IJCRR - 13(7), April, 2021
Pages: 185-190
Date of Publication: 12-Apr-2021
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
Capsicum Plant Leaves Disease Detection Using Convolution Neural Networks
Author: Himanshu Pant, Manoj Chandra Lohani, Janmejay Pant, Prachi Petshali
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Introduction: Plants are a significant source of energy. Crop protection and production can be increased using the early and accurate diagnosis of plant diseases. In the old-fashioned environment, the identification is processed whether the plant leaf is healthy or infected either by visual observation or by testing leaves in the laboratory. The visual identification is done by the experts of the plant domain but opinion may vary from expert to expert. Testing of the plant leaf in the laboratory is a very time consuming and strenuous process and hence results may not come on time. Aims: The aim of this research article indicates that the proposed Convolutional neural networks (CNN) provide a healthier solu�tion in disease control for capsicum leaf with high accuracy of validation and a faster convergence rate. Methodology: To overcome these issues, image-based plant diseases classification and detection using Convolutional neural networks (CNN) have been presented in the literature. The authors have focused on the capsicum plant (Bell pepper) for this purpose, which belongs to the Grossum cultivar group of the species Capsicum annuum disease. Results: After model development and fitting, the operational performance and quality can be evaluated on the unseen testing dataset. The performance is measured in terms of accuracy. The model accuracy of each block VGG model can be calculated by increasing the convolutional layer and pooling layer. The model accuracy is improved from 84% to approx. 96%. Conclusion: Convolutional neural network is performed to detect, identify and classify the capsicum plant disease in this re�search. This research article reconnoitred three different improvements to the baseline model. The performance of the different results can be summarized in the terms of model accuracy.
Keywords: Accuracy, Capsicum, Computer vision, Classification, Convolutional neural networks, Leaf disease
Full Text:
India is a rich country having a huge amount of natural and human resources. Almost 70% of the Indian economy is based upon the agriculture and horticulture sectors.1 This agriculture sector contains numerous ingredients. Plants are one of the significant factors among them. Fit and healthy plants provide health.2 However, plant diseases are bullying the maintenance of this natural resource. Production and economic losses increases due to plant diseases in the agriculture and forestry sector. Capsicum (Capsicum annum) is the most used food crop in the world. Bell pepper bacterial spot (a fungal disease in capsicum) has caused a momentous economic and commercial loss and just by eliminating 20% of this bacterial infection, the farmers may benefit from an extraordinary profit. Therefore, early detection and identification of capsicum bacterial diseases play the utmost important role to take timely measures for the quality of the plant. There are numerous ways to perceive plant pathologies. Some plants have no visible symptoms of diseases associated with them or diseases may appear only when too late to cure. So it is necessary to perform a classy analysis of the plant diseases in the laboratories by the experts using powerful microscopes or employing different electromagnetic spectrum that is not visible to humans.3
Early-stage identification and classification of crop plant disease is a major problem in agricultural practices. Farmers bear a great loss in the economy every year due to infection in the crops and plants cultivation.4 Therefore, fast, efficient, less expensive and accurate diagnosis is required to prevent bacterial infection in the capsicum. These accurate and automated methods may help to inhibit the loss of crops, improves the quality of the product and helps in the economic growth of the country as well.5
This research study focuses on disease detection and classification of capsicum plant (Bell pepper) based on the bacterial symptoms of the diseases that show unhealthy signs on the leaves of the plant. Capsicum plants are dumpy shrub in nature with woody trunks. These plants nurture with colourful fruits. Capsicum leaves disease detection model to perform various steps. The primary step is to obtain a feature vector and another important step is to classify the feature vectors of the given input data. Mostly, the identification of the disease is guessed first by the human’s visualization. Experts of the domain may be efficiently recognizing the disease present in the particular plant but in most cases, there is no domain professional present in the particular area to give feedback on the disease to the farmers after data analysis on the plant. Hence farmers are required a quick, cheap, accurate and automatic technique to detect the plant disease efficiently.6
Bacterial infection and fungus are the main reason for capsicum plant diseases. Numerous diseases may appear in the capsicum plant. This article considered the images of bacterially infected leaves along with the healthy leaves (HL) images. The Xanthomonas campestris (black rot) is the primary bacterial species of the capsicum plants. Therefore, digital Image-based plant disease identification and classification models have been developed in the literature for plants.7
Computer vision, artificial intelligence, machine learning and deep learning techniques are more popular research areas for object detection and classification from images, text and videos.8 Digital image processing technique minimized the inaccurate manual disease detection and improve the accuracy, feasibility and efficiency to predict the disease on a time from a plant.9 This paper leverages the identification and classification of the disease and healthy images from the capsicum plant using recent advancement in computer vision with the help of a convolutional neural network (CNN).
