IJCRR - 13(5), March, 2021
Pages: 115-120
Date of Publication: 03-Mar-2021
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
Assessment of Toxicity Profile Among Patients Receiving Concurrent Chemoradiotherapy in Head and Neck Cancer Patients with or Without Glutamine Supplements
Author: U. Umamaheswara Reddy, Pratap Kumar Reddy S
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Introduction: Chemoradiation is commonly used curative treatment option for many forms of thecancer and produce synergistic effects than chemotherapy or radiation, per se. Objective: This study aims at assessing and comparing the toxicity profile and treatment breaks in patients receiving concurrent chemoradiation with 3D-Conformal Radiotherapy with or without glutamine supplements in head &neck cancers. Methods: 80 patients diagnosed with squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck who were treated with 3D-Conformal Radiotherapy in the as a prospective non-randomized double-arm observational study. 40 patients who received glutamine supplements and 40 patients who didn't receive glutamine supplements were reviewed weekly once for assessment of toxicity profile. Results: Out of the 80 patients, 64 patients were male and 16 female. Mean age was 54 years (range 13-74 years). 40 patients received glutamine supplements and 40 patients didn't receive glutamine supplements. The mean maximum grade of oral mucositis, dysphagia, skin reactions was less severe in the patients receiving glutamine compared to the patients not receiving glutamine ((p=0.0001).7.5% of patients who received glutamine supplements developed grade 3 skin reactions compared to 20% of patients who didn't receive glutamine supplements. 7.5% in the glutamine arm had treatment breaks with a range of 2-5 days. 32.5% in the control arm had treatment breaks with a range of 3-10 days. Conclusions: Glutamine supplementation in head and neck cancer patients receiving concurrent chemoradiotherapy may delay the onset of mucositis reactions, skin reactions, dysphagia and also the progression of the mucositis reactions, skin reactions, and dysphagia.
Keywords: Radiotherapy, Glutamine, 3DCRT, Concurrent chemoradiation, Toxicity profile, Mucositis, Skin reactions, Dysphagia, Head and neck cancer
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION
The greatest challenge in cancer treatment is to attain the highest probability of cure with the least morbidity. The simplest theoretical way is to increase the therapeutic ratio. With radiation this is possible by encompassing all cancer cells with sufficient doses of radiation during each fraction, simultaneously sparing surrounding normal tissues at the same time.1,2 In several types of cancer, radiation therapy may be curative if it is localised to one part of the body. To avoid tumour recurrence, it can also be used as part of curative treatment following surgery to remove a single malignant tumour. Radiation therapy is synergistic with chemotherapy and has been used with sensitive cancers before, during and after chemotherapy.1,2
Over the last quarter of a century, clinical trials have shown improvement in treatment results for patients with squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck, including greater local control, lower frequency of systemic recurrences, improved disease-free survival and most significantly improved overall survival. Prospective randomised phase III trials and meta-analyses and more significantly, population-wide statistics have shown an increase in overall survival. At the National Cancer Center, the Screening, Epidemiology, and End Results (SEER) programme assess improvements in cancer mortality rates in the United States.3,4
The goal of radiation therapy is to provide the specified tumour volume with an appropriately measured dose of irradiation with as little damage as possible to the surrounding healthy tissue, resulting in tumour eradication, high quality of life and extended survival. In addition to curative efforts, in the successful palliation or prevention of symptoms of the disease, radiation therapy plays a significant role in cancer management: pain can be alleviated, luminal patency can be restored, skeletal integrity can be maintained, and with minimal morbidity, organ function can be restored. Our ability to recognise tumours has been significantly enhanced by technological advances in the application of x-rays, computed tomography scans, magnetic resonance imaging with and without spectroscopy, ultrasound, positron emission tomography scans, and electronic portal imaging and our awareness of their limitations. We recognised that high doses to the salivary glands caused dry mouth, reduced taste, and poor dental health while treating patients with head and neck cancers, but we were unable to eliminate these side effects without risking a cure compromise. From non-site-specific approaches using bony anatomy and hand-drawn blocking, modern radiotherapy has developed into advanced preparation combining three-dimensional image reconstructions and algorithms for computer optimization.5,6
Concurrent Chemoradiation (CCRT) has proven to be the standard treatment option as an organ-preserving approach in early/ loco-regionally advanced head and neck cancers. With the improvement in tumour control and potential survival, issues regarding toxicity profile have become more pertinent.
