IJCRR - 13(6), March, 2021
Pages: 67-71
Date of Publication: 20-Mar-2021
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
Analysis of Cataract in Diabetic and Non-Diabetic Patients
Author: Manasvi P, V. Panimalar A. Veeramani, Divya N, Bindu Bhaskaran
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Introduction: Cataract is one of the most common causes of avoidable blindness accounting for 51% of the world's total blind�ness. Diabetes mellitus is a metabolic disorder that causes several complications such as a cataract. Cataract tends to develop at an earlier age in diabetics, and progression of cataract is much more rapid in diabetics. Objective: To assess cases of cataract between diabetic and non-diabetic patients based on factors such as age, sex, type of cataract, HbA1C, duration and treatment for diabetes, and other associated comorbidities. Methods: 35 patients of two groups, diabetic and non-diabetic admitted for cataract surgery in Saveetha Medical College and Hospital were analyzed. Detailed ophthalmic evaluation on visual acuity, slit-lamp examination and fundus examination was done and associated comorbidities were noted in each group. Results: The prevalence of cataract was higher in age-group 40-60 years among diabetic patients, largely in diabetic females; and higher in the age-group 60-80 years among non-diabetics. In Diabetic cases, the Posterior subcapsular cataract(50%) was the common type of cataract, while among Non-diabetics, the nuclear cataract(56.66%) was the most common. 58.82% of all diabetics were hypertensives. Conclusion: The research proves that prevalence of cataract occurs commonly at a younger age in diabetics compared to the non-diabetics with female diabetics more prone to cataract formation. Good glycemic control and early detection of cataract help to retard the progression of cataract and thus prevent blindness due to cataract.
Keywords: Cataract, Cortical cataract, Diabetes Mellitus, Nuclear cataract, Posterior subcapsular catarac
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION
A cataract is defined as the loss of transparency and opacification of the clear lens.1 It is the most common cause of blindness accounting for 51% of the world’s total blindness and 33% of the world’s visual impairment.2 It is one of the most common causes of avoidable blindness and if left untreated, many patients will face the tragic outcome of partial or total blindness. It becomes increasingly common with advancing age.
Diabetes mellitus is a metabolic disorder which is characterized by hyperglycaemia.3 There are currently 351.7 million people of working age (20–64 years) with diabetes in 2019. This number is expected to increase to 417.3 million by 2030 and to 486.1 million by 2045.4 Diabetes mellitus is a multisystem disorder that causes several complications in various organs of our body. In the eyes, it most commonly causes cataract and diabetic retinopathy. Cataract tends to develop at an earlier age in diabetics, and progression of cataract is much more rapid in diabetics.5-8 This increases the burden both visually and financially on the community as a more young population are being affected. In a study by Leske, evaluating the relationship between diabetes and lens opacities among the black population it was found that a history of diabetes mellitus (18% prevalence) was related to all lens changes at a younger age.9
The purpose of this study is to assess the differences in the parameters such as age, sex, type of cataract, systemic comorbidities that contribute to the formation of cataract among diabetics and non-diabetics.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
This is a cross-sectional study conducted between January to March of 2020 among patients admitted to the ophthalmology department of Saveetha Medical College and Hospital, Chennai for cataract surgery. A total of 35 patients were taken in this study, out of which 17 were diabetic and 18 were non-diabetic. 4 diabetic eyes and 6 non-diabetic eyes were pseudophakic and was excluded from the study. A complete examination of the remaining 60 eyes was done which included visual acuity, slit-lamp examination, and fundus examination. The type of cataract was noted by slit-lamp examination.
The inclusion criteria for the patient with diabetes was fasting blood glucose level ≥126 mg/dL, postprandial blood glucose ≥200 mg/dL and HbA1c ≥6.5%. The duration of diabetes was taken as the period from the diagnosis of DM to the day of examination for cataract surgery as informed by the patient. Their medication status was also recorded. Other comorbidities such as hypertension and dyslipidemia were also taken into account.