The first aim of the current research was the collection of a sufficient capsicum image dataset from the field and then classifies the images into two categories (Bacterial spot images and healthy images). The overview of the proposed system architecture of capsicum plant disease identification and classification is shown in figure-1.
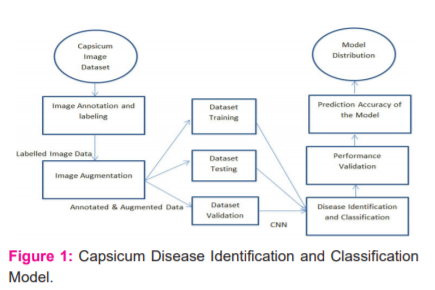
Nowadays, researchers pay attention to convolutional neural network techniques due to their great performance in image classification. The advantage of the convolutional neural network is that it avoids extraction of complex hand-crafted features unlike traditional machine learning techniques and provides end-to-end learning.10 For image classification and accurate prediction, the CNN model provides a relationship between layers and spatial information of the image.11 Along this line, there are limited works on capsicum leaves disorders identification and classification using CNN. Some author inspected the capability of the deep CNN technique for the classification of numerous rice diseases. A total of 597 images has been considered and used the CNN model with three convolution layers, three stochastic pooling layers and a softmax layer at the end. The classification accuracy of 91.620% has been reported. After augmentation of the dataset, the model achieved 94.972%% accuracy. A total of 418 images belonging to the training dataset and 179 images belong to the test dataset out of 597.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
In this section, the authors performed the various steps and operations on the capsicum plant image dataset. To identify and classify the infected capsicum leaves from the huge dataset, numerous operations can be performed as shown in figure-2. These steps describe the complete architecture from image acquisition to image disease classification through which farmers can easily predict the healthy plant from the mixture of infected and bacterial image sets. The methodology followed is discussed in detail.
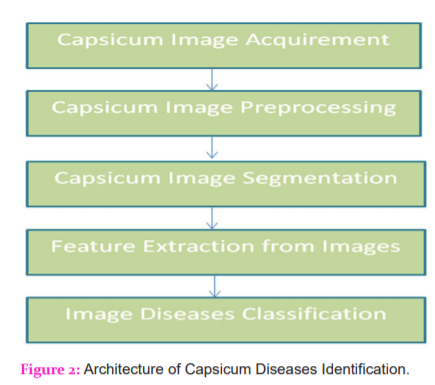
Dataset Descriptions
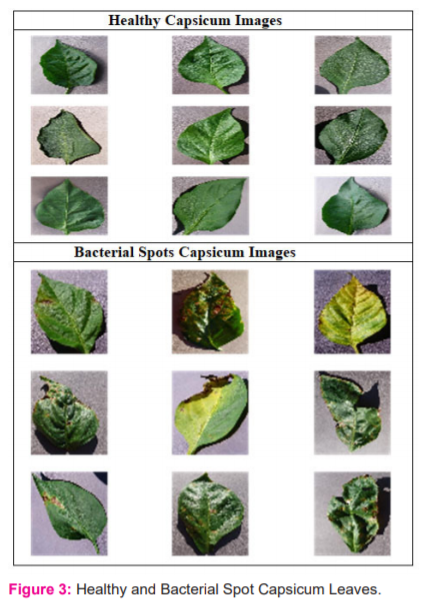
In this article, a huge amount of the capsicum plant’s leaf images are required to identify and classify the diseases associated with it. The images are captured from the different agricultural fields and various gardens in Nainital, a district of Uttarakhand, India. These datasets are required for image disease classification research during the training, testing and validation phase. The images are acquired using numerous types of standard cameras, captured from both front and back end leaves. The Apple iPhone 8, the Samsung Galaxy M3 and Redmi note 5 pro cameras are used for image acquisition. It contains a collection of images taken in a different environment. A dataset containing 597 capsicums leaves of two image classes including bacterially infected leaves and healthy leaves. The sample images of both categories are shown in the figure-3.