In patients with cancer, marked glutamine depletion develops over time. Cancer cachexia is marked by massive depletion of skeletal muscle glutamine. This can hurt the function of host tissues that are dependent upon adequate stores of glutamine for optimal functioning. Furthermore, the extent of normal tissue damage from radiation or chemotherapy may be influenced by the presence of adequate tissue glutamine stores. Both of these facts support a possible therapeutic role for glutamine in the prevention of host normal tissue toxicity during cancer treatment.7,8 In the present study, we tried to assess the toxicity profile and compare them with the patients receiving and not receiving glutamine supplements.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Prospective non-randomized observational clinical study This study involved the assessment and comparison of toxicity profile in 80 patients who were diagnosed with biopsy-proven squamous cell carcinoma of head and neck region between April 2014 to May 2015 at Apollo Speciality Hospitals, Chennai. (Consent form approval number:141-41102-131-107619). The study was designed as a prospective non-randomized double-arm observational study. Each arm consisted of 40 patients of a biopsy-proven, non-metastatic Squamous cell carcinoma of head and neck region. . The patient and attendant were explained regarding the mechanism of action, tolerance, usefulness, available literature about glutamine administration in head & neck cancer. This study was commenced after obtaining clearance from the hospital ethics and scientific committee
After staging workup was completed, patients were subjected to radiation concurrent with chemotherapy. Radiation technique [3DCRT] and frequency of chemotherapy (weekly) was planned for all the patients.
Inclusion Criteria:
-
Head & Neck cancers (Subsites to be included: Oral cavity, Oropharynx, Hypopharynx, Larynx) with documented Squamous cell carcinoma histopathology.
-
Stage - T2-4 N1-2c M0.
-
Performance status - Karnofsky >80.
-
Concurrent Chemoradiation with Cisplatin-based chemotherapy.
-
Patients who were willing to participate in this study.
Exclusion Criteria:
1. Prior Radiation to the neck region.
2. Age > 75 yrs.
3. Patients who are unable to undergo Radiation treatment.
4. Patients who are unable to undergo Chemotherapy concurrent with radiation.
5. Non-squamous cell cancers of head & neck.
6. Patients with N3 nodes/ any distant metastases at the time of diagnosis.
7. Concurrent chemo other than Cisplatin-based chemotherapy.
After obtaining informed consent, patients were taken up for radiotherapy preparation. All the demographic data of the patients were collected at the time of preparation. All patients were properly immobilized with a suitable neck rest and aquaplanet mask. Shoulder retractor was used when necessary. After proper immobilization in treatment position technique – Plain CT images of head and neck were taken from the base of the skull to clavicle with a Simulator CT machine.
The acquired axial images were transferred to the treatment planning system (Oncentra Treatment planning system version 4.1) in DICOM format. These images received in the Treatment planning system were first registered and re-constructed for contouring. The primary and node volume with adequate margins (gross tumour volume & clinical target volume ) were contoured along with organs at risk (OAR) in the axial plane. All the contours were verified by the radiation oncology consultant before treatment planning. The treatment planning was done by the qualified medical physicist using Oncentra (version 4.1) treatment planning system. Each plan was evaluated by the radiation oncology author, consultant and the thesis guide. On approval of the plan, treatments were delivered on linear accelerator 6 MV photons.
In 3D-CRT, the dose to the spinal cord was limited to 44 Gy. Patients were treated with three dimensional conformal RT (3D-CRT) with concurrent cisplatin-based chemotherapy as per protocol. 40 patients who received glutamine supplements (Glutamine arm) and 40 patients who didn’t receive glutamine supplements (Control arm) were reviewed weekly once for assessment of toxicity profile.
