IJCRR - 13(6), March, 2021
Pages: 167-171
Date of Publication: 20-Mar-2021
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
Upper Airway and its Association with Neck Circumference and Hyoid Position in OSA Subjects - A Cephalometric Study
Author: Parvathy Ghosh, N. K. Sapna Varma, V. V. Ajith, Anand Suresh
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:ntroduction: Obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) is a common disorder characterized by recurrent pharyngeal obstruction during sleep. Upper airway anatomy plays a major role in pathogenesis of OSA. Neck obesity as measured by neck circumference and position of hyoid are independently associated with OSA severity, but their relation with anatomical variables and pharyngeal collapsibility is less well known. Objective: To determine the association of upper airway collapsibility with hyoid position and neck circumference among OSA patients. Methods: Records of polysomnography diagnosed 40 OSA patients satisfying the inclusion criteria were selected. Lateral cephalograms were recorded at natural head position. Upper airway variables measured are superior pharyngeal airway space (SPAS), middle pharyngeal airway space (MPAS), inferior pharyngeal airway space (IPAS) and length of soft palate. Hyoid posi�tion was assessed by the distance from hyoid to mandibular plane and hyoid to C3 vertebrae. Neck circumference (cm) was measured for all subjects at the level of cricothyroid membrane. Results: Inferiorly positioned hyoid bone, increased length of soft palate and larger neck circumference showed statistically significant correlation with increased upper airway collapsibility among OSA patients (P< 0.05). Conclusion: As the study shows the association of upper airway collapsibility with neck obesity and hyoid position, during routine clinical and radiographic examination larger neck circumference, inferiorly displaced hyoid and increased length of soft palate helps in identifying high risk candidates for OSA.
Keywords: Airway space, Apnea hypopnea index, Body mass index, Cephalometry, Neck circumference, Obstructive sleep apnea
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION
Obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) occurs as a result of intermittent reduction or complete pause in breathing due to constriction of upper airway during sleep leading to excessive daytime sleepiness (ESS).1 It is often associated with obesity, hypertension, type II diabetes mellitus, cardiovascular diseases resulting in reduced quality of life and increased risk for road traffic and workstation accidents.2,3 Both anatomical and functional abnormalities of the upper airway contributes to compromised airway space and thus increases upper airway collapsibility during sleep. Although changes in ventilatory and neuromuscular control mechanisms can result in the reduced airway patency, anatomical factors play an essential role in the development of OSA.4
Polysomnography (PSG) is regarded as the gold standard in diagnosing OSA,5 but it does not explain the structural flaws in an individual. Upper airway imaging techniques like Computed tomography, Magnetic resonance imaging, lateral cephalograms have provided significant insights regarding the pathogenesis of OSA. Lateral cephalometric radiographs which is more economical method can be used as a primary screening tool for studying the upper airway obstruction, tongue and hyoid positioning caused by skeletal and soft tissue abnormalities.6
Obesity is regarded as one of the major risk factor for the occurrence and progression of OSA and a number of parameters such as altered body mass index (BMI), neck as well as waist circumference, and waist to hip ratio (WHR) are all considered as risk factors for OSA7.Neck circumference (NC) is a strong predictor of OSA,8 and the differences in the severity of OSA explained by central obesity also depends on the variation in the NC. Obesity and craniofacial abnormalities have shown to account for more than two-thirds of the variations in the Apnea-Hypopnea (AHI) score.9 In the majority of the diagnosed patients, the association with anatomic factors together with other symptoms are the main contributing factors for the development of OSA. Although Neck circumference and hyoid bone position are known to be related to the severity of OSA, the correlation between this pharyngeal collapsibility and anatomical variables is less studied. Thus this study aimed to establish any correlation between neck circumference and hyoid position on upper airway collapsibility among OSA patients.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Records of 40 PSG diagnosed OSA patients (males=30 & females=10) aged above 20 years satisfying the inclusion criteria were selected from the Department of Orthodontics, Amrita School of Dentistry, Kochi, Kerala. The study protocol was evaluated and accepted by the institutional review board (IRB-AIMS-2020-113) at Amrita Institute of Medical Sciences, Kochi, Kerala. All the included subjects had undergone Overnight PSG using a home sleep test using Philips Respironics AliceNight machine. An experienced laboratory technician recorded the sleep data according to the standard criteria. Apnea and hypopnea were described according to the Chicago criteria as proposed by the American Academy of Sleep Medicine.6 Inclusion criteria were patients with AHI >15 indicating moderate to severe OSA (Apnea-Hypopnea Index, AHI) and exclusion criteria were those with severe periodontal disease, edentulous arch, pathologic airway obstruction, TMJ disorders.
