IJCRR - 13(5), March, 2021
Pages: 183-187
Date of Publication: 03-Mar-2021
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
Milk Spoilage Detection by Impedance Measurement
Author: Kannampilly NJ, Thangavel K, Peter D, Rose L
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Introduction: Monitoring milk quality is very crucial to maintain food safety and human health. The identification or detection of milk spoilage holds a prominent role in the improvement of milk preservation methods. Objective: The focus of this work lies on rapid, reliable and cost-effective method of milk spoilage detection for milk quality determination. Methods: Various physio-chemical properties of milk including fat, acidity, pH, ultrasonic velocity, thermal conductivity were performed to identify the major changes associated with spoilage parameter responsible for spoilage. This method emphasized milk spoilage detection using impedance measurement by using chip AD5933. These spoilage parameters were correlated with microbial spoilage of milk. Results: The pH and acidity value of fresh raw milk was 6.68 and 0.17% respectively. These two key parameters to evaluate milk freshness. There was significant difference in ultrasonic velocity from 1504.41 + 0.12m/sec to 1692.24 + 0.16m/sec at 72 hours. An impedance measurement apparatus was set up using chip AD5933 that shows a higher impedance reading when the microbial count was high. There is a prominent correlation between impedance and microbial growth. Therefore, electrical impedance could be considered as an indicator for the determination of milk quality. Conclusion: This study demonstrated a rapid, cost-effective measurement technique to determine spoilage of milk using an apparatus set up for Impedance measurement.
Keywords: Milk spoilage, Rapid, Impedance measurement, Physio-chemical properties, Quality determination, Cost-effective
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION
Food freshness indicators or spoilage detectors should meet criteria such as specificity, analysis time and cost. The instrument specification may vary according to end-use such as checking the quality of raw material and their changes occurring during storage and transportation. Milk spoilage is an undefined term and challenging to determine with precision. This ambiguity causes difficulty in dairy industries. Most often the uncertainty in expiry dates on milk packets, deceive the customers and hence dispose of the unspoiled milk. These dates are mostly imprecise due to variations in storage conditions, shipment and processing factors of milk.1 Researcher has been focusing on the improvement of existing tools for milk spoilage detection. There are various milk spoilage detection techniques, which are accurate and efficiently such as gas-sensor arrays, Infrared/Near-Infrared (IR/NIR) Spectroscopy, Optical sensors, pH sensors, and amperometric sensor. However, the main drawback of these is its time consuming and expensive. Recently there has been a great demand and interest in novel developments in environment-friendly intelligent packaging.2 Therefore, a novel technique to measure milk quality is in a great need in the market today.
Electrical parameters of milk change linearly concerning the mass of the substance. This change was observed due to the different amount of charge carried by it and is dependent on the period of storage.3 The opposition of a material to the flow of electric charges can be termed as the impedance of a material. It is chiefly the frequency domain ration of the voltage to current. The terms resistance and reactance are also associated with impedance. Every substance disperse and store energy. Resistance (R) and Reactance (Xc) are an indicator of energy dissipation and storage.4 Therefore, high-frequency resistance reduces than at low frequency. Here, the research focused on variation in electrical impedance as the milk spoils. The increase in impedance value was observed in spoiled milk than fresh milk. Thus, by studying the change in impedance of milk, it was possible to determine the spoilage of milk.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
The current investigation was performed for cow’s milk. The fresh milk sample was obtained from a farm in Coimbatore, Tamil Nadu. The physiochemical properties of milk samples were taken at certain intervals namely 0, 6, 12, 18, 24, 30, 36, 48 and 72hours interval. Acidity, pH, fat, ultrasonic velocity, thermal conductivity and impedance value were the few measurements observed for fresh milk at a specified period.
