IJCRR - 13(4), February, 2021
Pages: 139-146
Date of Publication: 16-Feb-2021
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
KI-67 Index as a Prognostic Factor in Correlation with Other Clinico-Pathological Factors in Breast Cancer - An Institutional Experience
Author: Mahin Nallasivam, Mohanapriya Thyagarajan, Balaji Singh Krishna, Manuneethimaran Thiyagarajan, Nitesh Navrathan
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Introduction: Breast cancer is a complex aggressive disease with different subtypes due to multiple biomolecular interactions (genetic heterogeneity) and demonstrates the extensive variation in patients clinical feature based on the ethnic group that makes the diagnosis and treatment challenging. Numerous breast cancer markers had been established like Progesterone Receptor (PR), Estrogen Receptors (ER), Human Epidermal growth factor Receptor (HER2neu) as well as clinical-pathological factors such as the stage of the disease, extent of axillary lymph node involvement, tumour size, histological grade, a mitotic rate, patient age, menopausal status etc. Ki?67, cyclin D1, cyclin E, and ER\? had been advocated to exhibit both the predictive and prognostic value in breast cancer patients. Objectives: The objective of the current study is to evaluate the relevance and correlation of Ki-67 index in relation with other clinicopathological factors that determine the prognosis in Carcinoma breast and thereby, defining the staining thresholds and cut-off of Ki-67 immunohistochemistry. Methods: A consecutive number of 200 patients who had undergone modified radical mastectomy were included in this study. The postoperative specimen was for the assessment of histopathology diagnosis and the tumour size, nodal status, histological grading, tumour pathological type, mitotic rate, and lymphovascular invasion apart from Estrogen Receptor status, Progesterone Receptor status, Human Epidermal growth factor Receptor 2neu status and Ki-67 protein expression. Patient's clinical data were collected prospectively. SPSS software version 19 was used for statistical analysis. One way Anova and chi-square analysis was applied to assess the relation of Ki-67 index score with other prognostic factors. Results: Ki-67 protein expression showed no correlation with age (irrespective of age classification), menopausal status, histological subtypes, lymphovascular invasion, mitotic rate, ER and HER2neu, but still the levels of Ki-67 protein increases with ER negativity (p>0.05). The overall histological grading showed statistical significance between grade I Vs III and grade II Vs III which reflects the linear relationship whereas chi-square analysis did not show. Progesterone Receptor showed an inverse relationship with Ki-67 expression (p=0.0005) and whereas, tumour size and nodal involvement revealed a linear relationship(p=0.02). Conclusion: Hence, the study had lucidly established the fact that Ki-67 index is superior to the mitotic rate and can be routinely employed for predicting the prognosis in breast cancer patients. The current paper recommends the use of the staining thresholds and cut-offs of Ki-67 immunohistochemistry used in the current study for future studies since all the patients expressed Ki-67 protein.
Keywords: Carcinoma breast, Correlation, Ki-67 index, Prognostic factors, Tumour size
Full Text:
Introduction
Breast cancer is a complex aggressive disease with different subtypes due to multiple biomolecular interactions (genetic heterogeneity) and demonstrates the extensive variation in patients clinical feature based on an ethnic group that makes the diagnosis and treatment challenging.1 Carcinoma breast constitutes about 22% of women malignancy and it is the second commonest malignancy in females.2,3 Among the different types of cancers, worldwide data suggested that breast cancer in females occupies 25% which is nearly a quarter with a projected 1.67 million new cases every year. According to GLOBOCAN(The Global Cancer Observatory) 2018 report, the incidence of breast cancer is 11.6%, of which the mortality is documented to be 6.6% in females globally. At the same time, age-standardized risk and cumulative risk (age up to 75 yrs in %) are found to be 46.3 and 5.03 respectively.4In India, breast cancer ranks first with an incidence of age-adjusted rate and mortality to be 25.8 and 12.7 per 100,000 women.5 A recent Indian study had revealed that age-adjusted incidence of breast cancer in Chennai (37.9 per 100,000 women) was higher next to Delhi (41 per 100,000 women) when compared over the other states and also showed that the incidence is escalating annually.6
