IJCRR - 13(5), March, 2021
Pages: 163-167
Date of Publication: 03-Mar-2021
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
Comparing the Effect of Fast Tempo Music and Slow Tempo Music During Aerobic Exercise on Cardiovascular Endurance in Overweight Adolescents
Author: Sharayu Agre, Ronika Agrawal, Memon F, Ammarah Ravi
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Introduction: High prevalence of overweight has been found among adolescents in an urban population in developing countries. Physical activity habits track from youth to adulthood, therefore, adolescence may be a critical period for establishing a physically active lifestyle to enhance health and prevent chronic diseases in adulthood. Objective: To compare the effect of fast tempo and slow tempo music during aerobic exercise on cardiovascular endurance (CVE) in overweight adolescents. Methods: This was an interventional study with pre-test- post-test study design. Subjects were assessed using the 20mt Shuttle run test and VO2 max was calculated. The intervention was carried out for four weeks and aerobic exercise in the form of circuit training was administered to 90 overweight adolescents who were divided into 3 groups of 30 subjects each. The same exercise protocol was given with Group A exercising too fast tempo music, Group B to slow tempo music & Group C, the control group, with no music. Results: Intragroup comparison in Group A, B and C showed a highly significant increase in VO2max Intergroup analysis using Anova showed, that the average increase of VO2max in Groups A and C is similar. The results also show that the VO2 max in group B was significantly higher than in Groups A and C. Conclusion: Our findings conclude that exercising with music shows more improvement in VO2 max and slow tempo music shows better results than fast tempo music or no music.
Keywords: Music-Tempo, Aerobic exercise, Cardiovascular endurance, Circuit training
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION
Music is known to capture attention, trigger a range of emotions, alter or regulate mood, increase work output, induce states of higher functioning, reduce inhibitions and encourage rhythmic movement. Music also has an evident ergogenic effect as it improves exercise performance by either delaying fatigue or increasing work capacity.1 Music is comprised of several facets like rhythm, mode, genre, tempo, etc. The tempo is one of our study’s main focuses, is defined by the oxford dictionary as the speed at which passage of music is played, which is often described in terms of beats per minute (bpm).
In 2007, Carpentier and Potter studied how tempo affects arousal from a physiological perspective. They showed that fast-paced music (high bpm) induced a greater activation of the sympathetic nervous system than slow-paced music.2 Fast tempo music increased the plasma epinephrine level whereas slow tempo music decreased the plasma epinephrine level compared with baseline while listening to music 20 minutes before exercise.3 Hence, the tempo is found to be positively correlated with psychological and physiological functions.
High prevalence of overweight has been found among adolescents in an urban population in developing countries. It points towards greater morbidity from diseases such as diabetes, Cardiovascular disease (CVS) and hypertension in years to come.4 Physical activity habits track from youth to adulthood, therefore, adolescence may be a critical period for establishing a physically active lifestyle to enhance health and prevent chronic diseases in adulthood.5 Most adolescents lack the motivation, time, interest or companionship to perform physical activity.6,7
Thus, to address the limitations of traditional exercise protocols and to provide an enjoyable, effective and efficient program, Circuit Training was used which can be performed by a large group of people together without the need for specialized equipment. Thus, a combination of different tempos of music along with circuit training may help in improving the cardiovascular endurance (CVE), reduction of fatigue, adherence to exercise program and promotion of a healthy lifestyle for overweight and obese adolescents.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
After the approval of the institutional ethical committee, 90 subjects having BMI between 85th to 95th percentile (WHO guidelines), aged 10-19 years were included in this interventional study.8 Subjects with hearing disabilities, cardiovascular/ pulmonary disease, any musculoskeletal injury within 6 months, those involved in weight reduction programmes or having continuous medications for 1 month or more for systematic illness were excluded from the study.
Written consent was taken from all the parents/guardians as well as subjects before their participation. Pre and post-treatment assessment was done using the 20 M Shuttle Run Test and VO2max was calculated.
The shuttle run test was performed using a standardized procedure.9
VO2Max was calculated using the following formula:
VO2max=41.76799+(0.49261×PACER)-(0.00290×PACER²)-(0.61613×BMI)+(0.34787×gender×age)
(where PACER is the number of laps completed;
For gender, boy=1 and girl=0; and age is in years)
[r=0.75, r2 = 0.56, SEE =6.17 ml ⁄ kg ⁄min]9
Familiarization session was held before beginning the protocol in which the exercises and the method for monitoring intensity were demonstrated and practically explained to the participants.
