IJCRR - 13(5), March, 2021
Pages: 64-69
Date of Publication: 03-Mar-2021
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
Chromium (III) Complexes of Metformin, Dapagliflozin, Vildagliptin and Glimepiride Potentiate Antidiabetic Activity in Animal Model
Author: Fahima Aktar, Md. Zakir Sultan, Mohammad A. Rashid
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Introduction: Diabetes is a chronic disease which increases morbidity, mortality along with social and economic costs. Chromium [Cr(III)] is a trace element which plays an important role in glucose and lipid metabolism i.e. in the treatment of diabetes. Objective: To synthesize some new chromium complexes with different classes of oral antidiabetic drugs and studied their antidiabetic potentials in mice. Methods: To increase the therapeutic efficacy of the drugs i.e, Metformin, Dapagliflozin, Vildagliptin and Glimepiride, Cr(III) complexes of these drugs were prepared and characterized by TLC, DSC, TGA and FTIR spectroscopy. The antidiabetic activity of the complexes was also evaluated in mice model. Results: At a dose of 150 mg/kg body weight of Cr(III)-drug complexes, the serum glucose levels reduced by 20.61% for Crmetformin( Cr-Met), 13.07% for Cr-dapagliflozin (Cr-Dapa), 7.61% for Cr-vildagliptin (Cr-Vilda) and 4.07% for Cr-glimepiride (Cr-Glim) than the corresponding parent drugs metformin, dapagliflozin, vildagliptin and glimepiride, respectively after 14 days of treatment. Conclusion: The complexes were found to be effective in lowering the serum glucose level in alloxan-induced diabetic mice.
Keywords: Metformin, Dapagliflozin, Vildagliptin, Glimepiride, Chromium (III), Antidiabetic
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION
Diabetes increases morbidity, mortality, social and economic burden. It is reported that diabetes is among the top ten causes of disabilities and about 4-4.6 million people annually die worldwide.1 In 2011, it was estimated that11% of total healthcare spending occurred worldwide for the management of patients with diabetes.1 Nowadays, diabetes is a highly increasing chronic disease all over the world. It is a disease that impairs the body’s ability to process blood glucose. Diabetes can lead to the buildup of sugars in the blood which increases the risk of life-threatening adverse complications, including kidney failure, amputations, blindness, stroke and heart failure.2 The diabetic patients often have some other co-existing problems like dyslipidemia, hypertension, insomnia and so on. Now, the total number of diabetic patients in Bangladesh is about 8 million and it causes 6.4 % of total deaths in the country.3 A recent survey in Bangabandhu Sheikh Mujib Medical University (BSMMU) on 2,000 adults in Dhaka slums found 19 % of adults (15.60 % men and 22.5 % women) had diabetes.3 This indicates a rising trend of diabetes in urban areas. Anti-diabetic drugs are used in diabetic patients for lowering the sugar level in blood and several antidiabetic drugs (metformin, vildagliptin, glimepiride and dapagliflozin) are available, and their volition depends on the nature of diabetes, situation and age of the persons and other factors as well. The chemical structures of metformin, dapagliflozin, vildagliptin and glimepiride have been shown in figure 1. Metformin is a drug of biguanide group which increases peripheral glucose utilization and decreases gluconeogenesis, possibly through its action on membrane phospholipids. It also inhibits glucose absorption from the intestinal lumen.4 Vildagliptin is the dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4) inhibitors for the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). The mechanism of inhibition of DPP-4 inhibitors depends on their ability to increase the level of incretin hormones, glucagons like peptide-1 (GLP-1) and glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP) in the systemic circulation.5 Dapagliflozin, a glucose-lowering agent used in the treatment of patients with type 2 diabetes. It is known as sodium-glucose co-transporter-2 (SGLT2) inhibitor. By inhibiting the transporter protein SGLT2 in the kidneys, dapagliflozin reduces renal glucose reabsorption, leading to urinary glucose excretion and a reduction in blood glucose levels. Glimepiride is a drug of sulphonylurea group. Sulfonylureas cause hypoglycemia by stimulating insulin release from pancreatic β-cells. It increases insulin release in type 2 DM patients from the pancreas. This group of drugs also may further increase insulin levels by reducing hepatic clearance of the hormone.4,5 Human beings require essential trace elements for displaying a variety of functions, e.g. regulatory, catalytic, immune etc. There are many reports on the metal-antidiabetic drug complexations.6-16
Chromium (III) is required at a tiny amount as about 100 µg/day and much of the daily intake comes from grains, fruits, vegetables, potatoes, seafood, mushrooms and egg yolk.17 Metformin, dapagliflozin, vildagliptin and glimepiride are common anti-diabetic drugs (Figure 1). Cr (III) is one of the important trace elements that the body can absorb. It is claimed that Cr (III) is the most stable and essential form, and accumulated in liver, spleen, soft tissues and bone. In the body, Cr (III) plays important roles in carbohydrate and lipid metabolism. It may increase the action of insulin by the interaction with the insulin receptor on the cell surface. Chromium also inhibits the liver hydroxymethylglutaryl-CoA reductase (rate-limiting enzyme of cholesterol synthesis). Cr deficiency in serum is reported in patients with glucose intolerance, diabetes mellitus, and hypercholesterolemia and also in aged people.18,19,20
But it is somehow difficult to intake the trace amount of Cr (III). There are chances of co-administration of Cr (III) as antidiabetic drug complexes to promote the therapeutic efficacy of antidiabetic drugs. Since it is reported that Cr (III)-metformin complex reduced the glucose level of diabetic rat.21 Therefore, we tried to synthesize some new chromium complexes with different classes of oral antidiabetic drugs and studied their antidiabetic potentials in mice. This paper describes the complex formation of Cr (III) with four popular antidiabetic drugs viz. metformin, dapagliflozin, vildagliptin and glimepiride, and in vivo study of their antidiabetic property in mice model (Figure 1).
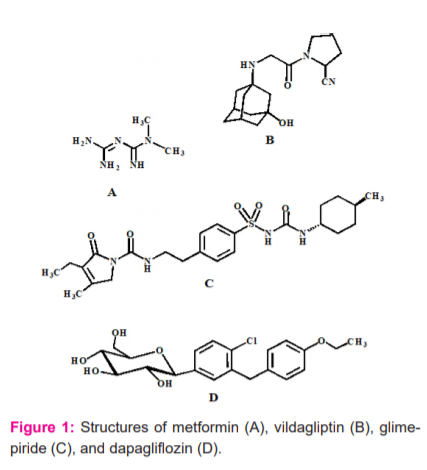
Figure 1: Structures of metformin (A), vildagliptin (B), glimepiride (C), and dapagliflozin (D).
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Materials
Analytical grade chemicals, solvents and chromium (III) chloride were used for all experimental purposes without further purification. The API of antidiabetic drugs metformin (purity 99%), vildagliptin (purity 99%), glimepiride (purity 99%), and dapagliflozin (purity 99%) were received as gift samples from ACI Pharmaceuticals Ltd., Dhaka, Bangladesh. Alloxan monohydrate (98%) was purchased from Loba Chemie Pvt. Ltd., Mumbai, India.
Synthesis of chromium (III) complexes with antidiabetic drugs
The Cr(III)-metformin, Cr(III)-glimepiride, Cr(III)-dapagliflozin, Cr(III)-vildagliptin complexes were synthesized by dissolving each drug e. g. metformin hydrochloride (2 mmol, 0.388g,), glimepiride (0.5 mmol, 0.245 g), dapagliflozin (0.5 mmol, 0.2051 g), vildagliptin (0.5 mmol, 0.1517 g) in 25 mL of methanol and then mixed with 25 mL methanol solution of 1 mmol CrCl3,6H2O (0.202g). The mixtures were heated at 70oC in a water bath (J.P.Selecta, Spain) with continuous stirring for 3.30 hours. Then the mixtures were left overnight for precipitation.