The methods adopted for determining the physio-chemical parameters of milk were pH meter for determination of pH, Gerber’s method for fat determination, titratable acidity method for determination of acidity in milk, velocity meter for determination ultrasonic velocity and thermal conductivity measurement by thermal conductivity apparatus. The electrical impedance was measured by a prototype set up for Impedance apparatus. Microbial Analysis of milk was performed by spread plate method using standard plate count. The methodology and apparatus used for the determination of Physico-chemical properties of milk are:
pH: The pH of fresh milk was measured at regular intervals using a pH meter. It comprises a measuring probe made up of a glass electrode. This electrode was attached to an automatic display meter that shows the pH of the substance measured.5
Titratable Acidity: To measure the acidity, fresh milk of 10ml was taken in a conical flask. The milk sample was titrated with 0.1N NaOH using 2-3 drops of phenolphthalein as an indicator. The acidity of the sample was determined by the formula:
V1=Volume of NaOH, N=Normality of NaOH, V2=Volume of the sample. 5
Determination of fat content: The Gerber fat tests are done to check the butterfat percentage in milk. Lipid/Fat content is determined by the Gerber method, where 10ml sulfuric acid (specific gravity 1.823) at 15-21°C was taken in Butyrometer. 1ml of amyl alcohol was added to it and inserted with a lock stopper. This was shaken until the milk was completely digested and finally placed in a centrifuge.
Measurement of Thermal conductivity: The property of a substance to conduct heat can be termed thermal conductivity. The thermal conductivity of a material may depend on temperature. During milk processing, this property is very important to estimate the processing time required and to determine energy involved in thermal process.6, 7 Milk sample was measured for conductivity by thermal property analyzer (KD2 Pro model). This was fixed to a knob implanted in a beaker. The rate of heat transfer lowers with materials of less thermal conductivity.
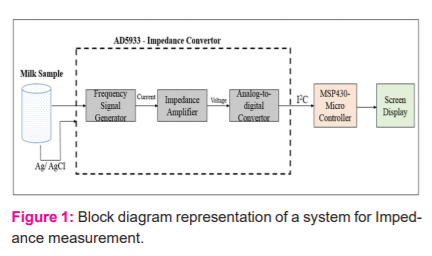
Measurement of Electrical Impedance: An impedance analyzer was set up to measure the electrical impedance of milk. In this setup, the Ag/AgCl electrodes were kept in contact with the milk sample. An impedance converter AD5933 was used to obtain high precision and accurate results. The AD5933 chip is generally used for assimilation of majority components essential for impedance analyzers such as signal generator and analogue-to-digital convertor. One major advantage of this chip is its lower power consumption. The impedance value of milk was taken at certain intervals concerning milk stored for a period. The fresh milk sample was placed between the electrodes and the electrodes are connected to the AD5933 signal generator and processing unit which in turn connected to the micro-controller. Figure 1 shows the block diagram representation of a system for Impedance measurement. The impedance reading was displayed on the LCD that is connected to the microcontroller. Both the values of impedance both real and imaginary values were noted.
Measurement of Ultrasonic velocity: An ultrasonic velocity meter was used to determine the velocity of milk. An ultrasonic transducer, an electronic circuit and a display meter that measures flow rate are the main parts of this velocity meter apparatus. The transducer in the ultrasonic velocity meter works in the principle of converting electrical signals to ultrasonic energy. These ultrasonic signals are received are amplified and displayed in the digital meter, thus provides supply flow rate.
Microbial analysis of Milk: The microbial analysis was carried out to determine the bacterial load present in the milk sample. Grams staining method was performed to distinguish whether the gram-positive or gram-negative bacteria were present in the milk sample. The peptone water needed for determination of standard plate count (SPC) was sterilized using autoclave at 121°C for 15-20 minutes.