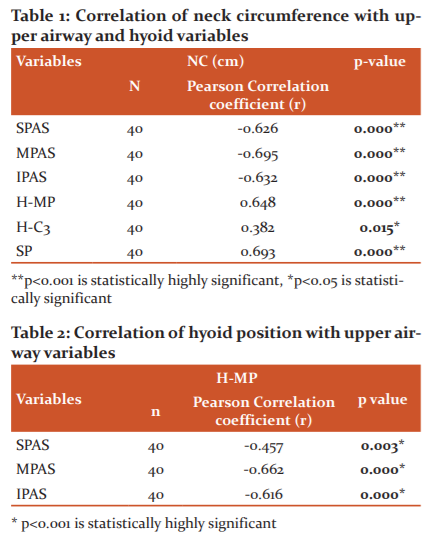
Neck circumference (cm) were measured for all subjects at the level of cricothyroid membrane (Figure 1).7 In obesity, NC will be >34cm for females and >37cm for males. Lateral cephalograms were recorded at the natural head position with voluntary relaxed lip position and with teeth in maximum intercuspation. All radiographs were recorded with the same machine, Cranes D X-ray digital unit, version 3 (Soredex Co., Tuusula, Finland) and hand traced on matte acetate by one investigator to eliminate any inter-examiner variability The airway was analysed as described by Battagel et al.10 Upper airway and hyoid position variables shown in Figure 2.
Superior pharyngeal airway space (SPAS) - measured from the point midway between posterior nasal spine to tip of the soft palate (PNS-P) parallel to the line that intersects the gonion and B point and it represents the distance between the dorsal surface of the soft palate and the posterior pharyngeal wall.
Middle pharyngeal airway space (MPAS)- measured through the posterior tip of the soft palate (P), parallel to the line that intersects B point and gonion and it represents the distance between the dorsal surface of the base of the tongue and the posterior pharyngeal wall.
Inferior pharyngeal airway space (IPAS) - measured on the line that intersects gonion and B point and represents the distance between the dorsal surface of the base of the tongue and the posterior pharyngeal wall.
Length of the soft palate (P-PNS) - measured by the length of the line that connects the tip of the soft palate with the posterior nasal spine.
-
H-C3- Distance of hyoid to C3 vertebrae
-
H- MP- Distance of hyoid perpendicular to mandibular plane
Statistical analysis
This was performed using IBM SPSS 20 (SPSS Inc, Chicago, USA). To determine the relationship between neck circumference and hyoid position variables Pearson correlation coefficient test was used. p-value < 0.05 was considered statistically significant. Ethical Clearance Number: IRB-AIMS-2020-113.
RESULTS
40 PSG diagnosed OSA patients were included in the study.
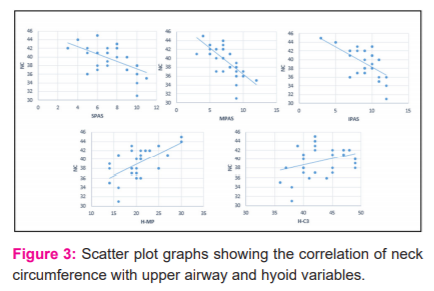
Correlation between neck circumference with upper airway and hyoid variables. Neck circumference shows a negative moderate degree of correlation correlated with superior airway space (r= -0.62), middle airway space (r= -0.69), inferior airway space (r= -0.63) and was statistically highly significant (p<0.001). Neck circumference was positively correlated with length of the soft palate (r= 0.69), distance from hyoid to the mandibular plane (r=0.64) and distance from hyoid to c3 vertebrae (r=0.38) and was statistically significant (p<0.05, Table 1 & Figure 3).
Correlation between upper airway and hyoid position. Distance from hyoid to the mandibular plane was negatively correlated with superior airway(r= -0.45), middle airway (r= -0.66), inferior airway space (r= -0.61) and was statistically significant (p<0.001). Distance from hyoid to C3 was negatively correlated with superior airway (r= -0.48), middle airway (r= -0.14) and inferior way space (r= -0.08) but was statistically not significant with middle and inferior airway space (Tables 2 and 3).
Correlation between length of the soft palate and upper airway. The length of the soft palate showed a negative correlation with superior airway (r= -0.34), middle airway space (r= -0.51) and inferior airway (r=-0.29) but was statistically significant only with upper and middle pharyngeal airway space (Table 4).
DISCUSSION
Undiagnosed OSA remains a major public health concern. Globally, the different population studies have estimated the prevalence of OSA to be 0.3-5.1%.11 More than 80% of moderate to severe OSA remain undiagnosed despite having adequate health care access. Limited availability of in-lab PSG’s, high cost, time and labour-consuming procedures are its main drawbacks. Therefore, more attention should be directed towards identifying high-risk subjects for OSA through routine clinical and radiographic examination.
