IJCRR - 13(7), April, 2021
Pages: 204-208
Date of Publication: 12-Apr-2021
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
Different Interaction Analysis of Receptors and Ligands in Suppressing Diabetics
Author: Balasankar Karavadi, Premalatha J, Vinothkumar C, Rajasekar B
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Introduction: Many recent studies are done on the efficiency of natural components for the treatment of diabetes, it has been found that many antioxidant components are present. Objective: The present study aims to study and identify the target sites which can be used as targets with appropriate ligands for diabetics. Methods: Structure-based drug design was performed and protein docking was done with known ligands. Analyzing the receptor-ligand interaction between the active site of the protein and the chemical molecules was performed. Results: All the compounds that satisfy the absorption, distribution, metabolism, excretion and toxicity (ADMET)properties are more favourable to bind with receptor. Discovery Studio tool was used to find the least energetic compound and based on the docking parameter against the receptor-ligand complex and which notified us of the acceptors and the donors in the analysis portion. from the study, we analysed that these components which contain bioactive compounds can be used in medical research. Nitenin showed a good dock score of 47.404 and can inhibit the overexpression of the CD62E gene. Conclusion: The finalized complex of Nitenincompound can be used for further medical studies in the preparation of drug molecule against diabetes. The docking study reveals that the antioxidant components that are present can be used in the treatment of diabetes.
Keywords: ADMET, Diabetic, Ligand, Docking, Drug
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION
Diabetes is described by unusually significant levels of sugar (glucose) in the blood.1 At the point when the measure of glucose in the blood increments, e.g., after supper, it triggers the arrival of the hormone insulin from the pancreas. Insulin invigorates muscle and fat cells to expel glucose from the blood and animates the liver to use glucose, causing the glucose level to diminish to ordinary levels.2
In individuals with diabetes, glucose levels stay high. This might be because insulin isn't being created by any means, isn't made at adequate levels, or isn't as compelling as it ought to be. The most well-known types of diabetes are type 1 diabetes (5%), which is an immune system issue, and type 2 diabetes (95%), which is related to stoutness. Gestational diabetes is a type of diabetes that happens in pregnancy, and different types of diabetes are extremely uncommon and are brought about by a solitary quality transformation.3
For a long time, researchers have been scanning for intimations in our hereditary cosmetics that may clarify why a few people are bound to get diabetes than others.4 The hereditary scene of diabetes presents a portion of the qualities that have been proposed to assume a job in the improvement of diabetes.5
As the incendiary reaction advances, chemokines discharged by harmed tissue enter the veins and initiate the moving leukocytes, which are presently ready to firmly tie to the endothelial surface and start advancing into the tissue. P-selectin has a comparable capacity, however is communicated on the endothelial cell surface inside minutes as it is put away inside the cell as opposed to delivered on request.6
ADMET screening is accomplished for the characteristic segments that are recovered from the database for testing their harmfulness and to locate the best lead particle that fulfils the ADMET parameter conditions (Figure 1).7,8 The ADMET screening process is finished utilizing Disclosure STUDIO programming. The ligand particles for which the AMET must be done is downloaded from PUBMED then stacked in the revelation page and checked for ADMET results.