Modification of Borg’s scale (0 – 10) was used to determine the intensity of the exercise sessions.
The tempo of each track was found on the website https://getsongbpm.com. It was then converted into percentage values of 60-80 bpm (slow tempo music) and 140-160 bpm (fast tempo music). The tempo of the tracks was changed using the Music speed changer app and the tracks were merged using the Music Editor app.
Interventions
-
5 minutes of the warm up was given before the exercises which included jogging on the place for 5min at RPE 2-3.
-
The exercise session was conducted for 4 weeks, 3 times/week with progression as the weeks progressed. The intensity of exercise was moderate for 1st two weeks and high for week 3-4.
Exercises in Circuit training included (Figure 1) skipping without the rope, push up, abdominal crunch, mountain climber, two count jumping jog & high knee running on the place. all exercises should be done with intensity according to Borg’s scale with perceived exertion to somewhat hard i.e. 4.11
-
5 minutes of cool down was given after the exercises which included 1 set of self-stretching of Biceps, Triceps, Long flexors of forearm, pectoralis major, Rectus femoris, Hamstring and Gastronomies muscles for 30sec with 2 repetitions.
-
The total duration of intervention was 40 min.
-
The rest period between each circuit was 30 sec.

RESULTS
Statistical software R-studio version 3.6.2.was used for data analysis. It was observed by Shapiro-Francia normality tests that data were normally distributed; hence parametric tests were performed. Student t-tests (one-tailed, paired) was used for Intragroup analysis, ANOVAs & multiple pair wise-comparison using Turkey HSD (honestly significant difference) test was used for intergroup analysis. Any p-value less than 0.01 was considered to be statistically significant. Of the 90 subjects enrolled in the study, 3 subjects dropped out.
The homogeneity of variance was checked using the residuals versus fits plot where no evident relationship between residuals and fitted values was seen. Thus, the homogeneity of variances can be assumed. Table 1 shows the comparison of VO2max pre and post-intervention in the fast tempo music group. It shows statistical significance with p<0.01 suggesting there was a significant improvement in VO2max post-intervention.
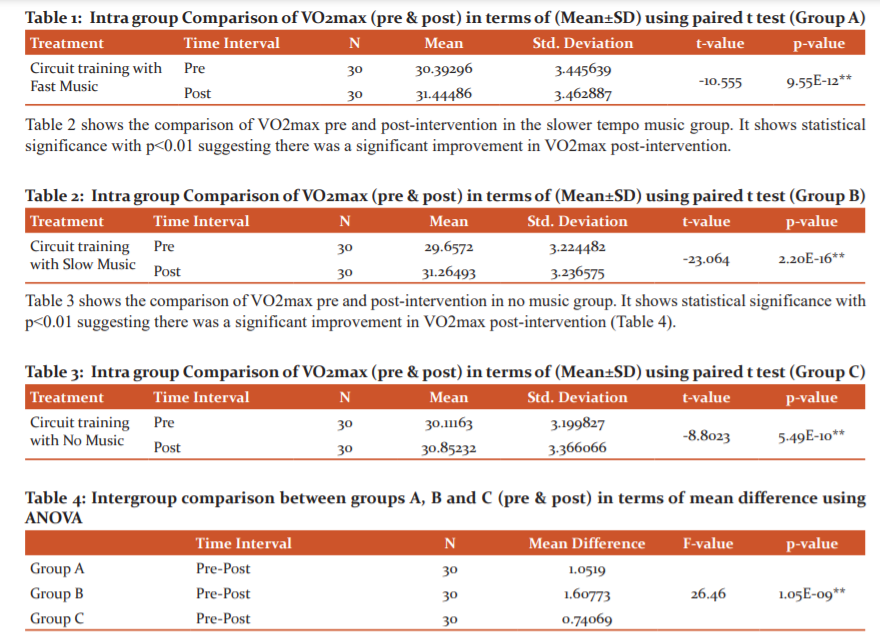
Inference Intergroup analysis using ANOVA shows that the difference between Group A- Group B and Group B- Group C is significant with p-value<0.01. Thus, the VO2max in group B was significantly higher than Groups A and C (Figure 2).
