IJCRR - 13(4), February, 2021
Pages: 103-111
Date of Publication: 16-Feb-2021
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
Reliability of Predicting the Final Treatment Outcome in Surgery First Orthognathic Approach (SFOA)
Author: Lakshmi Rathan AC, Vivek Narayanan, Saravanan Chandran, Karthik Ramakrishnan, Cynthia Scott
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Introduction: Face form is largely dictated by one's ethnic origin and genetic inheritance. Individuals presenting with significant facial disproportion may be disadvantaged both aesthetically and functionally. Surgery First Orthognathic Approach (SFOA) is a novel approach which was floated initially a decade ago. . The major driving factor for SFOA is the immediate esthetic results for the patient as well as reduction of the duration of treatment. Objective: To reliably predict the final structural, functional and esthetic outcome of patients with facial disproportion undergoing \"Surgery First Orthognathic Approach (SFOA)\" before the commencement of procedure and compare it with the final achieved result. Methods: Study conducted at our centre was a prospective study over 24 months. Participants with facial disproportion who met the criteria for SFOA were included in our study. Complete data acquisition was carried out for all the participants, following which both conventional and digital assisted cephalometric analysis was done. Based on these analyses, the treatment plan was formulated and the surgical procedure was finalized. At 6 month, post-op lateral cephalogram was obtained and both conventional and digital assisted cephalometric analysis was done and compared with a predicted outcome. Results: Twelve participants reported with facial discrepancy during our study period, of which seven participants met the criteria for SFOA. Among seven participants, all had manual and Digital assisted cephalometric tracing. Four Participants had Computer Assisted Surgical Simulation (CASS). Our result showed no statistically significant differences between the predicted and final outcome in both conventional and digital assisted cephalometric analysis. Conclusion: In our study, we found that the maxillary repositioning was reliably predicted by both Conventional and digital assisted Cephalometric prediction analysis whereas conventional prediction was still much better than the digital prediction for mandibular repositioning.
Keywords: SFOA, Orthognathic Surgery, Digital assisted cephalometric analysis, CASS, Prediction tracing, Virtual Planning
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION
The golden proportion of face has always been associated with classical beauty as described in our ancient painting and sculptures. Face form is largely dictated by one’s ethnic origin and genetic inheritance. Individuals presenting with significant facial disproportion may be disadvantaged both aesthetically and functionally.1,2 In such cases orthodontic treatment alone might be insufficient to correct deformities. A combination of orthodontic treatment with Orthognathic surgery is needed to achieve optimal results.3
In the mid 20th century with the advancement in orthodontic therapy in the form of fixed appliances, orthognathic surgery developed into a multidisciplinary exercise.4 This conventional approach involves a significant period of presurgical orthodontics followed by surgery. Most patients also need a varying period of post-surgical orthodontics to settle the dentoalveolar component into a more stable occlusion.5
Surgery First Orthognathic Approach (SFOA) is a novel approach which was floated initially a decade ago by a Nagasaka et al.6,7 There are many published case reports of surgery only approach to address facial disproportion with varying results. SFOA as a concept is primarily a combined approach where the phase of presurgical orthodontic decompensation is minimal. This included levelling and aligning of arches. The major driving factor for SFOA is the immediate esthetic results for the patient, which significantly increases the acceptability.8 It also may result in a reduction in the duration of treatment time. In its current format, SFOA is reserved for a few selected clinical conditions which include moderate to well-aligned arches with minimal transverse discrepancies.9
The study aims to evaluate the reliability of predicting the final treatment outcomes in Surgery First Orthognathic Approach (SFOA) using conventional cephalometric analysis and digital assisted cephalometric analysis
MATERIALS AND METHODS
This study was approved by the Institutional Ethics Committee (1258/IEC/2017) and was conducted over twenty-four months. Patients presenting with facial disproportion either to the Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery or to the Department of Orthodontics and Dentofacial Orthopaedics during the study period were included. Postoperative follow up was done for a period of minimum six months.
The inclusion criteria were patients with skeletal malocclusion (Angle’s class I, II, III), Age group between 18-35 years, American Society of Anesthesiologists (ASA) category I, II. Patients with severe crowding, the exaggerated curve of Spee, systemic illness, syndromic conditions and patients not willing to participate in the study were excluded.
