IJCRR - 13(3), February, 2021
Pages: 113-119
Date of Publication: 03-Feb-2021
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
Correlation of Risk Perception with the COVID-19 Related Knowledge and Preventive Measures: A Study on Indian Pharmacy Students
Author: Deepika Purohit, Parijat Pandey, Manish Makhija, Deeksha Manchanda, Jyoti Rathi, Deepak Kumar, Ravinder Verma, Pawan Jalwal, Vineet Mittal, Deepak Kaushik
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Introduction: A novel threat to mankind occurred in December 2019 which was an outbreak of infection caused by a novel coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2 or 2019-nCoV). The infection was first developed in Wuhan, China, and has affected more than 200 countries around the world till now. Objective: The present study aims to assess the knowledge related to coronavirus disease (COVID-19), risk perception and preventive behaviours among the Pharmacy students in a part of India approximately 3 months after the onset of this outbreak in India. Methods: This survey was conducted from 2nd to 5th of September 2020 with Indian Pharmacy students (1st to 4th year). The knowledge, self-reported preventive behaviours and risk perceptions of COVID-19 were assessed using an online questionnaire. A total of 21 questions were there in the questionnaire in which 14 questions were about knowledge related to COVID-19, 4 items regarding preventive behaviours and 3 about risk perception. Results: A total of 268 participants completed the questionnaire. The participants were under the age group of 15-30 years. A high level of disease-related knowledge was found in the participants (77.66%). On an average 96.1% of participants were practising preventive behaviours. The aggregate score of items in risk perception section was found to be in the moderate range i.e., 5.38 out of 8. A significant negative correlation was obtained between risk perception and preventive behaviours. Conclusion: The trajectory and severity of this outbreak are very high, therefore, effective treatment against this global threat is required to be developed as early as possible. In the present study, a high level of disease-related knowledge and preventive behaviours were observed among the participants with a moderate level of risk perception.
Keywords: COVID-19, Coronavirus, Outbreak, Preventive behaviours, Risk perception, SARS-CoV-2
Full Text:
Introduction
Recently, a global threat to human health has emerged in the form of Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) which is an outbreak of the respiratory disease and recognized in December 2019. It has been reported to be caused by a novel virus, named severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2 or 2019-nCoV) having structural similarity with the virus causing SARS.1,2 As per the reports of World Health Organization (WHO), till 15 October 2020, the different regions of the world have reported cases of COVID-19 with 38,202,956 confirmed cases and 1,087,069 deaths globally.3
Human coronaviruses (HCoVs) have been reported as a group of viruses causing multiple respiratory disorders/diseases of varying severity, such as common cold, bronchiolitis and pneumonia.4 The researchers have reported HCoVs as rapidly evolving viruses because of its high recombination and genomic nucleotide substitution rates.5 Among the six HCoVs, identi?ed so far, namely HCoV-229E, HCoV-NL63, HCoV-OC43, HCoV-HKU1, middle east respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV) and severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus (SARS-CoV), four HCoVs (HCoVNL63, HCoV-229E, HCoV-HKU1 and HCoV-OC43) are circulated in the human population globally and have been found to cause about one-third of the infections due to common cold in humans.6,7 When the infection gets severe, these four HCoVs can be responsible for causing life-threatening bronchiolitis and pneumonia especially in immunocompromised patients, children and elderly.8,9
COVID-19 infection is spreading at a great pace globally and people are getting infected when they come in close contact with the people or surface infected with the virus. Lack of proper knowledge about the disease among people and not following proper preventive measures can increase the risk of infection along with increased levels of anxiety and stress.10 A study of COVID-19 related knowledge, risk perception and preventive behaviours needed to be carried out since COVID-19 has affected worldwide. To our knowledge, no such study has been conducted yet to assess the COVID-19 related knowledge of pharmacy students in India along with the preventive behaviours they are observing and risk perception among them. Therefore, in this survey authors aim to evaluate these parameters in some Indian Pharmacy students.
