IJCRR - 13(7), April, 2021
Pages: 156-161
Date of Publication: 12-Apr-2021
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
Study to Compare the Efficacy of Orally Administered Melatonin and Clonidine for Attenuation of Hemodynamic Response During Laryngoscopy and Endotracheal Intubation in Gastrointestinal Surgeries
Author: Sarmila Guha Banerjee, Pradipta Sanyal, Ujjwal Bandyopadhyay
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Introduction: The haemodynamic response to anaesthetic induction with endotracheal intubation may be harmful in patients with cardiovascular disease, increased intracranial pressure, or anomalies of cerebral vessels. Objective: A comparative study for attenuating reflex hypertension and tachycardia by using oral administration of Clonidine and Melatonin before induction of general anaesthesia. Methods: After obtaining the institutional ethical approval total of 76 patients scheduled for gastro-intestinal surgeries under general anaesthesia were divided into 2 groups, Group 1( 38 patients) received oral Melatonin 6 mg tab before surgery and Group 2 (38 patients) received oral Clonidine 100mcg before surgery. Heart rate, Systolic blood pressure(SBP), Diastolic blood pressure (DBP) and Mean arterial pressure (MAP) were recorded in two groups at different point of time i,e before premedication, immediately before induction, after tracheal intubation and every 3 min thereafter for 15 min. Incidence of perioperative and postoperative complications in 2 groups was also observed. Result: The results of observation were compiled, tabulated and statistically analyzed using the Chi-square test and unpaired t-test as and where applicable. Oral Melatonin was found better than oral Clonidine in lowering Systolic blood pressure(SBP), Diastolic blood pressure (DBP) and Mean arterial pressure (MAP) and heart rate changes associated with laryngoscopy and intubation. Occurrence of peri and postoperative complication in both the groups which were mild. Conclusion: From the observation of the present study, it can be concluded that oral Melatonin is a better agent than oral Clonidine in maintaining haemodynamic stability during gastrointestinal surgery under general anaesthesia.
Keywords: Melatonin, Clonidine, Haemodynamic stress response, Laryngoscopy, Intubation, Premedication
Full Text:
Introduction
In 1940, Reid and Bracefirst described the hemodynamic response to laryngoscopy and intubation. The mechanisms of the responses to laryngoscopy and orotracheal intubation are proposed to be by somatovisceral reflexes.1 Laryngoscopy and endotracheal intubation cause stimulation of proprioceptors at the base of the tongue, that cause reflex sympathetic activation of vagal and glossopharyngeal afferents. This activation cause hypertension, tachycardia and increased intracranial tension.2 TheseeffectscanbewelltoleratedbyASA (American Society of Anaesthesiology) grade1and 2 patients but can be detrimental for elderly patients, patients with cardiologicalandneurologicaldiseases.3
This haemodynamic surge is a problematic issue for gastrointestinal surgeries especially prolonged and major surgeries.3 A large array of pharmacotherapy has been tried to prevent laryngoscopic surge with varying degree of success such as Lignocaine, opioid, vasodilator, Ca channel blocker, beta-blocker, Magnesium sulphate, Gabapentin, Pregabalin but none of the above-mentioned drugs has been proved fully efficacious to blunt haemodynamic stress response during laryngoscopy and endotracheal intubation, and all these agents have some limitations.4,5
Melatonin, (N_Acetyl_5_Methoxytryptamin) is an endogenous sleep-regulating hormone secreted by the pineal gland. Melatonin differs from other premedical because it exerts the sleep-promoting effect by amplifying day/night differences in alertness & sleep quality and displaying a modest sleep-inducing effect. The hypnotic, anti_nociceptive, anxiolytic properties of Melatonin makes this neurohormone a useful medicine in anaesthesia and critical care.2 Melatonin 6 mg tablet if taken 120 minutes before operation then it can significantly decrease laryngoscopic surge.1,3
Apart from all the above mentioned benefits, melatonin has a short half-life so prolonged sedation is less likely, as well as melatonin does not have any abuse potential. Clonidine is a centrally acting alpha2 agonist. Clonidine causes stimulation of presynaptic alpha2 receptors, which decreases plasma renin and norepinephrine and thus blood pressure also decreases, the vagolytic effects of Clonidine causes a decrease in heart rate. Oral clonidine100 mcg tablet taken 120 minutes before operation can significantly reduce haemodynamic surge due to laryngoscopy and endotracheal intubation.3
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Consenting patients of either sex, aged between 18 and 60 years, ASA physicalstatusIand2postedforelectivegastrointestinalsurgeries under general anaesthesia with tracheal intubation were selected for the study. Single laryngoscopic attempt and laryngoscopic period <20 seconds was adopted..(Ethical clearance No.MC/Kol/IEC/Non-spon/421/11-2016, Dated 19/11/2016 )
Unwilling patients, patients incapable of consent due to mental or physical illness, uncontrolled hypertension, uncontrolled diabetes mellitus, pregnancy, lactation, ASA physical status 3 or worse, anticipated difficult airway, the known presence of any absolute contraindication to any of the study drugs), bodyweight beyond (more or less) 30%ofidealbodyweight, patients on psychoactive drugs, significant disease of major organs like liver, kidney, hypersensitivity to study medicines, history of alcohol or substance abuse, were excluded from the study. After obtaining the approval for the study from the institutional ethical committee, informed consent was obtained from all the patients, patients were randomly allocated into one of the two study group.