Considering the elevating yearly incidence, mortality, different subtypes and the challenges faced in diagnosis and treatment strategy of breast cancer patients, identification of factors that possess both the predictive and prognostic values in breast cancer management becomes essential. Numerous breast cancer markers had been established like Progesterone Receptor (PR), Estrogen Receptors (ER), Human Epidermal growth factor Receptor (HER2neu) as well as clinical-pathological factors such as the stage of the disease, extent of axillary lymph node involvement, tumour size, histological grade, a mitotic rate, patient age, menopausal status etc. Ki?67, cyclin D1, cyclin E, and ERβ had been advocated to exhibit both the predictive and prognostic value in breast cancer patients. Gerdes et al (1983) had described Ki-67 (395kDa) as a master switch controller of cellular proliferation and found to have the most appropriate and superior correlation with histological parameter and proliferating (mitotic) activity by the previous literatures.7,8There exist a controversy regarding the staining thresholds and cut-offs of Ki-67 immunohistochemistry (not uniformly standardized) since different criteria have been employed by different studied authors.9-12 Also, few numbers of literature are available among the Indian population regarding Ki-67 status. Hence, the objective of the current study is to evaluate the relevance of Ki-67 index in relation with other clinicopathological factors that determine the prognosis in Carcinoma breast as well as to correlate Ki-67 protein expression with patient’s age, Menopausal Status, Tumour grade, Pathological type, Mitotic rate, Tumour size (T), Nodal status (N), Lymphovascular invasion, ER/PR status, HER2neu receptor status and thereby, defining the staining thresholds and cut-off of Ki-67 immunohistochemistry.
Materials and Methods
Patient selection
The present study was conducted after the approval of the Institutional Ethics Committee (IEC) of the hospital. A consecutive number of 200 patients who had undergone modified radical mastectomy for early-stage primary breast carcinoma in our hospital from January 2016 to 2019 were included in this study after obtaining their informed consent. Patients with metastatic breast cancer or presented with a previous history of neo-adjuvant chemotherapy, or breast surgery outside our hospital including male breast carcinoma were excluded from the study. The postoperative specimen was sent for routine hematoxylin and eosin stains for the assessment of histopathology diagnosis and the tumour size, nodal status, histological grading, pathological type of the tumour, mitotic rate, and lymphovascular invasion apart from ER status, PR status, HER2neu status and Ki-67 protein expression. Immunohistochemistry protocol for the analyses of ER, PR, HER2neu and Ki-67 status was performed according to the protocol.13 Ki-67 protein expression levels were classified based more than 20%, between 10 to 20%, between 1% to 10% and 0% staining as high, borderline, low and negative respectively. Patient’s clinical data were collected prospectively. The ethical clearance number: CSP – MED/15/OCT/25/89
Statistical analysis
SPSS software was used for the statistical analysis of the clinical data. One way Anova was applied to assess the relation of Ki-67 index score with other prognostic factors including patient’s age, menopausal status, grade of the tumour, pathological type, mitotic rate, tumour size (T), nodal status (N), lymphovascular invasion, ER/PR status and HER2neu receptor status. Correlations of Ki-67 index score level with clinicopathological parameters were determined using chi-square analysis. All the data were expressed as mean ± Standard Deviation (SD) or frequencies by per cent. The relationship between the prognostic factors and the Ki-67 index score was considered statistically significant only if the p-value is less than 0.05.