The study was conducted as per the guidelines and approval of the Institutional Ethics Committee, the ethical clearance number of which is: SMC/IEC/2020/03/373. Informed consent was obtained from the patient. Excel sheets were prepared and statistical analysis was done using SPSS software. The significant difference between types of cataract, gender and age was analysed by chi-square test and p-value were calculated.
RESULTS
Among the total number of patients (n=35) 14 were male and 21 were female.
The sex distribution is shown in table 1.
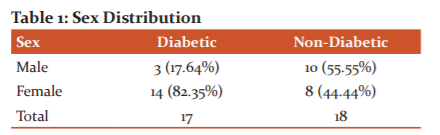
The chi-square statistic is 5.3814. The p-value is .020352. The result is significant at p < 0.05. Here, among the diabetics, there is a predilection of females to develop cataract than the males (female: 82.35%, male: 17.64%). And among the non-diabetics males developed cataract slightly more than the females (female: 44.44%, male: 55.55%). The result is significant at p < .05.
The age distribution is shown in table 2.
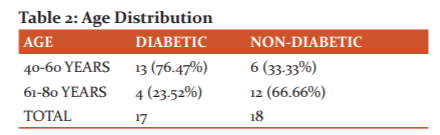
The chi-square statistic is 6.5557. The p-value is .010455. The result is significant at p < 0.05. Here, there is a marked difference between the distribution of cataract among the two age groups. Diabetics developed cataract earlier than non-diabetics. 76.47% of patients with diabetes developed cataract within the 40-60 year age group, whereas 66.66% of non-diabetics developed a cataract in the 61-80 year age group. The result is significant at p < .05.
The treatment for diabetic patients is shown in table 3.
Table 3: Treatment for Diabetes

41.1% of patients were on oral hypoglycaemic drugs, 47% were on insulin therapy and 11.7% were not taking any diabetes treatment. The distribution of type of cataract among diabetics and non-diabetics is shown in table 4.
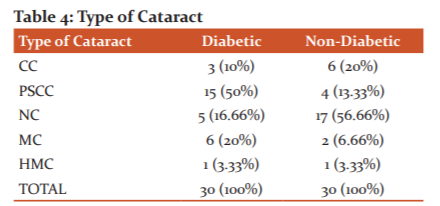
HMC: hypermature cataract; MC: mature cataract; NC: nuclear cataract; PSCC: posterior subcapsular cataract; CC: cortical cataract. The chi-square statistic is 15.9139. The p-value is .003137. The result is significant at p < 0.01. Here, among the diabetics, the most prevalent type was posterior subcapsular cataract (PSCC: 50%) which was followed by mature cataract (MC: 20%). Among the non-diabetics, the most prevalent type was nuclear cataract (NC: 56.66%) followed by cortical cataract (CC: 20%). The result is significant at p < .01.
Associated comorbidities are given in table 5.
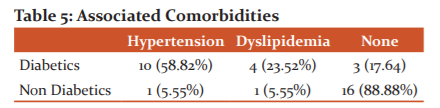
The chi-square statistic is 18.0445. The p-value is .000121. The result is significant at p < 0.01.
Prevalence of hypertension and dyslipidaemia is markedly higher among the diabetics compared to the non-diabetics. Among the diabetics, 58.82% were hypertensives, 23.32% had dyslipidemia. While, among the non-diabetics, 88.88% had no associated comorbidities.
The association between treatment for diabetes and the type of cataract is shown in figure 1. 1.
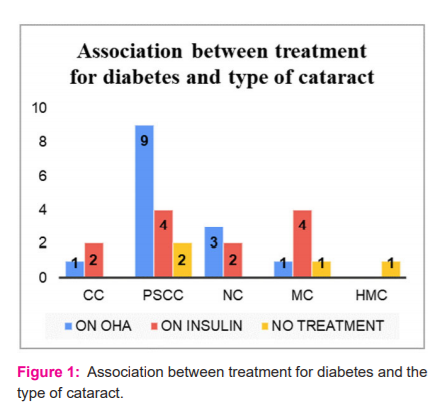
OHA: oral hypoglycemic agent; HMC: hyper mature cataract; MC: mature cataract; NC: nuclear cataract; PSCC: posterior subcapsular cataract; CC: cortical cataract.
