IJCRR - 13(5), March, 2021
Pages: 150-156
Date of Publication: 03-Mar-2021
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
Elicitation of Bioactive Molecule by Screening of Fungal Secondary Metabolites Against MDR Staphylococcus Aureus
Author: Renuka Bali N, Dandin CJ, Vedamurthy AB
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Introduction: Fungal secondary metabolites are a diverse group of bioactive compounds; in which many have been reported as bio-therapeutics. Objective: The present study, relates to fungal secondary metabolites produced by filamentous fungi and screened against 21 clinical isolates of Staphylococcus aureus procured from Shri Dharmasthala Manjunatheshwara Medical College and Hospital Dharwad, Karnataka. Methods: Antibiogram assay was performed for these clinical isolates against Methicillin, Chloramphenicol, Vancomycin, Oxacillin and Clindamycin by Kirby Bauer's method. The zones were measured and compared to the Clinical and Laboratory Standard's Institute chart. Results: The resistance pattern observed for Methicillin-90.47%, Chloramphenicol-4.76%, Vancomycin-14.28%, Oxacillin-80.95% and Clindamycin-9.5%. We infer that, out of 21 interactions, 5 distance, 7 overgrowth, 4 contact and 5 zone-line inhibitions were observed. The zone of inhibition range observed was 10-17 mm against all 21 S. aureus strains after 18 hr incubation at 37 \?C on Mueller Hinton Agar plates. Bio-activity against S. aureus was noticed for F4 isolate between the 4-6th day of incubation and not on 7th day or later. The maximum inhibition zone observed for ethyl acetate:water fraction. Conclusion: The isolated compound from P. polonicum showed potent activity against the Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) clinical isolates has not been used against any MRSA or Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (VRSA) clinical isolates.
Keywords: Antibiogram, Co-Culture assay, Biphasic separation, Ethyl acetate, Penicilium polonicum
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION
The organism which shows resistance to one or more class/es of antibiotics referred as Multidrug resistance (MDR) (predominantly bacteria) is a grave threat that can lead to deaths of 10 million people per year by 2050.1 Pathogens like Enterococcus faecium, Staphylococcus aureus, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Acinetobacter baumanii, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and Enterobacter species (ESKAPE) were reported to emphasize that they currently cause the majority of infections and effectively “escape” the effects of antibacterial mechanisms. More people now die of Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) infection in the United State (US) hospitals than of HIV/AIDS and tuberculosis combined.2,3 Furthermore, pan-antibiotic-resistant infections now occur with increasing frequency over the past several decades.4 Out of different dangerous Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria MDR strains of Staphylococcus aureus also reported as MRSA and VRSA which belongs to firmicutes family and Gram positive coccoid bacteria are realized as a major threat.4 MDR Staphylococcus aureus is a community associated infectious agent found globally. The continuous trials being carried out to resolve this multidrug resistance and in the context fungal secondary metabolites are promising as bio therapeutics to tackle these MDR S. aureus. The fungal secondary metabolites are defensive compounds that have emerged as better options due to pharmacological evidence of them being more efficient and versatile molecules. Co-culture method is one of the methods to induce the formation of new secondary metabolites which are highly relevant for novel drug research against MDR bacteria.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Isolation of fungi
Soil samples were collected in and around Karnataka University campus in sterile polythene bags. 1gram of finely sieved soil sample was serially diluted in sterile water. 1ml of sample uniformly inoculated by spreader in SDA and PDA plates and incubated for 3-5days at room temperature. Lush growth was observed in mother plates. 40 pure isolates were maintained as pure cultures, 20 isolates were distinct and unique. Out of 20 fungi, five fungi were randomly picked by their unique morphological features for further process.