Characterization of synthesized chromium (III) complexes with antidiabetic drugs
Differential scanning calorimetry (DSC)
The phase change properties of the Cr(III) complexes were studied by differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) (DSC-60, Shimadzu, Japan). The range of temperature was up to 300oC and temperature rising rate was 10 °C/min at a flow rate of 20 mL/min in a nitrogen gas atmosphere.
Thermogravimetric analysis (TGA)
The thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) of the chromium (III) complexes was carried out by thermogravimetric analyzer (TGA-50, Shimadzu, Japan) at the temperature of up to 600oC. A certain amount of each complex(~3mg) was taken in an aluminium pan and then subjected to heating with a flow rate of 10 oC/min under nitrogen atmosphere where mass, temperature, and time were considered base measurements in the thermogravimetric analysis.
Fourier transform infrared spectrophotometry (FTIR)
The FTIR analyses of the chromium (III) complexes were carried out at the wavelength ranges of 400 cm-1 to 4000 cm-1. In each sample, about 100 mg of dried, pure KBr was added to 1 mg of dried sample, homogenously mixed with a mortar-pestle and pressed mechanically to make a pellet under the pressure of 8-10 tons. The prepared disc was placed in the path of the IR beam for recording the spectrum.
Induction of diabetes in mice
Male Albino mice with an average weight of 26 g were purchased from the Department of Pharmacy, Jahangir Nagar University, Savar, Bangladesh and maintained on a normal diet and filtered tap water adlibitum were used in the experiment. The mice were randomly divided into 9 groups (Group-I to Group-IX) (6rats in each group). Group-I was treated as control and allowed to feed normal diet only. Neither alloxan nor drug was introduced to the Group-I. Diabetes was induced in the rest of the eight groups (Group-II to Group-IX) by intraperitoneal administration of alloxan at a dose of 150 mg/kg body weight following overnight fasting. Before induction of diabetes and after three days of alloxan treatment, blood was drawn from the tail of the all groups of fasting mice and serum glucose level was determined immediately by a glucometer (GlucoLeader-yasee, GLM-76, Yasee Co. Ltd., Taiwan). The alloxan-treated rats were considered to be diabetic due to a high serum glucose level (>20mmol/L). Group-II and Group-III weregiven150 mg/kg bw metformin hydrochloride and Cr-metformin complex, respectively in solution form for 14 days. Similarly, Group-IV and Group-V were given 150 mg/kg bw dapagliflozin and Cr-dapagliflozin complex, respectively, Group-VI and Group-VII received 150 mg/kg bw vildagliptin and Cr-vildagliptin complex, respectively, and Group VIII and Group IX were given glimepiride and Cr-glimepiride, respectively orally in solution form for 14 days. After 14 days s of treatment, blood was drawn from the tail of the all groups of fasting mice and serum glucose levels were determined immediately by a glucometer.
Statistical analysis
The data are expressed as mean ± SEM. Readings within a group were compared using the one-way ANOVA analysis and readings between groups were compared using the independent sample test. Statistical analysis was performed using Microsoft-Excel 2007.
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
After completing the reactions both crystalline and amorphous Cr-drug complexes were obtained. The formation of complexes with drugs was confirmed by TLC, DSC, TGA and FTIR spectroscopy.
At first, TLC of the Cr-drug complexes was carried in methanol-dichloromethane in the different ratio for different complexes. Single spot from the complexes which were varied from their precursor drugs was found (Table 1). Each spot indicated the presence of a new complex.
The phase changes of the pure anti-diabetic drugs and their Cr-complexes were investigated by DSC. Pure metformin displayed melting endotherm at 231oC and its Cr-complex exhibited at 224 oC (Figure2). Dapagliflozin showed melting endotherm at the point of 77.98 oC and its Cr-complex showed different peaks in the thermogram (Figure 2). Vildagliptin and glimepiride indicated melting points at 152 oC and 213 oC, respectively whereas their Cr-complexes showed different melting endotherms, which revealed the formation of new complexes (Figure2).