The different risk factors for developing OSA include altered BMI, increased neck circumference, waist circumference and waist-hip ratio. Craniofacial morphology is also increasingly accepted as a critical component for OSA pathogenesis.12 As cephalometric analysis allows quantitative assessment of craniofacial morphology several variables are allied with the development and progression of OSA. These include inferiorly positioned hyoid bone, an enlarged tongue and soft palate, a smaller cross-sectional of the velopharyngeal area and a more posteriorly placed maxilla and mandible.13,14 Even though advanced technologies like Computed tomography, Magnetic resonance imaging are available, lateral cephalometry is more preferred as it is less expensive, minimal radiation exposure, easy to access, and non-invasive nature but the main disadvantage being it produces a two-dimensional image of the three-dimensional space.
In this study upper airway dimensions like superior pharyngeal, middle pharyngeal and inferior pharyngeal airway showed a negative correlation with neck circumference, length of the soft palate and hyoid position. That is with increasing neck circumference, the upper airway narrowed resulting in severe forms of OSA. Also, when the length of the soft palate and distance of the hyoid to the mandibular plane increased resulted in the narrowing of the upper airway dimension. The associations between neck circumference and hyoid position with pharyngeal collapse have been controversial.15 Hyoid bone position is significantly important. According to the American Thoracic Society,16 in healthy individuals, the hyoid bone position is found at the C3-C4 cervical vertebrae, while in OSA patients it is usually at the C4-C6 level. Riha et al,17 Chang et al18 also reported inferior positioning of the hyoid bone in OSA subjects. As tongue muscles are attached to the hyoid bone, it causes an inferior displacement of the hyoid due to the increased fat accumulation in the neck region (increased NC) or can be due to macroglossia resulting in posterior displacement of the tongue reducing upper airway patency. This intensifies the risk of developing more severe grades of OSA. Ono et al19 also found a significant positive correlation between NC and hyoid to C3 vertebrae in OSA subjects, which was similar to this study.
The OSA subjects in this study had considerably longer soft palates, which occupied the majority of the space in the oropharyngeal area leading to airway constriction. This was in agreement with Malhotra et al,20 who first described that pharyngeal length will increase upper airway collapsibility using a finite element airway model. NC is a more effective factor in determining OSA. Obesity in the upper pharyngeal region is reflected by neck circumference, which modifies the dimension of the upper airway due to fat deposition around the neck region.8 Ferguson et al21 stated that subjects who were diagnosed with OSA had a larger neck compared with non-OSA subjects. Onat et al22 found that NC was a marker of central obesity and found that NC (Neck circumference) is greater among men than women. OSA is manifested during sleep as the repetitive collapse of the upper airway that occurs due to reduced tone of the airway dilator muscle. Increased NC may alter the normal upper airway mechanism and in different ways influence the pathophysiology of OSA. Fat deposition around the parapharyngeal area could result in reduced competence and change the shape of the upper airway leading to its increased collapsibility.23 Obesity is also coupled with the reduction in lung volumes, especially it affects the functional residual capacity, leading to reduced tracheal tug, constriction of upper airway size and causing increased airflow resistance. Thus, cephalometric analysis together with clinical parameters is highly recommended as one of the most important screening tools in diagnosing and treatment planning for OSA patients.24
CONCLUSION
In this study, upper airway collapsibility was strongly associated with increased neck circumference, increased length of the soft palate and inferior displacement of the hyoid bone. Thus patients should be screened carefully before referring them for expensive investigations such as overnight polysomnography. Despite the limitation of evaluating the airway which is a three-dimensional space using two-dimensional lateral cephalometric technique, it adequately reveals the anatomy of the head and neck region as well as the morphology of the upper airway which can be accurately interpreted by an experienced professional as a primary screening tool. Therefore, routine clinical and radiographic examinations can help in identifying high-risk subjects for OSA.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The support of all staffs and colleagues of the Department of Orthodontics and Department of Public Health Dentistry, Amrita School of Dentistry is gratefully acknowledged. The authors also acknowledge the immense help received from the scholars whose articles are cited and included in references to this manuscript. The authors are also grateful to authors/editors / publishers of all those articles, journals and books from where the literature for this article has been reviewed and discussed.
Conflicts of interest: Nil
Source of funding: Nil
Author Contributions
1. Dr Parvathy Ghosh- Concept, design, Definition of intellectual content, literature search, data collection, data analysis, manuscript preparation, Manuscript editing, Guarantor.
2. Dr N.K Sapna Varma- Concept, Definition of intellectual content, design, data analysis, manuscript review, Guarantor.
3. Dr V.V Ajith- Concept, design, Definition of intellectual content, manuscript review.
4. Anand Suresh- Literature search, data collection, manuscript editing.
References:
-
Sharma S, Lakshmy R, Agrawal S, Sreenivas V. Prevalence of metabolic syndrome in a north Indian hospital-based population with obstructive sleep apnoea. Indian J Med Res 2011;134(5):639.