Antibiotic assay
The antibiotic assay was performed according to Kirby-Bauer’s antibiotic susceptibility test developed in 1950 and standardized by World Health Organization (WHO) in 1961.2 It is used to determine the resistance or sensitivity pattern of pathogenic bacteria isolates for prescribed antibiotics and further evaluated by using Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI). The presence or absence of an inhibitory area around the antibiotic disc identifies the bacterial sensitivity to the drug. The bacterium (S. aureus isolate) was swab inoculated on the Muller-Hinton agar plates and the antibiotic discs (Methicillin, Chloramphenicol, Vancomycin, Oxacillin and Clindamycin,) were placed on top of swab-inoculated MHA media. The antibiotics diffuse from the disc into the inoculated agar media in decreasing concentration outwards in a circular pattern from the antibiotic disc. If the organism is killed or growth inhibited by the concentration of the antibiotic that diffuses from the filter disc, there will be a clear zone around the disc (Figure 2). This measure of the zone (in mm) of inhibition leads to understanding the minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) values of antibiotics with suitable concentration against S. aureus. The zone sizes were measured (in mm) and compared to the standard CLSI5 (Table 2) that evaluates the results of the organism showing sensitive, intermediate and resistant activity against that particular antibiotic concentration.
Co-culture assay
Co-culture assay is a method of inoculating 2 different micro-organisms with proximity (side by side, few mm apart) to observe their association interactions. The fungus was inoculated with all 21 Staphylococcus aureus to observe the types of association and interactions. The zones of inhibitions were recorded as the zone of contact inhibition, overgrowth inhibition, zone line inhibition and distance inhibition. Previously the classical work of Alexander Fleming’s unintended result shows the antagonistic property of fungus over Staphylococcus sps.6 In this association inducing/ triggering secondary metabolites of fungi which are proved to be many bio-therapeutics. The co-existence of several Micro-organisms that share the same niche can affect the organism growth, adaptation patterns, morphology and developmental patterns.5,7 Co-culture assay used to check the natural compounds released from the association interactions.2,3
Fermentation
Fermentation method provides rich culturing of fungi (quantitatively) and serves for qualitative analysis like the enzymes and metabolites secreted in the broth can be assessed by different methods. The fungi were inoculated in PDB broth of 200 ml in 1000 ml conical flask to provide the proper base and it is protein supplemented with 1% peptone. Microscopic observation was done to check the fungal contamination with bacteria. The fungal growth could be observed from 3rd day. The rich growth was observed in both static and rotary method. The fungal yield could be noticed as high in static fermentation. The induction of secondary metabolites was observed from 3 rd day to 10th day by well diffusion method. The fungal broth was decanted under sterilized conditions to eppendorf tubes. The crude broth was subjected to well diffusion method. The result was observed for crude broth from 4th day to 10th day the fungal broth was filtered by 0.2 μ bacterial filter under sterile conditions. And this clear fungal broth was subjected to well diffusion method. After 6th day the filtered fungal broth did not show any activity by well diffusion method. The old culture was inoculated to fresh PDB media and repeated the activity. Out of 5 fungi (F1, F2, F3, and F5), F4 isolate showed the best activity by this method.