Materials and methods
This study was conducted on some Indian Pharmacy students for investigating their knowledge of coronavirus disease, the preventive measures they are following and the self-reported risk perception. The target population was those getting directly or indirectly affected by COVID-19 which included some Indian Pharmacy students in Delhi/NCR with an expected population of 15000. For calculating the sample size, an online calculator Calculator.net was used.11 based on the projected population proportion of 50%, the sample size required for the study was 375 with 5% margin of error and a confidence level of 95%. This study was carried out from 2nd September to 5th September 2020 through an online questionnaire in the English language following all the recommendations given by the Government during the pandemic, including touch precautions and prevention in close contacts.
Measures
There were 4 sections in the online questionnaire including demographic data, knowledge of people on coronavirus disease, preventive measures and risk perception reported by participants.
Demographics
Demographic information involved a participant’s age, gender, occupation, and current working status. These items were designed based on published literature available online.
Coronavirus disease related-knowledge
The first section of the questionnaire included 14 items for assessing the knowledge of participants regarding COVID-19. These questions were framed based on studies conducted previously about Middle East Respiratory Syndrome (MERS) and a newly reported study on COVID-19.10, 12 This section included 5 questions related to basic science related to COVID-19 and the disease aetiology, 2 questions about incubation period and symptoms, 1 question about the diagnosis of the disease, 2 items about disease transmission, 2 questions on prevention, and 2 items related to treatment. The validity of items in this section was determined by some experts involving an epidemiologist, and three medical professionals. One point was assigned to each correct answer and 0 points to ‘no idea’ or an incorrect answer. The total score obtained by participants was then converted into a percentage. A score ≤50% was designated as low level, 50%−75% as moderate, and ≥ 75% as the high level of COVID-19 related knowledge. For testing the reliability, a pilot study was conducted on 25 participants and compared with the original study through Cronbach’s alpha calculation with alpha value = 0.85 and 0.78, respectively.
Self-reported preventive behaviours
The preventive behaviours of participants were determined using four items based on a previous study.12 This section involved two items about preventive measures taken during sneezing and coughing, surface disinfection and frequent hand washing and two items regarding reduced use of public places in daily life. These items were validated by four experts including an epidemiologist, and three medical professionals. The total score was in the range of 0 to 4 which was converted to a percentage. A score <75% was designated as low performance and score ≥75% as high performance in preventive behaviours. Further, the reliability was assessed by calculating Cronbach’s alpha in the original study and a pilot study with 25 participants. The value of alpha was found to be 0.86 and 0.82, respectively.
Risk perception
Based on previous studies, 3 items were used for determining the risk perception of coronavirus disease among participants. Scores were assigned to each response using a 3-point scale (1 = No, 2 = Maybe, and 3 = Yes) and the items were validated by two experts including an epidemiologist and a medical professional. The total score of this section was between 2 and 8. A score ranging from 6 to 8 was designated as high, 4 to 5 as moderate and 2 to 3 as low-risk perception. To assess the reliability Cronbach’s alpha approach was used for the original study and a pilot study with 25 participants. The alpha value was found to be 0.83 and 0.77, respectively.
Data analysis
For analyzing the data, SPSS version 26.0 (IBM, Armonk, NY, USA) was used. The normality of distribution of continuous variables was assessed using Kolmogorov-Smirnov. The major outcomes were not found to follow a normal distribution and were evaluated using the Pearson correlation test and Mann-Whitney test. For calculating the frequencies and percentages categorical variables were used and for the calculation of means and standard deviations, numerical variables were used.
RESULTS
A total of 268 pharmacy students responded to the online questionnaire, producing a response rate of 71.46%. The students were under the age group of 15-30 years. Among all the respondents, 168 (62.69%) were male and 100 (37.31%) were female. A significant difference was observed between female and male participants in respect of risk perception (p < 0.05). In statistical testing, the p-value is the probability of obtaining test results at least as extreme as the results observed, under the assumption that the null hypothesis is correct. A very small p-value means that such an extreme observed outcome would be very unlikely under the null hypothesis. Female respondents were found to have lower risk perception. The major variables according to gender are demonstrated in Table 1.