Data pre-processing
The capsicum plant images are initially unlabelled and not in annotated form. The labelling process of the images is processed by their filenames with the word “HL” and “BS”. Where HL belongs to healthy capsicum leaves while BS represents bacterial spot capsicum leaves. The file naming convention is in the form of HL.1.jpg, Hl.2.jpg, BS.20.jpg, BS.23.jpg etc. Primarily RGB coloured images are taken as a sample. In the captured images dataset, some images are in landscape format, some are in portrait format, and the remaining images are in square format.12
To classify and identify the disease from the capsicum images standardized photo size are required. All the images must be reshaped before modelling so that the size and shape of all images would be the same.13 Keras image processing API is applied to achieve this standardization by uploading all images to the ImageDataGenerator class and reshapes them to 200×200 square photos. The labels of the images are also determined based on the filenames. After standardizations of all images into 200 x 200 sizes, the next objective is to pre-process images into standard directories using flow_from_directory() application programming interface (API). This API divides all data into separate train/ and test/ directories, and under each directory to have a subdirectory for each class, e.g. a train/HL/ and a train/BS/ subdirectories and the same procedure is applied for test images. Images are then organized under the subdirectories.
EXPERIMENTAL SETUP AND PERFORMANCE ANALYSIS
The experiment was designed to appraise the performance of the baseline convolution neural network model for the capsicum image dataset to classify and identify whether a specific image is infected or not. This baseline CNN model is established to compare the model performance of other CNN models. The general architectural principles of the VGG models are used for the experiment.14This architecture involves assembling convolutional layers with small 3×3 filters followed by a max-pooling layer. A combination of convolutional layers and pooling layers form a block, and when the number of filters in each block is increased with the depth of the network, these blocks can be repeated. Padding is used on the convolutional layers to ensure the height and width shapes of the output feature maps matches the inputs. The authors applied this VGG architecture to the healthy capsicum plant image and bacterial spot image problem and then compare a developed model with this architecture using the first three blocks. In this designed architecture each layer is used the ReLU activation function and the he_uniform weight initialization.
The designed baseline CNN model is fitted with stochastic gradient descent and start with a conservative learning rate of 0.001 and a momentum of 0.9.15The proposed model can be fit using train iterator and dataset validation is done by test iterator. The number of steps for the train and test iterators concerning one epoch must be specified for the model fitting and it can be calculated by dividing the total number of capsicum images (both HL and BS) in the train and test directories by the batch size of 64.
Once the model is fitted, the performance and quality can be evaluated on the unseen testing dataset. The performance is measured in terms of accuracy. The model accuracy of each block VGG model can be calculated by increasing the convolutional layer and pooling layer.16
One Block baseline Visual Geometry Group (VGG) model performance
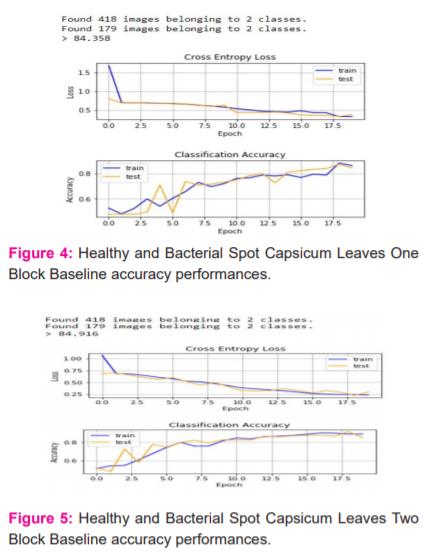
The one-block baseline Visual Geometry Group (VGG) model has only one convolutional layer with 32 filters followed by a max-pooling layer. The images are in the form of matrices and have to convert two-dimensional matrixes into dimensional form to create a neural network. For this purpose, the flattening technique is used. The dense layer is used to create a fully connected neural network by which each input node is connected to all output nodes. The classification accuracy of one block VGG model to classify the capsicum image dataset to predict whether the given image is infected or not and the cross-entropy loss on the test and training dataset at the end of each epoch is shown in figure-4. The one-block VGG baseline model gives 84.358% prediction accuracy.