Glutamine was administered as 10 grams of L-Glutamine mixed with 200 ml of water two times a day. Every 15 grams of sachet contains L-Glutamine 10 grams, Vitamin C 250 mg, Zinc sulphate equivalent to elemental zinc 10 mg, Astaxanthin 10% 4 mg, Copper Sulphate equivalent to elemental Copper 1 mg and Selenium Selenomethionine equivalent to elemental selenium 100 mcg Other ingredients are Mannitol, Sucralose. All the patients were reviewed weekly for toxicity assessment and were given grades using RTOG Acute Radiation Morbidity Grading System. All documented toxicity profile was taken up for analysis.
Data entry was done in Micro Soft Excel spreadsheet. Data validation and analysis were carried out by SPSS version 16.0. All the continuous variables were assessed for the normality using Shapiro Wilk’s test. If the variables are normally distributed, they are expressed as Mean ± Standard deviation. Otherwise Median (Interquartile range). All the categorical variables were expressed either as percentage or proportions. Comparison of non normally distributed continuous variables was carried out by the Mann-Whitney U test. Comparison of categorical variables was done by chi-square test or fisher’s exact test based on the number of observations. All the p values <0.05 was considered as statistically significant.
RESULTS
The study was designed as a prospective non-randomized double-arm observational study. Each arm consisted of 40 patients of a biopsy-proven, non-metastatic Squamous cell carcinoma of head and neck (HNSCC) region. The patient population was divided into two groups, one who received glutamine supplements and another who did not receive glutamine supplements (Table 1).
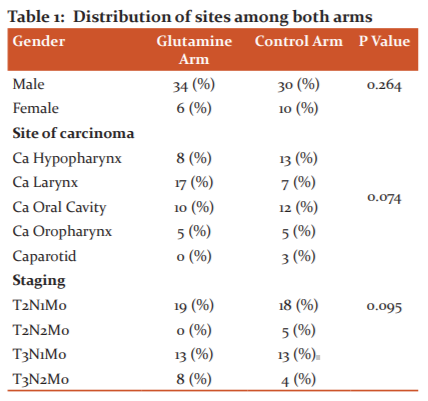
Effect on skin reactions
Skin reactions were not significantly different between both the arms for gender, cancer site and staging distribution (Table 2). There was statistical significance between both the arms for skin reactions after 2 and 4 the week of treatment (p=0.001).
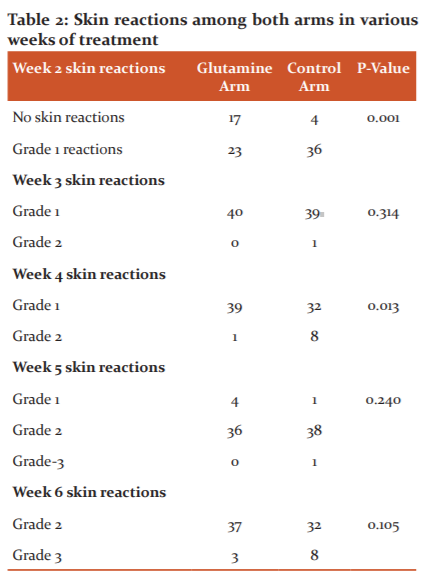
Effect on mucositis
There was no statistical significance between both the arms for skin reactions after 3 rd,5th and 6th weeks of treatment (Table 3). There was statistical significance between both the arms for mucositis reactions after 2,3 rd,5 th and 6 th week of treatment (p=0.001).
