IJCRR - 13(7), April, 2021
Pages: 09-15
Date of Publication: 12-Apr-2021
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
Prevalence of Premenstrual Syndrome and its Influence on Job Performance Among Nurses
Author: Reham Mohammad Kharabah, Abdulaziz Saleh Eid Aljohani, Khalid Ahmad Amara
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Introduction: Premenstrual syndrome (PMS) is characterized by a wide range of emotional and physical symptoms and behav�ioural changes, happening before the menstruation phase of the menstrual cycle and dropping after the starting of the menstrual period. Objective: To determine the prevalence of premenstrual syndrome and its influence on job performance among nurses. Methods: This cross-sectional study was conducted on a population of 310 nurses working at Madinah maternity and child hospital and affiliated Primary Health care Centers in AlMadianh, from January to February 2019 in Al-Madinah, Saudi Arabia. Data were collected using the Premenstrual Syndrome Scale (PMS). The data were analyzed with Version 22.0 of the Statistical Package for Social Science. Descriptive statistics, Pearson's correlation, independent t-test and one way ANOVA test was used. Results: The prevalence of PMS among the nurses was 52.0%, with a mean score of 114\?32. The premenstrual syndrome was significantly higher in younger nurses, those with less number of children, those who had pain before and during the period, those with disappearance symptoms before and with the onset of menstruation, those who use regulated medicine, those who experienced dysmenorrhea, cramps and back pain (p< 0.05). The premenstrual syndrome was significantly affected daily work (p< 0.0001). Conclusion: The premenstrual syndrome was found in more than half of the nurses who participated in the study. The pre�menstrual syndrome was higher in younger nurses who suffered from pain before and during the period and used regulated medicine. There was a statistically significant negative effect of PMS on daily work performance.
Keywords: Premenstrual syndrome (PMS), Nurses, Work related quality of life, AlMadinah, Saudi Arabia
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION
Premenstrual syndrome (PMS) is characterized by a wide range of emotional and physical symptoms and behavioural changes, happening before the menstruation phase of the menstrual cycle and dropping after the starting of the menstrual period, 1-6and it is classified as physical disease in the 10th revision list of the international classification of disease (ICD).6,7,8
PMS is variously defined.2 The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG) defined PMS as “a clinical condition characterized by the cyclic presence of physical and emotional signs and symptoms unconnected to any organic illness that show during the 5 days before menses in each of the three previous menstrual cycles and vanish within 4 days of the onset of menses, without repetition until at least the day 13th of the cycle.4,9 Also, the American Psychiatric Association (APA) has determined criteria for the diagnosis of severe PMS or premenstrual dysphoric disorder (PMDD).4,10 Where women are diagnosed with PMDD when their lives are considerably affected by moderate to severe symptoms as defined in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, fifth edition.4,11
PMS disturbs the daily lives of women and can worsen their quality of life and social skills.3,12,13 The severity of PMS symptoms is associated with its duration in how it ruins the daily lives of women.3,13 Known risk factors for PMS are hormonal imbalance, fluid retention, thyroid dysfunction, genetic factors, hypoglycemia, stress and psychological factors.6,14,15 Over 200 premenstrual symptoms have been reported; however, very few are explained by changes in the menstrual cycle.5,16
Symptoms widely associated with PMS include physical symptoms such as bloating, headache, breast swelling and tenderness, nausea, weight gain and sweating, and psychological symptoms such as restlessness, anger and irritability.1-6 The incidence of PMS is very common among women of reproductive ages.3 Studies have stated that the rate of PMS with moderate and severe symptoms ranges from 4.1% to 80.2%.1-6,17-19 Where PMS prevalence rates can vary due to cultural characteristics, sample differences, and diagnostic methods.3
Few epidemiological studies have investigated the prevalence of premenstrual syndrome and its influence on job performance among nurses, particularly in Saudi Arabia. The current study aimed to investigate the prevalence of premenstrual syndrome and its influence on job performance among nurses in Al-Madinah, Saudi Arabia,
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Study design
This was a cross-sectional descriptive study conducted among nurses working at Madinah maternity and child hospital and affiliated Primary Health care Centers in Madinah. The calculated sample size was 300 with 95% confidence limits, 5% accepted errors, the prevalence of premenstrual syndrome =4.1% to 80.2%, 1-6and a 10% (27 nurses) was added to the sample to avoid withdrawing and refusing to participate.
