IJCRR - 13(3), February, 2021
Pages: 168-174
Date of Publication: 03-Feb-2021
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
Comparison of Effectiveness of Diode Laser with Er: Yag Laser on Fluoride Uptake of Enamel Surface Using Acidic and Neutral Topical Fluorides: An In-Vitro Study
Author: Rutika Baid, Nilesh Rathi, Shreyans Aditya Jain, Nilima Thosar, Sudhindra Baliga, Jayati Mehta
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Introduction: Topical fluoride plays a vital role in the prevention of dental caries. Fluoride reduces enamel dissolution during acid attack.Laser irradiation also an adjunct to conventional caries prevention techniques. Objective: To compare \"the effectiveness of\" diode \"laser with\"Er:YAG laser on fluoride uptake of enamel surface using acidic and neutral topical fluorides. Methods: Enamel of each halved tooth specimens were painted with nail polish \"varnish leaving a window\" of 5x5 mm of exposed enamel. One half of the sectioned tooth was taken as the control group, (n=40) and it's corresponding half as the experimental group (n=40). These two groups were further subdivided into 4 subgroups of 10 samples each depending upon the pH of topical fluoride and wavelength of the laser used. \"Group A, Group B, Group C and Group D\" were marked as control groups and Group E, Group F, Group G and Group H marked as the experimental groups. Results: Fluoride ion-selective electrode and potentiometric analysis was used to calculate the mean fluoride uptake on the enamel surface of teeth. Er: YAG laser and diode laser after fluoride application on teeth demonstrated higher uptake of fluoride not only on enamel surface but also into the deeper structures. But, Er: YAG laser showed better results than diode laser for the incorporation of fluoride in teeth. Conclusion: APF-Er: YAG laser combination is most effective in the incorporation of fluoride in the teeth followed by NaF-Er: YAG, APF-Diode and NaF-Diode combination being the least.
Keywords: Topical Fluoride, Diode Laser, Er: Yag Laser
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION
Dental caries caused by excessive consumption of fermentable sugar, inadequate consumption of fluoride, improper oral hygiene and various systemic and oral conditions. Prevention is mandatory to identify patients with caries high risk and should be given individualized prophylactic and preventive support.1
Topical fluoride plays a vital role in the prevention of dental caries. Fluoride reduces enamel dissolution during the acid attack.2 Topical fluoride treatment is one of the most widely accepted treatment regimens which helps in reducing demineralization of the hard dental tissues.3,4 Various forms are used for topical application of fluoride such as fluoridated kinds of toothpaste, gels, mouthwash contains fluoride preparation and varnishes.
Laser irradiation also is as an adjunct to conventional caries prevention techniques.5 Application of lasers on dental hard tissues creates certain morphological and structural changes, resulting in an increase in “the acid resistance of the lased enamel and altering resistance to acid and permeability. These changes are attributed to various characteristics of the laser such as wavelength, exposure time, laser irradiation emission and various optical characteristics of each lased tissue. Diode lasers are soft tissue lasers and Er: YAG lasers are hard tissue lasers. The diode laser has several unique characteristics for its use in dentistry such as low cost compared to other lasers, smaller size and easy application in the mouth because of the optic fibres. Er:YAGemit light at 2940 nm wavelength, this coincides with the peak absorption of water and hydroxyapatite and can also ablate enamel, dentin, and carious tissues effectively than other lasers.7 The combination of topical fluoridation and laser has been used by various researchers but there is no study comparing both diode lasers and Er: YAG lasers with acidic and neutral fluorides.
So, the present study aimed to compare the effectiveness of diode laser with Er: YAG laser on fluoride uptake of enamel surface using acidic and neutral topical fluorides.
MATERIALS AND METHOD
A sample of forty extracted human premolar teeth, not older than 1 month were collected and stored at 4ºC in 0.1% thymol solution at room temperature until the experimental procedure was initiated. Non-carious intact teeth, teeth extracted for orthodontic or periodontal purposes or free from any visible developmental defects were selected. All teeth were sectioned into two halves longitudinally (mesiodistally) using a diamond disc to obtain a total of 80 specimens. These specimens were mounted on acrylic blocks formed in moulds of size 2×2 cm individually. The enamel of each halved tooth specimens was painted with nail polish varnish leaving a window of 5x5 mm of exposed enamel. One half of the sectioned tooth was taken as the control group, (n=40) and it's corresponding half as the experimental group (n=40). These two groups were further subdivided into 4 subgroups of 10 samples each depending upon the pH of topical fluoride and wavelength of the laser used. Group A, Group B, Group C and Group D were marked as control groups and Group E, Group F, Group G and Group H marked as the experimental groups.