Structure-based drug design is the method of performing docking using the known protein docking with known ligands. This has been the frequently used method of analyzing the receptor-ligand interaction between the active site of the protein and the chemical molecules.9
MATERIALS AND METHODS
The template structure was obtained from protein data bank.10 The modeled structures were validated using SAVS, an online server.11 The CASTp server was used to analyze binding sites of the protein molecules. Further, on the basis of high throughput method lead molecules having more affinity with the target proteins were obtained from DrugPort database.12 Then the structurally similar compounds were obtained using PubChem database.3 Finally a datset was created for potential ligands inhibiting the target proteins using vegaZZ software. Accelrys Discovery Studio 2.0 was used to analyze specific protein-ligand docked complexes and finally toxicity of the ligand molecules were analysed using ADMET descriptors.4
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
Receptor Ligand Interaction: Ligand-Nitenin
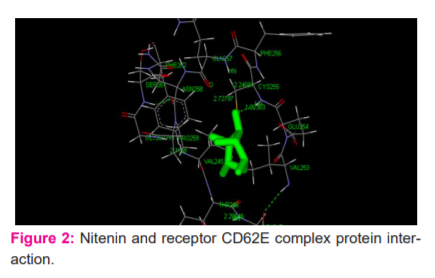
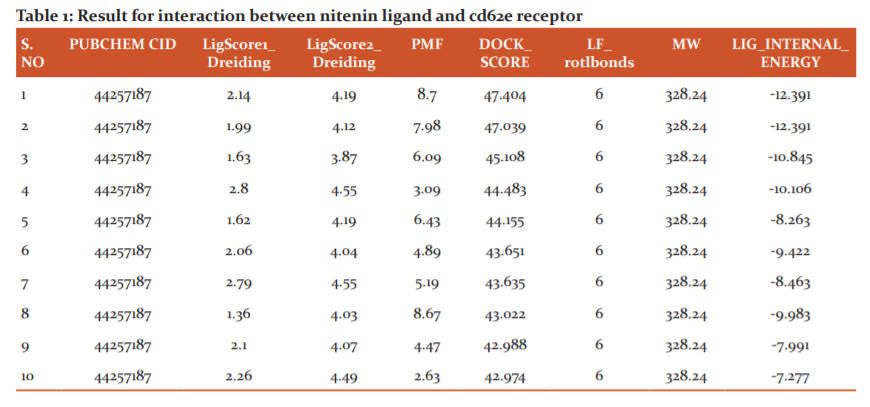
The docking score of this interaction is 47.404 and LigScore1_Dreiding and LigScore2_Dreiding values are 2.14 and 4.19, -PMf value is 8.7 and the internal energy is 12.391 (Figure 2).
Ligand- Fulvinervin A
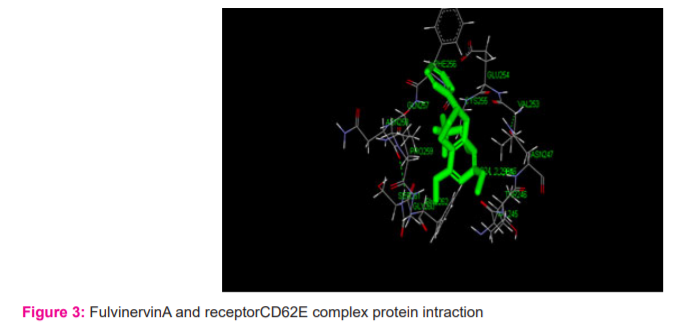
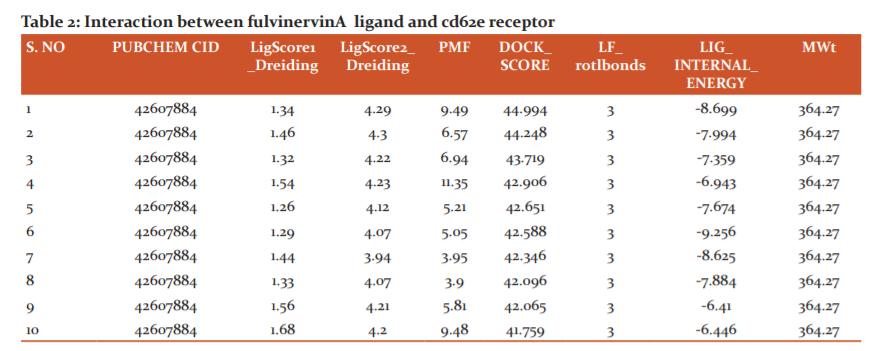
The docking score of this interaction is 44.994and LigScore1 and LigScore2 values are 1.34 and 4.29, -PMF 9.49 value is and the internal energy is 364.27 (Figure 3).
Ligand- Emoroidenone

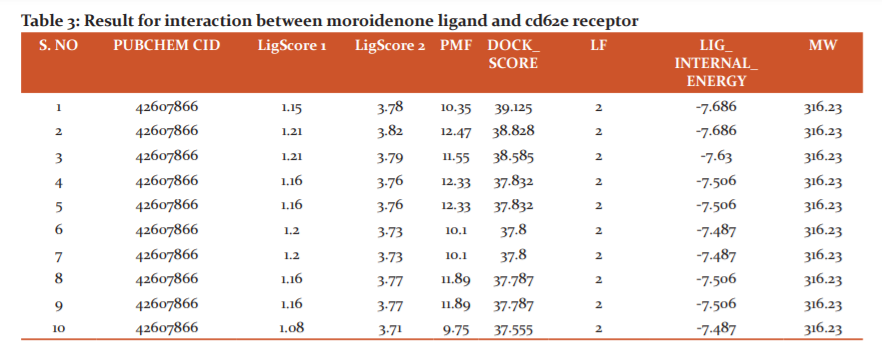
The docking score of this interaction is 39.125 and Lig1Score 1.15,Ligscore2 3.78 PMF value is 10.35 and the internal energy is -7.686 (Figure 4).