Procedure
Pre-operative
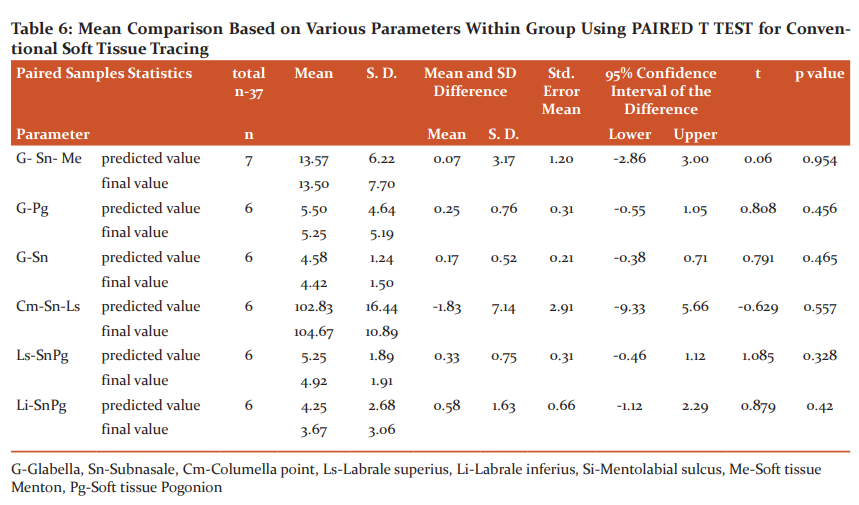
All patients underwent complete data acquisition, which included clinical examinations, clinical photographs (Figure 1), standardized digital lateral cephalogram (Figure 2a) and study models. High Resolution Computed tomography (HRCT) in a prescribed format was also obtained. Patient in natural head position and gently biting in centric relation, with the lips in a relaxed position, all the images were obtained in 1mm slice thickness DICOM (Digital Imaging and Communications in Medicine) format. Once the data acquisition, clinical evaluation and cephalometric analysis were done, problem list was made for all the participants based on which treatment objectives were obtained.
Conventional cephalometric tracing and cephalometrics for Orthognathic Surgery (COGS) analysis for both hard and soft tissue was done using acetate paper. Cephalometric prediction tracing was carried out for all the participants with the simulation of proposed surgical movements.
Digital lateral cephalogram was incorporated into Dolphin Imaging version 11.0 Premium software and calibrated. COGS analysis was done for all the participants and skeletal linear measurements were obtained. Using the software, surgical movements were simulated thereby achieving the proposed surgical plan and skeletal linear measurements were recorded. However soft tissue prediction analysis was not possible due to its unavailability in the current software.
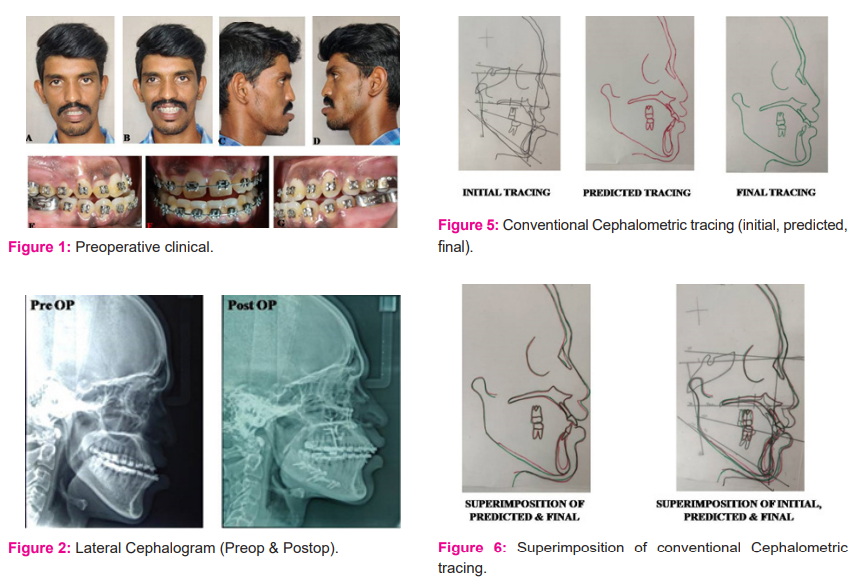
HRCT in DICOM format was incorporated into Materialise™ (Materialise Interactive Medical Image Control System) MIMICS medical version 21.0 software. Masking was done and virtual Skull models were created. Using the software templates, surgical osteotomies were performed and the planned surgical movements were simulated (Figure 3).