Well, the diffusion method
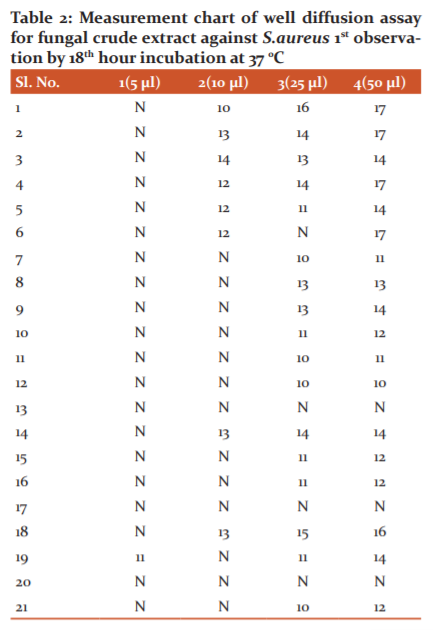
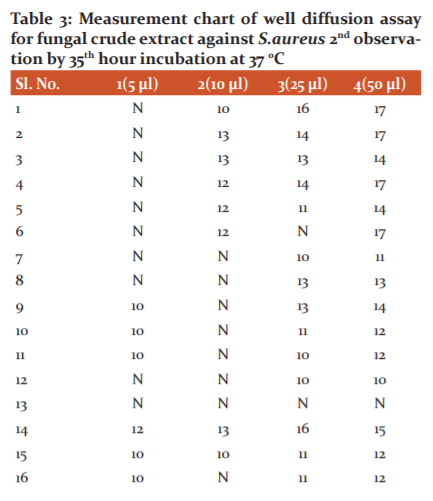
Well, the diffusion method is one of the well established bio-assay activity methods where the sample was diffused to form inhibition zones. Here 21 S. aureus samples were cotton swab cultured on MHA plates in clock and anti-clock strokes for uniform spreading. Different cotton swabs (sterile) were used for all 21 S. aureus samples. The wells were prepared using cork borer and these were equidistant from each other. The filtered fungal broth was loaded to 4 different wells marked as 1, 2, 3 and 4 with fungal broth volume loaded to these were 5, 10, 25 and 50μls respectively. The fungal broth was properly loaded within the good space so to take care of the overflow on the agar surface. The samples thus loaded on S. aureus inoculate MHA plates were allowed to diffuse for some time in LAF only. These were aseptically stretch wrapped and kept for incubation at 37 °C for 18 to 24 hrs. The results were recorded for 12th and 18th hour. These MHA plates were arrested in refrigerator after recording the zone measurement and documenting the results.
Biphasic separation
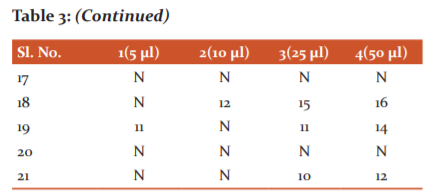
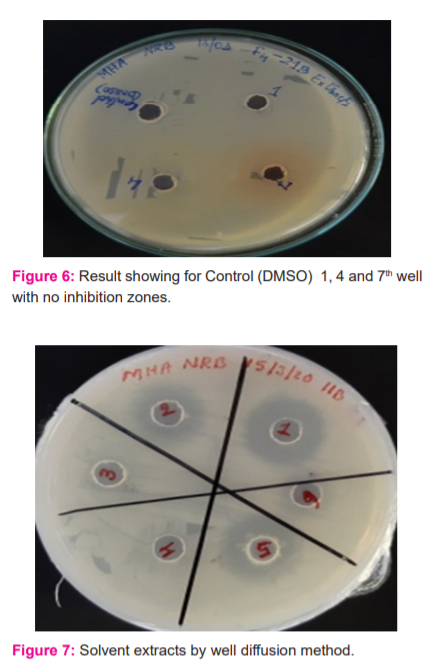
The crude broth activity showing positive results from well diffusion method was subjected to biphasic separation to understand the active molecule’s polarity continued by bio-activity assessment. Biphasic separation is one of the methods used to separate and solubilise the desired compound in a polar and non-polar combination ratio. Separating funnel was used for this method it was thoroughly washed and ethanol rinsed. The 5 different solvents used were Chloroform, Ethyl acetate, Benzene and Toluene. 5 ml of fungal broth and 5 ml solvent poured into the separating funnel, swirled for 5 to10 minutes. Arrest for 30 minutes and again continued this process till the aqueous and solvent phase separates distinctly. The aqueous and solvent phase was decanted slowly in separate vials. These vials kept for drying and it is solubilised with ½ ml of Dimethyl sulphoxide (DMSO). The aqueous phase and solvent phase have been separately taken in a petri dish and dried. These reconstituted solvent extracts were subjected to a good diffusion method. 75μl of all the sample aliquots were dispensed to the respective wells and DMSO as control. Extract samples in well no. 1 and 4 are aqueous phases and chloroform, 2 and 6 are aqueous phase and ethyl acetate, 3rd and 5th are aqueous phase and Benzene and the 7th one was Toluene and 8th as an aqueous phase of Toluene did not dry. So this was not considered for well diffusion method.