Procedure
A stratified random technique (proportional allocation) was applied to select the required sample size representing different clinical departments. Targeted departments were: Emergency department, Intensive care Units, medical department, surgical department, pediatric department, Oncology Physiotherapy and 7 primary healthcare centres PHCCs.
A structured self –administered questionnaire. The questionnaire was taken from previous studies4,5,20,21 and modified by two experts from family medicine, it contains four main parts; A – Socio-demographic characters of the nurses. B –Menstrual and premenstrual characteristics. C –Premenstrual symptoms. D- Premenstrual syndrome scale.
Variables
The dependent variable of the study was Job performance. And the independent variable were sociodemographic characteristics, menstrual and premenstrual characteristics, and premenstrual symptoms.
Statistical analysis
Data was entered and processed by using SPSS software version 21 for analysis and interpretation. P-Value is considered statistically significant if it is ≤ 0.05.
Study approvals
The following approvals were obtained: the research ethical committee, ministry of health, and the general Directors of Madinah maternity and child hospital (MMCH) and affiliated primary healthcare centres (PHCCs) in AL-Madinah. Written consent was obtained from each participant. And the collected data was handled confidentially.
RESULT
The Shapiro-Wilk statistic test was done for the following continuous variables (PMS score, age, children number, body mass index (BMI), absence days by week, absence days by months and age at first ministration). The result for PMS score was ( 0.991, p value= 0.745) indicating normal distribution. On the other hand the result for the rest continuous variable were (0.943, 0.851, 0.321, 0.465,0.485 and 0.963) with (p<0.001, p<0.001, p<0.001, p<0.001, p<0.001, p<0.001, and p<0.001). Indicating non normally (non-parametric) distributed.
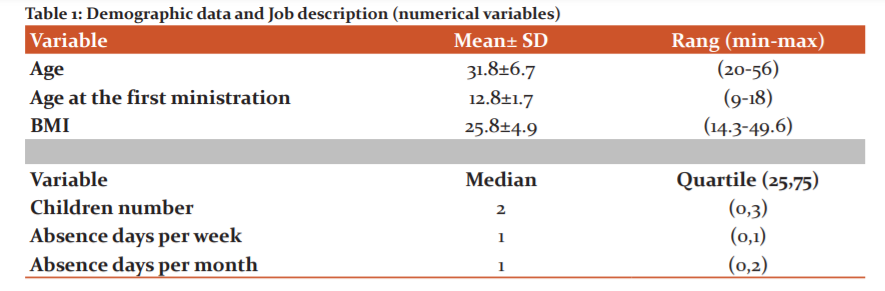
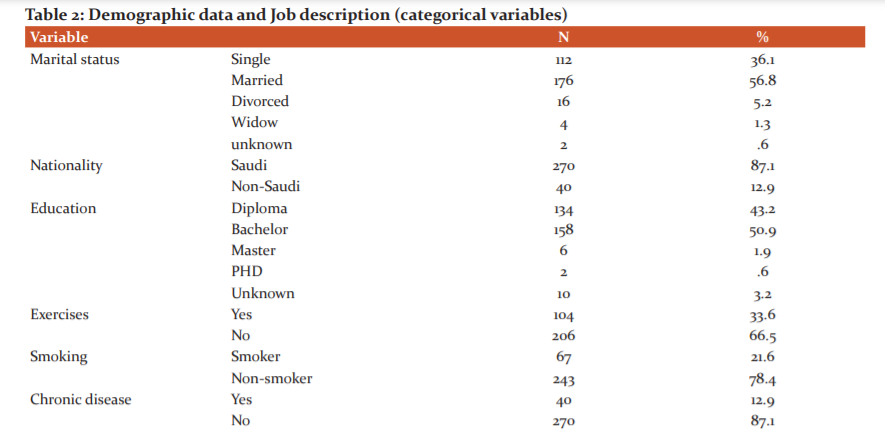
Out of 310 female nurses, 176 (56.8%) were married and 112 (36.1%) were single, with an average age of 31.8±6.7. The majority 270 (87.1%) were Saudi. Half of the nurses 158 (50.9%) had a bachelor degree, 134 (33.6%) reported regular exercises,67 (21.6%) were smokers. Less than fifth 40 (12.9%) had a chronic illness. The mean score of BMI was 25.8±4.9, where 134 (43.2%) had normal weight, were 96 (31%) overweight, and 62 (20%) were obese. More than half 174 (56.2%) worked day shift, and 100 (32.2%) worked rotating shift. The median scores of days absence weekly and monthly were 1 & 1 respectively (Tables 1 & 2).