The fixed appliance was placed three to five days before the surgery for all the patients. The surgical procedures as planned were carried out under general anaesthesia.
Post-operative
Postoperatively, orthodontic teeth movements were initiated three to four weeks following surgery for all participants to utilize Rapid Accelerated Phenomenon (RAP).
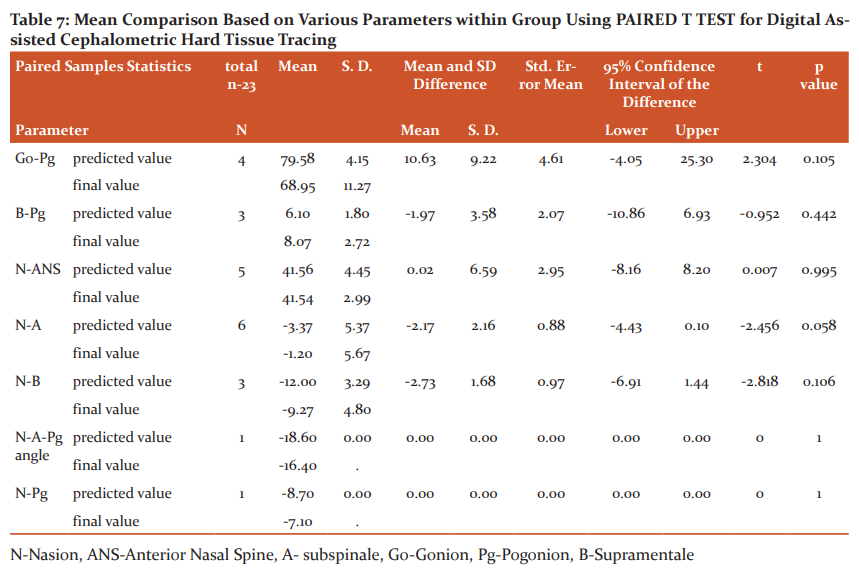
The postoperative lateral cephalogram (Figure 2b) and cephalometric tracing are done at six months were considered as the outcome tracing. This tracing was superimposed over the predicted tracing (Figure 5, Figure 6). The linear differences in the landmarks were measured and analyzed.
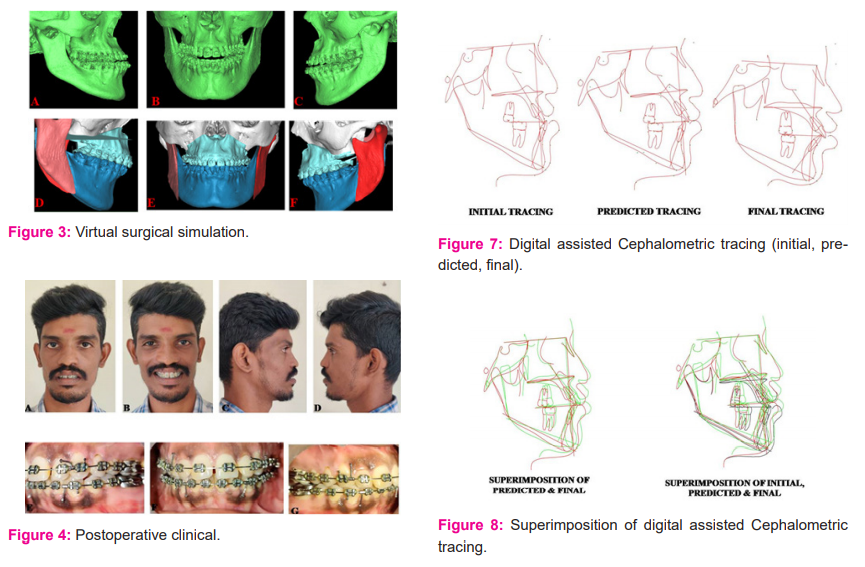
Similarly six months postoperative digital lateral cephalogram was incorporated into the dolphin software. Cephalometric tracing was made following calibration and Skeletal linear measurements were recorded. Tracing superimpositions were done using software and the linear difference in the landmarks were measured as well as analyzed (Figure 7, Figure 8).
