IJCRR - 13(4), February, 2021
Pages: 97-102
Date of Publication: 16-Feb-2021
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
Mental Health and Lifestyle of University Students During Lockdown Period of COVID-19 Pandemic
Author: Lokanath Mishra, N. Pramoda Kumar
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Introduction: The flare-up of Covid-19 in India caused an open frenzy and emotional wellbeing pressure. At first, it was about the course finishing later the issues have been moved to assessment. This scourge expands the mental issues, stress, dissatisfaction, sorrow and nervousness. Objective: The main objective of this study was assessing the mental health and lifestyle of Mizoram University students during Covid-19 lockdown period. Methods: This study was a cross-sectional investigation and a snowball method was utilized for an assortment of information from the students. Results: There was 65.2 per cent of members who revealed that they were giving more consideration to their emotional wellbeing during the pandemic. Most of the members revealed that they got expanded social and family support and they were giving more consideration to their psychological wellbeing, investing more time, resting and practising after the beginning of the pandemic. Majority of the participants expressed that they have expanded worry of learning, worry for conclusive university assessment, career stress and upset during the lockdown time. Very fewer members expressed that they were giving more consideration to their psychological wellness, investing more time, resting and practising after the beginning of the pandemic. Conclusion: These positive effects on psychological wellbeing may have helped the students adapt to other negative effects on emotional wellbeing, and expanded pressure. This pandemic impact will probably be engraved on every individual included.
Keywords: Academics, Lifestyle, Mental health, Pandemic, Stress
Full Text:
Introduction
Government of India proclaimed an across the country lockdown for 21 days on 24th May 2020, as a preventive measure against the Covid-19 pandemic in India. The national wide lockdown in India has been reached out past 4th May 2020 for an additional fourteen days. Once more, it was extended out up to 31st May 2020. The flare-up of Covid-19 in India caused an open frenzy and emotional wellness worry, with an expanding number of cases being analysed. Psychological wellbeing is more than insignificant nonattendance of mental issues. It alludes to a perspective which is described by enthusiastic prosperity, relative opportunity from tension and crippling manifestations, and an ability to set up useful connections and adapt to the conventional requests and worries of life.
All the instructive organisations have been shut due to Covid-19 episode. In the interim, school and college students are worried about inns, residence clearing and wiping out of foreseen occasions, exchange studies and graduation functions. Final year students are anxious about the job market they are going to enter soon. The assessments were deferred because of the lockdown impact and the genuine date of the test is nobody knows and questionable. In this context, numerous students were experiencing mental pressure and there is a solid need to think about their psychological wellness status. The constant spread of the pandemic, exacting disconnection measures and postponements in beginning schools, colleges, and universities across the nation are expected to impact the mental health, emotional wellbeing of the students.
There have been provided details regarding the psychological effect of the pandemic on the overall public, patients, clinical staff, youngsters, and more established grown-ups. Studies have revealed that a greater part of the students are experiencing nervousness issue and anxiety.1-3 However, even those students who are living at home have grumbled about experiencing suffering from interpersonal issues. Indian Psychiatry Society study revealed that there is up to a 20 per cent expansion in cases related to emotional wellbeing and mental health issues. Initially, it was about the course completion and the University and college educators began a web based instructing, however, the issues have moved to assessment. Students, particularly from the more vulnerable segment who may not have a computer, laptop and smartphone are worried about the method of assessment and examinations. Numerous uncertain family issues come out which were not tended to yet being bound to one space for the day has constrained these issues to come out and these students are in the middle of it.
Different studies have affirmed the effect of communicable disease episodes on open psychological wellbeing, such as serious intense respiratory disorder in 2003 and the 2009 novel influenza epidemic. These kinds of pestilences increase mental issues, such as stress, disappointment, discouragement, stress, frustration, depression, anxiety, and tension. A few investigations have demonstrated that post-traumatic stress disorder is firmly identified with melancholy, depression, psychological problems, and other mental issues. Some studies conducted concerning the mental health risks of Covid-19 in vulnerable populations include older adults4, the homeless destitute5, migrant workers 6 the intellectually ill7,8, pregnant ladies 9 and Chinese students studying abroad.10 A considerable number of people are working in IT, ITES, education, and other industries where they can work from home. Hence, their arena physical contacts which helped for better social distancing.11 An investigation conducted in China12 on the impact of Covid-19 on youth psychological well-being, mental health and in India13 discussed the significance of therapists during the Covid-19 pandemic is featured on teaching critical thinking, problem-solving strategies to adapt to the current emergency. Haimin14 investigated to look at university students’ family life in the Covid-19 and found that an alternate learning experience in this situation from the time with this circumstance from when they were on campus previously. There are various ways a student can use this time profitably and gain something out of it. However, technology and innovation have made our life simpler and easier as well as entertaining.