-
Standard Plate Count (SPC): The total bacterial count was performed at various dilutions at a specific time interval and the total viable count was determined. To sterile plates, 9ml of sterile peptone water and 1ml of the milk sample was added. Serial dilution up to 10-6 was performed. Using the pour plate method, the 15-20ml sample was poured into Petri plates. Duplicates of the analysis were performed. All the Petri-plates were incubated for 48hours at 37°C. The standard plate count (SPC) was calculated by taking the average of the plates and represented in cfu/mL. The microbial count (cfu/mL) was correlated to other Physico-chemical parameters of milk.8
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
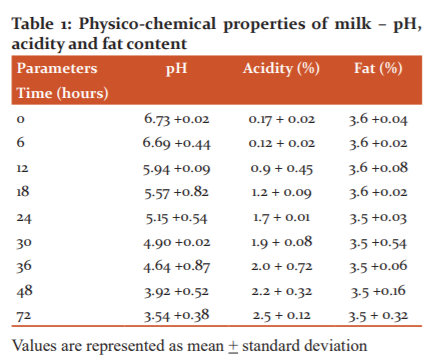
Fresh cow milk was used for the analysis of physio-chemical parameters such as pH, acidity fat, as presented in Table 1. The analysis was conducted at a time of 6, 12, 18, 24, 30, 36, 48 and 72hours interval. Table 2 presents the thermal conductivity, ultrasonic velocity and impedance values of milk.
Physico-chemical properties of fresh milk
pH and acidity: The acidity is generally articulated as pH. As milk is a complex buffer system, change in temperature is dependent on pH change. Variations in pH causes change in the structure of phenolic components present in pigments such as anthocyanin. Thus, pH parameter plays a vital role in many compounds. 9 It was observed that the pH of fresh milk was 6.73 +0.02 and the acidity level was 0.17%. From Table 1, it can be observed that there has been a drastic decrease in the pH once the milk is stored for a period at room temperature. After the first 6hours of milk storage, no much change in pH and acidity is visible. However, after a storage period of 18hours, a drastic decrease in pH to 5.57 +0.82 and increase in acidity to 1.2 +0.09 was observed. This was due to the spoilage started in milk due to the higher level of lactic acid produced by microbial metabolism.10, 11 As the milk is stored at room temperature, it is observed that the milk become sour and the acidity level increases to 2.5% at 72hours of storage of milk. This acidity level shows that the milk is spoiled and correspondingly the pH value of milk decreased to 3.54. The pH value can be considered as milk spoilage indicator. The pH change was due to the acidity developed in milk due to the increase in bacterial growth.8 The pH and acidity values were correlated with the microbial analysis of the milk.
The fat content of milk: There was no prominent change observed in the fat content of milk. The fat content determined is presented in Table1. The fat content in fresh milk was determined as 3.6% and slight variation in value was seen after 24hours of storage period. The values were in concordant to [12], [13] and [14].
Thermal conductivity: One of the significant property, which affects the pasteurization of milk, is thermal conductivity. The conductivity of milk also depends on its rheology, composition of milk and process temperature.15 Data on thermal conductivity helps in determining heating or refrigeration process and physical and chemical changes occurring in milk.16 The milk sample to be measured was poured into a beaker. The thermal property analyzer (KD2 Pro model) was kept in contact with the milk sample to be measured. Table 2 shows the values of thermal conductivity of milk. The thermal conductivity of fresh milk was found to be 0.530 +0.09 W/m K at ambient temperature and increased to 0.64 +0.35 W/m K once stored for 72hours. The values were found to be following [12]. This shows there was less effect on the thermal property of milk when the milk was subjected to spoilage. A prominent distinguishing variation could not be seen in thermal conductivity as the acidity of the milk increased. Therefore, thermal conductivity cannot be considered as an important spoilage parameter to indicate milk spoilage.