Results
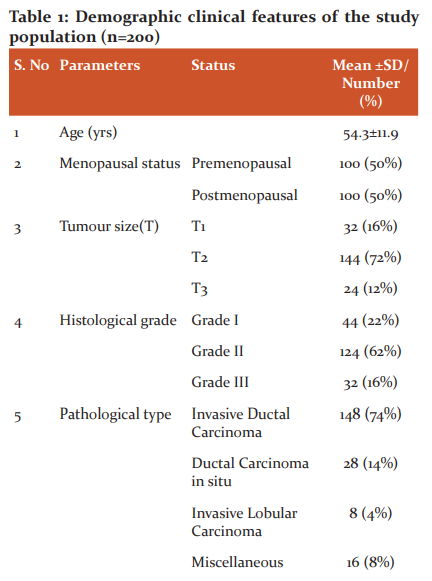
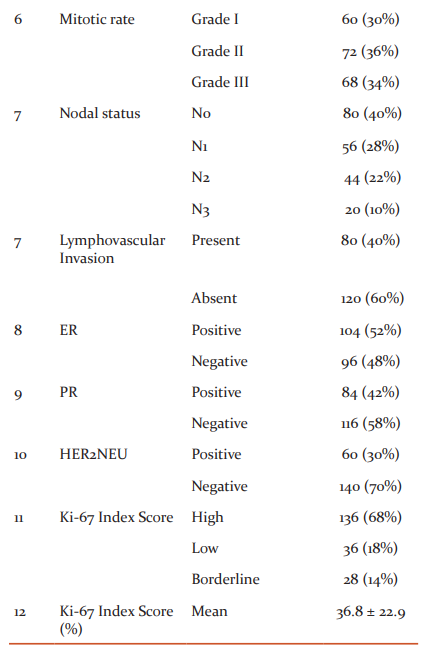
Patient characteristics
The median age of the study population at the time of presentation was 53 years, ranging from 27 to 84 years. There was no difference in frequency distribution observed concerning menopausal status among the studied populations (50% in each group). Majority of the patients had tumour size ranging from 2cm to 5cm (T2) followed by less than 2cm (T1) and larger than 5 cm (T3). According to the histological analysis, the predominate percentage was observed in well-differentiated carcinoma (grade II). Invasive Ductal Carcinoma (IDC) was the commonest pathological diagnosis and the least miscellaneous groups comprise of Invasive Papillary Carcinoma (IPC), Papillary Carcinoma Variant (PCV), Squamous Cell Carcinoma (SCC), Invasive Medullary Carcinoma (IMC) with one patient each. All the patients had non-metastatic status. Almost all the patients had a nearly similar frequency of proliferation (mitotic rate) but still, moderate (grade II) was prominent followed by rapid (grade III) and low (grade I). A maximum number of patients had the absence of lymph node involvement and lymphovascular invasion. ER, PR, HER2neu positivity was documented in the 52%, 42% and 30% of the population accordingly. The Ki-67 index score levels according to the Ki-67 protein staining cells, patients had high levels in 68% followed by low levels in 18% and then, borderline levels in 14% among the studied population. The mean percentage of Ki-67 protein expression was found to be 36.8 ± 22.9 (range from 2 to 80%) of the complete cases. Patient’s detailed information’s is presented in Table 1. The median age of the study population at the time of presentation was 53 years, most of the patients had tumour size ranging from 2cm to 5cm (T2), Grade II was the most common tumour grade. Invasive Ductal Carcinoma (IDC) was the commonest pathological diagnosis. A maximum number of patients had the absence of lymph node involvement and lymphovascular invasion. ER, PR, HER2neu positivity was documented in the 52%, 42% and 30% of the population accordingly. The mean percentage of Ki-67 protein expression was found to be 36.8 ± 22.9.
Ki-67 protein expression correlation with clinical characteristics
To identify the significance of Ki-67 protein expression percentage with demographic and clinic-pathological parameters, the prognostic factors were divided into subcategories as shown in Table 2. On association analysis through student t-pair test, it was observed that the subcategories within age, menopausal status, histological tumour type, mitotic rate, lymphovascular invasion, ER, HER2neu concerning Ki-67 index score level of the total studies cases do not exhibit any correlation. In converse, tumour size, histological grade, nodal involvement and PR showed a positive correlation. The comparison within the PR status showed a statistically high significant correlation concerning the percentage of Ki-67 protein expression than the other parameter. The statistically significant association was found only between T1 and T2 (tumour size), grade I and grade III, and grade II and grade III (histological grade) and N0 with N2 and N3 (Nodal involvement) when compared against the respective percentage of Ki-67 score index.
Ki-67 protein expression correlation with clinical characteristics
To identify the significance of Ki-67 protein expression percentage with demographic and clinic-pathological parameters, the prognostic factors were divided into subcategories as shown in Table 2. On association analysis through student t-pair test, it was observed that the subcategories within age, menopausal status, histological tumour type, mitotic rate, lymphovascular invasion, ER, HER2neu concerning Ki-67 index score level of the total studies cases do not exhibit any correlation. In converse, tumour size, histological grade, nodal involvement and PR showed a positive correlation. The comparison within the PR status showed a statistically high significant correlation concerning the percentage of Ki-67 protein expression than the other parameter. The statistically significant association was found only between T1 and T2 (tumour size), grade I and grade III, and grade II and grade III (histological grade) and N0 with N2 and N3 (Nodal involvement) when compared against the respective percentage of Ki-67 score index.