In Group A, 1.23% APF gel was applied, in Group B, 2% NaF gel was applied, in Group C, 1.23% APF gel was applied and in Group D, 2% NaF gel was applied for 4 minutes each. Similarly, in Group E, 1.23% APF gel application was followed by diode laser irradiation, in Group F, 2% NaF gel application was followed by diode laser irradiation, in Group G, 1.23% APF gel application was followed by Er: YAG laser irradiation and in Group H, 2% NaF gel application was followed by Er: YAG laser irradiation, for 4 minutes each.
Teeth were lased from a standard distance of 4 mm each. Two treatments of irradiation were given for 20 seconds each of diode laser (power- 2 W) and Er: YAG laser (power- 0.3 W) in respective groups. After treatment, both control and experimental specimens were stored at 100% humidity in a humidifier at room temperature for 24 hours. Tooth specimen of each group containing 10 samples were further divided into subgroups of 5 samples for analysis of fluoride uptake on the enamel surface and subsurface in teeth using Fluoride ion-selective electrode and potentiometric analysis respectively.
Statistical analysis:
Statistical analysis of the data was done by using descriptive and inferential statistics both using SPSS 17.0 software and p<0.05 considered as the level of significance. The statistical tests used for the analysis of the result were one way ANOVA, multiple comparison Tukey and Student’s unpaired t-test.
RESULTS
In the present study, the mean fluoride uptake on the enamel surface of teeth was done using a fluoride ion-selective electrode and potentiometric analysis.
Mean fluoride uptake on the enamel surface of teeth using fluoride ion-selective electrode
Group A and Group E showed non-significant mean fluoride uptake on enamel surface of teeth after the application of acidulated phosphate fluoride using fluoride ion selective electrode on teeth with or without diode laser treatment.Group B and Group F showed the mean fluoride uptake on enamel surface of teeth using fluoride ion-selective electrode after the application of sodium fluoride on teeth with or without diode laser treatment ,which was found to be statistically significant. Group C and Group G showed significant mean fluoride uptake on the enamel surface of teeth using fluoride ion-selective electrode after the application of acidulated phosphate fluoride on teeth with or without Er: YAG laser treatment. Group D and Group H showed the mean fluoride uptake on the enamel surface of teeth using fluoride ion-selective electrode after the application of sodium fluoride on teeth with or without Er: YAG laser treatment, which was found to be statistically significant (Table 1).
Mean total fluoride uptake on the enamel surface of teeth using potentiometric analysis
In Group A and Group E, the mean total fluoride uptake on the enamel surface of teeth using potentiometric analysis after the application of acidulated phosphate fluoride on teeth with or without diode laser treatment was not found to be statistically significant. Group B and Group F showed the mean total fluoride uptake on the enamel surface of teeth using potentiometric analysis after the application of sodium fluoride on teeth with or without diode laser, which was found to be statistically significant. Group C and Group G showed the mean total fluoride uptake on the enamel surface of teeth using potentiometric analysis after the application of acidulated phosphate fluoride with or without Er: YAG laser, which was found to be statistically significant. Group D and Group H showed the mean total fluoride uptake on the enamel surface of teeth using potentiometric analysis after the application of sodium fluoride with or without Er: YAG laser treatment, which was found to be statistically significant (Table 2).
