IJCRR - 13(3), February, 2021
Pages: 50-53
Date of Publication: 03-Feb-2021
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
Role of Red Cell Distribution Width and Neutrophil: Lymphocyte Ratio in Adults with Sepsis
Author: Pavan MR, Madhav H Hande, JayakumarJeganathan, Meenakshi Shetty, Chakrapani M
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Introduction: Sepsis is a significant contributor to morbidity and mortality in admitted patients. A large number of markers have been studied as biomarkers for sepsis. Most of them are either expensive or lack good sensitivity and specificity. Objective: In this study, we want to evaluate the role of simple blood tests such as Red cell distribution width (RDW) and neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) in the evaluation of the severity of sepsis cases. Methods: 173 sepsis patients were included in this ICU cross-sectional study. Red cell distribution width and neutrophil-lymphocyte ration were measured at admission. Both these parameters were compared with quick sequential organ failure assessment (qSOFA) score. They were also compared with the outcome of patients. Results: The mean RDW was 14.455 and it showed a significant correlation with qSOFA score and outcome of sepsis patients. An RDW of 15.050 was found to predict the worse outcome with a sensitivity of 82.4% and specificity of 74.7%. The mean NLR was 5.1645 and it also correlated with qSOFA score in sepsis patients. An NLR of 3.22 predicted worse outcome but only with the sensitivity of 66.2% and specificity of 65.7%. Conclusion: RDW and NLR both showed good correlation with sepsis outcome. However, RDW had a better sensitivity and specificity in predicting worse outcomes in sepsis.
Keywords: Neutrophil lymphocyte ratio, Outcome, Red cell distribution width, Sepsis, Severity, Intensive care unit
Full Text:
Introduction
Sepsis continues to be a major cause of morbidity and mortality in Intensive Care Units (ICU) despite the better understanding of its pathophysiology in recent years. Bloodstream infections are an important cause of serious morbidity and mortality and the incidence of sepsis is reported up to 30% in patients admitted in the intensive care units.1,2 Since sepsis is a heterogenous process with various manifestations, severity levels and cellular processes involved, a definitive biomarker that could aid in the diagnosis, staging, prognosis, and response to intervention has been difficult to determine. Scores such as APACHE II score on admission are associated with high mortality.3 Researchers have proposed more than a hundred different molecules as useful biomarkers of sepsis. C?reactive protein (CRP) and Procalcitonin (PCT) have been frequently used in the evaluation of the severity of sepsis and deciding the duration of therapy in ICU patients. Nevertheless, they are expensive and have insufficient predictive value for an individual.4 Since the definition of the new criteria was published, qSOFA score and SOFA score have been used to predict severity of sepsis and related in-hospital mortality for patients in the emergency department or the ICU.5 Red cell distribution width (RDW) is routinely done as a part of the routine blood count. Various studies have shown that it may be used as a prognostic marker in hypertension, coronary artery disease, stroke, and acute kidney injury. It has also been shown to correlate with all-cause mortality and nutritional status. 6 Total White blood cell (WBC) count is recognised as an important systemic inflammation marker. Leucocytosis has also been shown to independently predict all?cause mortality. Previous studies have also shown relative lymphocytopenia and neutrophilia in patients with sepsis. In critically ill patients the “neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio” (NLR) is a simple, rapid and inexpensive novel marker of inflammation and stress. It has also been found to have predictive value in patients with suspected bacteraemia in medical emergencies; and also found to be associated with short-term and long-term clinical outcomes in critically ill patients.7 With this background, the current study aims to study the relationship between RDW and neutrophil: lymphocyte ratio with the severity of illness in patients admitted to medical ICUs with sepsis has been undertaken.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
The study design was a cross-sectional study. The study type was an analytical study. It was done in an ICU in a tertiary care centre in South India. Permission from the local ethics committee was obtained. Informed consent was obtained from all participants.
Inclusion criteria: All participants who were more than 18 years and diagnosed to have sepsis in ICU and in whom blood sampling was done within 24hrs of admission were included in the study.
Exclusion criteria: Immunosuppressed patients such as HIV infection, cancer or patients receiving immunosuppressive therapy, patients with haematological disorders and pregnancy.