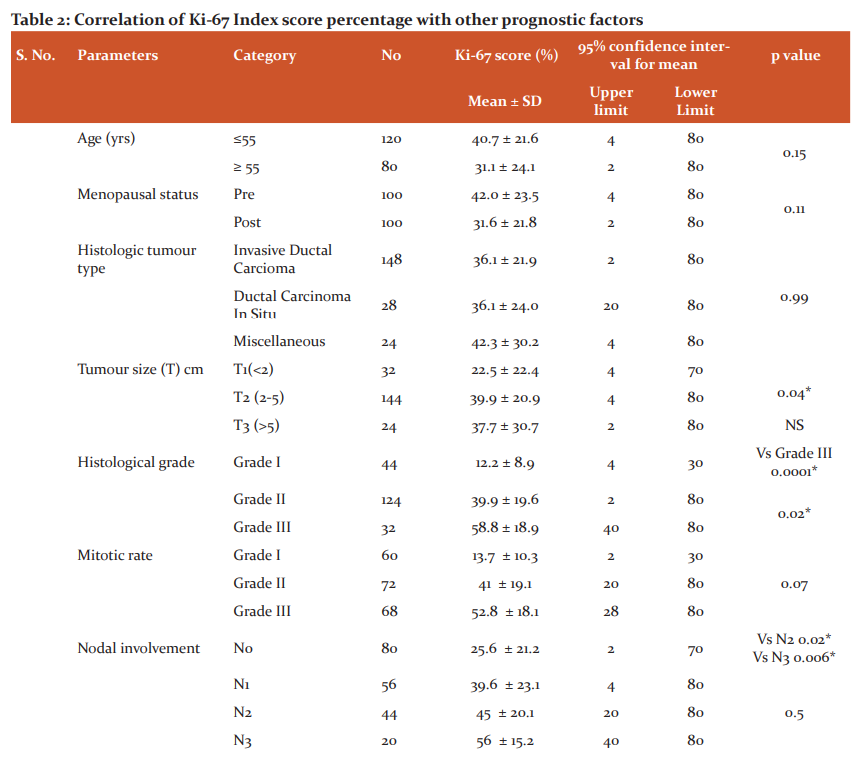
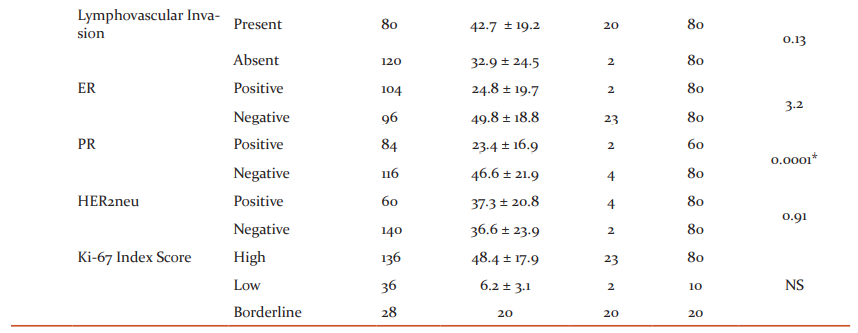
UL-Upper Level; LL-Lower Level; Miscellaneous-Invasive Papillary Carcinoma, Papillary Carcinoma Variant, Squamous Cell Carcinoma, Invasive Medullary Carcinoma and Invasive Lobular Carcinoma; Vs-Versus; NS-Non significant;*- represents the statistical significance.