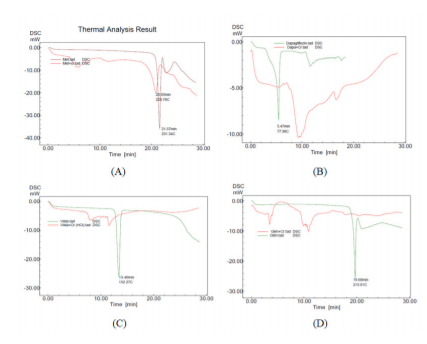
Figure 2: Overlaid DSC thermograms: metformin and Cr-metformin complex (A), dapagliflozin and Cr-dapagliflozin complex (B), vildagliptin and Cr-vildagliptin complex (C), glimepiride and Cr-glimepiride complex (D)
The percentages of weight loss against the increase in temperature for pure antidiabetic drugs and their complexes were investigated by thermogravimetric analysis. For pure metformin, 4.29%was found to be degraded at 205 oC. It also degraded by 88% at 356 oC probably by the removal of methyl groups.22 It was also found to be degraded by 97% at 599 oC due to the loss of amino groups. However, Cr-metformin complex showed completely different degradation pattern (Figure 3).
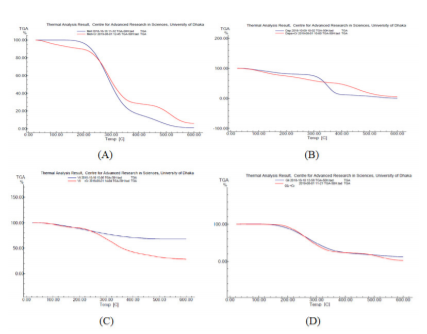
Figure 3: Overlaid TGA thermograms: metformin and Cr-metformin complex (A), dapagliflozin and Cr-dapagliflozin complex (B), vildagliptin and Cr-vildagliptin complex (C), glimepiride and Cr-glimepiride complex (D)
In the case of pure dapagliflozin, the degradation pattern showed17% degradation at 189 oC, 86% at 389oC and 94% at 516oC, which are due to release of hydroxyl molecules and methyl groups.23 Similarly, vildagliptin and glimepiride and their Cr-complexes, were showed different degradation pattern from pure drugs. The FTIR spectra were studied to measure the wavelength and intensity of transmission/absorption which have characteristics of specific types of molecular vibration and stretching that help to identify functional groups of new complexes. The FTIR spectra of pure drugs metformin, dapagliflozin, vildagliptin, glimepiride and their Cr-complexes are shown in figure 4. If the pure drugs and complexes displayed same IR spectrum it can be claimed that they are the same compounds. Therefore, any disappearance or shifts of peaks will indicate the presence of new compounds.

Figure 4: Overlaid IR spectra of metformin and Cr-metformin complex (A), dapagliflozin and Cr-dapagliflozin complex (B), vildagliptin and Cr-vildagliptin complex (C), glimepiride and Crglimepiride complex (D)
The characteristic stretching peak of -NH2 of metformin seen at 3742.93 cm-1 was obtained in the downfield at 3706 cm-1for Cr-metformin complexes (Figure 4). Likewise, the characteristic peaks of OH stretching of dapagliflozin, vildagliptin and glimepiride observed at 3352.28 cm-1, 3741 cm-1, 3772 cm-1, respectively shifted in the IR spectra of the respective Cr-drug complexes to 3390 cm-1 for Cr- dapagliflozin and 3402.00 cm-1 for Cr-vildagliptin and 3569.54cm-1 for Cr-glimepiride. These changes in the absorption in the IR spectra indicated the formation of the complex between the drug and chromium.
The Cr-drug complexes and standard antidiabetic drugs when administered to alloxan-induced diabetic mice significantly reduced the blood glucose level as compared to alloxan control mice which received distilled water and normal food (Table2). Cr-metformin complex reduced blood glucose level significantly and it was found to be 15.10 mmol/L whereas pure metformin reduced blood glucose level to 19.02 mmol/L after 14 days of treatment.

