IJCRR - 13(6), March, 2021
Pages: 138-142
Date of Publication: 20-Mar-2021
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
Correlation between Diabetic Retinopathy and Cognitive Impairment in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes
Author: SG Mathupriya, V Panimalar A Veeramani, Divya N, Bindu Bhaskaran
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Introduction: Diabetes Mellitus is a metabolic disease that can cause various complications. Increased duration of diabetes and poorer glycemic control paved way for the development of diabetic retinopathy and cognitive impairment. It became a medical and social challenge to prevent the disease in advance. Objectives: Type 2 Diabetes has become one of the major causes of morbidity worldwide. Many studies reveal that retinal microvascular diseases and diabetic retinopathy are associated with cognitive function. In this study, the severity of diabetic retinopathy is correlated with cognitive function in patients with type 2 Diabetes. Methods: A hundred patients with type 2 diabetes attending the outpatient department in a tertiary care centre were included in the study. Diabetic retinopathy was classified using the Early Treatment Diabetic Retinopathy Study classification. Patients were interviewed using three cognitive tests, Montreal Cognitive Assessment, Mini-Mental State Examination, Mini-cog and the cognitive function was assessed. HbA1c was checked on the day of administering cognitive tests and the values were noted. Results: Out of a hundred patients involved in the study, 75% of patients with diabetic retinopathy have cognitive impairment. The mean score of the more sensitive cognitive test Montreal Cognitive Assessment (MoCA), in mild and moderate Non-Prolif�erative Diabetic Retinopathy (NPDR) [23.42 \? 2.45] is lower when compared to severe Non-Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy (NPDR) and Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy (PDR) [25.34 \? 2.43]. HbA1c of patients with cognitive impairment [11.79 \?1.85] is higher than patients without cognitive impairment [7.87\?1.65]. Conclusion: Patients with diabetic retinopathy have more cognitive impairment than with no diabetic retinopathy. On comparing the grades of diabetic retinopathy, mild and moderate Non-Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy have more cognitive impairment than severe Non-Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy and Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy. Yet it cannot be proved insight be�cause the minimum number of patients with severe Non-Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy and Proliferative Diabetic Retinopa�thy was involved in the study.
Keywords: Cognitive function, Early Treatment Diabetic Retinopathy Study classification, Mini-cog, Mini-Mental State Examination, Montreal cognitive assessment, HbA1c
Full Text:
Introduction
The incidence of type 2 diabetes is increasing worldwide and became a leading cause of morbidity and mortality.1 Diabetic retinopathy is an important ocular neurovascular complication that was the leading cause of blindness 2 decades back.2,3 Diabetes is associated with an increased risk of cognitive decline and an independent risk factor for the development of Alzheimer disease. Even mild cognitive impairment may lead to the development of dementia and Alzheimer disease.4 This mild cognitive impairment might hamper everyday activities depending on the work and situation, which requires various cognitive domains such as general intelligence, processing speed, psychomotor efficiency, attention, perception, learning, memory, and executive functions. Retinal and cerebral small vessels have similar embryological origin, anatomy and physiological characteristics.5 Hence retinal microvascular abnormalities have been associated with cognitive impairment, possibly serving as a marker of cerebral small vessel disease. Therefore the purpose of this study is to find the association between diabetic retinopathy and cognition impairment in patients with type 2 diabetes. This could be useful for identifying patients with risk of dementia and Alzheimer disease and for the development of preventive measures in diabetic patients.