Sample size was estimated using the formula n= 2(Zα +Zβ)2 x σ2 / d2where Zα =1.96 at 95% confidence interval, Zβ = 1.28 at 90% power, σ = SD and d=mean difference. With 95% confidence level and 90% power the sample size came to 180. Sampling strategy followed was convenient sampling. Adult patients presenting to ICU diagnosed as sepsis as per 2016 Sepsis – 3 guidelines2, were considered for the present study. Basic demographic data, comorbidities, source of a new infection, presenting vital signs were recorded as per the proforma. Patients were stratified according to Q-SOFA scoring. q-SOFA score and SOFA score were calculated on the fifth day of admission to ICU, to assess the progress of the patient.
Blood samples were collected at the time of admission for the following tests: Complete blood counts with RBC indices. Blood urea, serum creatinine and serum electrolytes. Liver function test (LFT), coagulation studies (INR, aPTT), Serum glucose, Blood culture and other cultures (e.g., of sputum, stool, urine, wounds, catheters, prosthetic implants, epidural sites, pleural or peritoneal fluid). Arterial blood gas (ABG). Chest x-ray, ECG was performed as per protocol. Other investigations as appropriate were carried out such as lumbar puncture, echocardiogram (trans-thoracic or trans-oesophageal), ultrasound scan, CT chest or abdomen. RDW was measured at admission to ICU. The RDW is a measure of variability or red blood cells in size. It may be elevated due to ineffective production or increased destruction of red blood cells. This happens usually in inflammation and infections. Neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio (NLR) was determined by dividing the absolute neutrophil count by the absolute lymphocyte count. The patients were followed to check their condition whether SOFA score improved or worsened. The patient outcome on Day 5, including mortality, was recorded.
Statistical Methods
Data was entered and analyzed by using statistical software- Statistical Package for Social Sciences (SPSS) Version 17.0. Descriptive statistics like proportions, mean (standard deviation) and median (IQR) was used for expressing the results. For qualitative data Chi-square test and ANOVA was applied and P < 0.05 was considered as a statistically significant association.
Results
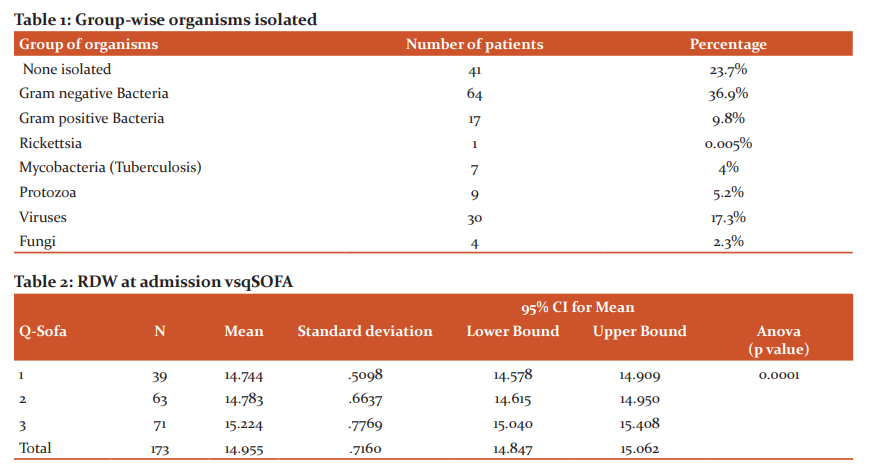
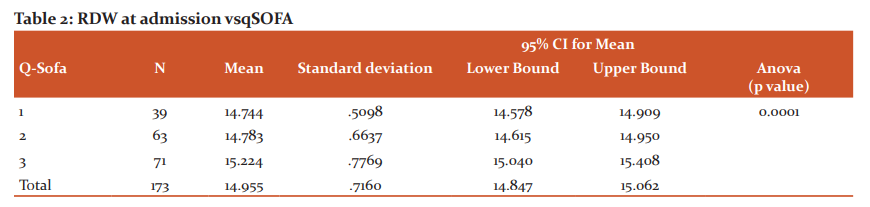
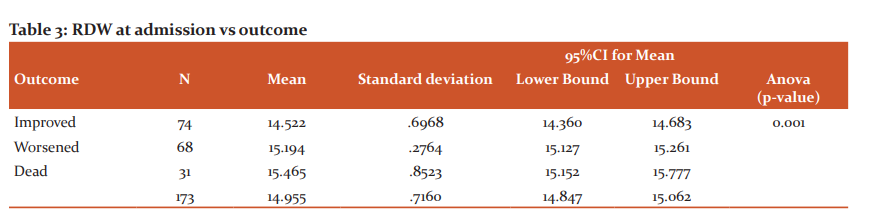
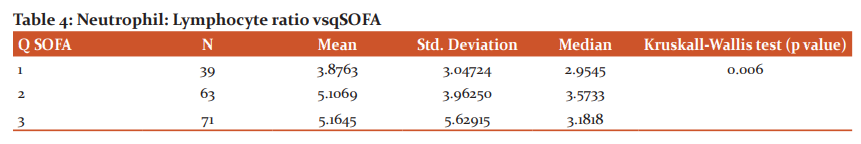
A total of 173 patients were included in the study. Males formed 62.4% of the subjects. Majority of the patients with sepsis were over 50 years of age. Pulmonary infections (38.2%) were the most common source of infection in the majority of sepsis cases, followed by tropical infections (27.2%). Table 1 shows the organisms responsible for sepsis. Gram-negative sepsis was the most common cause of sepsis in the study population. Dengue fever, detected by dengue IgM positivity, was the most common individual cause of sepsis in the study population. No organisms could be isolated in around 23.7% of the cases. Hypertension (41.6%) and Diabetes (41%) were the most common co-morbidities present in this study. Outcomes on day 5: 43% of the patients improved, 39% of the patients worsened and 18% of the patients died. RDW was found to be between 14.2 and 15.2 in the majority (59%) of patients with sepsis in the study group. Most of the patients belonged to qSOFA score of 3 (41%). 