Posterior subcapsular cataract (9) was found to be more prevalent in patients taking oral hypoglycaemic agents. Posterior subcapsular cataract (4) and Mature cataract (4) occurred equally among patients on insulin therapy. And Posterior subcapsular cataract (2), Mature cataract (1), Hypermature cataract (1) occurred almost equally in patients who did not take any diabetes treatment.
The Association between duration of diabetes and type of cataract is shown in figure 2.
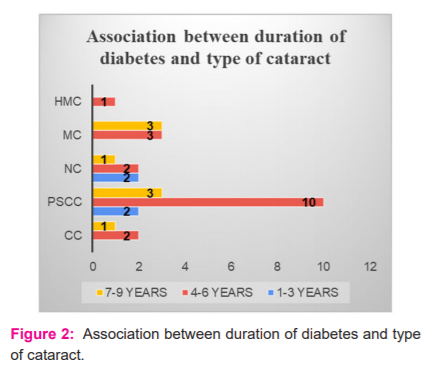
HMC: hyper mature cataract; MC: mature cataract; NC: nuclear cataract; PSCC: posterior subcapsular cataract; CC: cortical cataract.
4 eyes (13.3%) developed cataract within 1-3 years of onset of diabetes, 18 eyes (60%) developed cataract within 4-6 years and 8 eyes (26.6%) developed cataract within 7-9 years of onset of diabetes.
The association between HbA1C levels and type of cataract is shown in the figure: 3.
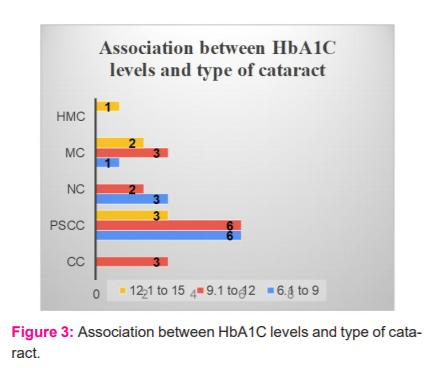
HMC: hyper mature cataract; MC: mature cataract; NC: nuclear cataract; PSCC: posterior subcapsular cataract; CC: cortical cataract.
Here, at HbA1C levels of 6.1 to 9, 6 developed PSCC, 3 developed NC and 1 developed MC. At HbA1C levels of 9.1 to 12, 6 developed PSCC, 3 developed MC, 3 developed CC and 2 developed NC. At HbA1C levels of 12.1 to 15, 3 developed PSCC, 2 developed MC and 1 developed HMC.