Statistical analysis
Statistical analysis was carried out using version 20 SPSS software. Statistical analysis was made using a Paired t-test to compare the predicted value and final value of both conventional hard and soft tissue parameter and digital hard tissue parameter. the p-value of ≤0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Results
During the study period, twelve patients reported to our department with the facial disproportion of which seven patients met our inclusion criteria. Among the seven patients, four of them were males and three were females. Distribution of age among the study group ranged from 21 to 31 years, with the mean being 25 years.
Out of the seven patients, two of the patients had a major discrepancy in a single jaw. One patient had a maxillary discrepancy whereas the other had a mandibular discrepancy. The remaining five patients had the combination of both maxillary and mandibular discrepancies. The types of osteotomy procedure performed for various discrepancies are tabulated in table-1.
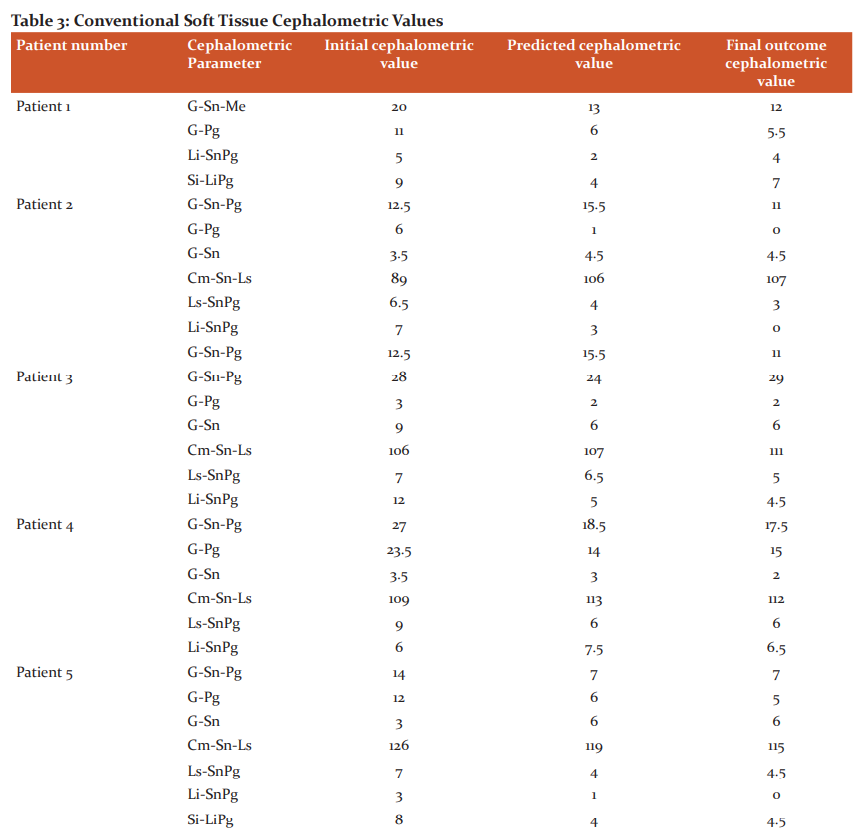
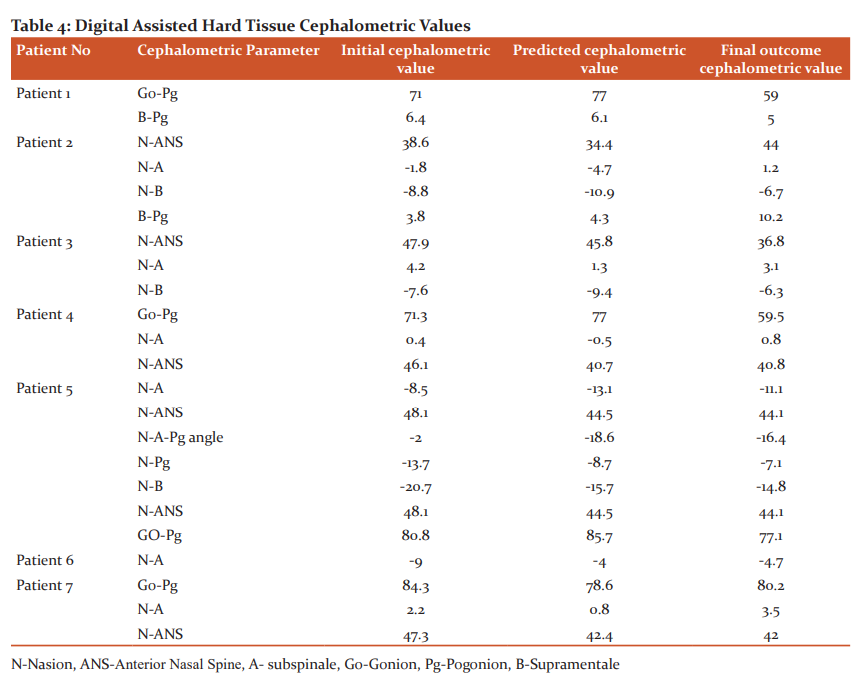
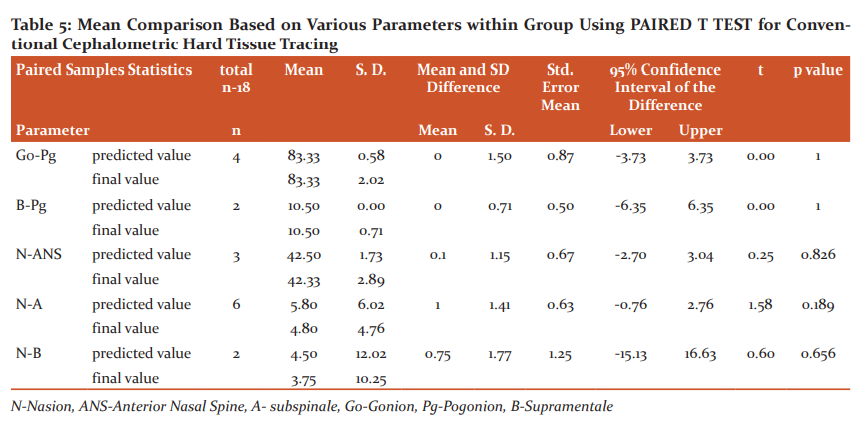
The initial predicted and final tracing values of both conventional hard and soft tissue analysis are summarized in table-2 and table-3 respectively. Similarly, the values of digital hard tissue analysis are summarized in table-4.
The mean comparison between predicted and final values within the group was analysed using the Paired t-test for conventional hard tissue tracing are summarized in table-5. No statistically significant difference was evident between the predicted and final values in all the parameters within the conventional cephalometric hard tissue tracing.
The mean comparison between predicted and final values within the group was analyzed using Paired t-test for conventional soft tissue tracing are summarized in table-6. No significant difference was statistically evident between the predicted and final values in all the parameters within the conventional cephalometric soft tissue tracing.