However, sometimes it is an absence of interest that individuals feel exhausted significantly in the wake of being involved by the electronic devices. Fatigue is an opportunity for the individual to improve their life in a few or another manner. The University Grant Commission has been utilising customary warning to all Universities to take conceivable precautions and measures for wellbeing and security of students. To maintain a strategic distance from any sort of stress Universities will take a few measures for the psychological wellbeing psychosocial viewpoints and prosperity of the students. From the above, it was discovered that a couple of studies have detailed the effect of the Covid-19 pandemic on emotional wellness, mental health and way of life of public and adolescent youths. No such study has been conducted on psychological wellbeing and way of life of University students of India. Therefore, the study intended to explore the mental health and lifestyle of University students during the lockdown period and whether there was a quick effect of the Covid-19 pandemic.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
The present study was a cross-sectional investigation. A snowball sampling strategy was utilised for the collection of information from university students. Before conduct the research study, ethical approval has been taken from Mizoram University Research Ethical Committee having no MZU/DoE/249 and also consent was taken from the Mizoram University students. An online semi-organised survey questionnaire was utilised for an assortment of data by utilising Google forms. The connection of the semi-organized poll was sent through messages, What Sapp and other social media to the students who have connected with the contacts of the investigator. The members were urged to reveal the study to whatever number individuals as would be prudent. Accordingly, the link was sent to the students apart from the primary purpose of contact. Part-A of the survey which incorporates sex, the stream of instruction, area of residence and course. Part-B of the survey questionnaire was to gauge the mental health of the students. Respondents are solicited to answer the Part-C from the poll for examining the effect of the Covid-19 pandemic on mental health-related lifestyle changes having yes and no responses. Furthermore, students are approached to answer their learning experiences with online courses, assessment of the government measures against the Covid-19 spread, view of the impact of the pestilence on their thoughts, behaviours, and practices.
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
The information was gathered from 894 university students with 513 females and 381 males. Out of total participants 224 Arts, 107 commerce, 284 science and 279 students are from professional courses. Concerning the area of residence, 376 students are from urban and 518 students are from rural background (Table 1).
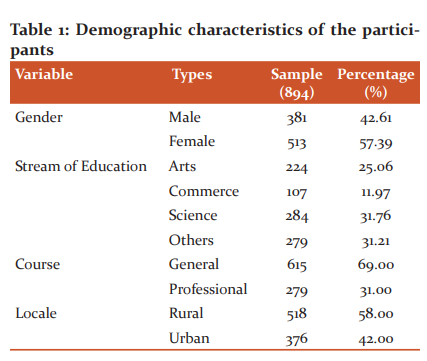
From the above table, it tends to be seen that 69 per cent of students are in general course participated in the study and 31 per cent students are from a professional course like Engineering, MBA, M.Ed. MSW, M. Lib., and MJMC course. Concerning stream of instruction 25.06 per cent are from Arts 11.97 per cent students are from commerce and 31.76 per cent are from science background remaining students were from other streams. Fifty-eight per cent of students are from rural and 42 per cent of students are from an urban background.