DISCUSSION
Results of the present study found that the formation of cataract occurs at a younger age among diabetic patients as compared to non-diabetics. 76.47% of patients with diabetes developed cataract within the 40-60 year age group, whereas 66.66% of non-diabetics developed a cataract in the 61-80 year age group. The result is significant at p < .05. This is supported by a study by Klein, where cataracts were seen among the younger population.5 Similarly, in a study by Aslam, (71.1%) cataracts developed frequently in the 35-50 years age group among the diabetics.10
The prevalence of cataract in our study was higher in diabetic females (82.35%) compared to non-diabetic females (44.4%), this corresponds to a study done by Delcourt where there was an increased risk of cataract among the females.11 Also in a study done by Raman the prevalence of cataract was higher in females (51.4%).12 In our study, 13.3% developed cataract within 1-3 years of onset of diabetes, 60% developed cataract within 4-6 years and 26.6% developed cataract within 7-9 years this can be compared to the study by Raman where known diabetics (50.3%) and long-standing diabetes (64.5%) developed cataract 12 Similarly, in a study by Kim showed that long duration of diabetes mellitus is the most significant risk factor for the development of cataract in diabetics as accumulated hyperglycemia is related to lens opacity.13
In our study, among the diabetics, the most prevalent type of cataract was posterior subcapsular cataract (PSCC: 50%) which was followed by mature cataract (MC: 20%). Among the non-diabetics, the most prevalent type was nuclear cataract (NC: 56.66%) followed by cortical cataract (CC: 20%). The result is significant at p < .01. In a study done by Chen, the prevalence of nuclear cataract, cortical cataract, and posterior subcapsular cataract among type II diabetics were 22.5, 20.2, and 19.9% respectively.14 Similarly, in a study done by Olafsdottir, the prevalence of nuclear cataract, cortical cataract, and posterior subcapsular cataract among type II diabetics were 48%, 65.5% and 42.5%, respectively.15 A study done by Lathika associating grade of cataract with the duration of type II diabetes mellitus showed that immature senile cataract was the most common type of cataract detected in patients who had diabetes for 15 years or more.16 In an epidemiological study done by Hiller, diabetics have a higher risk of developing PSCC than NC or CC.17 Similarly, a study done by Miglior found that PSCC was the most prevalent type of cataract in diabetics.18 Diabetic patients have an increased risk of developing posterior subcapsular, cortical, and mixed cataracts.19 But, in contrast to the Beaver Dam Eye Study, it was found that older onset diabetes was associated with age-related lens changes and cortical opacity.20
In our study, there was a markedly increased number of patients with associated hypertension and dyslipidaemia among the diabetics which could suggest the increased prevalence of cataract among patients with metabolic syndrome. In a study done by Nirmalan in a rural population in Southern India, it was found that hypertension and diabetes were associated with the development of cataract.21 In a study done by Chen among type II diabetics in Kinmen, Taiwan it was found that increased triglyceride levels may increase the risk of development of PSCC and NC.15 Similarly, in the Framingham studies, hypertriglyceridemia is associated with the development of posterior subcapsular cataract in men.22 In a study done by Shabana, there was an increased prevalence of lipid abnormalities among female diabetics.23
The present study was able to find a statistically significant correlation between age, sex and the type of cataract which develops in the two groups. Appropriate glycemic control was established among the uncontrolled diabetic patients and all were operated on with intraocular lens implantation. The main limitations of this study are the sample size as the study was completed within the given time constraints. Other parameters like BMI, Socioeconomic status was not included in the study.
CONCLUSION
Incidence of cataract occurs at a younger age among diabetics and there is a predilection towards females. Posterior subcapsular cataract was the most common type of cataract among diabetics followed by mature cataract. Longer duration of diabetes and poor glycaemic control were the risk factors for the development of cataract in diabetics. Proper control of blood sugar at the early stage of disease will hamper the development of cataracts among diabetic, thereby reducing the burden on society.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT:
Authors of this manuscript are grateful to the management of Saveetha Medical College and Hospital who provided us with all necessary facility for this study and also grateful to all the patients who are involved in this study. We acknowledge the immense help received from the scholars whose articles are cited and included in references to this manuscript. The authors are also grateful to authors/editors/publishers of all those articles, journals and books from where the literature for this article has been reviewed and discussed. The authors are also grateful to the editors of this journal for providing the necessary guidelines for the publication of this study.
CONFLICT OF INTEREST: NIL
SOURCE OF FUNDING: NIL
References:
1. Tandon R. Parsons' Diseases of the Eye. Elsevier India; 2019 Aug 10.
2. https://www.who.int/blindness/causes/priority/en/index1.html
3. Jameson JL, Fauci AS, Kasper DL, Hauser SL, Longo DL, Loscalzo J. Harrison's Principles of Internal Medicine, 20e
4. International Diabetes Federation. IDF diabetes atlas. Ninth edition, 2019.
5. Klein BE, Klein R, Moss SE. Prevalence of cataracts in a population-based study of persons with diabetes mellitus. Ophthalmology 1985;92(9):1191-1196.