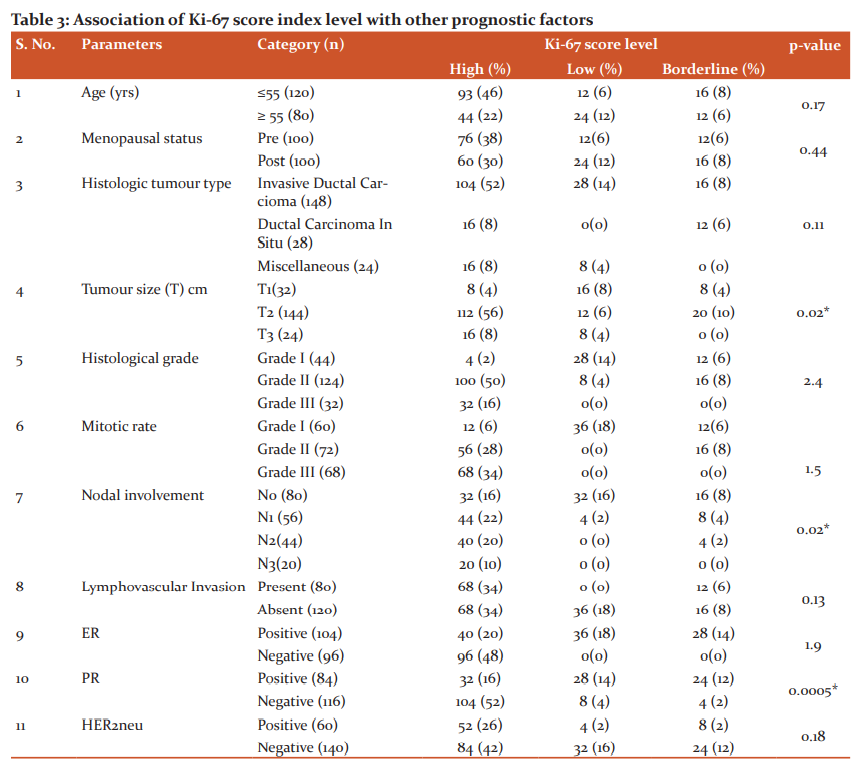
Correlation of Ki-67 scoring with clinical characteristics
Ki-67 protein expression scoring levels were assessed for correlation with the prognostic factors. In similar to the findings of Table 2, the correlation analysis (chi-square) of Table 3 also further provided the profound findings of tumour size, nodal involvement and PR status positively related with different Ki-67 score levels with statistical significance except for histological grade. Concerning the histological tumour type, Invasive Ductal Carcinoma and ductal carcinoma in-situ combined (60%) showed the higher level of expression than the rest of the pathology but statistical significance was not identified within the groups. Table 3 showed a linear relationship when compared the tumour size with ki-67 proteins levels. As the tumour grade increases, Ki-67 protein expressions also raised and in converse, when the tumour grade decreases, the respective expressions levels also minimized (p=0.02). When the nodal system involvement advances, Ki-67 protein expressions levels also increased and had decreased expression, when the nodal involvement is less (0.02) in similar tumour grade findings. There was no statistical significance difference observed either between the presence and absence or the positivity and negativity of the lymphovascular invasion or ER and HER2neu respectively concerning the either high or low or borderline levels of Ki-67 protein expression. The majority of the patients who had shown negative results for ER, PR and HER2neu demonstrated increased levels of Ki-67 proteins. The higher level of statistical significance was noted between the positivity and negativity of PR with the Ki-67 score index levels among the studied cases.
