when all the predictor variables equal to zero. Hence we reject the first null hypothesis (H01) and the result predicts there is a relationship between the choice of healthcare services and age, gender and monthly income of the respondents. As there is no impact on choice of healthcare due to changes in the community, the second null hypothesis (H02) is accepted at a 95.0 % CI level. People from different community background choose their hospital not based on their community.
Conclusion
Patients choose healthcare services based on socio-economic factors such as age, education, gender, direct and indirect cost and insurance. The findings show that people’s choice of health care services was not identical and needs to be improved. Patients’ awareness of healthcare services has led to an improvement in their long-term management of diseases. This tends to change not only the quality of healthcare services but also the individual’s health behaviour. The study was performed considering only a limited number of socio-economic factors. Future studies taking into account more socio-economic variables are needed to validate our findings. A knowledge of factors that directly or indirectly influences the patient’s healthcare choice helps policymakers and managing authorities to understand the importance of their healthcare services from the provider’s perspective. The study suggests that increasing employment opportunity and formal education of patients with diabetes would help them in choosing the appropriate healthcare services and they would be able to afford healthcare charges on their own.
Acknowledgement: The authors acknowledge the immense help received from the scholars whose articles are cited and included in references to this manuscript. The authors are much grateful to the authors/editors/publishers of all those articles and journals from where the literature for this article has been reviewed and discussed.
Conflict of Interest: The authors declare there is no conflict of interest.
Source of Funding: Nil
Ethical Clearance: No experiment was done on humans or animals.
Authors Contribution: Dr. N. Savitha and P. Gokulakrishnan contributed to the design and implementation of the research work.

References:
-
Al-Doghaither AH, Rahman A, Saeed BM, Magzoub AA. Factors influencing patient choice of hospitals in Riyadh, Saudi Arabia. R Soc Health J Health 2003;123(2):105-109.
-
Al-Rubeaan K, Al-Manaa H, Khoja T, Al-Sharqawi A, Aburisheh K, Youssef A, et al. Health care services provided to type 1 and type 2 diabetic patients in Saudi Arabia. Saudi Med J 2015;36(10):1216-1225.
-
Alsubaie A, Almohaimede K, Aljadoa A, Jarallah O, Althnayan Y. Socioeconomic factors affecting patients′ utilization of primary care services at a tertiary teaching hospital in Riyadh, Saudi Arabia. J Family Community Med 2016;23(1):6-18.
-
Chauhan V, Sharma A, Sagar M. Exploring patient choice in India: A study on hospital selection. Int J Healthc Manag 2019;1(11):89-103.
-
Cowling K, Dandona, Dandona L. Social determinants of health in India: Progress and inequities across states.Int J Equity Health 2014;13(88):1-12.
-
Hassan A, Mahmood K, Bukhsh HA. Healthcare System of Pakistan.Int J Adv Res. 2017; 1(4):171-73.
-
Ewert B. Is patient choice the future of health care systems? Int J Health Policy Manag. 2013;1(3):227-228.
-
Islam M. Social determinants of health and related inequalities: Confusion and implications. Front Public Health 2019;7:232-24
-
Khalid A, Al-Rubeaan, Hamad A. Al-Manaa, Tawfik A. Khoja, Ahmad H. Al-Sharqawi, Khaled H. Aburisheh, Amira M. Youssef, et al. Health care services provided to type 1 and type 2 diabetic patients in Saudi Arabia. Saudi Med J 2015;36(6):1216-1225.
-
Hokshi MC, Patil B, Khanna, Neogi SB, Sharma J, Paul VK, et al. Health systems in India. J Perinatol 2016;36:9-12.
-
Mohammad MA. Patient choice of a hospital: Implications for health policy and management. Int J Health Care Qual Assur 2014;27(2):152-164.
-
Ul Haq NW, Taneja K, Adlakha N. Health System in India: Opportunities and Challenges for Enhancements. Int J Manag Bus 2013;9(12):74-82.
-
Oladigbolu R, Oche M, Kaoje A, Gana G. Socio-economic factors influencing utilization of healthcare services in Sokoto, north-western Nigeri. Int J Trop Dis Health 2017;27(2):1-
-
Rout SK, Sahu KS, Mahapatra S. Utilization of health care services in public and private healthcare in India: Causes and determinants. Int J Healthc Manag 2019;(5):1-8.
-
Shumaila A, Iqbal J, Waris H, Ismail M, Naseer A. Health Care System in Pakistan: A Review. Res Pharm Sci 2016; 2(3):211-216.
-
Siddique MK, Islam SM, Banik PC, Rawal LB. Diabetes knowledge and utilization of healthcare services among patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus in Dhaka, Bangladesh. BMC Health Serv Res 2017;17(1):552-558.
-
Singh B, Singhi, R. Servqual. Impact on overall satisfaction and brand loyalty: An empirical study in Delhi-NCR hospitals. Int J Technol Manag 2018;17(1):49-60.
-
Sperandei S. Understanding logistic regression analysis. Biochem Med 2014;5:12-
-
Chatterjee S, Riewpaiboon A, Piyauthakit P, Riewpaiboon W, Boupaijit K, Panpuwong N, et al. Cost of diabetes and its complications in Thailand: A Complete Picture of Economic Burden. Health Soc Care Community 2011;19(3):289-298.
-
Victoor A, Delnoij DM, Friele RD, Rademakers J. Determinants of patient choice of healthcare providers: A scoping review. BMC Health Serv Res 2012;12(1):25-38.
-
Yadav A, Hui L, Ali M, Anis M. Analysis of healthcare data of Nepal hospital using multinomial logistic regression model. Int J Inf Technol 2016;11(2):2720-2730.
-
Yu W, Li M, Xue C, Zhang L. Patient preference and choice of healthcare providers in Shanghai, China: A cross-sectional study. BMJ Health Care Inform 2017;7(10):16-20.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License