IJCRR - 13(6), March, 2021
Pages: 156-160
Date of Publication: 20-Mar-2021
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
Detection of Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome using Convolutional Neural Networks
Author: Vikas B, Radhika Y, Vineesha K
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Introduction: Deep Learning is a rapidly growing technology that can find practical approaches to problems in various fields. Deep learning is assisting healthcare professionals and researchers to identify the hidden opportunities in data thereby serv�ing the medical sector better. It also assists doctors to analyze any kind of disorders precisely and helps them to medicate the patients better, thus resulting in better medical decisions. Medical illness such as Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome (PCOS) does not have an effective diagnosis and proper treatment options. It is a prevalent endocrine disorder, which leads to the growth of ovarian cysts in child-bearing women, which further leads to infertility. Objective: To assist in the diagnosis of PCOS, deep learning methods such as Convolutional Neural Networks can be applied which produce effective results in image classification tasks. Methods: In this present study, an attempt has been made to compare the accuracies and other performance metrics of prior mentioned deep learning methods, and the problem of Over-fitting is discussed. Results and Conclusion: The main motto of using these deep learning methods is to precisely prognosticate whether a person is expected to have PCOS or not.
Keywords: Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN), Data Augmentation, Deep Learning, Over-fitting, Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome (PCOS), Transfer Learning
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION
Fertility is the most important reason which affects the uprightness of a household while infertility is a complication that occurs in the reproduction system of women or men. Polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS) is a heterogeneous endocrinal disorder that affects most women of their reproductive age. The first recognition of an association between the presence of polycystic ovaries and signs of hirsutism and amenorrhea was by Stein and Leventhal.1 It causes a wide range of symptoms such as an increase in weight, growth of ovarian cysts, ovulation disorders, acne, facial hair, depression, anxiety2 and heavy menstrual periods, and it may take years for women to get diagnosed. Almost 5-10% of women in their childbearing age are affected by this abnormality.3 Moreover, current studies have shown that women have high risk of miscarriage in their first trimester. Women with PCOS may develop sleep apnea.4 The treatments for PCOS comprises of changing lifestyle, usage of birth control pills to avoid irregular periods and the usage of drugs like Metformin and anti-androgens.5 Also 6% to 10% of women worldwide, generally those between the ages of 18 to 44 are affected with PCOS.
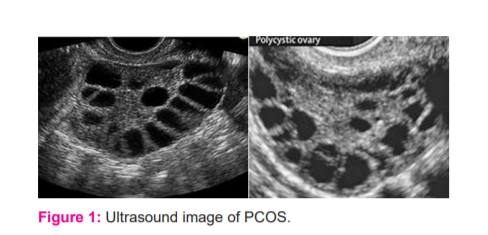
As stated in the Rotterdam conference,1 a woman has PCOS if she is said to possess two of the three symptoms: (1) ovulation failure, (2) higher androgen levels, or (3) the presence of polycystic ovaries. As in structure, when one or both the ovaries contain 12 or more follicles of diameter 2-9 mm, or when the ovarian size exceeds 10 cm3 it can be said that polycystic ovaries are present2 and a woman is said to be infected with this disorder. So, to precisely predict this syndrome the doctor manually examines the Ultrasound image of PCOS as shown in figure 1 by counting the number and size of follicles in the ovaries. Moreover, this investigation takes plenty amount of time and needs very high accuracy to detect whether the patient has polycystic ovarian syndrome or not.
Despite the gravity of conditions and available choices of medication, there are very little options to treat this disorder. So, it is very important to provide awareness among patients about this ovarian dysfunction at an early stage to prevent any consequences because it is the main cause of infertility and no cure has been discovered yet.