CONCLUSION
Chromium (Cr) (III) reacted with four antidiabetic drugs namely metformin, dapagliflozin, vildagliptin, glimepiride at high temperature and produced complexes which were justified by studying their thermochemical properties e.g. DSC, TGA, TLC and IR spectroscopy. The Cr-drug complexes and standard antidiabetic drugs when administered to alloxan-induced diabetic mice significantly reduced the blood glucose level as compared to alloxan control mice which received distilled water and normal food. It was found that after 14 days of treatment with metformin, dapagliflozin, vildagliptin, glimepiride, the average glucose levels of mice reduced from 31.54 to 19.02, 30.37 to 17.60, 31.50 to 19.70 and 30.24 to 17.20 mmol/L, respectively; whereas chromium complexes of these drugs i.e. Cr-metformin, Cr-dapagliflozin, Cr-vildagliptin and Cr-glimepiride were found to be reduced blood glucose levels in mice from 31.0 to 15.10, 29.40 to 15.30, 31.60 to 18.20 and 21.70 to 16.50 mmol/L, respectively. The Cr-complexes were found to be more potent than the corresponding pure drugs viz. Cr-metformin, Cr-dapagliflozin, Cr-vildagliptin and Cr-glimepiride showed 20.61%, 13.07%, 7.61%, 4.07% more effective than metformin, dapagliflozin, vildagliptin, glimepiride drugs, respectively. Among them, Cr-metformin complex reduced blood glucose level significantly and it was found to exhibit 20.61% higher antidiabetic activity than the pure metformin. However, the untoward effects of these complexes could not be established at this moment. Whether the Cr-complexes have long-term health benefits or untoward effects are not yet known, although the mice model experimental data indicated that Cr-complexes can improve glucose metabolism. Therefore, comprehensive studies, including in vivo model will be required to establish other beneficial and/or untoward effects of these Cr-drug complexes. Conducted study reveals that the chromium complexes of traditionally used antidiabetic drugs increase the efficacy of the drugs. The finding opens the possibility to promote the production and utilization of chromium complexes of metformin, dapagliflozin, vildagliptin and glimepiride for treating diabetes mellitus.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
The authors are thankful to Centre for Advanced Research in Sciences (CARS), the University of Dhaka, Bangladesh for providing some laboratory facilities to conduct the research; ACI Pharmaceuticals Ltd., Dhaka, Bangladesh for providing APIs for the research; and Rajia Sultana (Research Fellow, Drug Analysis and Research Laboratory, CARS) for helping us during the research work.
Conflict of interest: None
Financial support: None
References:
-
Plosker GL. Dapagliflozin: A review of its use in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Drugs 2012; 72:2289-2312.
-
Hippisley-Cox J, Coupland C. Diabetes treatments and risk of amputation, blindness, severe kidney failure, hyperglycaemia, and hypoglycaemia: Open cohort study in primary care. Br Med J 2016;352:1450.
-
Porimol P. Worlddiabetes day 2018: A worrying picture of diabetes in Bangladesh. 2018. World Diabetes Day 2018: A worrying picture of diabetes in Bangladesh (thedailystar.net)
-
Laurence LB, John SL, Keith LP. Goodman & Gilman’s the pharmacological basis of therapeutics, eleventh edition, The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. Manufactured in the United States of America, 2006;1634-1638.
-
Ahren B, SchweizerA, Dejager S, Villhauer EB, Dunning BE, FoleyJE. Mechanisms of action of the dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor vildagliptin in humans. Diabetes Obes Metab 2011;13:775-783.
-
?liwi?ska-Hill U, Wiglusz K. The interaction between human serum albumin and antidiabetic agent - exenatide: determination of the mechanism binding and effect on the protein conformation by fluorescence and circular dichroism techniques. Biomol Struct Dyn 2019;22:1-9.