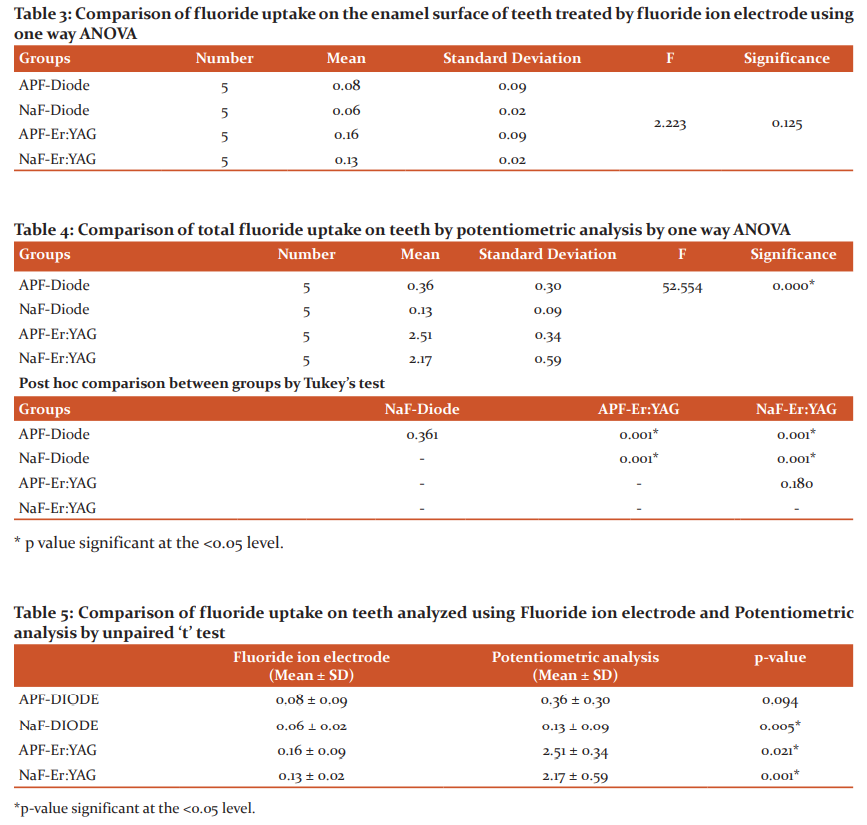
The mean fluoride uptake by fluoride ion electrode observed in APF-Diode treated teeth was 0.08 ± 0.09 and in teeth treated by NaF-Diode, it was 0.06 ± 0.02. Similarly, the teeth which were treated by APF- Er: YAG, the mean fluoride uptake was 0.16 ± 0.09 and in teeth treated by NaF-Er: YAG, the mean uptake was 0.13 ±0.02 and statistically, all these differences were found to be not significant (Table 3).
The mean total fluoride uptake on teeth by potentiometric analysis observed in APF-Diode treated teeth was 0.36 ± 0.30 and in teeth treated by NaF-Diode, it was 0.13 ± 0.09. Similarly, the teeth which were treated by APG- Er: YAG, the mean uptake was 2.51 ± 0.34 and in teeth treated by NaF-Er: YAG the mean uptake was 2.17 ±0.59 and all these differences were found to be statistically significant. Post-hoc analysis showed that the significant difference was present in APF-Diode vs APF-Er: YAG, APF-Diode vs NaF-Er: YAG, NaF-Diode vs APF-Er: YAG and NaF-Diode vs NaF-Er: YAG (Table 4).
The mean fluoride uptake on teeth in APF-Diode group by fluoride ion electrode was 0.08 ± 0.09 and by potentiometric analysis was 0.36 ± 0.30 and this difference was found to be statistically not significant. Mean fluoride uptake on teeth NaF-Diode group by fluoride ion electrode was 0.06 ± 0.02 and by potentiometric analysis was 0.13 ± 0.09 and the difference was found to be statistically significant. Mean fluoride uptake on teeth APF-Er: YAG group by fluoride ion electrode was 0.16 ± 0.09 and by potentiometric analysis was 0.13 ± 0.09 and the difference was found to be statistically significant. Mean fluoride uptake on teeth NaF-Er: YAG group by fluoride ion electrode was 0.13 ± 0.02 and by potentiometric analysis was 2.17 ± 0.59 and the difference was found to be statistically significant (Table 5).