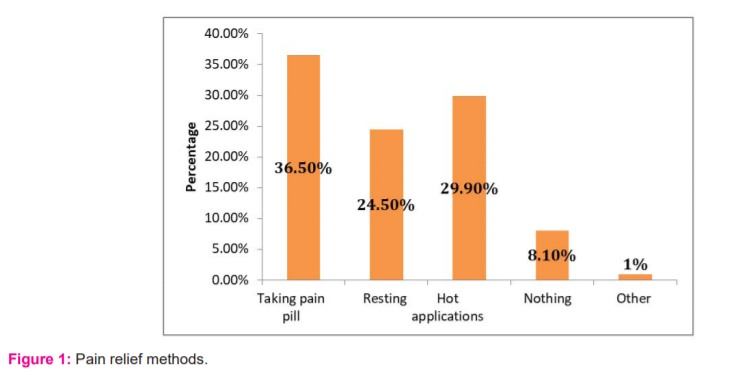
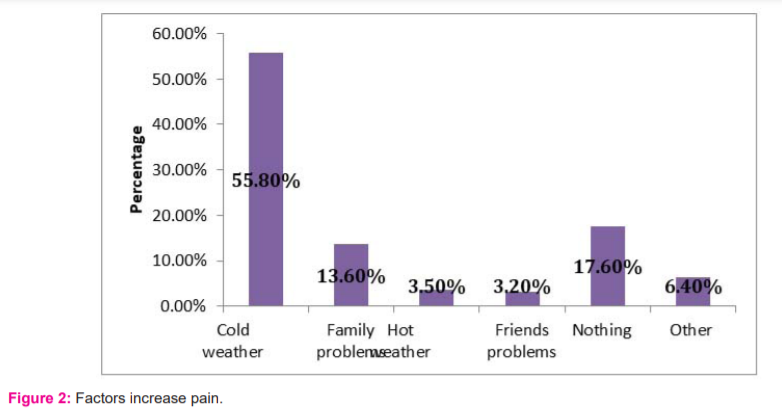
Out of 310 nurses, 166 (54.5%) reported a positive family history of PMS, with the average age at first ministration 12.8±1.7. The majority 272 (87.7%) reported pains before and during mensuration and 236 (76.1%) had regular mensuration, 144 (45.5%) reported dysmenorrhea, only 37 (11.9%) received regulated medications. Almost half had moderate cramps 147 (47.4%) and back pain 144 (45.5%). The most common pain relief methods were Taking pain pill by 140 (36.5%), hot applications by 115 (29.9%), and resting by 94 (24.5%). While the most common reasons for increasing pains were cold weather by 193 (55.8%) and family problems by 47 (13.6%). Regarding Premenstrual syndrome 26 (8.4%) diagnosed with it and 33 (10.6%) received treatment for it. More than half 177 (57.1%) stated that Premenstrual syndrome affected their daily work. Symptoms disappear in almost half 151 (48.7%) (Figures 1 & 2).