All the patients fasted as per ASA guideline and premedicated with oral alprazolam0.25 mg tab. plus oral pantoprazole 40 mg tab. on the night before surgery. All patients were premedicated with injection glycopyrrolate 10 mcg/kg intravenous (IV), ondansetron 0.08 mg/kg IV, before induction of anaesthesia. On spontaneous ventilation, patients’ lungs were pre-oxygenated with 100% oxygen for 3 minutes, and general anaesthesia was induced with inj propofol 2 mg/kg IV administered over 20 seconds. Tracheal intubation was facilitated with inj succinylcholine 1.5 mg/kg IV. Immediately after completion of tracheal intubation and commencing intermittent positive pressure ventilation, nasogastric tube insertion was performed in all patients.
General anaesthesia was maintained with 0.2% -0.6% isoflurane and 40% oxygen in nitrous oxide. Surgical muscle relaxation was maintained with a loading bolus of 0.5 mg/kg atracurium besylate IV and 0.1 mg/kg IV at 30 minutes intervals. Intraoperative analgesia will comprise fentanyl 2 mcg/kg IV plus paracetamol 15 mg/kg into a venous infusion (IVI). Ringer lactate solution 500 mL IV Infusion initially over 30 min, followed by 100 mL/h IV through till the end of surgery was infused to replace fasting fluid deficits and hourly maintenance fluid therapy.
Intraoperative patient monitoring was done with the continuous presence of a qualified anaesthetist, continuous pulse oximetry, capnography, ECG(Electrocardiogram) monitoring, heart rate and non-invasive blood pressure monitoring. At the end of the surgery, anaesthetic agents were turned off and patients were clinically assessed for spontaneous return of neuromuscular function. Residual neuromuscular blockade was reversed with inj neostigmine 50 mcg/kg plus inj glycopyrrolate 10 mcg/kg IV given slowly over 3 minutes.
Vital parameters like systolic blood pressure (SBP), diastolic blood pressure (DBP), mean arterial blood pressure (MAP) and heart rate (HR ) were measured and the same parameters were also measured before premedication and, before induction, The average of these 3 measurements (i.e. measurements of SBP, DBP, MAP, HR at the night before the operation, before premedication and before induction) was taken as baseline values. A 20% rise from baseline values was taken as tachycardia and hypertension and a 20% fall from baseline values was taken as bradycardia and hypotension.
Intraoperative bradycardia managed by injection atropine 0.6 mg i.v bolus, Intraoperative hypotension treated with a bolus of i.v fluid and i.v vasopressors (Phenylephrine and Mephentermine). Intraoperative hypertension managed by nitroglycerin (1 mg/ml) infusion and intraoperative tachycardia will be managed with proper analgesia and appropriate anaesthetic manoeuvres.
RESULTS
Collected data was plotted in a microsoft office excel sheet and graphically represented and explained through various charts and tables. Data were analyzed by SPSS version 20. P value was considered significant if <0.005 and highly significant if <0.001.
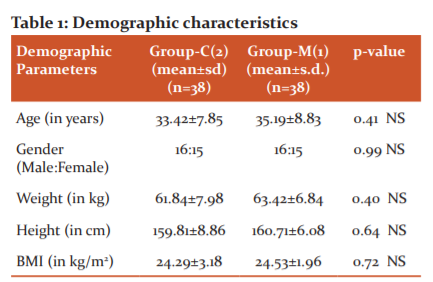
t-test showed that there was no significant difference in mean ages, weight, height and BMI of the two groups (p>0.005). Thus the patients of the two groups were matched for all demographic parameters.