The mean comparison between predicted and final values within the group was analyzed using Paired t-test for digital hard tissue tracing are summarized in table-7. No statistically significant difference was found between the predicted and final values in all the parameters within the digital assisted cephalometric tracing.
Discussion
Facial disproportions are a deviation from the normal facial harmony. The acceptable level of variation from normal facial proportion is still debatable.1,2 These discrepancies can happen in various planes. Individuals with facial disproportions often encounter with aesthetic, functional and psychological disturbances. The goal of orthognathic surgery is to restore facial form and function.10
Until the introduction of fixed orthodontic appliances therapy in mid 20th century, most of the osteotomies performed were surgery only approach which has major limitation such as occlusal instability, relapse as a result of the type of muscle attachment to osteotomized segments. In 1976, Worms et al advocated the orthodontics-first concept for individuals with facial disproportion and stated that the best possible surgical repositioning of the maxillomandibular complex (MMC) is only possible following pre-surgical orthodontics.4
Conventional orthognathic surgery includes presurgical phase followed by orthognathic surgery and postsurgical phase was considered as standard protocol. The main purpose of presurgical phase is decompensation of the dentition by correcting severe crowding and rotated teeth, levelling of the curve of Spee, levelling and alignment of teeth thereby achieving interarch relationship.3 It has been argued that repositioning of jaws is only possible after decompensation of dental discrepancies.