DISCUSSION
In this era of preventive dentistry, many techniques are available for the prevention of dental caries. Application of fluoride acts as a preventive measure during the eruption period of teeth. Thus, for preventing the enamel caries formation, fluoride application in the form of topical gels has been proven to be the most accepted treatment to elude demineralization of dental hard tissues.3,4
Lasers are also known to enhance the effect of fluoride on teeth. Stern RH and his colleagues began laser studies on dental hard tissues. The investigation was done to evaluate the use of a laser in reducing the subsurface demineralization. The study concluded that there was reduction permeability to acid demineralization of the visible enamel.10-12 Combination of laser irradiation and topical fluoride have synergistic effects.13,14
Various methods are used for the estimation of fluoride ions in teeth. Fluoride ion electrode determines the fluoride uptake on enamel on the surface of teeth and potentiometric analysis determines the total fluoride uptake in teeth. It was observed in this study, that the mean uptake of fluoride on the enamel surface and total fluoride uptake on teeth was found to be increased in all the experimental groups treated with diode and Er: YAG laser after application of APF and NaF topical fluorides. These results were in conjunction with the studies carried out by Bahrololoomi et al and Moslemi et al that showed improved fluoride absorption on the enamel surface and deeper into its crystalline structure after laser irradiation.15,16 Vitale et al also demonstrated that lasers enhanced fluoride uptake of enamel and also provided protection to enamel surface from acid attack.1 The reason for this fluoride uptake is due to the chemical and morphological alterations that occurred on enamel surfaces that increased its resistance to demineralization. Villalba-Moreno et al found that laser treatment on enamel surface significantly enhanced the binding of fluoride, without damaging it, to the enamel surface.17 Similar results were found in a study carried out by Santaella et al on primary teeth using diode laser along with fluoride.9Kato et al, in contrast, concluded that any additional application of laser will not cause any significant increase or decrease in acid resistance of dental enamel.18
In the present study, as seen that most of the mean uptake of fluoride was seen in APF-Er: YAG group (0.16±0.09). This was followed by fluoride uptake on dental enamel of NaF-Er: YAG group (0.13±0.02) and APF-Diode group (0.08±0.09). But the least uptake was observed in NaF-Diode group (0.06±0.02). As observed in the results, Er: YAG laser enhanced the fluoride uptake of both acidic and neutral fluoride gels. The mechanism of the effect of Er: YAG laser on enamel is attributed to the structural and chemical change induced by it. When infrared light from the laser is absorbed by specific components of the dental enamel, it is converted directly into heat and further carbonate is released from the heated enamel and water evaporation occurs with the consequent formation of pyrophosphate which is more stable and less soluble.19,20,21 Thus, Er: YAG laser prevents demineralization of the enamel surface.
These results were in conjunction with the study by Maung et al who determined the alteration in diffusion coefficients in enamel using fluorescence recovery after photobleaching (FRAP).22 The enamel was lased with Er: YAG and it was found that there was lower diffusion (30%) on the surface region when compared to deeper layers. This may be attributed to the fact that there is an increasing amount of organic matrix, loosely bound water,23,24 porosities25 and water sorption capacity26 from the natural surface of the enamel towards dentin enamel junction. Various studies concluded that Er: YAG laser irradiation in combination with fluoride treatment improved fluoride uptake on enamel and reduced mean lesion depth.24,27,28Delbem et al found in his study that “Er: YAG laser has an influence on the deposition of CaF2 on the enamel and showed a superficial anti-cariogenic action.20Leamy et al demonstrated that heating the enamel structure by lasers stimulated the trapping of fluoride due to synthetic hydroxyapatite.29 The reactive accumulation of CaF2 on the enamel surface shows excessive fluoridation. The relationship between the precipitate formation of CaF2 on the enamel surface and excessive fluoridation has been confirmed in studies of hydroxyapatite behaviour in solutions of fluoride ions.30,31
Diode laser showed decreased uptake of fluoride in enamel when compared with Er: YAG laser. Two mechanisms have been proposed regarding the action of diode laser with fluoride: (i) incorporation of fluoride in enamel as a result of the thermal effect of the laser treatment32 and (ii) retention of fluoride in surface alterations.33 Of these, diode laser predominantly has the thermal effect which enhances the uptake in the enamel of fluoride. Sub-ablative effect of Er: YAG laser proves to be more effective than the thermal effect of the diode laser.