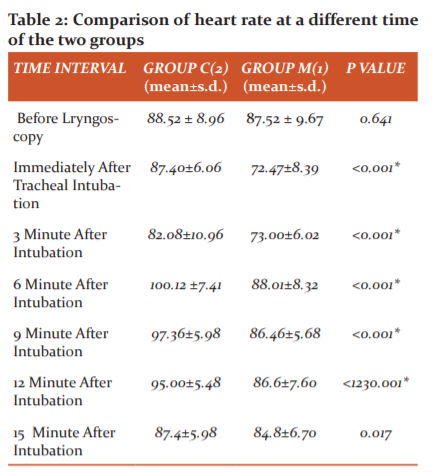
t-test showed that the mean heart rate of the patients of Group-2 was significantly higher than that of Group-1 for all the time intervals after intubations (p<0.0001).
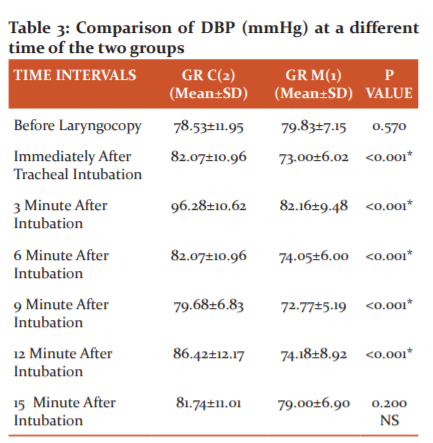
t-test showed that the mean DBP of the patients of Group-2 was significantly higher than that of Group-1 for all the time intervals after intubations (p<0.001) except after 15 minutes.
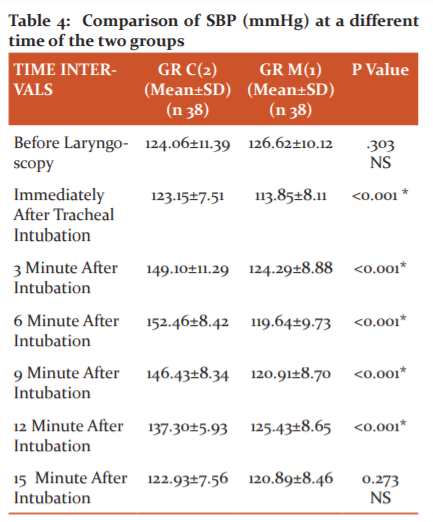
t-test showed that the mean SBP of the patients of Group-2 was significantly higher than that of Group-1 for all the time intervals after intubations (p<0.0001).
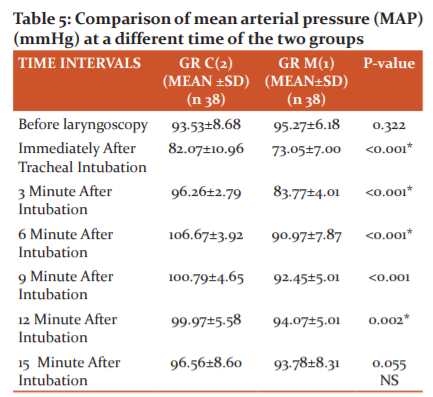
t-test showed that the mean MAP of the patients of Group2 was significantly higher than that of Group-1 for all the time intervals after intubations except after 15 minutes.
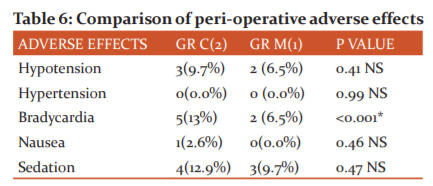
There was no incidence of hypertension in both groups. The proportion of patients with bradycardia was significantly higher in Group-2 (p<0.001). Though all other complications were higher in Group-2 as compared to Group-1 test of proportion showed that there was no significant difference in the proportions. (p>0.005).