Two Block baseline VGG model performance
The working procedure of the two blocks VGG model is almost same but in two-block VGG model. It is the extend version of one block VGG model by adding a second block (convolutional layer and max pooling layer) with 64 filters (just double from the first convolutional layer filter) as shown in figure-5. After compiling, the model had achieved a small improvement in the performance of accuracy and prediction from 84.358% to 84.916%.
Three-Block baseline VGG model performance
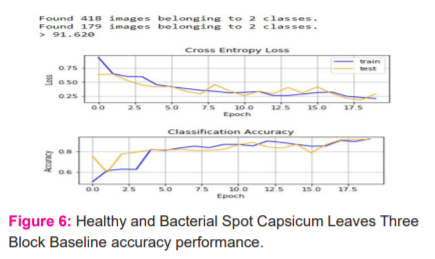
The architecture of three-block VGG model extends the two block VGG model by adding a third block (additional convolutional layer and max pooling layer) with 128 filters (just double from second convolutional layer filter). Repeating the compilation process using these three layers, model achieved a great improvement in the performance of accuracy and prediction from 84.916% to 91.620%. The classification accuracy and cross-entropy loss with respect to epoch is shown in figure-6.
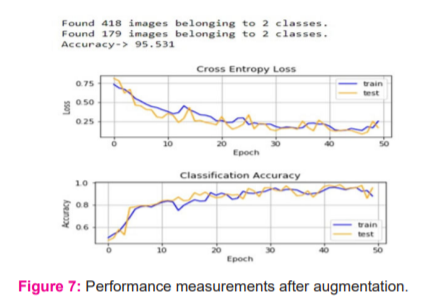
Performance measurement after capsicum image data augmentation:
Image data augmentation techniques are used to modify the training images in the dataset. It is an approach that allows us to increase the existing training dataset without collecting new. The augmentation process involves cropping the images, padding, and horizontal flipping of the images on the existing dataset to create a new one. Small changes in the input data of healthy capsicum images and bacterial spot capsicum images might generate a huge amount of new data by applying translation, rotation, small shifts and horizontal flips. The augmentation should be used only for training dataset using ImageDataGenerator in Keras.
Images are augmented in the training dataset with small shifting in random horizontal and vertical shifts and used random horizontal flips which create a mirror image of a photo. When this baseline three-block VGG model is compiled with augmentation, the model performance is improved. It is observed that the model lift an excellent performance of about 10% from the baseline one block VGG performance which was 84.358%. Now after augmented model predicts perfectly whether a given image healthy or infected with 95.531% accuracy on the given dataset. The classification accuracy and cross-entropy loss concerning each epoch are shown in figure 7.
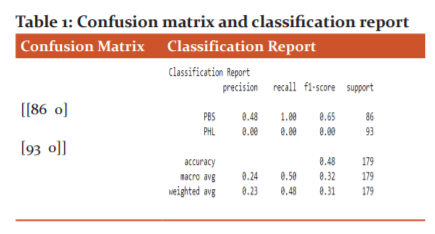
To describe the performance of the developed classification VGG model with three layers after augmentation, the confusion matrix is used for which the true values are known on a set of test data. The performance of the classification algorithms in deep learning and machine learning model is summarized by the confusion matrix. This matrix allows the visualizing of the performance of the developed CNN model in the matrix form. It is also used for decision making for selecting the right observations and can help to reduce errors. This binary classification problem is used to categorized and identify the capsicum plant disease. The confusion matrix and the classification report for three block baseline VGG model after augmentation with 95.531% accuracy are shown in the table-1.