RESULTS
Isolation of fungi
The fungal isolates (F1, F2, F3, F4 and F5) were observed for their colony characterization. These were stained with Lactophenol cotton blue and microscopic observation was done up to genus level. These isolates were picked for its unique and distinct morphological features to perform co-culture assay against S. aureus after confirming the resistance pattern by Antibiogram Assay (Figure 1)

Antibiogram assay for Staphylococcus aureus
Antibiogram assay was conducted for 21 Staphylococcus aureus procured from SDM Medical College, Dharwad, Karnataka. These were revived in Muller-Hinton broth and incubated for 12-24 hours at 37 °C and used as the source for S. aureus pure culture isolates in further studies. The fresh cultures on attaining an optical density of 1.0-1.5 checked through turbidometric/ spectroscopic method and were used to conduct antibiogram assay by Kirby Bauer’s method using reference antibiotics, MHA plates (21 nos.) were cotton swabbed with 21 S. aureus isolates individually and the antibiotic discs were gently placed on the media equidistantly without disturbing the media and incubated 18-24 hours at 37 °C. The 5 antibiotics used for antibiogram assay were observed Methicillin, Vancomycin, Clindamycin, Oxacillin and Chloramphenicol (Meth, Va, Cd, Ox and C respectively). The 24 hour incubated plates were observed for the inhibition zones, which were measured by the scale (Hi-media) designed to measure the zone of inhibition diameter. The concentration and measurement zones for different antibiotics for S. aureus samples were assessed as susceptible, intermediate and resistant by referring CLSI chart. These clinical S. aureus isolates were further subjected to Co-culture assay against the fungal isolates (Figure 2).
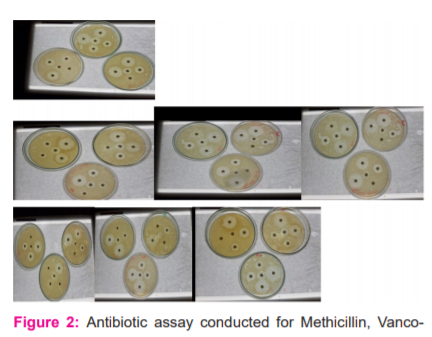
Figure 2: Antibiotic assay conducted for Methicillin, Vancomycin, Clindamycin, Oxacillin and Chloramphenicol against S. aureus clinical isolates (21 plates).
The antimicrobial assay was conducted for 21 clinical isolates obtained from SDM Medical College, Dharwad, Karnataka for Methicillin, Vancomycin, Clindamycin, Oxacillin and Chloramphenicol
Outcome
The resistance pattern of Antibiotic assay against each antibiotic in % of total S. aureus screened (Table 1). Methicillin (90.47%), Chloramphenicol (4.76%), Vancomycin (14.28%), Oxacillin (80.95%) and Clindamycin (9.5%) found among the 21 isolates against the microorganism S. aureus.