DISCUSSION
Laryngoscopy and endotracheal intubation are associated with rising heart rate, blood pressure and occasional disturbances in cardiac rhythm.6 Although in normotensive subjects these responses of blood pressure and heart rate are transient and short-lived, they may prove to be detrimental in high-risk patients especially in those with cardiovascular disease, increased intracranial pressure and anomalies of cerebral blood vessels.7 So, effective attenuation of hemodynamic response to laryngoscopy and tracheal intubation is of great importance in the prevention of perioperative morbidity and mortality.7
Several studies have been proposed to attenuate stress response-omitting inj atropine as premedical, nitroglycerine(GTN) administration intranasally etc. Also, the IV administration of lignocaine prevented the increase in MAP. Beta-blocker ca channel blocker have also been used successfully to prevent haemodynamic response to tracheal intubation.8-10
Several studies revealed the use of oral clonidine on attenuation of haemodynamic response to laryngoscopy and tracheal intubation.11 The possible mechanism of attenuating these responses is its ability to decrease central sympathetic outflow as clonidine is a centrally acting selective partial alpha 2 adrenergic agonist.12,13 Melatonin, an endogenous sleep-regulating hormone differs from other premeditates because it has a short half-life so prolonged sedation is unlikely. The hypnotic, antinociceptive and anxiolytic properties of Melatonin makes this hormone a useful medicine in anaesthesia.14-16 The randomised double-blind study was undertaken to compare the usefulness of this two-drug tab clonidine 100 mcg and tab Melatonin 6 mg.17
Consenting patients of either sex, aged between 18 and 60 years, ASA physical status 1 & 2, posted for elective gastrointestinal surgery under general anaesthesia were selected for this study. Difficult intubation takes a longer time and invariably associated with marked hemodynamic changes even in well-premedicated patients. So, patients with anticipated and unanticipated difficult intubation were excluded from this study.18
Melatonin undergoes negligible metabolism in the human body and is excreted mainly through urine. Following oral administration of Clonidine, about 40% to 60% of the absorbed dose is recovered in the urine as an unchanged drug in 24 hours and 50% of the absorbed dose is metabolized in the liver. So, the duration of action and bioavailability of the drugs may be altered in renal failure and hepatic failure patients.19 Therefore, patients with altered liver functions and renal functions were not included in this study.20 Both Melatonin and Clonidine are used as anti-anxiety and have a sedative effect. So, patients on psychoactive drugs were excluded in this study to avoid synergistic or added effect of these drugs in the postoperative period.21 The most significant factors influencing cardiovascular responses in this study are the duration of laryngoscopy during intubation.22 In this study duration of laryngoscopy and intubation were limited to less than 20 seconds.
Melatonin had a better effect than clonidine in controlling heart rate after intubation. The mean heart rate of the patients of Group-C was significantly higher than that of Group-M for all the time intervals after intubations (p<0.0001) except after 15 minutes. Melatonin prevented the increase in SBP significantly throughout the first 12 minutes following laryngoscopy as compared to the Clonidine group. T-test showed that the mean SBP of the patients of Group-C was significantly higher than that of Group-M for all the time intervals after intubations (p<0.0001)except after 15 minutes. The DBP of the patients of Group-C was significantly higher than that of Group-M for all the time intervals after intubations (p<0.001) except after 15 minutes. The mean MAP of the patients of Group-C was significantly higher than that of Group-M for all the time intervals after intubations (p<0.005) except after 15 minutes.
Serum catecholamine is the most important markers to assess the sympathoadrenal stress response. But in this study, we could not measure its level in every patient due to scarcity of resources. Post-operative patients were monitored for any adverse effects like nausea, vomiting, sedation, bradycardia, hypotension and hypertension. There was no incidence of hypertension in both groups. The proportion of patients with bradycardia was significantly higher in Group-C (p<0.001). Though all other complications like sedation were higher in Group-C as compared to Group-M, the test of proportion showed that there was no significant difference in the proportions (p>0.005). There was no abnormal ECG during induction and intubation.
CONCLUSION
This prospective randomised double-blind study showed that Melatonin 6mg dose attenuate haemodynamic stress response in term of Heart Rate, Systolic Blood Pressure, Diastolic Blood Pressure, Mean Arterial Pressure better than clonidine 100mcg dose during laryngoscopy and intubation. A few patients in both the groups presented with minor peri and postoperative complications (e.g. nausea, postoperative bradycardia, dizziness) which were mild. But the incidence of postoperative bradycardia was more with oral Clonidine. So from these observations, we can conclude that melatonin 6mg is a better agent than oral clonidine 100mcg in attenuating the hemodynamic responses to laryngoscopy and intubation.
Acknowledgement: Authors acknowledge the immense help received from the scholars whose articles are cited and included about this manuscript. The authors are also grateful to authors/editors/publishers of those articles, journals and books from where the literature of this article has been reviewed.
Financial support: No special financial support needed.