36% of the patients had a qSOFA score of 2 and 23% of the patients belonged to qSOFA score of 1. As the RDW increased the qSOFA score also increased as shown in Table 2. It was statistically significant. As seen in Table 3 patients with high RDW had poorer outcome and it was statistically significant. ROC was plotted for RDW vs outcome: The area under the curve was found to be 0.834, which implied RDW was a good test to predict the outcome. An RDW of 15.050 was found to predict the worse outcome with a sensitivity of 82.4% and specificity of 74.7%. It was found in the study that as the q SOFA score increases, median NLR increases as seen in Table 4. ROC was plotted for NLR vs Outcome. The area under the curve was found to be 0.663, which showed that NLR was only a fair test to predict the outcome. An NLR of 3.22 predicted worse outcome with the sensitivity of 66.2% and specificity of 65.7%.
Discussion
In this study, 173 patients who were admitted to the ICU, diagnosed as sepsis as per the 2016 Sepsis – 3 guidelines, were studied. Respiratory infections were the most common source of sepsis, and this was by previous studies.8 However, tropical/non localised diseases such as dengue fever, leptospirosis and malaria had a much higher incidence in our study population, this might be explained by the endemicity of these diseases to this region. Hypertension and diabetes mellitus were the most common comorbidities seen in this study. In another study of sepsis in India, 28% of those patients had diabetes and 16.5% of the patients had hypertension.9 In our study mortality rate was 18%. In another study by Pandya et al. they found a mortality rate of 28% in sepsis patients.10 In our study there was a good correlation between RDW and qSOFA score. RDW correlated well with the APACHE II score in sepsis patients.11 In our study RDW correlated well with the outcomes and as the RDW increased the outcome of the patients worsened. In another study, RDW not only predicted short term mortality but also had a good correlation with the 4-year mortality rate.12 In our study an RDW greater than 15.050 predicted a worse outcome. In the study by Jandial A, they found that an RDW greater than 17.3 showed significant correlation with mortality in sepsis patients.11In our study the median NLR showed a reasonable correlation with the qSOFA score. As the median NLR increased the clinical outcome of the patient worsened. De Jager et al. observed NLR as a better predictor of severity and outcome in bacteremia than conventional markers.13 In our study NLR of 3.22 predicted worse outcome in sepsis patients however it was not as strong a predictor as the RDW. Martins EC in their study showed that the cutoff point of 5.0 for the NLR was associated with a high risk for sepsis.14
Conclusion
We found that RDW correlated well with qSOFA score in sepsis patients and offered a clinically reliable cut off for prognostication of sepsis. We determined such a cut off to be 15.050 above which the outcome was bad. But we found Neutrophil lymphocyte ratio to be of limited clinical value as it lacked a discernible cut off and had a weak association with clinical outcome.