-
Scior T, Guevara-Garcia JA, Do QT, Bernard P, Laufer S.Why antidiabetic vanadium complexes are not in the pipeline of "big pharma" drug research? A critical review. Curr Med Chem 2016;23(25):2874-2891.
-
Zhang Y, Wu M, Dai W, Li Y, Wang X, Tan D, et al. Gold nanoclusters for controlled insulin release and glucose regulation in diabetes. Nanoscale 2019;11:6471-6479.
-
Lockwood TD. Biguanide is a modifiable pharmacophore for recruitment of endogenous Zn2+ to inhibit cysteinyl cathepsins: review and implications. Biometerials 2019; 32:575-593.
-
Gülfen M, Özdemir A, Lin JL, Chen CH. Investigation of manganese(II)-insulin complexes using electrospray ionization mass spectrometry. Int J Biol Macromol 2018;120:557-565.
-
Dong Y, Stewart T, Zhang Y, Shi M, Tan C, et al. Anti-diabetic vanadyl complexes reduced Alzheimer's disease pathology independent of amyloid plaque deposition. China Life Sci 2019;62:126-139.
-
Chen F, Moat J, McFeely D, Clarkson G, Hands-Portman IJ, Furner-Pardoe JP, et al. Biguanide iridium(iii) complexes with potent antimicrobial activity. J Med Chem 2018; 61:7330-7344.
-
Gondolova G, Taslimi P, Medjidov A, Farzaliyev V, Sujayev A, Huseynova M, et al. Synthesis, crystal structure and biological evaluation of spectroscopic characterization of Ni(II) and Co(II) complexes with N-salicyloil-N'-maleoil-hydrazine as anticholinergic and antidiabetic agents. J Biochem Mol Toxicol 2018; 32:e22197.
-
Kongot M, Dohare N, Singh V, Reddy DS, Singhal NK, Patel R, et al. Novel biocompatible Ni(II) tethered moiety as a glucose uptake agent and a hit against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Eur J Pharm Sci 2018;123:335-349.
-
Vasantha P, Sathish KB, Shekhar B, Anantha Lakshmi PV. Copper-metformin ternary complexes: Thermal, photochemosensitivity and molecular docking studies. Mater Sci Eng C 2018; 90:621-633.
-
Philip JE, Shahid M, Prathapachandra Kurup MR, Velayudhan MP.Metal based biologically active compounds: Design, synthesis, DNA binding and antidiabetic activity of 6-methyl-3-formyl chromone derived hydrazones and their metal (II) complexes. J Photochem Photobiol B 2017;175:178-191.
-
Achmad RT, Budiawan, Auerkari EI.Effects of chromium on the human body. Ann Res Rev Biol 2017;13(2):1-8.
-
ZimaT, MestekO, Tesar V, TesarovaP, NemecekK, Zak A, et al. Chromium levels in patients with internal diseases. Biochem Mol Biol Int 1998;46:365-374.
-
Richard AA. Chromium, glucose intolerance and diabetes. J Am Coll Nutr 1998;17:548-555.
-
Wallach S. In vitro clinical and biochemical aspects of chromium deficiency. J Am Coll Nutr 1985;4:107-120.
-
El-Megharbel SM. Synthesis, characterization and antidiabetic activity of chromium (III) metformin complex. J Microb Bioch Tech 2015;7:2.
-
Agrawal YK, Gogoi PJ, Manna K, Bhatt HG, Jain VK. A supercritical fluid chromatography/tandem mass spectrometry method for the simultaneous quantification of metformin and gliclazide in human plasma. Ind J Pharm Sci 2010;72:50-57.
-
Amit SK, Iain GR, Scott O, Christopher LS, Ernesto C, Kirk RH, et al. A comprehensive listing of bioactivation pathways of organic functional groups. Curr Drug Metab 2005; 6:161-225.
-
Rahman F, Salam MA, Rahman A, Sultan MZ. Studies of interactions of valsartan, glimepiride and ciprofloxacin HCl by DSC and HPLC. Bangl Pharm J 2017;20:195-200.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License