Conflict of interest: Nil.
Author’s contribution
1 Dr.Sarmila Guha Banerjee: Principal Investigator.
2.Dr.Pradipta Sanyal: Co-investigator.
3. Dr.Ujjwal Bandyopadhyay: Drafting and designing the research article
References:
1) Reid LC, Brace DE. Irritation of the respiratory tract and its reflex effect upon the heart. Surg Gynae Obstet 1940;70:157-62.
2) King BD, Hartis LC, Greifenstein FE, Elder JD, Dripps RD. Reflex circulatory response to direct laryngoscopy and tracheal intubation performed during general anaesthesia. Anaesthesiology 1951;12:556-66.
3) Boralessa H, Senior DF, Whitman JC. Cardiovascular response to intubation. Anaesthesia 1983;38:6237.
4) Pernerstorfer T, Krafft P, Fitzgerald RD, Krenn CG, Chiari A, Wagner O, et al. Stress response to tracheal intubation: direct laryngoscopy compared with blind oral intubation. Anaesthesia 1995;50(1):17-22.
5) Forbes AM, Dally FG. Acute hypertension during induction of anaesthesia and endotracheal intubation in normotensive man. Br J Anaesth 1970;42:618-24.
6) Fox Ej, Sklar gs, Hill CH, Vilanueva R, King BD. Complication related to the pressor response to endotracheal intubation. Anaesthesiology 1977;47:524-25.
7) Randel T, Hemodynamic response to intubation: what more do we have to know? Acta anaesthesiology Scand 2004;48:393-95.
8) Low JM, Harvey JT, Prys-Roberts C, Dagnino J. Studies of anaesthesia concerning hypertension. VII: Adrenergic responses to laryngoscopy. Br J Anaesth 1986;58(5):471-7.
9) Fassoulaki A, Kaniaris P. Does atropine premedication affect the cardiovascular response to laryngoscopy and intubation? Br J Anaesth 1982;54:1065-80.
10) Fassoulaki A, Kaniaris P. Intranasal administration of nitroglycerin attenuates the pressure response to laryngoscopy and intubation of the trachea. Br J Anaesth 1983;55:113.
11) Rani R, Nesargi SS. Oral Clonidine for Attenuating Hemodynamic Stress Response to Laryngoscopy and Intubation. Karnataka Anaesth J 2015; 1(2):50-54.
12) Raval D, Mehta M. Oral clonidine premedication for attenuation of haemodynamic response to laryngoscopy and intubation. Indian J Anaesth 2002;46:124-29.
13) Das M, Ray M, Mukherjee G.Clonidine attenuate haemodynamic response during laparoscopy. Indian J Anaesth 2007;51:205-210.
14) Hoseini VS, Yekta R, Marashi S, Marashi SM. Melatonin, Gabapentin and Clonidine in reducing anxiety and pain in cholecystectomy. Arch Anesth Crit Care 2015;15:120-125.
15) Gupta P, Jethava D, Choudhary R, Jethava DD. Role of melatonin in attenuation of haemodynamic responses to laryngoscopy and intubation. Indian J Anaesth 2016;60:712-18.
16) Naguib M, Gottumukkala V, Goldstein AP. Mini-Review: Melatonin and Anaesthesia, a clinical perspective. J Pineal Res 2007;42:12–21.
17) Taittonen MT, Kirvela OA, Santana R, Kanto JH. Effect of clonidine and dexmedetomidine premedication on perioperative oxygen consumption and haemodynamic state. Br J Anaesth 1997;78:400–406.
18) Ionescu D. Melatonin as premedication for laparoscopic cholecystectomy SAJAA 2008; 14:8-11.
19) Kurdi MS, Patel T. The role of melatonin in anaesthesia and critical care. Indian J Anaesth 2013;57:137-44.
20) Mihara T, Nakamura N, Ka K, Goto T. Melatonin for paediatric emergence reaction. Eur J Anaesth 2015;32:1–10.
21) Ahmed M, Hosam A, El-Din A, Kassaby M, Ismail A, Helmy A. Effects of Melatonin Premedication on the Hemodynamic Responses and Perfusion Index During Laryngoscopy and Endotracheal Intubation. Med J Cairo Univ 2014;81:859-867.
22) Cardinalii DP, Pagano ES, Bernasconi, Pablo AS. Disrupted chronobiology of sleep and cytoprotection in obesity;possible therapeutic values of melatonin. Act Nery Super Rediviva 2011;53(4):159-176.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License