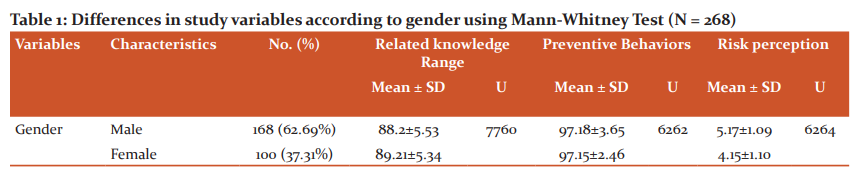
SD, standard deviation; U, Mann-Whitney U value calculated at the significant level of P < 0.05 and 95% confidence interval
The items related to disease knowledge are listed in Table 2. 87.52% answers were found to be correct on an average with 77.66% of respondents having high, 14.13% moderate and 8.21% of participants were having a low level of knowledge related to COVID-19.

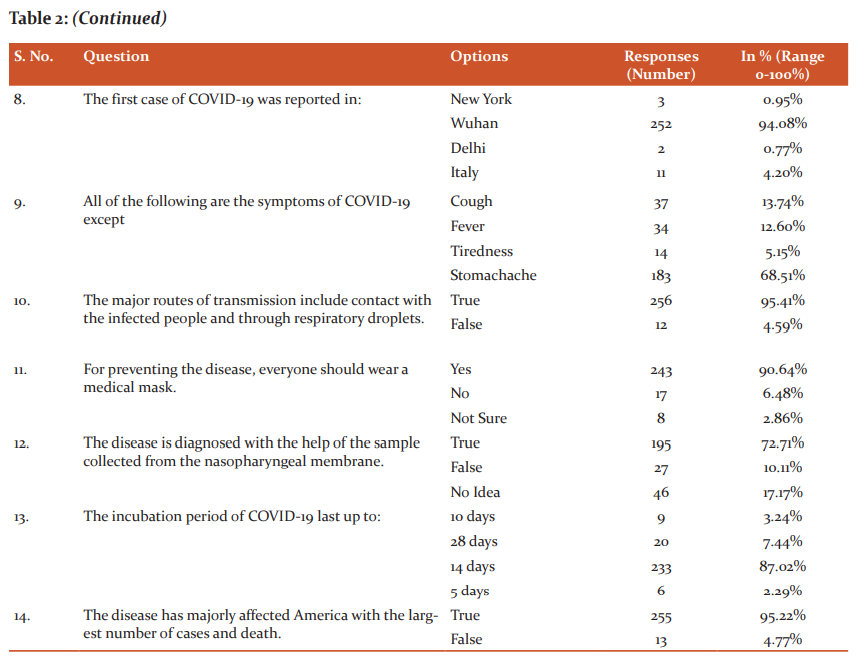
The lowest score related to one item; ‘For preventing the disease, everyone should wear a medical mask: Answer should be False’.
In the section of self-reported preventive behaviours, 96.1% answers were correct on an average with the majority (96.2%) of participants having a high score in preventive behaviours and only 3.8% had low performance. The lowest score was observed in the item ‘How frequently you go for buying essential commodities?’. Detail of items in the preventive behaviour section is listed in Table 3.


The risk perception (Table 4), included three items; ‘Do you have thoughts that you will get infected more easily than others?’, ‘Do you or do you know anyone who is suffering from stress as a consequence of this pandemic’ and ‘Do you think that you and/or your family will be impacted by the events brought on by the COVID-39 pandemic?’. The mean scores were 1.49, 1.31 and 2.56, respectively (out of 3, 2 and 3). The aggregate score was 5.38 out of 8 which indicated that participants had moderate risk perception. A total of 33.78% respondents were found to have low, 46.25% moderate and 26.87% had a high level of risk perception.

Further, the study involved computing correlation between variables i.e., risk perception and preventive behaviours. A significantly negative correlation was found as a result of analysis (Pearson correlation coefficient = -0.13; P<0.05, Table 5) which suggests that when preventive behaviours are followed properly, the risk perception declines. As pharmacy students would have the idea about significances of following preventive behaviours in overcoming risk perceptions which may be the possible reason for this negative correlation.