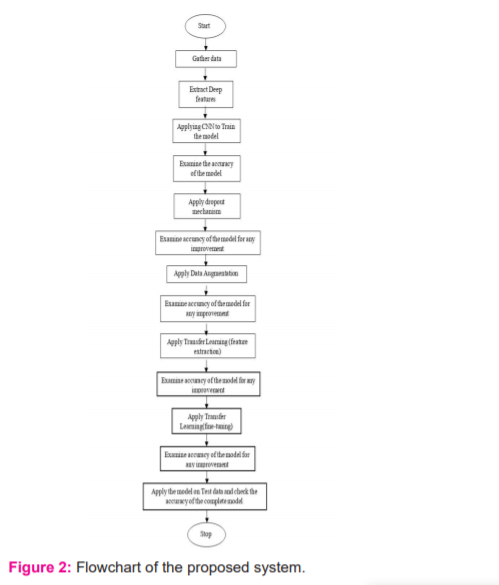
Convolutional Neural Networks has been considered as the best approach for the classification of images.6 In previous studies, some systems classify the ultrasound image by using many methods. But still, all the approaches manually extract features from an ultrasound image. The present study aims to compare the performance of popular deep learning techniques. The flowchart of the proposed system is shown in figure 2. Firstly, CNN is used to train the model and then by applying the regularization method, the importance of drop out mechanisms is shown. Then, data augmentation is another technique that is applied to the CNN model. The dataset used in this paper is the Ultrasound images of PCOS, which is very confidential and has privacy issues and around 100 images of PCOS affected and another 100 images of Non-PCOS images have been gathered and are separated as train, validation and test sets and then data augmentation has been applied only to the train set to increase the effectiveness of the data. Finally, by using the VGG-16 model, the Transfer Learning technique is applied which produced results with improved accuracy without over-fitting when compared to the basic CNN model.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
The retrieved PCOS dataset is given as input and the class label is set appropriately. Next, the most popular deep learning method Convolutional Neural Network is applied to the collected dataset. Then accuracy measures of the implemented technique were examined and later checked whether the model is overfitting or not. The dataset collected is very small, so, Data Augmentation technique is applied to the dataset to multiply data’s effectiveness and improve the accuracy of the data. Later the model is checked for overfitting. Then finally Transfer Learning, which is another deep learning method is implemented where a model that is built and trained for a particular task is re-used on a similar task to improve the optimization performance of the model. Transfer Learning is applied when there exists a new dataset smaller than the original dataset which is used to train the pre-trained model. Finally, after implementing both the mentioned deep learning methods, accuracies of the models are checked and compared and then the model is tested on the test dataset which predicts whether the image is PCOS or Non-PCOS. In this project, 50 per cent of the data is taken for training, 25 per cent of the data for validation and 25 per cent of the data for testing the model. The entire process is shown in figure 2.
CONVOLUTIONAL NEURAL NETWORKS
Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN) has achieved great success in recent years. CNN is composed of an input layer, multiple hidden layers and an output layer. The hidden layers of CNN include convolutional layers, pooling layers, fully connected layers and normalization layers (RELU). In the proposed architecture, a three-layered CNN model is designed, combined with a max pooling layer, to extract the features from the acquired dataset and to downsample the output of feature maps from the convolutional layer.
The output from the third convolution layer is 128 of the 17 x 17 feature maps. So, a flatten layer is used to flatten this obtained output. This is then passed to the dense layers to obtain the final prediction of whether the image is PCOS (1) or non-PCOS (0). All of this comes under the model training process, and the model is trained using the fit() function. The train set consisting of 100 images i.e., 50 images of PCOS and non-PCOS each is trained over a total of 25 epochs and validated simultaneously on the validation set which consists of 50 images i.e., 25 images of PCOS and non-PCOS each.
From the basic CNN performance, it is understood that the model started to overfit after 2-3 epochs. The reason for the overfitting of the model is the dataset acquired contains fewer training data, so the model keeps on seeing the same images overtime during each epoch. So, the basic CNN model is enhanced by including one more convolution layer, and a dense hidden layer. Apart from these, a dropout of 0.2 is included after every hidden dense layer to implement regularization. Dropout is a very powerful mechanism that is used for regularization in deep neural networks. It is applied to input layers and hidden layers separately. Generally, dropout hides the outputs by a fraction of units from a layer by making their output zero (in this case, it is 20% of the units in the dense layers). From the CNN Regularization performance, it is observed that over-fitting has been gradually reduced and, the accuracy was around 88%.
DATA AUGMENTATION
When a machine learning model is trained, parameters of the model are adjusted so that they map a specific input (an image) to a specific output (a label). The main aim is to build an effective model where the loss of the model is low, this takes place only when the parameters are adjusted in the right way.7 When there are a lot of parameters, the machine learning model also needs a greater number of examples, so that the model can perform well.
Also, the number of parameters required corresponds to the complexity of the task the machine learning model must carry out. Sometimes things might still go wrong even if we have the right sized training set. An important point to remember is algorithms will not think like humans: while humans are capable of classifying images based on a natural understanding. If a user creates a model that identifies cats/dogs and nearly all the training images of dogs consists of snowy surroundings, then the algorithm might learn the wrong rules. So, having images from different viewpoints and with different conditions is very important. So, to get more data, it is necessary to augment the dataset: to make it more effective without collecting more training data. It means, users just need to make minor changes to the existing dataset such as flips, translations and rotations which is termed as Data Augmentation. The neural network would think that these are different images.
Dataset augmentation can multiply the data’s effectiveness. Data augmentation is the process of increasing the amount and diversity of data. New data need not be collected; rather the already existing data can be transformed. By carrying out augmentation, the neural network can be avoided from learning irrelevant patterns, essentially boosting overall performance. There are various ways to transform and augment the image data. The most used operations are7-
-
Rotation- image is rotated in random directions.
-
Shifting- an image is shifted to left or right, and the translation range is specified manually to alter the location of the image.