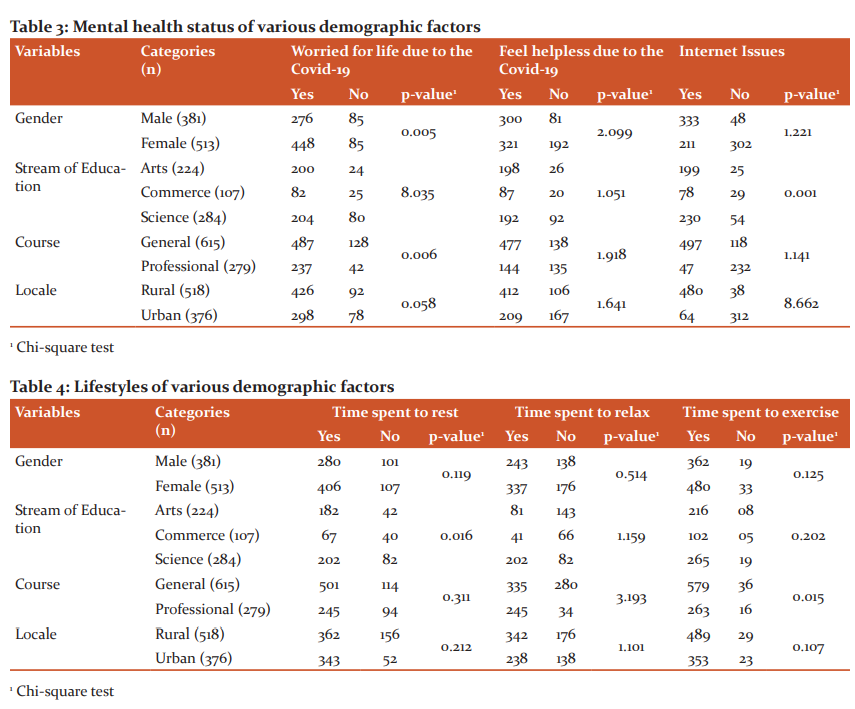
Following the onset of the pandemic, more than half of the participants 67.2 per cent reported no expanded worry, stress from scholastics. Additionally, 78.2 per cent mentioned that they did not experience increased financial stress arising from the pandemic. A total of 74.5 per cent of participants reported that they did not encounter increased stress from home. There was 65.2 per cent of participants who reported that they were paying more attention to their emotional wellness, mental health following the pandemic. Additionally, 66.3 per cent of participants reported that they were investing more time to rest. The majority of participants 65.2 per cent expressed that they were spending more time to relax. More than half of the participants 69.7 per cent reported that they were spending more time exercising.
Since the pandemic is not finished at this point and there is a further spread of the pandemic throughout the country, it is conceivable that the Covid-19 pandemic will cause an extreme frenzy, excessive panic, uneasiness, and anxiety in inhabitants living inside and outside states of India on account of the expanding number of Covid-19 cases around the world. Along these lines, some may contend that the reactions from the relevant authorities should have been quicker and progressively proactive. Simultaneously, government and private clinics to battle the Covid-19 pandemic were assigned by the concerned specialists. However, it was imperative to ensure that these quarantine facilities were not planned simply for lodging huge quantities of individuals, indeed, which can spread the contamination further. Occasion periods were additionally delayed and school openings were stretched out to decrease the quantities of new Covid-19 cases.
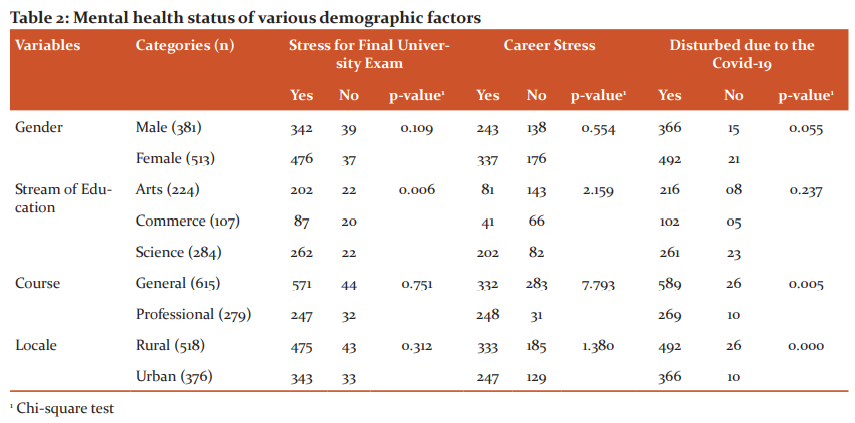
The overall score in participants showed a gentle distressing effect. One potential reason behind this finding is that the infection flare-up was not viewed as serious during the time that there was conducted. Moreover, it is conceivable that members despite everything probably would not have been all around educated about the seriousness of the infection, as referenced beforehand. When this investigation was conducted, the whole India was locked down as had happened in Mizoram University is located in the Aizawl (Northeast of India) and the road distance between plane India state Assam and Aizawl is approximately 400 km.
By the month May 2020, the quantity of affirmed Covid-19 cases in Mizoram is just one, which is extremely little than that of the rest of India. Besides, most of the members reported that they got extended social and family support. The present study also documented that the vast majority of the members had positive mental health, psychological well-being connected way of lifestyle changes. Spending more time to rest was also associated with a lower score in the respondents of the present study.