Also, in the present study, there was higher uptake of fluoride in APF gel as compared to NaF gels group on laser irradiation. AFP has been proven to increase fluoride absorbance in dental tissues.34A study by Arief et al concluded that APF gel can resist high enamel demineralization on acid exposure, so it can maintain the hardness of enamel surface.35 A greater fluoride concentration in the APF gel, application regimen, its lower pH and porosity of the lesion increases fluoride absorption. PDF reacts with hydroxyapatite of enamel and forms fluorapatite which is highly resistant towards acid. It also increases the concentration of fluoride in saliva. Instantaneous and initial surface adsorption process has been noted whereby dissolution of enamel mineral and re-precipitation of fluoride-rich reaction products onto enamel surface occurs after application of APF gel. Diffusion-controlled process of fluoride penetration into interprismatic areas of enamel and its interaction with enamel crystallites is followed thereafter.36Delbem et al compared APF with NaF toothpaste and concluded “that professionally applied fluoride gel or frequent fluoride application in low concentration is an effective preventive measure for the control of dental caries”.37
Delbem and Curry also found that APF gel increased the formation of more fluoride in enamel than neutral NaF gel and also was more efficient in minimizing the demineralization of the enamel blocks subjected to a cariogenic challenge.38 In in-vitro conditions, calcium fluoride is formed at pH7 when fluoride concentrations are 300 ppm in contrast to 100 ppm at pH 5.39 Curylofo-Zotti et al in his study stated that NaF application on teeth followed by YAG irradiation significantly increases fluoride uptake and concluded that NaF can be used as an alternative to APF as NaF-Er: YAG laser combination.40
Fluoride ion-selective electrode was used in the present study to determine the uptake of fluoride on the enamel surface. There was high uptake of fluoride on enamel surface” of all the teeth lased with either diode or Er: YAG laser in this study when assessed by fluoride ion-selective electrode. Even though control and experimental groups had significant uptake of fluoride, the intergroup assessment of uptake of fluoride between APF-Er: YAG, NaF-Er: YAG, APF-diode, NaF-diode laser groups was not statistically significant. Villalba-Moreno et al used fluoride ion-selective electrode (ISE) in their study to quantitatively determine the incorporation of fluoride ion into the dental structure of teeth treated with diode laser and concluded that the laser treatment significantly increased the binding of fluoride to the enamel surface with no damage to the enamel.17 Vitale et al. conducted a study to analyse for compositional changes of enamel using a fluoride ion-selective electrode in enamel before/after laser irradiation with topical fluoride application.1 They confirmed an increased capability of lasers to enhance fluoride uptake of enamel and provide the enamel surface protection from acid attack.
In the present study (Table 4), the highest mean uptake of fluoride was seen inAPF-Er: YAG group (2.51 ± 0.34). This was trailed by NaF-Er: YAG group (2.17 ± 0.59) and APF-Diode group (0.36 ± 0.30) and the least uptake of fluoride was seen in NaF-Diode group which was 0.13 ± 0.09. The fluoride was deposited not only on the enamel surface but also absorbed into deeper tissues. The total uptake of fluoride on teeth was carried out using potentiometric analysis. Pai et al calculated “the concentration and pattern of fluoride ion uptake into enamel” using fluoride ion-selective electrode and found that the uptake of fluoride ion was up to the depth of 45-54 µm.41 However, Delbem et al found that: YAG laser causes alterations to the surface and sub-adjacent tissues up to 1mm in teeth which were determined by potentiometric analysis.20
Similar results were found in the total uptake of fluoride on teeth in all the groups by potentiometric analysis as observed for fluoride uptake on enamel surface by fluoride ion electrode, but the results were highly significant in the potentiometric analysis (Table 5) However, the present study was carried out in in-vitro conditions and does not determine the exchange of fluorides in the oral cavity between saliva and teeth, which can also be an important factor to determine the uptake of fluoride in the teeth. Further studies should be carried out to determine the actual uptake of fluoride in in-vivo condition.
CONCLUSION
Er: YAG laser and diode laser after fluoride application on teeth demonstrated higher uptake of fluoride not only on enamel surface but also into the deeper structures. But, Er: YAG laser showed better results than the diode laser for the incorporation of fluoride in teeth. Also, APF-Er: YAG laser combination is most effective in the incorporation of fluoride in the teeth followed by NaF-Er: YAG, APF-Diode and NaF-Diode combination being the least. Potentiometric analysis method gave better results as it determined the total uptake of fluoride in teeth in comparison to fluoride ion-selective electrode which could determine only the uptake of fluoride on the enamel surface of teeth. Combination of either laser (Diode or Er: YAG) along with fluorides (acidic or neutral) showed higher uptake of fluoride on enamel as well as deeper surfaces of the tooth. This combination also provides a protective surface coating against caries providing a preventive approach to caries.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT:
Authors acknowledge the immense help received from the scholars whose articles are cited and included in references to this manuscript. The authors are also grateful to authors/editors/publishers of all those articles, journals and books from where the literature for this article has been reviewed and discussed.