-
Cropping- part of the original image is cropped and resized to a specific resolution.
-
Flipping- the image is flipped in the horizontal direction.
-
Changing the brightness level- images are randomly darkened and brightened.
The images in figure 3 obtained from data augmentation operations mentioned above
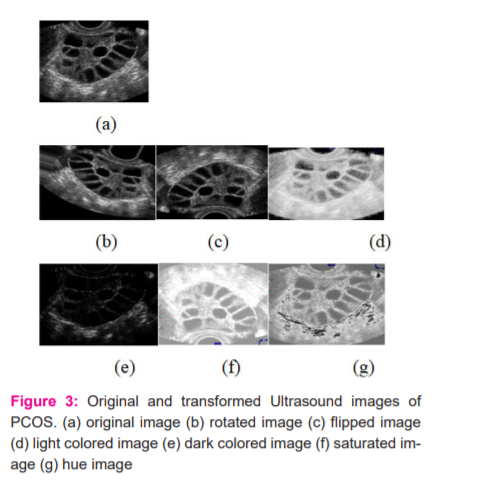
Now the regularized CNN model is enhanced by including more data by using the above-listed data augmentation methods. From its performance, over-fitting has been gradually reducing and, the accuracy was around 91% which is better than the previous models.
TRANSFER LEARNING
Transfer Learning is a deep learning method where a model that is built and trained for a particular task is then re-used on a similar task to improve the optimization performance of the model.8 Transfer Learning is applied when there exists a new dataset smaller than the original dataset which is used to train the pre-trained model.9 Pre-trained models can be used in two ways whenever a new model is developed, or a model is being re-used:
-
By making use of a pre-trained model to extract features.
-
By fine-tuning the pre-trained model.
In this work, the proposed system uses a model VGG-16 (Visual Geometry Group from Oxford) which was previously trained on a base dataset (ImageNet) and is currently being reused for a similar task to learn features (or transfer them), to be trained on a new dataset which consists of ultrasound images of PCOS and non-PCOS
VGG-16 Pre-trained Model
The VGG-16 model comprises 16 layers (convolution and fully connected) that are set up on the ImageNet database, developed for image recognition and classification tasks. This model was developed by Karen Simonyan and Andrew Zisserman.10
From the figure 4, it can be observed that the model consists of 13 convolution layers applying 3 x 3 convolution filters combined with max-pooling layers for downsampling. There are two fully connected hidden layers of 4096 units in both the layers and a dense layer of 1000 units. Here each unit indicates one of the image categories in the ImageNet database.
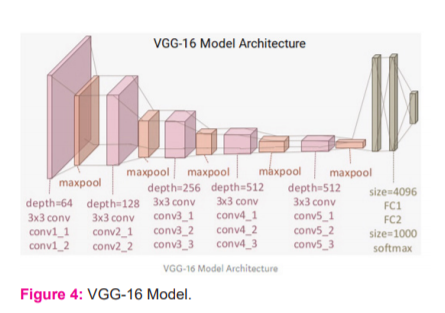
In the proposed system the last three layers are not needed since we will be using our own fully connected dense layers to predict whether the image will be a PCOS affected or a non-PCOS image.
VGG-16 as a Feature Extractor
In this method, as shown in figure 5 the five convolution blocks in the VGG-16 model are frozen so that their weights will not be updated after every epoch. The last activation feature map in the VGG-16 model i.e., the output from block5 pool gives us the bottleneck features, which are flattened and passed as an input to the fully connected layers.
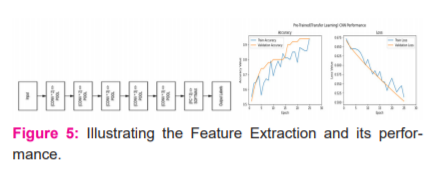
In this work bottleneck feature vectors of size 8192 is passed as input to the classification model. The same model which has been developed previously is used here regarding the dense layers and a dropout of 0.1 is added after every dense layer and the model has trained over 25 epochs. From the graph in Figure 5, it can be observed that the model’s validation accuracy is close to 94%, which is almost a 2-3% improvement from the basic CNN model with image augmentation, which is excellent. The model is not overfitting. This is the best model so far.
VGG-16 with Fine-tuning and Image Augmentation
In this method, the last two blocks of the VGG-16 model i.e., Block 4 and Block 5 are set to unfreeze so that their weights get updated in every epoch (per batch of data) as the model is trained.
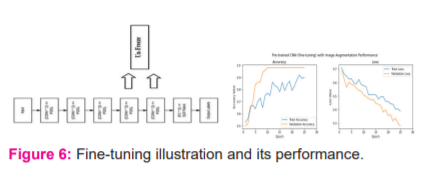
From figure 6, blocks 4 and 5 are set to unfreeze and, they are now trainable. It means in every epoch; the weights of these layers will get updated with backpropagation as each batch of data is passed. Here there is no need to extract the bottleneck features because training is done on data generators; hence, the VGG model is passed as object as an input to the model and dropout of 0.2 is added after each dense layer and then the model is trained over 25 epochs.