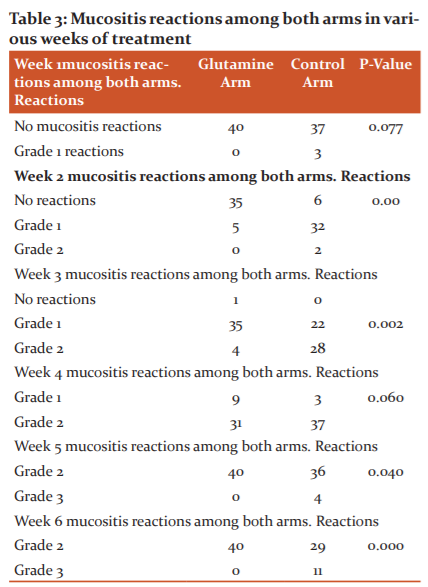
Effect on dysphagia
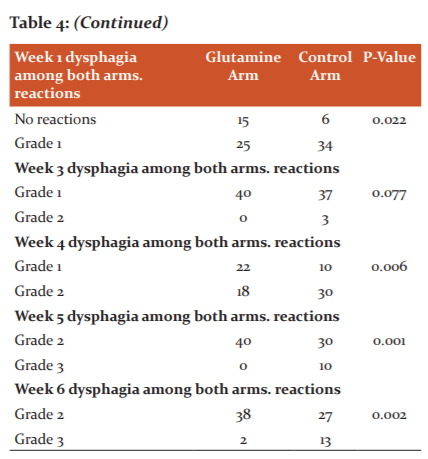
There was no statistical significance between both the arms for mucositis after 1 st, and 4 th weeks of treatment (Table 4). There was statistical significance between both the arms for dysphagia reactions after 2 nd, 4th, 5 th and 6 th week of treatment. There was no statistical significance between both the arms for dysphagia after 1 st and 3 rd weeks of treatment.
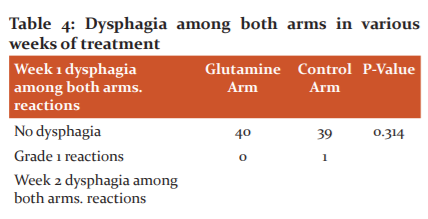
Treatment Breaks
3 (7.5%) out of 40 patients in the glutamine arm had treatment breaks with a range of 2-5 days. 13 (32.5%) out of 40 patients in the control arm had treatment breaks with a range of 3-10 days. From the above observations, it is understood that glutamine supplementation reduced the percentage of patients requiring treatment breaks and also the number of days.
DISCUSSION
Radiotherapy and Chemotherapy are the cornerstones in the management of head and neck malignancies. However, it leads to unavoidable toxicities in the form of systemic alterations and local lesions such as mucositis, loss of taste, decreased salivation, microbial colonization, dysphagia, and osteoradionecrosis (Table-1)The local toxicities outweigh the systemic complaints both in severity and difficulty in management.1,2
In our study, 7.5% of patients in the glutamine arm developed grade 3 skin reactions (Table-2) Similarly in Zygogianni et al.11, 9.7% of patients in the glutamine arm developed grade 3 skin reactions. In Imai et al.12 18.8% of patients in the glutamine arm developed grade 3 skin reactions. In our study, 7.5% of patients in the glutamine arm had treatment breaks with a range of 2-5 days. 32.5% of patients in the control arm had treatment breaks with a range of 3-10 days (p<0.001). In Pachon et al.10, they found that 19.8% of patients who did not take glutamine discontinued treatment versus 6.9% of patients who took (p=0.002).