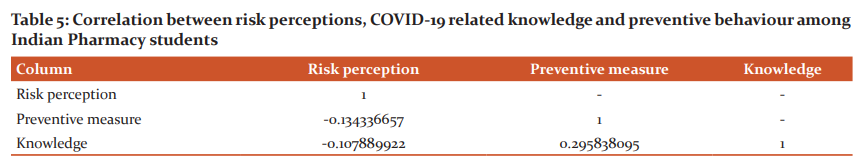
At significance level P<0.05 and 95% confidence interval; Pearson correlation coefficient.
Discussion
Since it has been discovered, COVID-19 has affected population throughout the global and has become a pandemic now. The novel coronavirus is capable of affecting people from any group, and the spread of this disease has increased the risk to a great extent.13 Hence, it is the need of the hour to evaluate the knowledge of people about the virus and disease, the preventive behaviours they are observing and to understand the associated anxiety level and risk perception among them. Such information can be useful for health policymakers for making the proper planning to tackle the pandemic. According to our knowledge, this study is first of its kind in this field among pharmacy students after this outbreak. This study was carried out at approx. 6 months after the first case of COVID-19 reported in India. In this study, the authors tried to assess the level of COVID-19 related knowledge among participants; preventive behaviours reported by them and risk perception. Along with this, the study focused on to evaluate the correlation between these variables. It was found that among all the respondents i.e., Indian pharmacy students, 77.66% of had a high level of knowledge related to this disease which was almost equal to similar previous studies conducted on medical students and health care workers. A total of 96.2% of the participants were found to have a high level of performance in observing preventive behaviours. This was higher than a recent study performed on Iranian medical students and earlier on health care workers.12-13 The cumulative score for risk perception among all the respondents was found to be in the moderate range i.e., 5.38 out of 8. As there is not much-related literature available, the results of a recent study performed on Iranian medical students and previous studies about MERS were used for comparing the results of present study.12,13,15
In the discussion of items about coronavirus disease-related knowledge, 87.52% answers were correct on an average which was comparatively higher than the similar study in which they reported 86.96% of correct answers. In preventive behaviour section, the average score was 96.1% which was higher than the results of a previously conducted similar study on Iranian medical students.14 It is necessary to point out here that in its recommendations, the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare, Government of India has advised people to stay at home and avoid going out unless it is essential. The Indian Government is also educating people in every possible way regarding preventive behaviours.16 The results of this section as shown in Table 3 confirm this issue. Though, the following item in self-reported preventive measures had the lowest score; ‘Digital payment is more useful at this time to avoid infection’. This item specifically outlines that people should practice using digital payment mode as much as possible. The risk perception of males and females were found to be significantly different, with males having higher risk perception. This may be indicative of the females being more aware of the importance of preventive behaviours in dealing with SARS-CoV-2 infection.16 The most important finding of the present study was a significant negative correlation between risk perception and self-reported preventive behaviours. As people follow more preventive behaviours, the risk perception declines. Hence, for reducing the anxiety, stress and risk perception which are the major problems associated with pandemic diseases like COVID-19, it is most important to follow the preventive behaviors.13,18,19
Future aspects of the study
This study is preliminary research whose results can be useful for the health policymakers while focusing on risk communication effectively and planning proper education criteria to control the severe outcomes of COVID-19. Here, Pharmacy students were the target population who would have the idea about significances of following preventive behaviours and this is the possible reason for the negative correlation obtained. For Pharmacy students who are expected to play the duty of volunteers at COVID-19 centres in the future if required, more courses should be conducted about self-protection and disease-related knowledge.
Conclusion
The study results have concluded that Indian Pharmacy students had a high level of COVID-19 related knowledge and reported high performance in observing preventive behaviours. Along with this, the students were having a moderate risk perception resulting in a negative correlation between risk perception and preventive behaviours reported by the participants. Though the correlation was negative, the risk perception among pharmacy students is moderate even after having high performance in preventive behaviours. This can raise concerns about self-protective behaviours among them and therefore, proper training programs should be started at earliest.