Albeit the greater part of the members, 52.1 per cent reported that they felt stunned and uncertain because of the Covid-19 pandemic, they did not feel helpless because of the pandemic. Additionally, the majority of participants revealed that they were paying more attention to their mental health, psychological wellness, spending more time relaxing, resting and practising after the onset of the pandemic. These positive effects on mental health, psychological wellness may have helped the participants adapt with other negative impacts on mental health, including increased pressure and stress. Then again, an expansion in money related and family worry in a debacle could be related with some shirking practices, which would have compounded their psychological wellness, mental health and lead to a progressively latent way of life and more passive lifestyle.
The current study results were consistent with the findings reported by Lau et al. (2006) who explored mental health, psychological wellbeing, quality of life and personal satisfaction in Hong Kong residents during the Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome (SARS) epidemic in 2003. The authors also reported increased social and family support as well as positive psychological wellness, mental health-related lifestyle changes. One potential reason behind these findings was that during the pandemic, the pace of the entire society eased back down. This could have then created more chances and time among the community members to help, support and care for each other.
Besides, during the some Ugadi, Ramzan and other various festivals in each state, relatives, family members and companions were tremendously esteemed and there was expanded correspondence with relatives and companions. Family members were bound to think about one another and fraternize because they were approached to abstain from going to open places and remain at home, particularly during the celebrations and festivals. Besides, these festivals and celebrations are the most significant state festivals and celebration because it marks the beginning of a new year according to the traditional local calendar. It also signifies an opportunity for a new beginning and a hope of good things to come. Companions were likewise bound to send respects to one another using WhatsApp and potentially other social media.
This study was one of the first studies to investigate the impact of the Covid-19 pandemic, as this study was taken more than weeks after the lockdown in Aizawl other areas and cities in Mizoram were imposed by the Indian government. This is especially important, as this study serves as some of the main information about the mental health, emotional wellness impacts of the Covid-19 pandemic. Furthermore, the current study pilot-tested the legitimacy of the questionnaires used to ensure that they were appropriate in the present investigating context and setting. However, the present study conducted from the limitations associated with the modest number of the sample size and for little timeframe, poor adherence to the investigation and the sampling method, which constrained the speculation of present findings to the entire university student population in mainland India.
It is also possible that the members were limited to only those who have the passionate and mental scope to respond these questions, which may have skewed entirely of the appropriate responses towards those normal of a “healthier” population in this circumstance. During this moment of increased security, particularly digital security aimed at playing down the crisis, any sort of critical responses. Additionally, the conceivable recall inclination from members may have confounded the present findings. The pay level of participants’ family was not assessed in the study. Despite the fact in this study researcher collected the occupational information of the guardians, the researcher did not collect specific details including whether their parents’ occupation and income were related to healthcare. Additionally, the researcher did not collect information on whether participants had family members, relatives and friend who contracted the virus or who developed symptoms.
The researcher did not utilize any promotional material for the survey because, during this sensitive time, the degree to which members may sensibly perceive the survey as a sort of institutional surveillance may have affected the legitimacy of the responses. Participants were approached to refer to the data concerning Covid-19 updates and the prevention measures released by the administration. Enormous scope with both qualitative and quantitative techniques ought to be conducted in all districts of different nations to explore the mental health and quality of life among citizens and residents, especially in the areas most severely impacted by the pandemic.
Following the current study, the researcher will likewise research whether these members develop post-traumatic stress after the Covid-19 pandemic is over. Ideally, by at that point, researchers and scientists will have some ideas on what transmits the SARS-CoV-2 infection and how this infection comes through. Researcher emphatically urges that health workers ought to incorporate emotional mental health advancement as part of their follow-up after the pandemic.
Future investigation should also incorporate more issues related to mental health questions. Young members express a stronger sense of helplessness, which might be correlated with an expanded utilization of social media. These young members watch and tune in to increasingly more negative news which will at that point strengthen their sentiments of tension and discouragement during an emergency. Therefore, questions related to social media use, or internet use, or news consumption, would be useful to comprehend the effect of such epidemics on mental health. Also, questions regarding family members, relatives or friends who have contracted the infection, health history of the people, and their relationship with healthcare sectors in the case for work, and existing mental health issues ought to be included.
The ministry of health and family welfare, the government of India, has provided health advisories, videos, posters and even conducted webinars on handling mental health issues of peoples. Two sorts of devices cell phone 78.35 per cent and PC 21.65 per cent were utilized by the students for accessing the online course. Concerning the online course, live telecast, instead of recorded broadcast, of the courses was the best choice of most of the students 73.60 per cent. Nearly 55 per cent of students took part in the zoom class with a length of 35 to 40 minutes. About 65.7 per cent of students gain proficiency with their course employing the learning management system. Also, 72 per cent of students learn through WhatsApp and social media.
