IJCRR - 8(1), January, 2016
Pages: 06-08
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
PERCEPTION OF 2ND YEAR MBBS STUDENTS TOWARDS STUDENT- LED SEMINAR AS SMALL GROUP TEACHING METHOD
Author: Supriya Panda, D. Vijaya Bharathi, R. Sarath Babu, K. Bhaskar Rao
Category: Healthcare
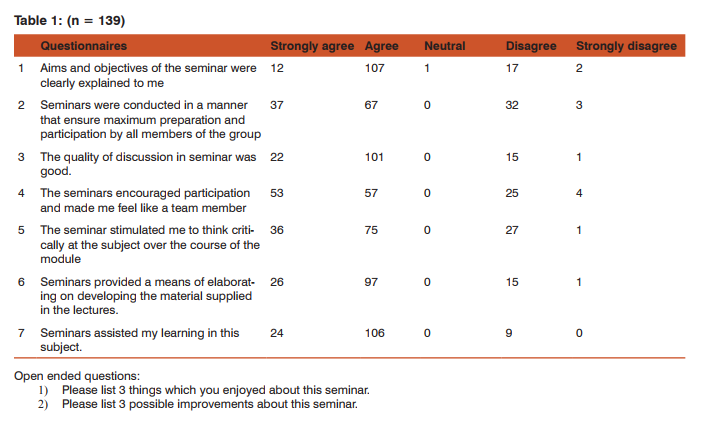
Abstract:Objectives: To introduce interactive teaching method like interactive student-led seminars and to know perception of students towards this method of teaching. Methods: The present batch of 4th semester undergraduate students (160 numbers) was divided into 4 batches of 40 students each after taking written consent from them. They were given the topics for the seminar 1 month prior for preparation. Seminar was conducted in four practical hours. Feedback forms were evaluated by 5-Likert's Scale. Results: Out of 160 students, 139 students participated in the seminar. Out of 139 students participated, 111 students (79.86%) agreed that it stimulated them to think critically at the subject, 130 students (93.53%) agreed that it assisted their learning and 110 students (79.14%) agreed that it encouraged their participation and made them feel like team members. Conclusions: Student-Led Seminar as small group teaching method is more effective in deep understanding of the subject and critical thinking than didactic lectures and helps the students to improve the communication skills.
Keywords: Small group teaching, Student-Led seminar, Perception
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION
In majority of the medical colleges in India theory classes are being taken by didactic lectures, which is a passive method of teaching. In this method, there is little retention of memory and student attention decreases after 20 minutes. Therefore, there is a need to introduce interactive teaching methods like interactive student-led seminars and small group discussions. In interactive student-led seminars, participants obtain increased understanding of the subject, develop greater ability to assemble and present information, welcome opportunities to think critically, become more articulate and speak better in public with increased confidence and are stimulated for self-learning(1,2).
AIMS AND OBJECTIVES: 1) To conduct student-led seminars for undergraduate students as interactive teaching in the department of Microbiology, MIMS, Vizianagaram. 2) To get the filled feedback form from the students to evaluate this method of teaching.
METHODOLOGY The present batch of 4 th semester undergraduate students (160 numbers) was divided into 4 batches of 40 students each after taking written consent from them. They were given the topics for the seminar 1 month prior for preparation. We have chosen the topic “Immunology “because it is a subject to understand by critical thinking and correlation. The students who presented the seminar were selected randomly. It was conducted during practical hours in batch-wise in the month of July 2015.Four practical hours (one hour per day and two hours per week) were utilized for the same. Feedback forms were given to the student immediately after completion of the seminar and were received from them after filling of the form. Sufficient time was given to fill up the forms. These were evaluated by 5 –Likert’s scale grading.
RESULTS Out of 160 students, 139 students participated in the seminar. The table number-1 shows the result of filled feedback forms received from the students. Out of 139 students participated, 111 students (79.86%) agreed that it stimulated them to think critically at the subject, 130 students (93.53%) agreed that it assisted their learning and 110 students (79.14%) agreed that it encouraged their participation and made them feel like team members. Fifty percent of the students did not respond to the open ended questions. Thirty one students have written there is better understanding of the subject, 22 students who were the presenters, have written there is improvement in communication skills and 9 students requested to conduct the seminars regularly. Improvement suggested by the students:
1) More students to be involved as presenters in the seminars.
2) Topic to be small and specific.
3) To increase the time allotted for each topic.
DISCUSSION In the present study, majority of the students agreed that interactive student-led seminars helped them to think critically with better understanding of the subject. The students, who presented seminar, felt that there is loss of stage fear with improvement in communication skill. K.G. Gomathi et al found that student led seminars encouraged students in self, active and peer-learning. Teamwork and communication skills were also learnt effectively (3). Zuzana de Jong et al. found that small group tutorial lead to greater satisfaction but better learning results were obtained with interactive seminars (4). In our study, majority of the students agreed that it made them feel like a team member. This is a good training for them as teamwork is being increasingly emphasized in healthcare and team training is now considered essential in medical education (5).
CONCLUSIONS: From the results obtained in the present study, it is concluded that:- 1) Seminar as small group teaching method is more effective in deep understanding of the subject and critical thinking than didactic lectures. 2) It helps the students to improve the communication skills.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT We acknowledge the immense help received from the scholars whose articles are cited and included in references of this manuscript. The authors are also grateful to authors / editors /publishers of all those articles, journals and books from where the literature for this article has been reviewed and discussed.
References:
1. Henry Walton (1997) Small group methods in medical teaching. Medical Education 31,pp459-464.
2. Mc Crorie P (2006) Teaching and leading small groups. Association for the study of medical education, Edinburgh.
3. Kadayam Guruswami Gomathi, Ishtiyaq Ahmed Shaafie and Manda Venkatramana1 Student-Led Seminars as a teaching-learning method- effectiveness of a modified format .South East Asian Journal of Medical Education.2014,Vol. 8 no. 1,pp 82.
4. Zuzana. de Jong, Jessica AB van Nies, Sonja WM Peters, Sylvia Vink, Friedo W Dekker and Albert Scherpbier. Interactive seminars or small group tutorials in preclinical medical education: results of a randomized controlled trial. BMC Medical Education. 2010, 10:79
5. Lerner, S., Magrane, D. and Friedman, E. (2009) Teaching Teamwork in Medical Education. Mount Sinai Journal of Medicine: A Journal of Translational and Personalized Medicine. 2009,76, 4, pp. 318-329.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License