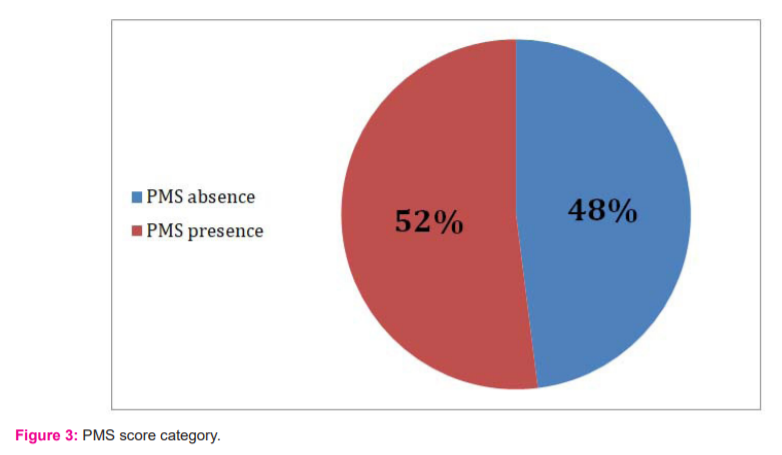
The PMSS mean score was 114±32 rang (51-211) and was divided into two categories with cut off > 110, of the 360 nurses, 164 (52%) had premenstrual Syndrome (PMSS score > 110), and 146 (48%) did not have premenstrual Syndrome (PMSS scores ≤110) (Figure 3).
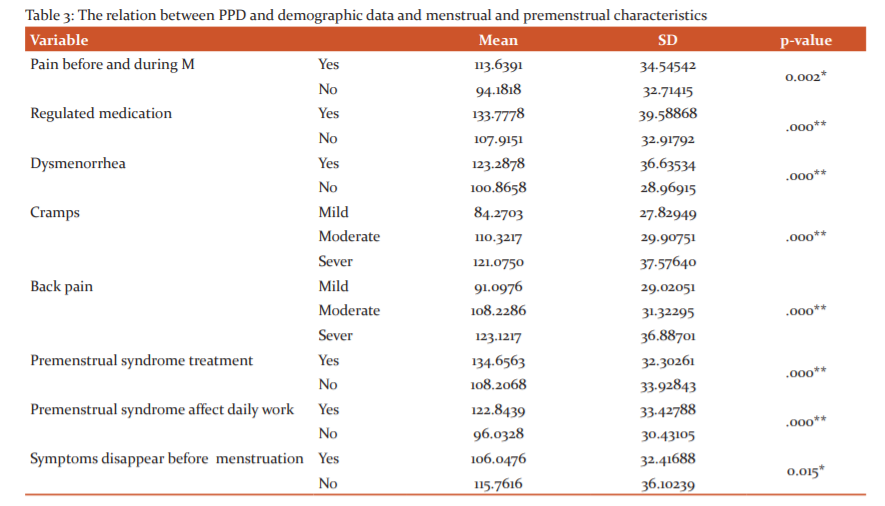
The results showed a significant association between PMS and the following demographic data, job discerption, and menstrual and premenstrual characteristics (Pain before and during M, Regulated medication, Dysmenorrhea, Cramps, Back pain, Premenstrual syndrome treatment, Premenstrual syndrome affect daily work, and symptoms disappear before menstruation ) where those who had pain before and during menstruation, those who received regulated medication, that who had dysmenorrhea, those who suffered from severe cramps and severe back pain, those who received premenstrual syndrome treatment, those who premenstrual syndrome affect their daily work, and those who’s symptoms don’t disappear before menstruation showed higher scores in PMSS (p=0.02, p<0.0001, p<0.0001, p<0.0001, p<0.0001, p<0.0001, p<0.0001, and p=0.015) respectively. On the other hand, the rest variables didn’t show any significant association (Table 3).