Consent for publication
Not applicable
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest, financial or otherwise
Acknowledgement
We thank Mr. Udit Malik for his valuable suggestions while designing the study.
Funding
No funding received.
References:
-
Zhu N, Zhang D, Wang W, Li X, Yang B, Song J. A novel coronavirus from patients with pneumonia in china. N Engl J Med 2020; 382:727-733.
-
Kushwaha D, Purohit D, Pandey P, Saif M, Katiyar P. A case study: The updated case history of India, with the impact of COVID-19 on the Indian economy. J Appl Biol Bioenergy 2020; 2(1):1-15.
-
WHO Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19) Dashboard. https://covid19.who.int/. [Cited 2020 August 26].
-
Pene F, Merlat A, Vabret A, Rozenberg F, Buzyn A, Dreyfus F. Coronavirus 229E-related pneumonia in immunocompromised patients. Clin Infect Dis 2003;37:929-932.
-
Vijgen L, Keyaerts E, Moës E, Maes P, Duson G, Van Ranst M. Development of one-step, real-time, quantitative reverse transcriptase PCR assays for absolute quantitation of human coronaviruses OC43 and 229E. J Clin Microbiol 2005;43:5452-5456.
-
Raoult D, Zumla A, Locatelli F, Ippolito G, Kroemer G. Coronavirus infections: Epidemiological, clinical and immunological features and hypotheses. Cell Stress 2020; 4(4): 66–75.
-
Rattanachaikunsopon P, Phumkhachorn P. A glimpse of COVID-19 situation in Thailand. Int J Cur Res Rev 2020;12(23):1-2.
-
Gorse GJ, O’Connor TZ, Hall SL, Vitale JN, Nichol KL. Human coronavirus and acute respiratory illness in older adults with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. J Infect Dis 2009;199: 847-857.
-
Walsh EE, Shin JH, Falsey AR. Clinical impact of human coronaviruses 229E and OC43 infection in diverse adult populations. J Infect Dis 2013;208:1634-1642.
-
Kim JS, Choi JS. The Middle East respiratory syndrome-related knowledge, preventive behaviours and risk perception among nursing students during the outbreak. J Clin Nurs 2016;25(1718):2542-2549.
-
https://www.calculator.net/sample-size-calculator.html. [Cited 2020 August 29].
-
Khan MU, Shah S, Ahmad A, Fatokun O. Knowledge and attitude of healthcare workers about Middle East respiratory syndrome in multispecialty hospitals of Qassim, Saudi Arabia. BMC Public Health 2014;14:1281-1288.
-
Taghrir MH, Borazjani R, Shiraly R. COVID-19 and Iranian Medical Students; A Survey on their related-knowledge, preventive behaviours and risk perception. Arch Iran Med 2020; 23(4):249-254.
-
Gentile I, Abenavoli L. COVID-19: Perspectives on the potential novel global threat. Rev Recent Clin Trials 2020;15(2): 84-86.
-
Nour MO, Babilghith AO, Natto HA, Al-Amin FO, Alawneh SM. Knowledge, attitude and practices of healthcare providers towards MERS-CoV infection at Makkah hospitals, KSA. Int Res J Med Med Sci 2015;3(4):103-112.
-
IndiaFightsCorona COVID-19. https://www.mygov.in/covid-19. [Cited 2020 May 29].
-
Purohit D, Saini M, Pathak N, Verma R, Kaushik D, Katiyar P, et al. COVID-19 ‘the pandemic’: An update on the present status of the outbreak and possible treatment options. Biomed Pharmacol 2020;13(4).
-
Wong TW, Gao Y, Tam WWS. Anxiety among university students during the SARS epidemic in Hong Kong. Stress and Health: J Int Soc Invest Stress 2007;23(1):31-45.
-
Cheong D, Lee C. Impact of the severe acute respiratory syndrome on anxiety levels of front-line health care workers. Hong Kong Med J 2004; 10(5):325-330.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License