Discussion
Cellular proliferation is the hallmark in any cancer and hence, regular examination of cell proliferation is suggested in the pathological assessment especially in invasive carcinoma breast, which in turn accounts for the traditional scoring of mitotic activity (simple and commonly employed tool). Hence, cell proliferation is an essential part of histological grading and well known as the prognostic marker. The major disadvantage of mitotic index assessment is that it is time-consuming and the results are non-reproducible but still are employed in clinical practice.13,14 Therefore, investigation on more sensitive tumour biomarker has led to the identification of several markers related to the patient and the tumour has been established in predicting the risk of mortality, recurrence and metastasis in breast malignancy. These factors are the number of positive axillary lymph nodes, size of the tumour, histological grade of the tumour, lymphovascular invasion, hormone receptor (ER/PR) positivity and Her2neu gene amplification.15 Recently, one such tumour proliferation biomarker known as Ki-67 protein (proliferating cell nuclear antigen) is being established as a prognostic and predictive indicator in patients with breast cancer and possesses strong association with cellular proliferation.16, 17
Ki-67 protein (non-histone) is expressed during all the phases of the cell cycle (late G1, S, G2 and M phase) except at early G1 and G0 (quiescent cells) phases, and are detected during M phase at the chromosomal surface which makes it unique and more specific biomarker.18,19 The expressions of Ki-67 protein is up-regulated in rapidly dividing cells and hence, the cells stains more positive. The role of Ki-67 has been well analyzed in various research studies for its prognostic value and reliability in breast carcinoma, cervical cancer, sarcomas, neurological malignancies, bronchogenic carcinoma and prostatic cancer.20-24 Many investigating modalities have used Ki-67 as a successful diagnostic marker.25-28 Positive immunostaining for the Ki-67 expression has been accepted as an investigative tool and positive staining ranging from 10 to 14% has been defined as high risk.29-31 The 2009 Saint Gallen consensus declared that the patients with higher levels of Ki-67 nuclear protein expression required additional chemotherapy and hormonal therapy for all ER PR positive breast malignancies.32
In our study, the protein expression levels of Ki-67 was defined as negative, high, low and borderline only when the positive tumour cells percentage (Ki-67-LI) is 0%,>20%,<10 and 10-20% respectively. All breast cancer patients showed positive results in the present study. In contrast, Bouzubar et al.10 defined negative tumour cell percentage as less than 5%, while Tan et al11 considered 0% as negative is similar to our study. Tan et al.11 and Bouzubar et al10 defined > 10% and >20% staining as high in dissimilar and similar to our study respectively. To coincide with our classification, Marwah N et al13 defined high as >20% except <5% and 5-20% as negative and positive accordingly. In the current study, the positive correlation of Ki-67 protein expression was observed with different clinicopathological factors as compared with other studies10,12At the same time, our study had recommended the cut-offs of Ki-67 immunohistochemistry to be between 10 to 20% as in disagreement with Cho et al (20%).33 Hence, we advocate the use of histoimmuno chemistry staining cut-off of Ki-67 used in the current study because all the breast cancer patients showed positive and at least low or minimal expression.
Kermani et al34 studied 220 patients who had presented with primary breast cancer and evaluated the relationship of Ki-67 immunohistochemistry index expression with age (less than or equal and more than 50 years respectively) and concluded that there exists no association is similar to our study and Li FY et al (age less than or equal to 35 and more than 35).35Hence, we conclude that there exists no correlation between the expression of ki-67 protein and the patient's age (irrespective of age classification).
A recent Indian study on 75 patients who had undergone radical or modified radical mastectomy was analyzed for the relationship of Ki-67 index score with the clinicopathological parameters.13 The study resulted that there was no correlation between the Ki-67-LI index and menopausal status, lymph node involvement and HER2/neu. The same result also showed a direct association with tumour size, and histological grade and whereas, an inverse association with ER and PR status. The current study had shown a similar result with menopausal status, HER2neu, tumour size, histological grade (Table2: Grade I vs III, Grade II vs Grade III for over-all Ki-67 protein percentage and not concerning the levels of expression), PR and dissimilar result with lymph nodal involvement and ER. Kermani et al.34concluded the relationship between Ki-67 expression, and tumour size, ER in disagreement, and lymph node, PR in agreement concerning our study. Querzoli et al.12 had shown a direct association of tumour size concerning the expression of Ki-67-LI except few other authors.36
Haroon S et al.37 performed the study on 194 subjects diagnosed with primary breast carcinoma and examined the relationship of Ki-67 with other prognostic factors. The mean age and Ki-67 index were found to be 51.7 years (similar to our study: 54.3 years) and 26.9% (lesser than our study: 36.8%) accordingly. The study had a similar and contrast observation with PR, ER, tumour grade, lymph node status, and with tumour size, HER2neu in comparison to our study.