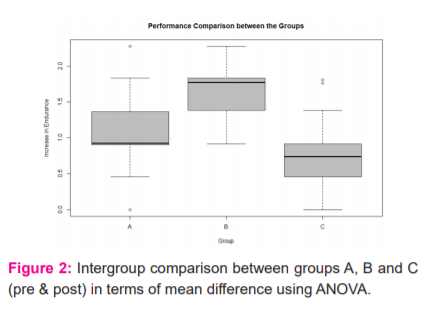
Discussion
Tables 1, 2, 3 and Figures 2 show that there was a statistically significant improvement in VO2max in all three groups. Circuit training includes a series of exercise activities. At the end of the last activity, the participant starts from the first activity and moves through the series and this series of activity is repeated several times. Exercise is known to improve cardiovascular endurance. Circuit training produces numerous respiratory and cardiovascular effects.10,12,13
Oxygen transport and utilization chain are enhanced which comprises of increase in blood volume (BV), O2-carrying capacity of the blood and cardiac output; skeletal muscle adaptations such as augmented capillarization and mitochondrial content13. Hence, in the present study, all three groups were doing circuit training, showed a significant increase in VO2max post-intervention.
An individual is predisposed to respond to rhythmical elements during continual submaximal activity, the outcome being synchronization between the musical tempo and the participants’ movement making physical activity or exercise a more coordinated or less demanding experience.14 Fast tempo music causes generic stimulation of those parts of the brain that govern arousal, namely the limbic and reticular activating systems. It is known to ameliorate the effects of fatigue-related symptoms during exercise.14,15 Individuals experience more pleasant sensations and lower perceived exertion than under normal circumstances while exercising too fast tempo music.16 An ergogenic effect with music improves exercise performance by delaying fatigue or improving work capacity. Sensory stimuli such as music can hinder the physiological feedback signals associated with physical exertion.16 Pleasurable stimuli promote electrical activity in one sensory pathway while inhibiting unpleasant stimuli in another sensory pathway leading to a reduced feeling of fatigue.17 Pleasurable stimuli promote electrical activity in one sensory pathway of the brain. This also inhibits electrical activity, hence the excitatory state is reduced.18 At high-intensity exercise physical signs of fatigue cannot be delayed but the perception of fatigue can be changed. This whole process prolongs the total duration of the exercise. Hence, the fast tempo music group showed better results than no music group.
The slow tempo of music makes it easier to synchronize to the music. Synchronization to the music possesses motivational qualities that enhance performance. Listening to music increases interpersonal synchronization of cardiovascular and respiratory rhythms. Slow music is known to down-regulate theta waves in the frontal, central, and parietal regions of the brain during exercise.19 It also induces a partial attentional switching from associative thoughts to task-unrelated factors (dissociative thoughts) during exercise, which leads to improvements in task performance. Kornysheva et al. (2010) reported the involvement of pre-motor and cerebellar brain sectors during preferred as opposed to non-preferred musical rhythms and indicated that activity in the ventral premotor cortex is enhanced by a preferred tempo.20 This study suggested that music that’s enjoyable by the brain the metabolic cost of exercise by promoting greater neuromuscular or metabolic efficiency. Therefore, Group B showed better improvements in CVE as compared to Group C.
According to Table 4, Figure 2, intergroup comparison of CVE as measured by VO2max shows that the improvement was significantly higher in Group B in which slow tempo music was administered as compared to Groups A and C which had fast tempo music and no music respectively.
Fast-paced music induces a greater activation of the sympathetic nervous system than slow-paced music. However, the slow music group showed better results than the fast music group. This was because synchronizing to slow tempo music was easier as compared to fast tempo music. Even though group A continued the exercises they could not maintain full efficiency so VO2max shows less increment while Group B showed an increase in VO2max as compared to Group A.21 Many cross-sectional comparative studies demonstrated a decrease in the percentage of type I fibres and an increase in type II glycolytic fibres in overweight individuals.22,23 Type I (tonic, slow twitch) generate a low level of muscle tension but can sustain the contraction for a longer period whereas type II generate a large amount of tension in a short period. The subjects exercising with fast tempo music possibly had greater activation of type II muscles fibres which led to early fatigue as compared to slow tempo music where sustained periods of the exercise was achieved and possibly had greater activation of Type I oxidative fibres.24 This thus explains a greater increase in VO2max in Group B. Therefore, Group B showed better improvements in CVE as compared to Group A. The limitation of our study is that the volume of the music was being played varied concerning the size of the places where the experiment had been held.
CONCLUSION
We conclude that exercising with music shows more improvements in cardiovascular endurance and slow tempo music shows better results than fast tempo music or no music.
Conflict of interest NIL
Source of Funding NIL
References:
-
Thakare AE, Mehrotra R, Singh A. Effect of music tempo on exercise performance and heart rate among young adults. Int J Physiol Pathoph Pharmacol 2017;9(2):35.