Co-culture assay
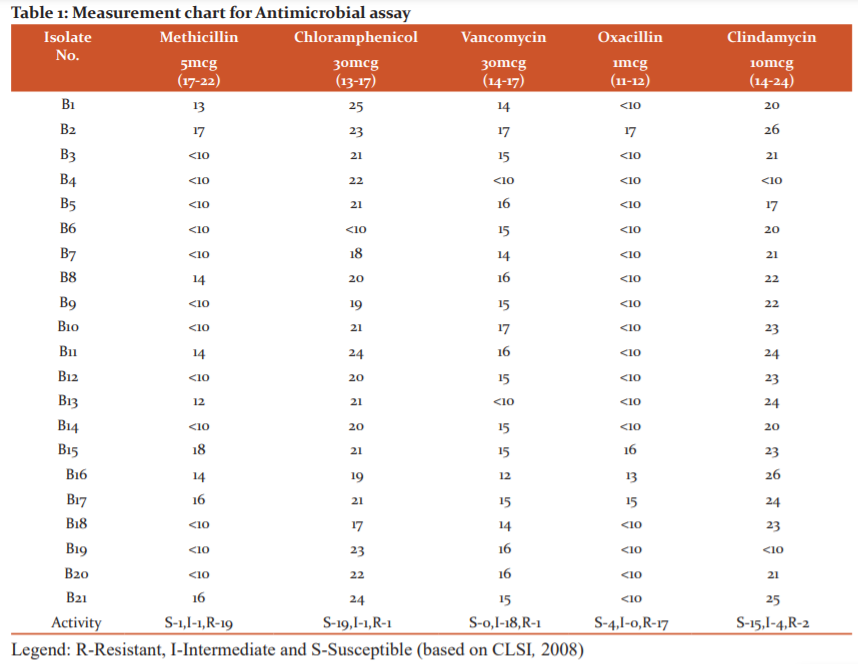
The clinical isolates were subjected to co-culture assay. The 21 S. aureus were co-cultured with fungal pure culture. Both the isolates were inoculated in PDA enriched with 1% peptone and incubated at 32 oC. The 3rd-day observation was recorded and the zones of interactions were categorized into the zone of contact, Distance inhibition, Overgrowth inhibition, zone line inhibition (Figure 3). In which the overgrowth is considered as antagonistic property, concerning the Alexander Fleming discovery of Penicillin pattern, this overgrowth inhibition was counted. Interpretation of the co-culture as denoted by the following method.
D=F4-A7, F4-A9, F4-A12, F4-A15, F3-A15 (5)
O=F4-A1, F4-A2, F4-A6, F4-A5, F4-A10, F4-A13, F3-A1 (7)
C=F4-A4, F4-A8, F4-A14, F3-A14 (4)
Z=F4-A3, F4-A7, F4-A11, F4-A16, F3-A16 (5)
Static fermentation of fungi
Five fungi were subjected to static and rotary fermentation to check the yield. The PDB media used with 1% addition of peptone for a protein supplement. Static fermentation was observed for a good yield. The fungi were inoculated in 500 ml conical flask for 200 ml volume to allow the fungal growth width wise. Duplicates were maintained for backup. The rich growth was observed 4th day without contamination of bacteria. Lacto phenol cotton blue staining was performed to observe the pure fungal spores. The Microscopic observation confirmed the pure fungal hyphae structure. The broth was decanted to Eppendorf vial in sterile condition to perform well diffusion method (Figure 4).

Well, the diffusion method
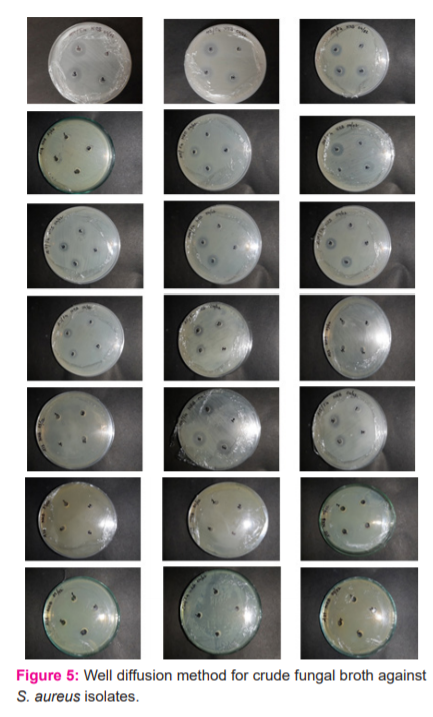
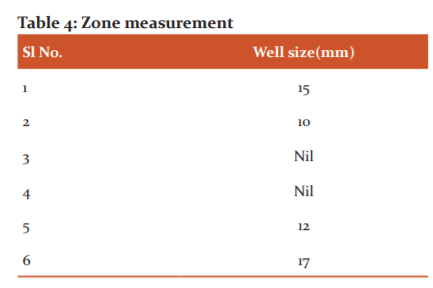
Uniform cotton swabbing of S.aureus was done for Mueller Hinton Agar media plates. The fungal broth of 5,25,40 and 50 μls loaded by micropipettes to 1,2,3 and 4 labelled wells respectively. It is filtered through a 0.2mm sterile filter disk. These plates were incubated at 35-37°. 12th and 24th observation were done and the good size in mm was reported as in the following figure and table (Figure 5 and Table 2 & 3).