Oral mucositis is the most frequently occurring painful and dose-limiting side- effect of therapeutic irradiation of the head and neck (Table-3) Conventional fractionation schedules cause grade 3 and grade 4 mucositis in approximately 25% of the Radiation Therapy Oncology Group (RTOG) studies whereas, accelerated regimes like concomitant boost or hyper-fractionation increase the same to 50%. Addition of concomitant chemotherapy during the radiotherapy further aggravates these lesions leading to significant morbidity, odynophagia, dysgeusia, and subsequent dehydration and malnutrition.2 Furthermore, modifications and dose reductions in the treatment schedule, more so with concurrent chemotherapy, to allow for resolution of these lesions can directly compromise patient survival. Different interventions are currently practised with varying benefits, but there is no consensus on the most effective way to prevent or treat this most distressing complication. Oral mucositis manifests first by thinning of oral tissues leading to erythema. As these issues continue to thin, ulceration eventually occurs.3 It has significant clinical implications in patients receiving radiation therapy for the treatment of head and neck cancer. It may cause severe pain and dysfunction that interfere with swallowing and speech and lead to serious consequences such as weight loss. More importantly, radiation-associated mucositis can have significant implications on tumour control or cure, if treatment has to be interrupted to allow for healing or the dose and volume have to be reduced. There are no established measures for the treatment of oral mucositis.3
A study showed that oral care to remove potential sources of infection provided in conjunction with cancer therapy is necessary to prevent serious complications, including rampant decay and osteoradionecrosis with radiation therapy and potentially life-threatening infections and bleeding with chemotherapy. Certain studies had shown that the use of topical antimicrobial lozenge containing polymyxin, tobramycin, and amphotericin B reduced oral mucositis with radiation therapy. Two hematopoietic growth factors granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (GCSF) and granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GMCSF) have been employed extensively to lessen mucositis. But these growth factors are expensive and would lead to economic burden to the patients.2
Dysphagia is a very common complaint that may occur before during and after chemoradiotherapy in patients with head and neck cancer. (table-4)This contributes to dietary malnutrition, weight loss, and excessive feeding and also has a substantial potential risk of aspiration. This has a major negative effect on the entire quality of life of the patient. Since dysphagia treatment is rarely successful in this setting, avoidance is paramount. To decrease dysphagia, several strategies have been developed. This include swallowing exercises, therapy adjustment strategies such as intensity-modulated radiotherapy, elective node selective delineation, parotid-sparing radiotherapy reduction of xerostomia, and the addition of radioprotectors.4
Acute skin reaction (radiation dermatitis) that ranges from a mild rash to extreme ulceration is one of the most common side effects of chemoradiation. There will be a moderate-to-severe skin reaction in about 85 % of patients infected with radiation therapy. Acute skin-induced radiation reactions often lead to itching and discomfort, treatment delays, and reduced aesthetic appearance, resulting in a decline in the quality of life.5
Klimberg et al.6 used a rat breast cancer model to show that glutamine-supplemented with mammary tumours had greater glutamine and glutathione concentrations, and decreased PGE production than rats that received no glutamine. In another study, PGE levels (prostaglandins) from the tissues obtained by serial mucosal biopsies from experiencing acute radiation effects increased with increased inflammation. In patients with cancer, marked glutamine depletion develops over time; cancer cachexia is marked by massive depletion of skeletal muscle glutamine. This can harm the function of host tissues that are dependent upon adequate stores of glutamine for optimal functioning.2
Furthermore, the extent of normal tissue damage from radiation or chemotherapy may be influenced by the presence of adequate tissue glutamine stores. Both of these facts suggest a possible therapeutic role for glutamine in the prevention of host normal tissue toxicity during cancer treatment.7 In our study, we found that the mean maximum grade of oral mucositis was less severe in the glutamine arm compared to the control arm (2 vs. 2.27) (p=0.0001). This is similar to Huang et al.8 where they found that the mean maximum grade of oral mucositis was less severe in the glutamine arm compared to the control arm (1.6 vs. 2.6) (p=0.0058). Similarly in Sarumathy et al.3, they found that the mean maximum grade of oral mucositis was less severe in the glutamine arm compared to the control arm (2 vs. 2.93). In Tsujimoto T et al. 9 they found that the mean maximum grade of oral mucositis was less severe in the glutamine arm compared to the control arm (2.9 vs. 3.3) (p=0.005). In our study, the mean dose of radiation at the time of occurrence of mucositis was 21 Gy without glutamine supplementation and 29 Gy with glutamine supplementation. Similarly in Sarumathy et al.3 the mean dose of radiation at the time of occurrence of mucositis was 15 Gy without glutamine supplementation and 21 Gy with glutamine supplementation.11,12
Our study showed the mean dose of radiation at the time of occurrence of mucositis and dysphagia was 21 Gy and 22 Gy respectively in patients without glutamine supplementation versus 29 Gy and 24 Gy in patients with glutamine supplementation (p<0.005). In Pachon et al.10 they found that the mean dose of radiation at the time of occurrence of mucositis and odynophagia was 30.9 Gy and 29.8 Gy respectively in patients without glutamine supplementation versus 43.5 Gy and 40.1 Gy in patients with glutamine supplementation (p < 0.001)
CONCLUSIONS
Based on the results of our study, Glutamine supplementation in head and neck cancer patients receiving concurrent chemoradiotherapy may delays the onset of skin reactions, mucositis reactions and dysphagia also the progression of the reactions. Glutamine supplementation may decrease the number of patients having treatment breaks and also the number of days of treatment interruptions.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
Authors acknowledge the immense help received from the scholars whose articles are cited and included in references to this manuscript. The authors are also grateful to authors/editors/publishers of all those articles, journals and books from where the literature for this article has been reviewed and discussed.