DISCUSSION
Premenstrual syndrome (PMS) is a natural situation that can cause psychological, physical, and social problems in women.22 Women with PMS are usually affected during the luteal phase of the menstrual cycle.23
There are no precise physical examination findings or lab tests definite to the diagnosis of PMS.4 A symptom calendar can help women recognize the most worrying symptoms and confirm the diagnosis of PMS.5 To diagnose PMS, the American Obstetric and Gynecologists Association stated that the symptoms should be seen 5 days before the onset of menstruation and disappear within 4 days post the onset of menstruation. 24Several previous studies reported the negative influence of PMS such as; decreasing the efficacy and capacity to work and to study.25 The present study aimed to investigate the prevalence of premenstrual syndrome and its influence on job performance among PHC nurses in Al-Madinah, Saudi Arabia.
Results of the current study showed that more than half of the nurses had PMS. In K?rcan et al study 60.1% of nursing students had PMS,26 and in Demirbas study PMS was determined in 56.6% of medical faculty students.27 In Sut study, 38.1% had a PMS diagnosis according to the PMSS.3 In a study conducted on Thai nurses, the PMS prevalence was reported as 25.1%.28 PMS incidence in women working in health care has been reported to be 20.1%.29 In a recently published meta-analysis, the PMS prevalence was reported as 47.8% for all studied groups; however, rates varied from 12% (France) to 98% (for Iran).30 This indicates that PMS prevalence differs from country to country.
These differences came from the number and structure of samples, cultural differences, or differences in diagnostic methods. Also, emotional and physical abuse in early life affects PMS prevalence.31 PMS symptoms can start at any age after menarche. In the current study, the mean age of first menstruation was 12.8±1.7. Similar results were found in Demirbas study, where the mean age of first menstruation was 13.07±1.07.27 The most prevalent (87.1%) menstrual disorders were cramped, followed by back pain (84.2%), then dysmenorrhea (45.5%). In Abdelmoty et al study, dysmenorrhea was the most prevalent (93%) menstrual disorder, followed by PMS (65%) and abnormal cycle lengths (43%).32
The main factors which increase pain were cold weather (55.8%) and family problems (13.6%). This consistent with two Turkish studies (66.5% & 15.9%) and (53.2% & 27%).27,33 Premenstrual complaints reduce job's productivity and quality and cause economical losses as well as an increase in the accident rate, as well as effect self-confidence, social relations, and attendance.34 In the current study, complaints due to the menstrual period affected daily work were 57.1%. In 2012 a study by Babacan-Gümü? done among college students, reported that premenstrual complaints influenced 31.2% of daily activities.34 Borenstein et al reported a greater number of lost workdays due to health reasons and a decrease in work productivity in women with PMS.35
In dealing with PMS, both nonpharmacological approaches and pharmacologic approaches can be used.36,37 Where, women prefer pharmacologic methods. In the current study, 36.5% used analgesic drugs, used 24.5% rest, and 29.9% used hot application. In Turkey study among married women, almost the third 32.5% used painkiller drugs, and the fourth 27.5% rest to decrease pain before menstruation.38 In a study by Weisz and Knaapen, they stated that hormonal treatment and painkiller drugs were the common utilized in France for PMS treatment, while herbal therapy was the common utilized in Germany.37
Findings of the present study showed that PMS were significantly higher (p<0.05) among those who had pain before and during menstruation, those who received regulated medication, those who had dysmenorrhea, those who suffered from severe cramps and severe back pain, those who received premenstrual syndrome treatment, those who premenstrual syndrome affect their daily work, and those who’s symptoms don’t disappear before menstruation. While age and running exercises weren’t significant but close to being statistically signi?cant (p=0.06), where younger age and who don’t perform exercises showed higher PMS score.
These findings indicate that PMS is a major health problem for nurses that negatively affects daily work activities and the compatibility of nurses in working with other health care professionals. Distractibility and irritability in clinical nursing practices, which may occur due to PMS, may cause incorrect applications and irreparable health outcomes. PMS also negatively affects a nurse’s patient communication and care, which in turn threatens patients’ safety.