Regarding the activities of the students performed in their home during lockdown period, they spare time, watching TV 75.4 per cent, reading books 38.7 per cent, writing assignments 34.8 per cent, and playing computer games 26.8 per cent. Further, 34.5 per cent of the students viewed the news from TV newspaper and social media about the covid-19 pandemic for each day. Overall, nearly 37.3 per cent students felt fairly exhausting dating comfortable, and 46.70 per cent of them perceived family life during the unique time as not terrible, but not great either and 17 per cent not exhausting. Although personal hygiene was profoundly accentuated, there were a little proportion of the students 12 per cent who believed that they did not pay more attention to personal hygiene than previously and 88 per cent of the students deemed that wearing facemasks would be necessary while heading outside and beneficial for themselves even when the epidemic is under control and vanishes.
Conclusion
Since the lockdown is not finished at this point and there is a further spread of the pandemic, the Covid-19 pandemic may cause extreme panic and anxiety among understudies living inside and outside the home. Albeit the maximum number of participants revealed that they have expanded worry of learning, worry for conclusive final university examination, career stress and upset during the lockdown time. Moreover, a very few percentages of participants reported that they were paying more attention to their emotional well-being, mental health, investing more energy unwinding, resting and practising after the beginning of the pandemic. These positive effects on psychological wellness, mental health may have helped the members adapt to other negative effects on emotional wellness, including expanded pressure. The present study results are depicting expanded social and family support just as positive psychological wellbeing connected way of life changes. One potential purpose behind these discoveries was that during the pandemic, the pace of the entire society eased back down. In this study, it was discovered that there were professional students with an inclination toward mental issues and psychological problems, which was higher than the proportion of mental issues in different studies.
Aknowledgement- The researcher acknowledged the students of Mizoram university who have helped a lot in the collection of data for the study. Further, the researcher acknowledged the authors whose articles have given in references and the university authorities who have permitted to conduct the study during the pandemic period.
Conflict of Interest – The research has no conflict of interest for publication in your reputed journal
Source of Funding – This project was not funded by any funding agency.
References:
-
Chen Q. Mental health care for medical staff in China during the COVID-19 outbreak. Lancet Psychiatry 2020;395:45-47.
-
Yang Y. Mental health services for older adults in China during the Covid-19 outbreak. Lancet Psychiatry 2020;20:79-81.
-
Li SW. Analysis of influencing factors of anxiety and emotional disorders in children and adolescents during home isolation during the epidemic of novel coronavirus pneumonia. Chinese J Child Health 2020;46:1-9.
-
Rajkumar RP. Covid-19 and mental health: A review of the existing literature. Asian J Psychiatry 2020:52.
-
Tsai J, Wilson M. Covid-19: A potential public health problem for homeless populations. Lancet Public Health 2020; 20: 30053-30060.
-
Liem A, Wang C, Wariyanti Y, Latkin CA, Hall BJ. The neglected health of international migrant workers in the Covid-19 epidemic. Lancet Psychiatry 2020;7(4):20.
-
Yao H, Chen JH, Xu YF. Rethinking online mental health services in China during the COVID-19 epidemic. Asian J Psychiatry 2020;51:102015.
-
Zhou X, The role of telehealth in reducing the mental health burden from Covid- 19. J Health 2020; E-pub ahead of print, https://doi.org/10.1089/tmj.2020.0068.
-
Rashidi FF, Simbar M. Coronavirus pandemic and worries during pregnancy: A letter to the editor. Arch Acad Emerg Med 2020;8 (1):21.
-
Zhai Y, Du X. Mental health care for international Chinese students affected by the Covid-19 outbreak. Lancet Psychiatry 2020;7(4):22.
-
Kannamani R, Jayakumar S. The Trend of COVID-19 at Bengaluru: Prediction to Continue the Better Epidemic Management. Int J Curr Res Rev 2020;12(13):56-60
-
Leilei L. The effect of Covid-19 on youth mental health. Psychiatric Quarterly 2020; E-pub ahead of print, https://doi.org/ 10.1007/ s11126-020-09744-3
-
Banerjee D. The Covid-19 outbreak: Crucial role the psychiatrists can play. Asian J Psychiatry 2020;51,102-104
-
Haimin PA glimpse of University Students’ family life amidst the Covid-19 virus. J Loss Trauma 2020; E-pub ahead of print, https://doi.org/10.1080/15325024.2020.1750194.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License