Bi-phasic separation
This is bioactivity guided separation performed by using polar and non-polar solvent system combinations. The polar and non-polar solvent extracts with fungal broth subjected to well diffusion method. 75μl of all the sample aliquots were dispensed to the respective wells and DMSO as control. Extract samples in well no. 1 and 4 are aqueous phase and chloroform, 2 and 6 are aqueous phase and ethyl acetate, 3rd and 5th are aqueous phase and Benzene and 7th one was Toluene as aqueous phase was not available. Ethyl acetate extract showed the best activity (Figure 5 & 6 and Table 4).
DISCUSSION
The work here is being conducted to obtain the understanding of the association between the co-culture assays and the metabolite induction against the MDR bacteria. Co-culture assay being an old concept has not been much attempted to obtain metabolite of biochemical importance and very few reports have been published with regards to metabolite induction4 and in particular for antibiotic induction.8 The simple method of isolation and screening to obtain active association between bacteria and fungi is seen in the present study showing a visible interaction in the form of different activities respectively as a zone of contact, distance inhibition, overgrowth inhibition and zone line inhibition and the same has been reported.9 Further, the broth culture of the active fungal isolate F4 that was later identified as P. polonicum showed the inhibiting activity of growth against the MRSA clinical isolates (S. aureus) and there are no reports of any bioactivity of P. polonicum producing a metabolite effective in growth inhibition of MRSA isolates. The recent study of identification and detail functional characterization of the metabolites produced by P. polonicum has been reported by Yanzhang Wen and co-workers.10 The authors have reported two new compounds apart from already reported seven compounds that have been known to show moderate anti-HCC activity, when tested against HepG2 hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) cell lines, compounds 4-8. Further, compound 1-3 have effects on increasing GLUT4 translocation and glucose uptake in vitro.10 The metabolite supposed to be part of the bio-active fraction obtained by bi-phasic separation using ethyl acetate: water has been dried and predicted as non-polar compound. This has been sent for molecular identification. The compound reported in this work, isolated from P. polonicum was showing efficient activity against the MRSA clinical isolates has not been used against any MRSA or VRSA clinical isolates and thus we claim this is the first report of a bioactive molecule isolated from P. polonium against clinical MRSA isolates.
CONCLUSION
Thereby we derive by our experimental evidence that using a powerful tool like antibiogram assay, co-culture assay, fermentation, well diffusion method, the bi-phasic separation that can enhance, diverse fungal metabolite production ability of the isolated fungi against the multi-drug resistant S. aureus. It will be the best future solution to the medical issues to act as a pharmacological potential drug by such organisms and which is safer and cost-effective natural source for microbial infection.
Acknowledgement: The authors are thankful to the PG Department of Microbiology and Biotechnology, Karnatak University, Dharwad, Karnataka for providing all the necessary facilities and University Grants Commission, for the award of NFHE fellowship from April 2016-17- March 2021.
Conflict of interest: None
Source of funding: Under NFHE Fellowship
1st Author: carried out all the experiments of the planned work
2nd Author: designed the experiments and methodology of the work
3rd Author: Guided and manuscript prepared for the work which was carried out by the students
References:
1. Exner M, Bhattacharya S, Christiansen B, Gebel J, Goroncy-Bermes P, Hartemann P, et al. Antibiotic resistance: What is so special about multidrug-resistant Gram-negative bacteria?
-
Antibiotic resistance: What is so special about multidrug-resistant Gram-negative bacteria?
-
Antibiotic resistance: What is so special about multidrug-resistant Gram-negative bacteria? GMS Hyg Infect Control 2017;12:5.