CONCLUSION
PMS was common among more than half of the nurses, even that the majority had regular ministration. Almost half had moderate cramps and back pain. The main pain relief methods were taking pills, rest, and hot application. While the main factors which increase the pain were cold weather and family problems. PMS was significantly higher among the nurses who had the following; pain before and during menstruation, received regulated medication, dysmenorrhea, severe cramps and severe back pain, received premenstrual syndrome treatment, the premenstrual syndrome affects their daily work, and whose symptoms don’t disappear before menstruation. While Younger age and who don’t perform exercises showed higher PMS score close to being statistically signi?cant. The authors recommended the following; Encourage nurses to request professional help to decrease PMS. Further nation-wide studies on detecting the prevalence of PMS need to be conducted in larger sample size and regions other than Am Madinah Almonawarah, to identify the prevalence and underlying causes. Present the most significant points in this study to hospitals and PHCCs administrators. And designing diverse interventional programs to improve effective preventive strategy for this problem.
Acknowledgement
We would like to thank all study participants for their participation kindly cooperation.
Source(s) of support: Nil
Presentation at a meeting: Nil
Conflicting Interest (If present, give more details): Nil

References:
-
Shameem I. Clinical Study of Mutlazima Qabl Haiz (Premenstrual Syndrome) and its Management with Unani Formulation-A Randomized Controlled Trial. Int J Curr Res Rev 2014;06(13):51-57.
-
Erbil N. Prevalence of depressive symptoms among Turkish women experiencing premenstrual symptoms and correlated factors. Alexandria J Med 2018;54:549–553.
-
Sut HK and Mestogullari E. Effect of Premenstrual Syndrome on Work-Related Quality of Life in Turkish Nurses. Safety Health Work 2016;7:78-82.
-
Buddhabunyakan N, Kaewrudee S, Chongsomchai C, Soontrapa S, Somboonporn W, Sothornwit J. Premenstrual syndrome (PMS) among high school students. Int J Women’s Health 2017;9:501–505.
-
Erbil N, Karaca A, Kiris T. Investigation of premenstrual syndrome and contributing factors among university students. Turk J Med Sci 2010;40(4):565-573.
-
Sahin S, Ozdemir K, Unsal A. Evaluation of premenstrual syndrome and quality of life in university students. J Pak Med Assoc 2014;64(8):915-922.
-
Nagata C, Hirokawa K, Shimizu H. Soy, fat, and other dietary factors in relation to premenstrual symptoms in Japanese women. BJOG 2004;111:594-599.
-
Domoney CL, Vashisht A, Studd WWJ. Premenstrual syndrome and the use of alternative therapies. Ann Ny Acad Sci 2003;997:330-343.
-
Frank RT. The hormonal causes of premenstrual tension. Arch Neurol Psychiatr 1931;26:1052–1057.
-
ACOG Practice Bulletin. Premenstrual syndrome. Clinical management guidelines for obstetrician – gynecologists. J Obstet Gynecol 2001;73:183–191.
-
American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders. 5th ed. Washington, DC: APA Press; 2012: 465–475.
-
Speroff L, Fritz MA. Menstrual disorder. Clinical Gynecologic Endocrinology and Infertile. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2011:568–578.
-
Direkvand-Moghadam A, Sayehmiri K, Delpisheh A, Sattar K. Epidemiology of premenstrual syndrome (pms)da systematic review and meta-analysis study. J Clin Diagn Res 2014;8:106-109.
-
Baker FC, Driver HS. Circadian rhythms, sleep, and the menstrual cycle. Sleep Med 2007;8:613-622.
-
Erbil N, Bolukbas N, Tolan S, Uysal F. Determination of the premenstrual syndrome and affecting factors among married women. Int J Human Sci 2011;8:427-438.
-
Halbreich U. The diagnosis of premenstrual syndromes and premenstrual dysphoric disorders-clinical procedures and research perspectives. Gynecol Endocrinol 2004; 19: 320-334.
-
Demir B, Algül LY, Güvendag? Güven ES. The incidence and contributing factors of premenstrual syndrome in health working women. Turk J Obstet Gynecol 2006;3(4):262–270.
-
Ad?güzel H, Task?n O, Danac? AE. The Symptomatology and Prevalence of Symptoms of Premenstrual Syndrome in Manisa. Turk Psikiyatri Derg 2007;18(2):215–222.