Conflict of interest-Nil
Financial support-Nil
References:
-
Vidal-Casariego A, Calleja-Ferne?ndez A, Ballesteros-Pomar MD, Urioste-Fondo A, Rodriguez-Domi?nguez D, Se?nchez-Aparicio E, et al. PP293 Prevention of oral and oesophagal radiation mucositis with glutamine: a retrospective study. Clin Nutr Suppl 2010;5(2):137-148.
-
Chattopadhyay S, Saha A, Azam M, Mukherjee A, Sur PK. Role of oral glutamine in alleviation and prevention of radiation-induced oral mucositis: A prospective randomized study. Sou Asi J Canc 2014 Jan;3(1):8-1
-
Sarumathy S, Ismail AM, Palasimany A. Efficacy and safety of oral glutamine in radiation-induced oral mucositis in patients with head and neck cancer. Asian J Pharm Clin Res 2012;5:138-40.
-
Platteaux N, Dirix P, Dejaeger E, Nuyts S. Dysphagia in head and neck cancer patients treated with chemoradiotherapy. Dysphagia 2010 Jun;25(2):139-152.
-
Salvo N, Barnes E, van Draanen J, Stacey E, Mitera G, Breen D, et al. Prophylaxis and management of acute radiation-induced skin reactions: a systematic review of the literature. Curr Oncol 2010 Aug;17(4):94-112.
-
Klimberg VS, Kornbluth J, Cao Y, Dang A, Blossom S, Schaeffer RF. Glutamine suppresses PGE2 synthesis and breast cancer growth. J Surg Res 1996 Jun;63(1):293-7.
-
Hensley CT, Wasti AT, DeBerardinis RJ. Glutamine and cancer: cell biology, physiology, and clinical opportunities. J Clin Invest 2013;123(9):3678-3684.
-
Huang EY, Leung SW, Wang CJ, Chen HC, Sun LM, Fang FM, et al. Oral glutamine to alleviate radiation-induced oral mucositis: a pilot randomized trial. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 2000;46(3):535-539.
-
Tsujimoto T, Yamamoto Y, Wasa M, Takenaka Y, Nakahara S, Takagi T, et al. L- glutamine decreases the severity of mucositis induced by chemoradiotherapy in patients with locally advanced head and neck cancer: a double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial. Oncol Rep 2015 ;33(1):33-3
-
Iba?n?ez JP, A?ngel BQ, Gironzini VS. Best oral presentation: Prevention of mucositis in head and neck cancer (HNC) with glutamine. Rep Pract Oncol Radiother 2013;18:S110.
-
Zygogianni A, Kyrgias G, Kouvaris J, Pistevou-Gombaki K, Capezzali G, Zefkili S, et al. Impact of acute radiation induced toxicity of glutamine administration in several hypofractionated irradiation schedules for head and neck carcinoma. Head Neck Oncol 2012;4(5):86.
-
Imai T, Matsuura K, Asada Y, Sagai S, Katagiri K, Ishida E, et al. Effect of HMB/Arg/Gln on the prevention of radiation dermatitis in head and neck cancer patients treated with concurrent chemoradiotherapy. Japan J Clin Oncol 2014 May;44(5):422-7.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License