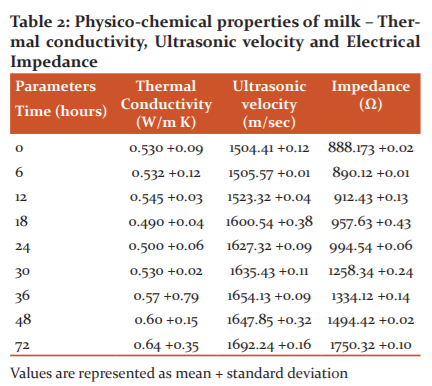
Electrical Impedance: To measure the electrical impedance of milk, an apparatus was set up using chip AD5933 circuit, as shown in Figure 1. This chip excites signals as it uses as a voltage-control oscillator. It consists of a direct digital synthesizer. The impedance measurement is performed by sensing the current flowing through it. This is converted to voltage and thereby to digital form using Analog-to-digital converter (ADC). The impedance of fresh milk was found to be 888.173 +0.02 Ω. There was a prominent difference in the impedance value (957.63 +0.43 Ω) of milk when the milk was stored for a period especially after 18hours. The impedance reading was corresponding to the microbial level of milk when the milk spoils. Thus, electrical impedance could be considered as an effective indicator for spoilage of milk. Similar findings were reported by [4] for the vitality detection of apple. Reference [3] also reported that the impedance measurement could distinguish statistically partially decayed apples and the fresh apple.
Ultrasonic velocity: The ultrasonic velocity of fresh milk was found to be 1504.41 + 0.12 m/sec. This is dependent on the moisture content and the temperature of the milk. There was a drastic change in ultrasonic velocity (1600.54 + 0.38m/sec) observed after 18hous of storage of milk at ambient condition. This proves that the ultrasonic velocity could be used as a parameter to check the quality of milk. The results proved that as the milk spoils, the ultrasonic velocity also increases.17 This change in velocity can be a correlation to milk spoilage characteristics. The feasibility of using ultrasonic techniques to evaluate the quality parameters for milk was investigated.
Microbial Analysis of Fresh Milk: The microbial analysis was performed for the determination and characterization of microorganism present in the milk by serial dilution and grams staining techniques respectively. The microbial count of milk at 0, 12, 24, 48hours were found to be 5x101, 20 x10¹, 3.2x104 and 10 x104cfu /mL respectively. After 48hours of analysis, the microbial growth was rapid and could not determine the bacterial count. It can be understood that as the milk storage time increases, the microbial count also increases. The average count of fresh raw milk was negligible compared to 10x104cfu/mL after 48hours of storage. A similar study showed a signi?cant increase in the microbial count and a relatively distinct decrease in pH during the storage at 21°C and 37°C for 8 to 30 hours, which is caused by the growth of bacterial cells. 18
Gram-staining technique was performed to characterize microorganism present in the fresh raw milk. A rod-shaped purple coloured, the non-sporulating organism was identified. Lacto bacillus spp. was found to have similar characteristic properties.
CONCLUSION
Milk is exceptionally nutritious and is considered a balanced diet by the majority of people. The Physico-chemical properties of fresh cow’s milk were analyzed for a specific time interval to identify the milk spoilage parameter. The pH and acidity value of fresh raw milk was found to be 6.68 and 0.17% respectively. These two parameters can be considered as the key parameters to evaluate milk freshness. There was significant difference in ultrasonic velocity from 1504.41 +0.12m/sec to 1692.24 +0.16m/sec at 72 hours. Electrical impedance was taken as an indicator for the determination of milk quality. An impedance analyzer apparatus was set up using chip AD5933. The impedance value of milk was measured and a drastic difference was seen which correlated to milk spoilage. Thus, the device for impedance measurement was found to be an effective tool for determining the milk spoilage. This system measures impedance by Ag/AgCl electrodes with high accuracy, less power consumption and is a microcontroller-based device. Thus, a cost-effective reliable solution for impedance measurement is performed by AD5933 chip. The impedance value of milk was found to increase with milk spoilage, thereby proving that as the impedance value increase, the milk quality decreases and leads to spoilage. Further studies can be focused on improving the stability of voltage using two AD5933 chip, as the electrical impedance of milk showed few fluctuations in the reading.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
Authors would like to express their gratitude towards the Department of Food Processing and Engineering and Department of Electronics and Instrumentation, Karunya Institute of Technology and Sciences for their constant support for the successful completion of the study and the facilities provided. The authors are also grateful to authors/editors/publishers of all those articles, journals and books from where the literature for this article has been reviewed and discussed. Authors also grateful to IJCRR editorial team and reviewers to bring the quality of this manuscript.