SOURCE OF FUNDING – Nill
CONFLICT OF INTEREST -Nill

References:
1. Raina R, Kumar V., Krishna M. A comparison of antibacterial efficacy of 0.5% sodium fluoride impregnated miswak and plain miswak sticks on streptococcus mutants-A randomized controlled trial. J Clin Diagn Res 2017;11:2.
2. Bahadure RN, Pandey RK, Kumar R. An estimation of fluoride release from various dental restorative materials at different Ph: In vitro study. J Indian Soc Pedod Prev Dentis 2012;30(2):122-126.
3. Marinelli CB, Donly KJ, Wefel JS, Jakobsen JR, Denehy GE. An in vitro Comparison of Three Fluoride Regimens on Enamel Remineralization. Caries Res 1997;31(6):418–422.
4. Itthagarun A, Wei SHY, Wefel JS. The effect of different commercial dentifrices on enamel lesion progression: an in vitro pH-cycling study. Int Dent J 2000;50(1):21–28.
5. Azevedo DT, Faraoni-Romano JJ, Derceli J dos R, Palma-Dibb RG. Effect of Nd: YAG laser combined with fluoride on the prevention of primary tooth enamel demineralization. Braz Dent J 2012;23(2):104–109.
6. Laser and its Applications. [last assessed 2016 Sep 21]
7. Baraba A, Miletic I, Krmek SJ, Perhavec T, Bozic Z, Anic I. Ablative potential of the erbium-doped yttrium aluminium garnet laser and conventional handpieces: a comparative study. Photomed Laser Surg 2009;27(6):921–927.
8. Chin-Ying SH, Xiaoli G, Jisheng P, Wefel JS. Effects of CO2 laser on fluoride uptake in enamel. J Dent 2004;32(2):161–167.
9. Santaella MRLA, Braun A, Matson E, Frentzen M. Effect of diode laser and fluoride varnish on initial surface demineralization of primary dentition enamel: an in vitro study. Int J Paediatr Dent 2004;14(3):199–203.
10. Stern R. Laser beam effect on dental hard tissues. J Dent Res 1964;43:307-312.
11. Stern RH, Renger HL, Howell FV. Laser effects on vital dental pulps. Br Dent J 1969;127(1):26–28.
12. Stern RH, Vahl J, Sognnaes RF. Lased enamel: ultrastructural observations of pulsed carbon dioxide laser effects. J Dent Res 1972;51(2):455–460.
13. Stern RH, Sognnaes RF, Goodman F. Laser effect on in vitro enamel permeability and solubility. J Am Dent Assoc 1966;73(4):838–843.
14. Hicks MJ, Parkins FM, Flaitz CM. Kinetic cavity preparation effects on secondary caries formation around resin restorations: a polarized light microscopic in vitro evaluation. J Dent Child 2001;68(2):115–21.
15. Bahrololoomi Z, Fotuhi Ardakani F, Sorouri M. In Vitro Comparison of the Effects of Diode Laser and CO2 Laser on Topical Fluoride Uptake in Primary Teeth. J Dent Tehran Iran 2018;12(8):585–591.
16. Moslemi M, Fekrazad R, Tadayon N, Ghorbani M, Torabzadeh H, Shadkar MM. Effects of ER, Cr: YSGG laser irradiation and fluoride treatment on acid resistance of the enamel. Pediatr Dent 2009;31(5):409–413.
17. Villalba-Moreno J, González-Rodríguez A, López-González J de D, Bolaños-Carmona MV, Pedraza-Muriel V. Increased fluoride uptake in human dental specimens treated with diode laser. Lasers Med Sci 2007;22(3):137–142.
18. Kato IT, Kohara EK, Sarkis JES, Wetter NU. Effects of 960-nm diode laser irradiation on calcium solubility of dental enamel: an in vitro study. Photomed Laser Surg 2006;24(6):689–693.
19. Mathew A, Reddy NV, Sugumaran DK, Peter J, Shameer M, Dauravu LM. Acquired acid resistance of human enamel treated with laser (Er: YAG laser and Co2 laser) and acidulated phosphate fluoride treatment: An in vitro atomic emission spectrometry analysis. Contemp Clin Dent 2013;4(2):170–175.
20. Delbem ACB, Cury JA., Nakassima CK, Gouveia VG, Theodoro LH. Effect of Er: YAG Laser on CaF2 Formation and Its Anti-Cariogenic Action on Human Enamel: An in Vitro Study. J Clin Laser Med Surg 2003;21(4):197–201.