Materials and method
This is a hospital-based descriptive cross-sectional study. The proposal for the study was submitted to the institutional ethics committee and approval was obtained. The ethical clearance approval number is SMC/IEC/2020/03/376. The study was conducted on 100 patients with type 2 diabetes in the age group 35-75 years attending the outpatient department over two months in a tertiary care centre. After obtaining informed consent, Vision, slit-lamp examination, detailed fundus evaluation was done. Retinal photographs were taken whenever needed. Known cases of Type 2 Diabetes mellitus attending outpatient department were included in the study. Other co-morbid conditions like hypertension, cardiovascular disease, chronic kidney disease, pre-existing dementia and hearing impairment were excluded. Diabetic Retinopathy (DR) graded as No DR, Mild NPDR, Moderate NPDR and Severe NPDR and PDR using ETDRS classification. Since the minimum number of patients are involved in the study, it categorized into three groups as No DR, Mild and Moderate NPDR, Severe NPDR and PDR. Cognitive function was assessed using the Montreal Cognitive Assessment (MoCA), Mini-Mental State Examination (MMSE) and Mini-cog. Data collection was done by face-to-face interviews in the outpatient department. The maximum score for MoCA and MMSE is 30. In MoCA, a score lesser than 26 is considered to have cognition impairment. In MMSE, a score of 23 or lower is indicative of cognitive impairment. In mini-cog, the total score is 5 and the score lesser than 3 is considered as cognition impairment 6. The most recent value of HbA1c, on the day of administering the cognition tests, were taken from the medical records and correlated with cognitive impairment. Descriptive statistics were presented as numbers and percentages. Pearson’s Chi-square test was used to evaluate how the distribution of categorical variables differed from another. A two-sided p-value less than 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Results
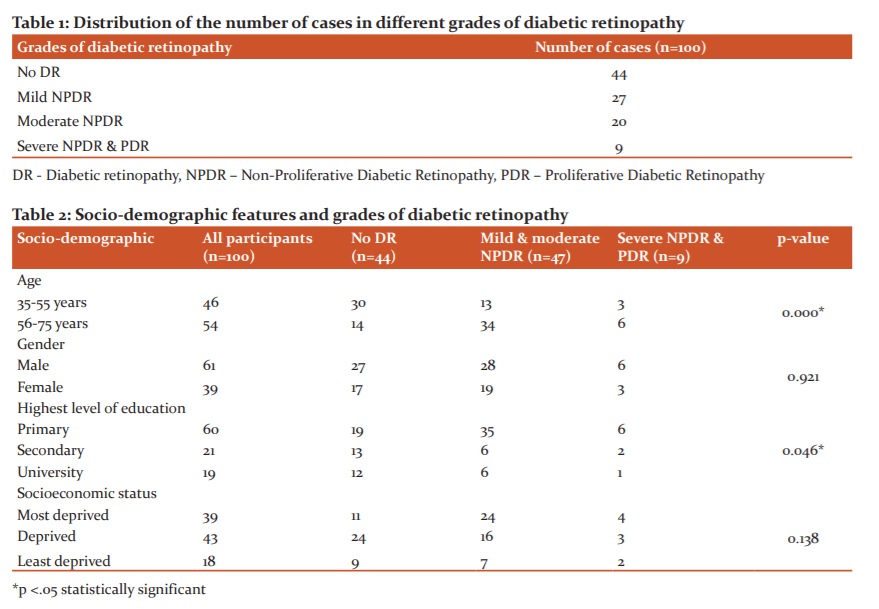
A total of 100 patients with type 2 diabetes were involved in the study. The distribution of the number of cases in different grades of diabetic retinopathy is given in Table 1.
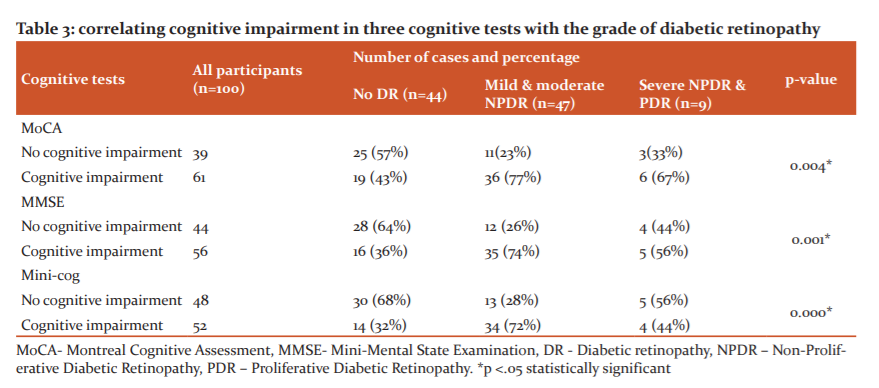
Out of this, 61 were male and 39 were female. The age group of the study population is between 35 and 75 years. Correlation of the socio-demographic features of the study population with the grades of diabetic retinopathy is given in Table 2.
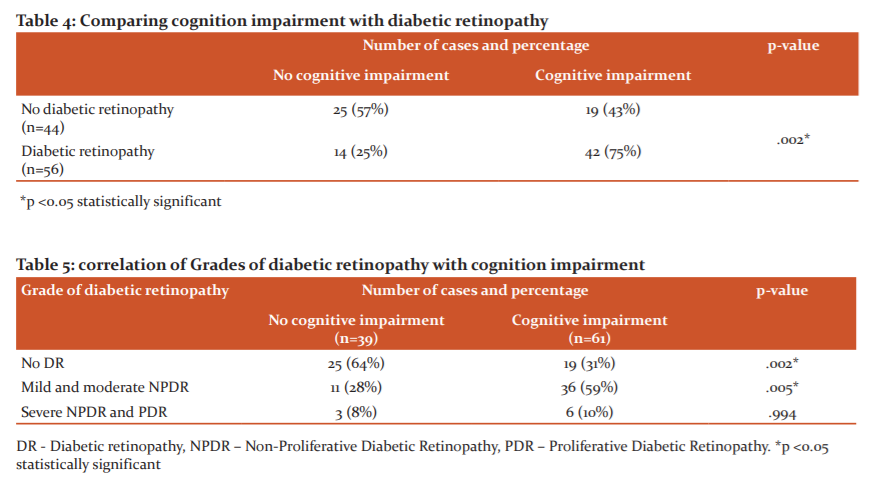
Cognitive function was assessed using three cognitive tests, Montreal Cognitive Assessment, Mini-Mental State Examination and Mini-cog. The results of the cognitive tests were correlated with the grades of diabetic retinopathy in Table 3.