The present study had shown that higher the histological grading of the tumour, the higher would be the Ki-67 index as similar to Haroon S et al.37 There was no significant relevance between the pathological subtype and Ki-67score. However, the majority of the patients in our study had the histological subtype of IDC in 74% of the population among the total population. Similar results were found in a study done by Haroon S et al. 37
In overall, our study had demonstrated that Ki-67 protein expression did not correlate with age, menopausal status, histological subtypes, lymphovascular invasion, mitotic rate, ER and HER2neu, but still the levels of Ki-67 protein increases with ER negativity. The overall percentage of Ki-67 (t-pair test) in histological grading showed statistical significance between grade I Vs III and grade II Vs III which reflects the linear relationship but chi-square analysis did not show any relevance. PR showed an inverse relationship with Ki-67 expression and whereas, tumour size and nodal involvement revealed a linear relationship.
Conclusion
Hence, the current study had lucidly established the fact that Ki-67 index is superior to the mitotic rate and can be routinely employed for predicting the prognosis in breast cancer patients. Also, the present study recommends the use of current staining thresholds and cut-offs of Ki-67 immunohistochemistry applied in the current study since all the patients expressed Ki-67 protein.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT: NIL
CONFLICT OF INTEREST: “The authors declares that there is no conflict of interest regarding the publication of this paper.”
FUNDING: The first author, Dr. Mahin Nallasivam has funded the study.
DATA AVAILABILITY: The data used to support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon request.
References:
-
Spitale A, Mazzola P, Soldini D, Mazzucchelli L, Bordoni A. Breast cancer classification according to immunohistochemical markers: Clinicopathologic features and short?term survival analysis in a population?based study from the South of Switzerland. Ann Oncol 2009;20:628?635.
-
Lukianova N. Role of MIRNA-122 and MIRNA – 200B in intratumor heterogeneity formation and human breast cancer prognosis. Int J Clin Res Rev 2016;8(17):50-59.
-
Ferlay J, Bray F, Pisani P. and Parkin DM. GEOBOCAN 2002. Cancer Incidence, Mortality and Prevalence Worldwide. IARC Cancer Base No.5, version 2.0. IARC Press, Eyon, 2004.
-
Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel RL, Torre LA, Jemal A. A Global Cancer Statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J Clin 2018;68:394–424.
-
Gupta A, Shridhar K, Dhillon PK. A review of breast cancer awareness among women in India: cancer literate or awareness deficit? Eur J Cancer 2015; 51: 2058–2066.
-
Malvia S, Bagadi SA, Dubey US, Saxena S.Epidemiology of breast cancer in Indian women. Asia Pac J Clin Oncol 2017;13(4):289-295.
-
Gerdes J, Schwab U, Lemke H. production of a mouse monoclonal antibody reactive with a human nuclear antigen associated with cell proliferation. Int J Cancer 1983;31:13-20.
-
Barnard NJ, Hall PA, Lemoine NR, Kadar N. Proliferative index in breast carcinoma determined in situ by Ki67 immunostaining and its relationship to clinical and pathological variables. J Pathol 1987;152:287?295.
-
Zhang R, Chen HJ, Wei B, Zhang HY, Pang ZG, Zhu H, et al. Reproducibility of the Nottingham modification of the Scarff?Bloom?Richardson histological grading system and the complementary value of Ki?67 to this system. Chin Med J (Engl) 2010;123:1976?1982.
-
Bouzubar N. Ki67 immunostaining in primary breast cancer: Pathological and clinical associations. Br J Cancer 1989;59:943?947.
-
Tan PH. Immunohistochemical detection of Ki67 in breast cancer correlates with transcriptional regulation of genes related to apoptosis and cell death. Mod Pathol 2005;18:374?381.
-
Querzoli P. MIB?1 proliferative activity in invasive breast cancer measured by image analysis. J Clin Pathol 1996;49:926?930.
-
Marwah N. Correlation of proliferative index with various clinicopathologic prognostic parameters in primary breast carcinoma: A study from North India. J Can Res Ther 2018;14:537-542.
-
Kontzoglou K. Correlation between Ki67 and breast cancer prognosis. Oncology. 2013;84(4):219–225.
-
Tewari M, Krishnamurthy A, Shukla HS . Predictive markers of response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy in breast cancer. Surg Oncol 2008;7:301-311.
-
Juríková M, Danihel S, Polák F, Varga I. Ki67, PCNA, and MCM proteins: markers of proliferation in the diagnosis of breast cancer. ActaHistochem.2016;118(5):544–552. Availablefrom: 10.1016/j.acthis.2016.05.002.