Conflict of Interest: Nil
Source of Funding: Nil
Contribution of Authors:
1. Nikki John Kannampilly : Conceptualisation, Data collection, Data analysis, Writing
2. K. Thangavel : Conceptualisation, Data analysis, Writing
3. Dayanand Peter : Conceptualisation, Writing
4. Lina Rose: Data collection, Data analysis
References:
-
Kim J, Twede D, Lichty J. Consumer attitudes about open dating techniques for packaged foods and over-the-counter drugs. J Food Produ Marke 1997;4(1):17-30.
-
Restuccia D, Spizzirri UG, Parisi OI, Cirillo G, Curcio M, Iemma F, et al. New EU regulation aspects and global market of active and intelligent packaging for food industry applications. Food Control 2010;21(11):1425-1435.
-
Euring F, Russ W, Wilke W. Development of an impedance measurement system for the detection of decay of apples. Procedia Food Sci 2011;1:1188-1194.
-
Rose EJ, Pamela D, Rajasekaran K. Apple vitality detection by impedance measurement. Int J Adv Res Comp Sci Soft Engg 2013;9:144-148.
-
AOAC (Association of Official Analytical Chemists), Official Methods of Analysis International, 17th Ed. AOAC, Washington, DC. 2000
-
Carson JK. Review of effective thermal conductivity models for foods. Int J Refrig 2006;29(6):958-967.
-
Muramatsu Y, Tagawa A, Kasai T. Thermal conductivity of several liquid foods. Food Sci Technol Res 2005;11(3):288-294.
-
Robertson AH, Black LA, Breed RS, Brito AG, Cowley RF, Gibbard J. Standard methods for the examination of dairy products. Am J Public Health Nations Health 1949;39(5 Pt 2):80–82.
-
Kannampilly NJ, Devadas CT. Kinetic Modelling of Anthocyanin Extraction from Grape (Vitis vinifera) using Response Surface Methodology. Int J Innov Technol Explor Engg 2019;8(11),3015-3019.
-
Pereira Jr VA, de Arruda IN, Stefani R. Active chitosan/PVA films with anthocyanins from Brassica oleraceae (Red Cabbage) as Time–Temperature Indicators for application in intelligent food packaging. Food Hydrocolloids 2015;43:180-188.
-
Liang T, Wang L. A pH-sensing film from tamarind seed polysaccharide with litmus lichen extract as an indicator. Polymers 2018;10(1):13.
-
Prasad N, Shukla.S. and Ramteke, P.W. Physico-chemical Properties of Milk and Dairy Products Collected from Allahabad City, India. Int J Curr Microbiol App Sci 2018;7(07):1662-1666.
-
Sodhi SS, Mehra ML, Jain AK, Trehan PK. Effect of non-genetic factors on the composition of milk of Murrah buffaloes. Indian Vet J 2008;85(9):46-48.
-
Dubey PC, Suman CL, Sanyal MK, Pandey HS, Saxena MM, Yadav PL. Factors affecting composition of milk of buffaloes. Indian J Animal Sci 1997;67(9).
-
Pradeep S, Lakshminarayana P, Varsha R, Kota SK. Screening of adulterants in milk. Int J Cur Res Rev 2016;8(12):25-29.
-
Sweat VE. Thermal properties of foods. Engg Propert Foods 1986;49.
-
Ali MH, Ahmad A. Ultrasonic Velocity and Allied Parameters of Milk Powder Reconstituted with Water. Int J Innov Res Sci Engg Technol 2017; 6(5).
-
Al-Qadiri HM, Lin M, Al-Holy MA, Cavinato AG, Rasco BA. Monitoring quality loss of pasteurized skim milk using visible and short wavelength near-infrared spectroscopy and multivariate analysis. J Dairy Sci 2008;91(3):95.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License