-
Carpentier FR, Potter RF. Effects of music on physiological arousal: Explorations into tempo and genre. Media Psych 2007;10(3):339-363.
-
Yamamoto T, Ohkuwa T, Itoh H, Kitoh M, Terasawa J, Tsuda T, et al. Effects of pre-exercise listening to slow and fast rhythm music on supramaximal cycle performance and selected metabolic variables. Arch Phys Biochem 2003;111(3):211-214.
-
Schjerve IE, Tyldum GA, Tjønna AE, Stølen T, Loennechen JP, Hansen HE, et al. Both aerobic endurance and strength training programmes improve cardiovascular health in obese adults. Clin Sci 2008;115(9):283-293.
-
Ramachandran A, Snehalatha C, Vinitha R, Thayyil M, Kumar CS, Sheeba L, et al. Prevalence of overweight in urban Indian adolescent school children. Diab Res Clin Pract 2002;57(3):185-190.
-
Robbins LB, Pender NJ, Kazanis AS. Barriers to physical activity perceived by adolescent girls. J Midw Women’s Health 2003;48(3):206-212.
-
Adamo KB, Rutherford JA, Goldfield GS. Effects of interactive video game cycling on overweight and obese adolescent health. App Physiol Nutr Metab 2010;35(6):805-815.
-
Kumar PP. The Effect of Circuit Training on Cardiovascular Endurance of High School Boys. Glob J Hum Soc Sci Res 2013;13(7):213.
-
Mahar MT, GuerieriAM, Hanna MS, Kemble CD. Estimation of aerobic fitness from 20-m multistage shuttle run test performance. Am J Prev Med 2011;41(4): S117-123.
-
Docherty DA, Wenger HA, Collis ML. The effects of resistance training on aerobic and anaerobic power of young boys. Med Sci Sport Exer 1987;19(4):389-392.
-
Herman L, Foster C, Maher MA, Mikat RP, Porcari JP. Validity and reliability of the session RPE method for monitoring exercise training intensity. Med Sci Sport Exer 2006;18(1):14-17.
-
Miller MB, Pearcey GE, Cahill F, McCarthy H, Stratton SB, Noftall JC, et al. The effect of a short-term high-intensity circuit training program on work capacity, body composition, and blood profiles in sedentary obese men: a pilot study. BioMed Res Int. 2014;20(1):114-117.
-
Paoli A, Pacelli QF, Moro T, Marcolin G, Neri M, Battaglia G, Sergi G, Bolzetta F, Bianco A. Effects of high-intensity circuit training, low-intensity circuit training and endurance training on blood pressure and lipoproteins in middle-aged overweight men. Lipids Health Dis 2013;12(1):131.
-
Daly I, Hallowell J, Hwang F, Kirke A, Malik A, et al. Changes in music tempo entrain movement related brain activity. In 2014 36th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society 2014:4595-4598.
-
Waterhouse J, Hudson P, Edwards B. Effects of music tempo upon submaximal cycling performance. Scand J Med Sci Sports 2010;20(4):662-669.
-
Seath L, Thow M. The effect of music on the perception of effort and mood during aerobic type exercise. Physiotherapy 1995;10(81):592-596.
-
Karageorghis CI, Priest DL. Music in the exercise domain: a review and synthesis (Part I). Int Rev Sport Exerc Psych 2012;5(1):44-66.
-
Maddigan ME, Sullivan KM, Halperin I, Basset FA, Behm DG. High tempo music prolongs high intensity exercise. Med J Tech 2019;6:e6164.
-
Thakare AE, Mehrotra R, Singh A. Effect of music tempo on exercise performance and heart rate among young adults. Int J Physiolo Pathophysiol Pharmacol 2017;9(2):35.
-
Patania VM, Padulo J, Iuliano E, Ardigò LP, ?ular D, Mileti? A, De Giorgio A. The psychophysiological effects of different tempo music on endurance versus high-intensity performances. Front Psychol 2020;11:74.
-
Szabo A, Small A, Leigh M. The effects of slow-and fast-rhythm classical music on progressive cycling to voluntary physical exhaustion. J Spo Med Phys Fit 1999;39(3):220.
-
American College of Sports Medicine. ACSM's exercise testing and prescription. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2017 Dec 26.
-
Kisner C, Colby LA: Therapeutic Exercise. Foundations and Techniques, 4th ed. Philadelphia: 2002; 151–152.
-
Husain G, Thompson WF, Schellenberg EG. Effects of musical tempo and mode on arousal, mood, and spatial abilities. J Mus Perc 2002;20(2):151-171.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License