-
Pharm LV, Schwartz AR. The pathogenesis of obstructive sleep apnea. J Thorac Dis 2015;7(8):1358-1372.
-
Desai J, Porwal AR, Mane UT, Thorat RS, Mane RA. Prevalence of Obstructive Airway Disease in Patients with Ischemic Heart Disease and Hypertension. Int J Curr Res Rev 2020;12(17):76-83.
-
Schwab RJ, Pasirstein M, Pierson R, Mackley A, Hachadoorian R, Arens R et al. Identification of upper airway anatomic risk factors for obstructive sleep apnea with volumetric magnetic resonance imaging. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2003;168(5):522–30.
-
Health Quality Ontario HQ. Polysomnography in patients with obstructive sleep apnea: an evidence-based analysis. Ontario health technology assessment series 2006;6(13):1-38.
-
Baik UB, Suzuki M, Ikeda K, Sugawara J, Mitani H. Relationship between cephalometric characteristics and obstructive sites in obstructive sleep apnea syndrome. Angle Orthod 2002;72(2):124?34.
-
American Academy of Sleep Medicine Task Force. Sleep-related breathing disorders in adults: recommendation for syndrome definition and measurement techniques in clinical research. Sleep 1999;22(5):667-89.
-
Davies RJ, Stradling JR. The relationship between neck circumference, radiographic pharyngeal anatomy, and the obstructive sleep apnoea syndrome. Eur Respir J 1990;3(5):509–514.
-
Kawaguchi Y , Fukumoto S, Inaba M, Koyama H, Shoji T, Shoji S et al. Different Impacts of Neck Circumference and Visceral Obesity on the Severity of Obstructive Sleep Apnea Syndrome. Obesity 2011;19(2):276–282.
-
Battagel J, Johal A, Kotecha B. A cephalometric comparison of subjects with snoring and obstructive sleep apnoea. Eur J Orthod 2000;22(4):353–365.
-
Reddy E V, Kadhiravan T, Mishra HK, Sreenivas V, Handa KK, Sinha S. Prevalence and risk factors of obstructive sleep apnea among middle-aged urban Indians: A community-based study. Sleep Med 2009;10(8):913–918.
-
Sutherland K, Lee RWW, Cistulli PA. Obesity and craniofacial structure as risk factors for obstructive sleep apnoea: Impact of ethnicity. Respirology 2012;17(2):213–222.
-
Maltais F, Carrier G, Cormier Y, Series F. Cephalometric measurements in snorers, non-snorers, and patients with sleep apnea. Thorax 1991;46(6):419–423.
-
Cilil VR, Sapana Varma NK, Gopinath S, Ajith VV. Efficacy of custom made oral appliance for the treatment of obstructive sleep apnea. Contemp Clin Dent 2015;6(3):341-347.
-
Sforza E, Bacon W, Weiss T, Thibault A, Petiau C, Krieger J. Upper airway collapsibility and cephalometric variables in patients with obstructive sleep apnea. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2000;161(2):347–352.
-
American Thoracic Society. Standards and indications for cardiopulmonary sleep studies in children. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 1996;153(2):866-877.
-
Riha RL, Brander P, Vennelle M, Douglas NJ. A cephalometric comparison of patients with sleep apnea/hypopnea syndrome and their siblings. Sleep 2005;28(3):315–320.
-
Chang E, Shiao G. Craniofacial abnormalities in Chinese patients with obstructive and positional sleep apnoea. Sleep Med 2008;9(4): 403–410.
-
Ono T, Lowe A, Ferguson K, Pae E, Fleetham J. The effect of the tongue retaining device on awake genioglossus muscle activity in patients with obstructive sleep apnea. Am J Orthod Dentofac Orthop 1996;110(1): 28–35.
-
Malhotra A, Huang YQ, Fogel RB, Pillar G, Edwards JK, Kikinis R, et al. The male predisposition to pharyngeal collapse. Importance of airway length. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2002;166(10):1388–1395.
-
Ferguson K, Ono T, Louise A, Rayan F, Fleetham J. The relationship between obesity and craniofacial structure in obstructive sleep apnea. Chest 1995;108(2): 375–381.
-
Onat A, Hergenç G, Yüksel H, Can G, Ayhan E, Kaya Z, et al. Neck circumference as a measure of central obesity: associations with metabolic syndrome and obstructive sleep apnea syndrome beyond waist circumference. Clin Nutr 2009;28(1):46–51
-
Schwartz AR, Patil SP, Squier S. Obesity and upper airway control during sleep. J Appl Physiol 2010;108(2):430-435.
-
Tangugsorn V, Krogstad O, Espeland L, Lyberg T. Obstructive sleep apnoea: multiple comparisons of cephalometric variables of obese and non-obese patients. J Craniomaxillofac Surg 2000;28(4):204–212.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License