6. Javadi MA, Zarei-Ghanavati S. Cataracts in diabetic patients: a review article. J Ophthal Vision Res 2008;3(1):52.
7. Nielsen NV, Vinding T. The prevalence of cataract in insulin?dependent and non?insulin?dependent?diabetes Mellitus. Acta ophthalmologica 1984;62(4):595-602.
8. Negahban K, Chern K. Cataracts associated with systemic disorders and syndromes. Curr Opin Ophthalmol 2002;13(6):419-422.
9. Leske MC, Wu SY, Hennis A, Connell AM, Hyman L, Schachat A. Barbados Eye Study Group. Diabetes, hypertension, and central obesity as cataract risk factors in a black population: the Barbados Eye Study. Ophthalmology 1999;106(1):35-41.
10. Aslam K, Sufyan M, Ansari A, Khalid I, Nafees K. Frequency of Cataract in Diabetic Verses Non-Diabetic Patients. Pak J Ophthalmol 2019;35(1).
11. Delcourt C, Cristol JP, Tessier F, Leger CL, Michel F, Papoz L. POLA Study Group. Risk factors for cortical, nuclear, and posterior subcapsular cataracts: the POLA study. Am J Epidemiol 2000;151(5):497-504.
12. Raman R, Pal SS, Adams JS, Rani PK, Vaitheeswaran K, Sharma T. Prevalence and risk factors for cataract in diabetes: Sankara Nethralaya Diabetic Retinopathy Epidemiology and Molecular Genetics Study, report no. 17. Investig Ophthalmol Visual Sci 2010;51(12):6253-6261.
13. Kim SI, Kim SJ. Prevalence and risk factors for cataracts in persons with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Korean J Ophthalmol 2006;20(4):201-204.
14. Chen SJ, Liu JH, Shih HC, Chou P, Tsai CY, Tung TH. Prevalence and associated factors of lens opacities among Chinese type 2 diabetics in Kinmen, Taiwan. Acta Diabetol 2008;45(1):7-13.
15. Olafsdottir E, Andersson DK, Stefánsson E. The prevalence of cataract in a population with and without type 2 diabetes mellitus. Acta ophthalmol 2012;90(4):334-340.
16. Lathika VK, Ajith TA. Association of the grade of cataract with the duration of diabetes, age and gender in patients with type II diabetes mellitus. Int J Adv Med 2016;3(2):304-308.
17. Hiller R, Sperduto RD, Ederer F. Epidemiologic associations with nuclear, cortical, and posterior subcapsular cataracts. Am J Epidemiol 1986;124(6):916-925.
18. Miglior S, Marighi PE, Musicco M, Balestreri C, Nicolosi A, Orzalesi N. Risk factors for cortical, nuclear, posterior subcapsular and mixed cataract: a case-control study. Ophthal Epidemiol 1994;1(2):93-105.
19. Leske MC, Chylack LT, Wu SY. The lens opacities case-control study: risk factors for cataract. Arch Ophthalmol 1991;109(2):244-251.
20. Klein BE, Klein R, Wang Q, Moss SE. Older-onset diabetes and lens opacities. The Beaver Dam Eye Study. Ophthal Epidemiol 1995;2(1):49-55.
21. Nirmalan PK, Robin AL, Katz J, Tielsch JM, Thulasiraj RD, Krishnadas R, Ramakrishnan R. Risk factors for age-related cataract in a rural population of southern India: the Aravind Comprehensive Eye Study. Br J Ophthalmol 2004;88(8):989-994.
22. Hiller R, Sperduto RD, Reed GF, D’Agostino RB, Wilson PW. Serum lipids and age-related lens opacities: a longitudinal investigation: the Framingham Studies. Ophthalmology 2003;110(3):578-583.
23. Shabana S, Sasisekhar T. Effect of gender, age and duration on dyslipidemia in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Int J Cur Res Rev 2013;5(6):104-107.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License