-
Scholzen T, Gerdes J. The Ki-67 protein: from the known and the unknown. J Cell Physiol 2000;182(3):311-322.
-
Cuylen S. Ki-67 acts as a biological surfactant to disperse mitotic chromosomes. Nature 2016;535(7611):308-312.
-
Brown DC, Gatter KC.Ki67 protein: the immaculate deception? Histopathology 2002;40(1):2-11.
-
Ishihara M, Mukai H, Nagai S. Retrospective analysis of risk factors for central nervous system metastases in operable breast cancer: effects of biologic subtype and Ki67 overexpression on survival. Oncology. 2013;84: 135?140.
-
Sorbye SW. Prognostic impact of Jab1, p16, p21, p62, Ki67 and Skp2 in soft tissue sarcomas. PLoS One. 2012;7(10):e47068.
-
Sorbye SW, Kilvaer TK, Valkov A, et al. Prognostic impact of CD57, CD68, M-CSF, CSF-1R, Ki67 and TGF-beta in soft tissue sarcomas. BMC Clin Pathol. 2012;12:7.
-
Ciancio N, Galasso MG, Campisi R, Bivona L, Migliore M, Di Maria GU. Prognostic value of p53 and Ki67 expression in fiberoptic bronchial biopsies of patients with non small cell lung cancer. Multidiscip Respir Med. 2012;7(1):29.
-
Josefsson A, Wikström P, Egevad L. Low endoglin vascular density and Ki67 index in Gleason score 6 tumours may identify prostate cancer patients suitable for surveillance. Scand J Urol Nephrol 2012; 46: 247-257.
-
Zizi Sermpetzoglou A, Moustou E, Petrakopoulou N, et al. Atypical polypoid adenomyoma of the uterus. A case report and a review of the literature. Eur J Gynaecol Oncol. 2012;33: 118-121.
-
Zini L, Porpiglia F, Fassnacht M. Contemporary management of adrenocortical carcinoma. Eur Urol 2011;60:1055-1065.
-
Viale G. Pathological workup of the primary tumour: getting the proper information out of it. Breast 2011;20Suppl 3:S82-6.
-
Leong AS, Zhuang Z.The changing role of pathology in breast cancer diagnosis and treatment. Pathobiology 2011;78(2):99-114.
-
Ibrahim T. Hormonal receptor, human epidermal growth factor receptor-2, and Ki67 discordance between primary breast cancer and paired metastases: clinical impact. Oncology 2013;84(3):150-157.
-
Chlebowski RT. American Society of Clinical Oncology technology assessment of pharmacologic interventions for breast cancer risk reduction including tamoxifen, raloxifene, and aromatase inhibition. J Clin Oncol 2002;20(15):3328-3343.
-
Blancato J, Singh B, Liu A, Liao DJ, Dickson RB. Correlation of amplification and overexpression of the c-myc oncogene in high-grade breast cancer: FISH, in situ hybridisation and immunohistochemical analyses. Br J Cancer 2004;90(8):1612–1619.
-
Jonat W, Arnold N. Is the Ki-67 labelling index ready for clinical use? Ann Oncol 2011;22(3):500-502.
-
Cho U, Kim HE, Oh WJ, Yeo MK. The Long-term Prognostic Performance of Ki-67 in Primary Operable Breast Cancer and Evaluation of Its Optimal Cutoff Value. Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol 2016;24(3):159-166.
-
Kermani TA, Kermani IA, Faham Z, Dolatkhah R. Ki-67 status in patients with primary breast cancer and its relationship with other prognostic factors. Biomed Res Ther 2018; 6(2):2986-2991.
-
Li FY. Prognostic value of Ki-67 in breast cancer patients with positive axillary lymph nodes: a retrospective cohort study. PLoS One 2014;9(2):e87264.
-
Moriki T. Proliferation marker MIB?1 correlates well with proliferative activity evaluated by BrdU in breast cancer: An immunohistochemical study including correlation with PCNA, p53, c?erbB?2 and estrogen receptor status. Pathol Int 1996;46:953?961.
-
Haroon S, Hashmi AA. The ki-67 index in breast cancer: correlation with other prognostic markers and potential in Pakistani patients. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev 2013;14(7):4353-4358.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License