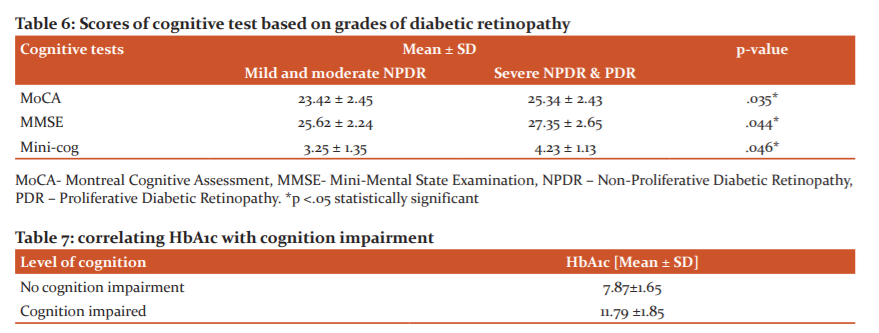
Since MoCA is more sensitive than MMSE and Mini-cog, cognitive function was calculated using MoCA and correlated with the grades of retinopathy in Tables 4 and 5
Scores of cognitive tests with the grades of Diabetic retinopathy was then correlated in Table 6.
Recent values of HbA1c of the study population on the day of administering cognitive tests are then correlated with the cognitive impairment in Table 7.
Discussion
The prevalence of type 2 diabetes and cognitive impairment has increased over the past 2 decades.4 Longer duration of diabetes and poorer glycemic control are highly associated with diabetic retinopathy and cognition impairment.7,8 Identifying the disease process that correlates the diabetic microvascular changes and cognitive impairment could be useful for the development of preventive measures in people with diabetes. The present study examined the prevalence of cognitive impairment in patients with diabetic retinopathy in a tertiary care centre in South India.
In this study, 100 patients with type 2 diabetes were included over two months in the outpatient department of a tertiary care centre and the results were analyzed. The patients are categorized based on their grades of diabetic retinopathy using ETDRS classification. On correlating the socio-demographic details, it was found that patients with older age are more affected with diabetic retinopathy. Several other studies also reveal that elderly people are more affected.5 In this study, diabetic retinopathy is higher among male but statistically, there is no significant association between diabetic retinopathy and gender. Yet several studies reveal male predominance.4,5 In the present study, patients with primary education are more affected by diabetic retinopathy. This shows that lack of awareness on regular eye checkup in diabetic patients with primary education paved way for the development of diabetic retinopathy. This was proved by another study that reveals that people with higher education have better awareness regarding the regular eye checkup and progression of the disease.9 The socioeconomic status of the patients involved in the study has no statistical significance. But some studies reveal that higher severity of retinopathy was found in deprived classes of society.10
In this study, three cognitive tests, MoCA, MMSE, Mini-cog were used to correlate the cognitive function with grades of diabetic retinopathy. All three cognitive tests reveal that a greater percentage of people with mild and moderate NPDR have cognitive impairment. In MoCA, 77% of patients, in MMSE 74% of patients and Mini-cog 72% of patients with mild and moderate NPDR have cognitive impairment and they are statistically significant with p<0.05. For accurate comparison of diabetic retinopathy with the cognitive impairment, a more sensitive cognition test MoCA is used.11 MoCA gives more insight into the cognitive function in diabetic retinopathy patients.12 On overall comparison in this study with MoCA, 75% of patients with diabetic retinopathy have cognitive impairment. This is statistically significant with p<.05. This proves that people with retinal microvascular abnormalities have more prevalence for the development of cognitive impairment. This concept was also proven by other studies.13 On comparing the grades of diabetic retinopathy with cognitive impairment, it is found that more patients with mild and moderate NPDR have cognitive impairment than severe NPDR and PDR. Patients with mild and moderate NPDR comprise 59% of people with cognitive impairment and this is also statistically significant with p<0.05. Other studies also reveal the same that mild and moderate NPDR have more cognition impairment than severe NPDR and PDR.4 On comparing the scores of cognitive tests, it is found that the mean value of the scores of mild and moderate NPDR is lower than severe NPDR and PDR. This is statistically significant with p<0.05. The finding of this study also correlates with other studies.4 But in contrast, several other studies reveal that severe diabetic retinopathy has more cognition impairment than mild and moderate diabetic retinopathy.5,14 When compared to the HbA1c level, it is found that the mean value of HbA1c is higher in patients with cognition impairment [11.79 ±1.85] than patients without cognitive impairment [7.87±1.65]. This was also proven by several studies.1,15
Conclusion
Patients with diabetic retinopathy have more chances of developing cognitive impairment. In the present study, mild and moderate NPDR have more cognitive impairment than severe NPDR and PDR. Since the study population with severe NPDR and PDR is very less, it cannot be proven insight. Hence regular eye checkup should be performed in diabetic patients to prevent the progression of diabetic retinopathy and all patients with diabetic retinopathy should be screened for cognitive impairment. As diabetes mellitus is a chronic disease, making everyday decisions about self-control and antihyperglycemic therapy which is crucial for diabetes mellitus management is difficult in the presence of cognitive impairment. Educating patients and their relatives for a regular eye checkup, maintaining optimum sugar level and HbA1c and screening for cognitive impairment will help in enhancing the quality of life and help to formulate an appropriate treatment plan for proper control of the disease.