From the results obtained it is analyzed that the antioxidants present in Tephrosia play a major role in the treatment of diabetes. It is concluded that they can use the CD62e receptor which increases estrogen production and bone mineral density.
CONCLUSION
In this study, we have noticed that the compounds present in herbal medicinal can be used as a diabetes medicine. The anti-diabetes properties related to the compound which use as a ligand to show the interaction between receptor CD62E structure tells that the compound can inhibit the overexpression of CD62E receptor by binding in the active site cavity. Discovery Studio tool was used to find the least energetic compound and based on the docking parameter against the receptor-ligand complex and which notified us of the acceptors and the donors in the analysis portion. Finally, from the study, we can conclude that these components which contain bioactivity can be used in future medical research. Nitenin showed a good dock score of 47.404 and can inhibit the overexpression of the CD62E gene. The finalized complex of nitenin compound can be used for further medical studies in the preparation of drug molecule against diabetes.
ACKNOWLEDGMENT: The authors acknowledge the scholars whose articles are cited and included in references to this manuscript. The authors are also thankful to authors/ editors/publishers of all those articles, journals and books from where the literature for this article has been reviewed and discussed. We acknowledge our institute management for their support.
CONFLICT OF INTEREST: Nil
References:
-
Anderson DM, Maraskovsky E, Billingsley WL, Dougall WC, Tometsko ME, et al. Homologue of the TNF receptor and its ligand enhance T-cell growth and dendritic-cell function. Nature 1997;390:175–179.
-
Boyce BF, Xing L, Shakespeare W, Wang Y. Regulation of bone remodelling and emerging breakthrough drugs for osteoporosis and osteolytic bone metastases. Kidney Int Suppl 2003;12: 2–5.
-
Simonet WS, Lacey DL, Dunstan CR, Kelley M, Chang MS, Luthy R, et al. Osteoprotegerin: a novel secreted protein involved in the regulation of bone density. Cell 1997;89:309–319.
-
Ida Leida M, Ridwan M. Thaha, Andi SelviYusnitasari, Afsahyana Effect of Sap Palm (Borassus flabellifer) on Blood Glucose Level in Pre-Diabetic Patients. Int J Curr Res Rev 2020;12(24):96-100.
-
Tolar J, Teitelbaum SL, Orchard PJ. Osteopetrosis. N Engl J Med 2004;351:2839–2849.
-
Breuil V, Schmid-Antomarchi H, Schmid-Alliana A, Rezzonico R, Euller-Ziegler L, Rossi B. The receptor activator of nuclear factor (NF)-kappaB ligand (RANKL) is a new chemotactic factor for human monocytes. FASEB J 2003;17:1751–1753.
-
Aswathy BK, Nisha H. Homology Modeling and Docking Studies to Identify the Targets in Pancreatic Cancer. Res J Pharm Tech 2017;10(7): 2032-2040.
-
Aswathy BK, Martina V. Insilico Analysis of Inhibitors Related to Aggressive Behavior in Human Beings. Res J Pharm Tech 2018;11(4):1436-1441.
-
Karavadi B, Suresh M. Homology modelling and molecular drug design approach in identifying drug targets of TIGR4 in Streptococcus pneumonia. Bio sci Biotechnol Res Asia 2014;11:517-522.
-
Karavadi B, Suresh MX. In silicomodeling of capsular polysaccharidebiosynthesis protein and tyrosine kinase of G54 strain in Streptococcuspneumoniae and their ligand identification. Int J Pharm Pharm Sci 2014;6:547-550.
-
Karavadi B, Suresh MX. Receptor identification and lead the molecular discovery of a phage-encoded protein in TCH8431/19A strain of Streptococcus pneumoniae: A computational approach. Int J Appl Pharm 2014;6:6-10.
-
Karavadi B, Suresh XM. Homology modelling of polymerase and CPS biosynthesis proteins in CGSP14 strain of Streptococcus pneumonia and its ligand identification: An in silico approach. Asian J Pharm Clin Res 2014;7:162-165.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License