-
Hamaideh SH, Al-Ashram SA, Al-Modallal H. Premenstrual syndrome and premenstrual dysphoric disorder among Jordanian women. J Psyhiatr Ment Health Nurs. 2014;21(1):60–68.
-
Gencdogan B. A new instrument for premenstrual syndrome. Psychiatry in Turkey 2006;8:81-87.
-
Padmavathi P, Sankar R, Kokilavani N, Dhanapal K, Ashok B. Validity and Reliability Study of Premenstrual Syndrome Scale (PMSS). Int J Adv Nurs Manag 2014; 2(1):4-5.
-
Marjoribanks J, Brown J, O’Brien PMS, Wyatt K. Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors for premenstrual syndrome. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2013;7: CD001396.
-
Cheng SH, Shih CC, Yang YK, Chen KT, Chang YH, Yang YC. Factors associated with premenstrual syndrome - a survey of new female university students. Kaohsiung J Med Sci 2013;29(2):100–105.
-
ACOG Committee on Practice Bulletins--Gynecology. Premenstrual Syndrome. ACOG Practice Bulletin No. 15. Obstet Gynecol 2000;95(4):1-9.
-
Anandha LS, Saraswathi I, Saravanan A. Prevalence of premenstrual syndrome and dysmenorhoea among female medical students and its association with college absenteeism. Int J Biol Med Res 2011;2:1011-1016.
-
K?rcan N, Ergin F, Adana F, Arslantas H. The prevalence of premenstrual syndrome in nursery students and its relationship with quality of life. J ADÜ Med Faculty 2012;13:19-25.
-
Kutlu R, Demirbas N, Dag?stan F. Frequency and Affecting Factors of Premenstrual Syndrome Among Turkish Female University Students. J Clin Anal Med 2017;8(5): 416-420.
-
Direkvand-Moghadam A, Sayehmiri K, Delpisheh A, Sattar K. Epidemiology of premenstrual syndrome (pms)da systematic review and meta-analysis study. J Clin Diagn Res 2014;8:106-109.
-
Chayachinda C, Rattanachaiyanont M, Phattharayuttawat S, Kooptiwoot S. Premenstrual syndrome in Thai nurses. J Psychosom Obstet Gynaecol 2008;29:199-205.
-
Demir B, Algül LY, Güven ESG. The incidence and the contributing factors of premenstrual syndrome in health working women. J Turk Obstet Gynecol 2006;3:262e70.
-
Bertone-Johnson ER, Whitcomb BW, Missmer SA, Manson JE, Hankinson SE, Rich-Edwards JW. Early life emotional, physical, and sexual abuse and the development of premenstrual syndrome: a longitudinal study. J Womens Health 2014;23:729-739.
-
Abdelmoty HI, Youssef MA, Abdallah S, Abdel-Malak K, Hashish NM, Samir D, et al. Menstrual patterns and disorders among secondary school adolescents in Egypt. A cross-sectional survey. BMC Womens Health 2015;15:70.
-
Erbil N, Karaca A, K?r?s T. Investigation of premenstrual syndrome and contributing factors among university students. Turk J Med Sci 2010; 40 (4): 565-573.
-
Babacan-Gumus A, Bayram N, Can N, E. Kader. Premenstrual syndrome in university students: an investigation in terms of somatization and some variables. Anato J Psychiatry 2012;13:32-38.
-
Borenstein JE, Dean BB, Endicott J, Wong J, Brown C, Dickerson V, Yonkers KA. Health and economic impact of the premenstrual syndrome. J Reprod Med 2003;48:515-524.
-
Ozturk S, Tanr?verdi D. Premenstrual Syndrome and Management. Journal of Anatolia Nurs Health 2010;13:3:57-61.
-
Weisz G, Knaapen L. Diagnosing and treating premenstrual syndrome in five western nations. Soc Sci Med 2009;68:1498–1505.
-
K?sa S, Zeyneloglu S, Güler N. Prevalence of Premenstrual Syndrome among University Students and Affecting Factors. Gümü?hane Uni J Health Sci 2012;1(4):284-297.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License