9. Chang HH, Cohen T, Grad YH, Hanage WP, O’Brien TF, Lipsitch M. Origin and proliferation of MDR in bacterial pathogens. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 2015;79(1):101-116.
2. Bauer AW, Kirby WMM, Sherris JC, Turck M. Antibiotic susceptibility testing by a standardized single disk method. Am J Clin Pathol 1966;45(4):493-496.
3. Bertrand S, Bohni N, Schnee S, Schumpp O, Gindro K, Wolfender JL. Metabolite induction via microorganism co-culture: a potential way to enhance chemical diversity for drug discovery. Biotechnol Adv 2014;32(6):1180-1204.
7. Tan ZQ, Leow HY, Lee DCW, Karisnan K, Song AAL, Mai CW, et al. Co-culture systems for the production of secondary metabolites: current and prospects. Biotechnol J 2018;13:18-26.
5. Azzollini A, Boggia L, Boccard J, Sgorbini B, Lecoultre N, Allard PM, et al. Dynamics of metabolite induction in fungal co-cultures by metabolomics at both volatile and non-volatile levels. Frontiers in Microbiol 2018. 9: 72.
6. Rico-Gray V. Interspecific interaction. In: encyclopedia of life sciences. John Wiley & Sons, Ltd. Nature 2001, 1-6.
-
Sunderland D, Graczyk TK, Tamang L, Breysse PN. Impact of bathers on levels of Cryptosporidium parvum oocysts and Giardia lamblia cysts in recreational beach waters. Water Res 2007, 41(15): 3483-3489.
4. Fleming A. On the Antibacterial action of cultures of a Penicillium, with special reference to their use in the isolation of B. influenzæ. Br J Exp Pathol 1929, 10(3):226-236.
-
Boucher HW, Talbot GH, Bradley JS, Edwards JE, Gilbert D, Rice LB, et al. Bad bugs, no drugs: No ESKAPE! an update from the infectious diseases society of America. Clin Infect Dis 2009, 1;48(1):1-12. doi: 10.1086/595011.
-
Fair RJ, Tor Y. Antibiotics and bacterial resistance in the 21st century. Perspectives in Med Chem 2014, 6: 25–64.
-
Grundmann H, Klugman K, Walsh T, Ramon-Pardo P, Sigauque B, Khan W, et al.A framework for global surviellance of antibiotic resístanse. Drug Resist Updat 2011, 14(2):79-87. doi: 10.1016/j.drup.2011.02.007.
8. Barlam TF, Cosgrove SE, Abbo LM, MacDougall C, Schuetz AN, Septimus EJ, et al. Implementing an antibiotic stewardship program: guidelines by the infectious diseases society of America and the society for healthcare epidemiology of America. Clin Infect Dis 2016, 62(10):e51–77.
-
Vandana K, Gargi Dangre, Abhay M. Healthcare setting and methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Int J Cur Res Rev. Modern Therapeutics Applications, July, 2020, 123-128, http://dx.doi.org/10.31782/IJCRR.2020.123128
-
Sonnenbichler J, Dietrich J, Peipp H. Secondary fungal metabolites and their biological activities, V. investigations concerning the induction of the biosynthesis of toxic secondary metabolites in Basidiomycetes. Biolog Chem Hoppe Seyler 1994, 375(1):71–80.
10. Mehta AP, Rodrigues C, Sheth K, Jani S, Hakimiyan A, Fazalbhoy N. Control of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in a tertiary care centre–a five-year study. J Med Microbiol 1998, 16(1): 31–34.
19. Nielsen JC, Nielsen J. Development of fungal cell factories for the production of secondary metabolites: linking genomics and metabolism. Synth Systems Biotechnol 2017, 2(1): 5-12.
20. Wen Y, Lv L, Hao Ji, Chen H, Huang Y, Liu C, et al. Two new compounds of Penicillium polonicum, an endophytic fungus from Camptotheca acuminate Decne. Nat Prod Res 2018, 34(13): 1879-1883. doi.org/10.1080/14786419.2019.1569003
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License