21. Apel C, Meister J, Götz H, Duschner H, Gutknecht N. Structural changes in human dental enamel after sublative erbium laser irradiation and its potential use for caries prevention. Caries Res 2005;39(1):65–70.
22. Maung NL, Wohland T, Hsu C-YS. Enamel diffusion modulated by Er: YAG laser (Part 1)--FRAP. J Dent 2007;35(10):787–793.
23. Brudevold F, Steadman LT, Smith FA. Inorganic and Organic Components of Tooth Structure. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1960;85(1):110–132.
24. Dibdin GH, Poole DFG. Surface area and pore size analysis for human enamel and dentine by water vapour sorption. Arch Oral Biol 1982;27(3):235–241.
25. Brudevold F, Tehrani A, Cruz R. The relationship among the permeability to iodide, pore-volume, and intraoral mineralization of abraded enamel. J Dent Res 1982;61(5):645–648.
26. Zahradnik RT, Moreno EC. Structural features of human dental enamel as revealed by isothermal water vapour sorption. Arch Oral Biol 1975;20(5):317–325.
27. Altinok B, Tanboga I, Peker S, Eren F, Bakkal M, Peker F. The effect of laser-activated Acidulated Phosphate Fluoride on enamel submitted to erosive solution only: an in vitro preliminary evaluation. Eur J Paediatr Dent 2011 Mar;12(1):13–16.
28. Ozturk E, Bolay S. Effect of Er: YAG laser irradiation on enamel caries prevention. Clin Dentis Res 2013; 37(1):19-23.
29. Leamy P, Brown PW, TenHuisen K, Randall C. Fluoride uptake by hydroxyapatite formed by the hydrolysis of alpha-tricalcium phosphate. J Biomed Mater Res 1998 ;42(3):458–464.
30. Mccann HG. Reactions of fluoride ion with hydroxyapatite. J Biol Chem 1953;201(1):247–259.
31. Yesinowski JP, Mobley MJ. Fluorine-19 MAS-NMR of fluoridated hydroxyapatite surfaces. J Am Chem Soc 1983;105(19):6191–6193.
32. Putt MS, Beltz JF, Muhler JC. Effect of temperature of SnF2 solution on tin and fluoride uptake by bovine enamel. J Dent Res 1978;57(7–8):772–776.
33. Oho T, Morioka T. A possible mechanism of acquired acid resistance of human dental enamel by laser irradiation. Caries Res 1990;24(2):86–92.
34. Botta AC, Mollica FB, Ribeiro CF, Araujo MAM de, Nicoló RD, Balducci I. Influence of topical acidulated phosphate fluoride on surface roughness of human enamel and different restorative materials. Rev Odonto Ciênc 2010;25(1):83–87.
35. Arief EP, Kunarti S. The effect of acidulated phosphate fluoride application on dental enamel surfaces hardness. Dent J 2007;40(3):145-147.
36. Joyston-Bechal S, Duckworth R, Braden M. The mechanism of uptake of 18F by enamel from the sodium fluoride and acidulated phosphate fluoride solutions labelled with 18F. Arch Oral Biol 1973;18(9):1077–1089.
37. Delbem ACB, Brighenti FL, Vieira AE de M, Cury JA. In vitro comparison of the cariostatic effect between topical application of fluoride gels and fluoride toothpaste. J Appl Oral Sci 2004;12(2):121–126.
38. Delbem ACB, Cury JA. Effect of application time of APF and NaF gels on microhardness and fluoride uptake of in vitro enamel caries. Am J Dent 2002;15(3):169–172.
39. Curylofo-Zotti FA, Tanta GS, Zugliani AL, Corona SAM. The combined use of sodium fluoride and Er: YAG laser to control the progression of enamel caries. Eur J Pharmac Med Res 2016;3(9):1-5.
40. Negi S, Krishnamurthy M, Ganji KK, Pendor S. Modulatory Effects by Neodymium-Doped Yttrium Aluminum Garnet Laser on Fibroblast Attachment to SingleRooted Tooth Surfaces Following Ultrasonic Scaling and Root Planning: An in Vitro Study. J Indian Soc Periodontol 2015;19(1):25–31.
41. Pai N, McIntyre J, Tadic N, Laparidis C. Comparative uptake of fluoride ion into enamel from various topical fluorides in vitro. Aust Dent J 2017;52(1):41–46.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License