Acknowledgement: The authors acknowledge with heartfelt gratitude to all the scholars whose work has been cited in this study and the immense guidance given by their work.
Financial support and sponsorship: Nil
Conflicts of interest: No conflict of interest.
References:
-
Lalithambika CV, Arun CS, Saraswathy LA, Bhaskaran R. Cognitive impairment and its association with glycemic control in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients. Indian J Endocrinol Metabol 2019;23(3):353-356.
-
Balamurugan J, Hariharasudhan R. Screening of subclinical sensory impairment in hand among diabetic blinds. Int J Curr Res Rev 2012;4:167-175
-
Fong DS, Aiello L, Gardner TW, King GL, Blankenship G, Cavallerano JD, et al. Retinopathy in diabetes. Diabetes Care 2004;27(suppl 1):s84-87.
-
Crosby-Nwaobi RR, Sivaprasad S, Amiel S, Forbes A. The relationship between diabetic retinopathy and cognitive impairment. Diabetes Care 2013;36(10):3177-3186.
-
Ding J, Strachan MW, Reynolds RM, Frier BM, Deary IJ, Gerald FF, et al. Diabetic retinopathy and cognitive decline in older people with type 2 diabetes: the Edinburgh Type 2 Diabetes Study. Diabetes 2010;59(11):2883-2889.
-
Galvin JE, Sadowsky CH. Practical guidelines for the recognition and diagnosis of dementia. J Am Board Family Med 2012;25(3):367-382.
-
Yau JW, Rogers SL, Kawasaki R, Lamoureux EL, Kowalski JW, Bek T, et al. Global prevalence and major risk factors of diabetic retinopathy. Diabetes Care 2012;35(3):556-564.
-
Bruce DG, Davis WA, Starkstein SE, Davis TM. Mid-life predictors of cognitive impairment and dementia in type 2 diabetes mellitus: the Fremantle Diabetes Study. J Alzheimer's Dis 2014;42(s3):S63-70.
-
AlHargan MH, AlBaker KM, AlFadhel AA, AlGhamdi MA, AlMuammar SM, AlDawood HA. Awareness, knowledge, and practices related to diabetic retinopathy among diabetic patients in primary healthcare centres at Riyadh, Saudi Arabia. J Family Med Pri Care 2019;8(2):373.
-
Kotancheri R, Ayoor AK, Jayan KP, Karuppali S, Bhaskar A. Influence of Socioeconomic and Demographic Factors on Diabetic Retinopathy. J Med Sci Clin Res 2017;5(9):28065-28071.
-
Trzepacz PT, Hochstetler H, Wang S, Walker B, Saykin AJ. Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative. Relationship between the Montreal Cognitive Assessment and Mini-mental State Examination for assessment of mild cognitive impairment in older adults. BMC Geriatr 2015;15(1):107-115.
-
O?urel T, O?urel R, Özer MA, Türkel Y, Da? E, Örnek K. Mini-mental state exam versus Montreal Cognitive Assessment in patients with diabetic retinopathy. Nigerian J Clin Pract 2015;18(6):786-789.
-
Lu X, Gong W, Wen Z, Hu L, Peng Z, Zha Y. Correlation Between Diabetic Cognitive Impairment and Diabetic Retinopathy in Patients With T2DM by 1H-MRS. Front Neurol 2019;10.
-
Gupta P, Gan AT, Man RE, Fenwick EK, Sabanayagam C, Mitchell P, et al. Association between diabetic retinopathy and incident cognitive impairment. Br J Ophthalmol 2019;103(11):1605-1609.
-
Marden JR, Mayeda ER, Tchetgen EJ, Kawachi I, Glymour MM. High haemoglobin A1c and diabetes predict memory decline in the health and retirement study. Alzheimer’s Dis Asso Disord 2017;31(1):48.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License