To overcome the shortcoming of Presurgical phase, Brachvogel et al in 1991 put forth the idea of “Surgery First and Orthodontic second Approach”. He also stated that tooth movements were facilitated by surrounding soft tissues which helps in reducing overall treatment time.11 Although in literature surgery first procedure has been emphasized, Nagasaka et al in 2009 popularised the protocol for Surgery First Orthognathic Approach.7 The major driving factor for SFOA is the immediate esthetic result as well as the reduction in the duration of overall treatment time.8 As per Liou et al certain criteria’s were mandatory for selection of individuals with facial disproportion for SFOA which includes moderate to well-aligned arches with minimal transverse discrepancies, minimal discrepancies in the inclination of the anterior teeth and flat to the mild curve of Spee.12
One of the basic requirements of successful orthognathic surgery involves the accurate prediction of the final position to assess the feasibility of the treatment. The conventional methods of treatment planning include cephalometric analysis and prediction as well as a simulated model surgery on an anatomical articulator with appropriate splint fabrication. Although these methods had certain limitations, these are widely used protocol for achieving optimal results. The cephalometric tracing also aids in assessing the positioning of the maxilla in the anatomical articulator. The major limitations of manual tracing are human errors and time consumption.13
A paradigm shift in planning the orthognathic surgical movements happened with the digital revolution. The availability of 2Dcephalometric planning software-enabled surgeon precise planning and with further application of the technology the 2Dimensional planning has now reached the next generation as three-dimensional virtual simulations.14 It improved the accuracy of predicting hard tissue as well as soft tissue profile and enabled to perform precise surgical movements. They also provide better outcome by transferring the predicted plan to the operating room with the fabrication of digitally assisted customized splints.15,16
Our study aimed to reliably predict the outcome in SFOA participants. In this period twelve participants reported, of which seven were planned for SFOA and five for conventional. In our study, the prediction tracing was done using a manual method for hard tissue and soft tissue and dolphin software for hard tissue parameters. Additionally, we also performed Virtual simulation for a few participants using CASS protocol.
The cephalometric landmarks were traced preoperatively and six months postoperatively. The preoperative prediction tracing was compared with six months of postoperative final tracing. On comparing the manual hard tissue tracing, the predicted value and final value were similar and there was no statistically significant difference between both the values. Likewise in the soft tissue manual and predicted tracing had no statistically significant difference with that of final values. It was in contrast to the study conducted by Pospisil et al. in 1987 as they reported that 60% of prediction tracing are inaccurate with that of postoperative tracing.17 However the study published by Bryan et al. in 1993 showed similar result to that of our study. They found that there is no significant difference between the planned postsurgical position of the jaws and the position achieved at the surgery.6
In Digital assisted hard tissue tracing, the predicted and final outcome was statistically similar, this result was in contrast to a systematic review reported by Kaipatur et al. in 2009 which stated that computer programs cannot consistently predict the skeletal changes occurring after orthognathic surgery.18 The manual prediction tracing and digital prediction tracing were compared. The maxillary parameters were reliably predicted in both Conventional Cephalometric analysis and Dolphin software. However, the mandibular parameters were reliably predicted with manual tracing. It was similar to the study conducted by Gossett et al. in 2005 for the conventional approach group. He reported that both the conventional visual treatment objectives and Dolphin assisted visual treatment objectives have a high level of reliability for the maxilla and conventional visual treatment objectives were slightly better at predicting the actual surgical changes in the mandibular arch.19 Yet another study conducted by Arslan et al. in the year 2018 yielded similar results to that of our study.20
In our study, the final orthodontic movements were not predicted. Most of the cases included in our study were participants belonging to strict SFOA criteria. These patients did not need a lot of orthodontic movements. We had prediction planning at immediate postoperative and six months postoperative period. However, our six months postoperative value was similar to that of predicted value and was taken into consideration.
The success of SFOA relies on case selection, accurate prediction and fixation which can yield good results even without orthodontic preparation. Given the present scenario, the conventional procedure for tracing is better, however, the next step would require at predicting the final orthodontic movements which can give more promising results.
Conclusion
Accurate prediction of the possible postoperative changes is of paramount impact in the success of orthognathic surgery. The different technique has been followed to achieve a reliable prediction including model surgery, cephalometric prediction and the contemporary digital planned visual surgery. This prediction becomes more challenging in the SFOA scenario due to the increasing variability which in overall to be achieved by orthodontic means. Our study focused on comparing the reliability of both manual and digital prediction in cases satisfying the SFOA criteria. Further studies which would also predict the orthodontic movements and incorporate in surgical planning can help to expand the envelope of the spectrum of the patients chosen to undergo SFOA. Further prediction should be able to accurately project both hard and soft tissue changes. However, the ultimate breakthrough in orthognathic planning will arrive when the dynamic soft tissue changes can reliably be predicted over the static hard tissue change.