From the graph in figure 6 the model’s validation accuracy is around 98%, which gave 4% enhancement from the previous model. Altogether, this model has gained a 10% improvement in validation accuracy from the first basic CNN model implemented in this work. This indicates that transfer learning can be very useful. The model’s performance is excellent here.
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
This work deals with the application of three deep learning methods on the obtained data set. Models built were evaluated by testing them on the test set. The performance of the model from the three selected techniques namely Convolutional Neural Networks, Data Augmentation and Transfer Learning after testing are shown below.
Based on the various model performance metrics mentioned in the below-mentioned table, it can be observed that the models have provided improved results in each case. Each successive model performed better than the previous model since each of the models consists of advanced techniques. The best model is transfer learning with fine-tuning as well as image augmentation, which provided a model accuracy and F1-score of 98% and this model showed an improvement of 10% from the basic CNN model as shown in below Table 1.

a) CNN with Regularization, b) CNN with Data Augmentation, c) Transfer Learning Feature Extraction, d) Transfer Learning Fine-tuning with Data Augmentation
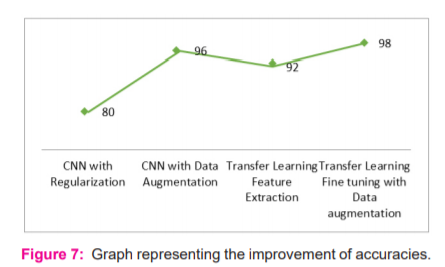
From the above figure, when data is limited the best results can be obtained by data augmentation and transfer learning. Also, the issue of overfitting can be resolved with this approach. In this dataset where the data is very less, transfer learning on such augmented data helped in getting a better accuracy, 98%.
CONCLUSION
In this work, Deep Learning methods were selected to assess the performance of a deep neural network in terms of performance metrics such as accuracy, precision, recall and F1-score to classify whether a particular patient is suffering from PCOS or not. Deep Learning techniques were considered in this study as it assists doctors to analyze any kind of disorders precisely and helps them to medicate the patients better, thus resulting in better medical decisions. The dataset used in this study is the ultrasound images of PCOS and NON_PCOS collected from Kaggle and various other resources. It has also been noticed that all the opted techniques show near about accuracies, allowing the user to select any of the methods. By summing up the information to these deep learning techniques, doctors can predict whether a particular patient is susceptible to the syndrome and helps in curing PCOS by seeking medical help and switching to a healthier lifestyle.
Conflict of Interest: Nil.
Funding: Nil.
Acknowledgements: We would like to pay our heartfelt gratitude to Dr. Vijaya Lakshmi Chandrasekhar, Department of Obst. & Gyn., GIMSR, GITAM (Deemed to be University), Visakhapatnam for her generosity in accumulating the data and apprising us about the relationships among various symptoms.
References:
-
Dewi RM, Wisesty AU, Jondri N. Classification of polycystic ovary based on ultrasound images using competitive neural network. J Physics 2018;971:012005.
-
The Rotterdam ESHRE/ASRM?sponsored PCOS consensus workshop group. Revised 2003 consensus on diagnostic criteria and long?term health risks related to polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS). Human Reprod 2004;19(1):41–47.
-
Trivax B, Azziz R. Diagnosis of polycystic ovary syndrome. Clin Obstet Gynecol 2007;50(1):168-177.
-
Does PCOS Put Women at Risk for Other Health Problems.
http://totalpregnancycare.com/pre-conception/polycystic-ovariansyndrome/doespcos-put-women-at-risk-for-other-health-problems/
-
Polycystic ovary syndrome. http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Polycystic_ovary_syndrome
-
Wisesty UN, Nasri J, Adiwijaya. Modified Backpropagation Algorithm for Polycystic Ovary Syndrome Detection Based on Ultrasound Images. International Conference on Soft Computing and Data Mining 2016;141-151.
-
Connor S, Taghi M. Khoshgoftaar, A survey on Image Data Augmentation for Deep Learning, J Big Data 2019;6(60):1-48.
-
Yuqing G, Khalid M. Deep Transfer Learning for Image-Based Structural Damage Recognition. Computer-Aided Civil Infrastruc Engi 2018; 33(9): 748-768.
-
Larsen-Freeman D. Transfer of Learning Transformed. Language Learning 2013;63:107-129.
-
Simonyan K, Zisserman A. Very Deep Convolutional Networks for Large-Scale Image Recognition. 2014 arXiv:1409.1556v6.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License