CONCLUSION
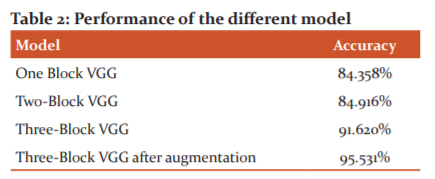
A convolutional neural network is performed to detect, identify and classify the capsicum plant disease in this research. Limited research has been done on capsicum plant disease classification and automation. In this paper different baseline, Visual Geometry Group (VGG) model with one two and three blocks of CNN was explored to classify the capsicum plant disease. Moreover, the designed model had applied augmentation on the training dataset to improve efficiency and accuracy. The proposed model can classify infected or healthy plants with a classification accuracy of 94.972%. The dataset is split into 80:20 ratios of training and testing respectively. This research article reconnoitred three different improvements to the baseline model. The performance of the different results can be summarized as given table-2. It is shown that the result may be improved when the three-block augmentation approaches further increases the number of training epochs.
FUTURE SCOPE
The performance of the proposed model can be further improved with a large dataset of capsicum plant images with both healthy and infected leaves. The CNN model is trained using the images captured from the natural environment by cameras. The purposed model has achieved 95.531% accuracy of classification and identification of the disease. This accuracy may be increased by applying the transfer learning model on pre-trained model like VGG 16, VGG 19, Alexnet, etc. In the future authors will apply computer vision techniques like image segmentation and object detection on plant leaves.
References:
-
India economic survey 2018: Farmers gain as agriculture mechanisation speeds up, but more R&D needed. The Financial Express. 29 January 2018. Retrieved 8 January 2019
-
Phadikar S, Sil J, Das AK. Rice diseases classification using feature selection and rule generation techniques. Comp Electr Agricult2013;90:76–85.
-
Barbedo JGA. A review of the main challenges in automatic plant disease identification based on visible range images. Bio Syst Engi 2016;144:52-60.
-
Al Bashis D. A Framework for Detection and Classification of Plant Leaf and Stem Diseases. IEEE International Conference on Signal and Image Processing (ICSIP), Chennai 2010, pp.113-118.
-
Sannakki SS. Diagnosis and Classification of Grape Leaf Diseases using Neural Networks. IEEE proceedings of 4ICCCNT, 2013.
-
Smith JS. An image-processing based algorithm to automatically identify plant disease visual symptoms. Biosyst Eng 2009;102:9–21.
-
Liu K. Identification method of rice leaf blast using multilayer perception neural network. Transactions Chinese Soc Agricult Engi 2009;25(S2).
-
Barbedo J. A review on the main challenges in automatic plant disease identification based on visible range images. Biosyst Eng 2016;144:52-60.
-
Asefpour K. An artificial neural network approach to identify fungal diseases of cucumber (Cucumissativus L.) Plants using digital image processing. Arch Phytopathol Plant Protect 2013; 46(13):1580-1588.
-
Lu. Identification of rice diseases using deep convolutional neural networks. Neurocomputing 2017;267:378–384.
-
Arel. Deep Machine Learning - A New Frontier in Artificial Intelligence. IEEE Computational Intelligence Magazine. 2010;5(4):13-18.
-
Dhakate M. Diagnosis of Pomegranate Plant Diseases using Neural Network. IEEE 5th National Conference on Computer Vision, Pattern Recognition, Image Processing and Graphics (NCVPRIPG), Patna2015.
-
Nam Y. A representation and matching method for shape-based leaf image retrieval. J KIISE: Softw Appl 2005;32(11):1013-1021.
-
Simonyan K. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. 2015. Available https://arxiv.org/cs/1409.1556
-
Wang L. Training deeper convolutional networks with deep supervision,” 20 Available https://arxiv.org/cs/1505.02496
-
Leaf recognition algorithm for plant classification using probabilistic neural network. Available http://flavia.sourceforge.net/
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License