Acknowledgement of technical support: Dr. Shantanu Patil, Head and Consultant, Department of Translational Medicine and Research, SRM Medical College, Hospital and Research Centre
Source(s) of support: NIL
Conflicts of Interest: NIL

References:
-
Lu CH, Ko EWC, Huang CS. The accuracy of video imaging prediction in soft tissue outcome after bimaxillary orthognathic surgery. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 2003. 61:333–342.
-
Aristizábal JF, Martínez-Smit R, Díaz C, Pereira FVA. Surgery-first approach with 3D customized passive self-ligating brackets and 3D surgical planning: A case report. Dental Press J Orthod 2018;23:47-57.
-
Hafiz TM, Maheen A, Mubassar F, Adeel TK, Fatima F. Concepts, protocol, variations and current trends in surgery first orthognathic approach: a literature review. Dental Press J Orthod 2018;23(3):36.e1-36.e6
-
Worms FW, Spiedel TM, Bevis RR, Waite DE. Posttreatment stability and esthetics of orthognathic surgery. Angle Orthod 1980;50(4):251-273
-
Choi JW, Lee JY, Yang SJ, Koh KS. The reliability of a surgery-first orthognathic approach without presurgical orthodontic treatment for skeletal class III dentofacial deformity. Ann Plast Surg 2015;74:333-341.
-
Bryan DC, Hunt NP. Surgical accuracy in orthognathic surgery. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg 1993;31:343-350
-
Nagasaka H, Sugawara J, Kawamura H, Nanda R. “Surgery-first” skeletal class III correction using the skeletal anchorage system. J Clin Orthod 2009;43:97-105.
-
Liao Y, Lo SH. Surgical Occlusion Setup in Correction of Skeletal Class III Deformity Using Surgery-First Approach: Guidelines, Characteristics and Accuracy. Sci Rep 2018;8:11673.
-
Liou EJ, Chen PH, Wang YC, Yu CC, Huang CS, Chen YR. Surgeryfirst accelerated orthognathic surgery: postoperative rapid orthodontic tooth movement. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 2011;69:781-785.
-
Jeyaraj P, Chakranarayan A. Rationale, relevance, and efficacy of “surgery first, orthodontics later” approach in the management of cases of severe malocclusion with skeletal discrepancy. Ann Maxillofac Surg 2019;9(1):57-71.
-
Brachvogel P, Berten JL, Hausamen JE. Surgery before orthodontic treatment: A concept for timing the combined therapy of skeletal dysgnathias, Deutsche Zahn. Mund. Kieferheilk. Zentralb 1991;79(7):557-563.
-
Kwon TG, Han MD. Current status of surgery first approach (part II): precautions and complications. Maxillofac Plast Reconstr Surg 2019;41:1–10
-
Kolokitha OE, Topouzelis N. Cephalometric methods of prediction in orthognathic surgery. J Maxillofac Oral Surg 2011;10(3): 236–245.
-
Tankersley AC, Nimmich MC, Battan A, Griggs JA, Caloss R. Comparison of the Planned Versus Actual Jaw Movement Using Splint-Based Virtual Surgical Planning: How Close Are We at Achieving the Planned Outcomes? J Oral Maxillofac Surg 2019;77(8):1675-1680.
-
Lee J, Kim YI, Hwang DS, Kim KB, Park SB. Effect of occlusal vertical dimension changes on postsurgical skeletal changes in a surgery-first approach for skeletal Class III deformities. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop 2014;146(5):612-619.
-
Yuan P, Mai H, Li J, Ho D, Lai CY, Liu Y, et al. Design, development and clinical validation of computer-aided surgical simulation system for streamlined orthognathic surgical planning. Int J Comp Assis Radiol Surg 2017;12(12):2129-2143.
-
Poposil OA. Reliability and feasibility of prediction tracing in orthognathic surgery. J Craniomaxillofac Surg 1987;15:79-83.
-
Kaipatur NR, Flores-Mir C. Accuracy of computer programs in predicting orthognathic surgery soft tissue response. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 2009;67(4):751–759.
-
Gossett CB, Preston CB, Dunford R, et al: Prediction accuracy of computer-assisted surgical visual treatment objectives as compared with conventional visual treatment objectives. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 2005;63(5):609-617.
-
Arslan C, Altu? AT, Toygar Memiko?lu TU, Arslan EM, Ba?p?nar E. Comparison of the Accuracy of Manual and Digital Cephalometric Prediction Methods in Orthognathic Surgical Planning: A Pilot Study. Turk J Orthod 2018; 31(4): 133-138.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License