Ethical clearance: Taken from the institutional local ethics committee before the start of the study. (IEC KC MLR 09-17/167)
Source of funding: Self
Conflict of interest: Nil
Acknowledgement: Authors acknowledge the immense help received from the scholars whose articles are cited and included in references to this manuscript. The authors are also grateful to authors/editors/publishers of all those articles, journals and books from where the literature for this article has been reviewed and discussed.
References:
-
Singer M, Deutschman CS, Seymour CW. The Third International Consensus Definitions for Sepsis and Septic Shock (Sepsis-3). JAMA 2016;315(8):801–810.
-
Anamika V, Ramavtar S, Pooja G, Mrityunjay K. Bloodstream infections in Intensive care unit patients: A single centre retrospective study of the distribution and antibiotic resistance pattern in clinical isolates. Int J Cur Res Rev 2012;4(12):154-162.
-
Bhadade RR, DeSouza RA, Harde MJ, Prarthana P. Prospective evaluation and mortality outcome of nosocomial infections in medical intensive care unit at Tertiary care teaching centre in Mumbai. Int J Cur Res Rev 2013;5(19):26-40.
-
Lichtenstern C, Brenner T, Bardenheuer HJ, Weigand MA. Predictors of survival in sepsis: what is the best inflammatory marker to measure? Curr Opin Infect Dis 2012;25(3):328-336.
-
Freund Y, Lemachatti N, Krastinova E. Prognostic Accuracy of Sepsis-3 Criteria for In-Hospital Mortality Among Patients With Suspected Infection Presenting to the Emergency Department. JAMA 2017;317(3):301–308.
-
Patel KV, Ferrucci L, Ershler WB. Red blood cell distribution width and the risk of death in middle-aged and older adults. Arch Intern Med 2009;169(5):515–523.
-
Salciccioli JD, Marshall DC, Pimentel MA. The association between the neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio and mortality in critical illness: an observational cohort study. Crit Care 2015;19(1):13.
-
Vincent JL, Sakr Y, Sprung CL, Ranieri VM, Reinhart K, Gerlach H, Moreno R, Carlet J, Le Gall JR, Payen D. Sepsis in European intensive care units: results of the SOAP study. Crit Care Med 2006;34(2):344-353.
-
Anand AK, Kumar N, Gambhir IS. Clinicomicrobiological profile of the Indian elderly with sepsis. Ann Trop Med Public Health 2016;9:316-320.
-
Pandya H, Pabani N, Shah K, Yadav R, Patel P, Raninga J. Study of various prognostic factors for sepsis patients requiring intensive medical care with special emphasis on APACHE II score in prognostication. J Integr Health Sci 2015;3:14-22.
-
Jandial A, Kumar S, Bhalla A. Elevated Red Cell Distribution Width as a Prognostic Marker in Severe Sepsis: A Prospective Observational Study. Indian J Crit Care Med 2017;21(9):552–562.
-
Han YQ, Zhang L, Yan L. Red blood cell distribution width predicts long-term outcomes in sepsis patients admitted to the intensive care unit. Clinica Chimica Acta. 2018;487:112-116.
-
deJager CP, van Wijk PT, Mathoera RB. Lymphocytopenia and neutrophil-lymphocyte count ratio predict bacteremia better than conventional infection markers in an emergency care unit. Crit Care 2010;14(5):2-8.
-
Martins EC, Silveira LDF, Viegas K. Neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio in the early diagnosis of sepsis in an intensive care unit: a case-control study. Razãoneutrófilo-linfócito no diagnósticoprecoce de sepseemunidade de terapiaintensiva: um estudo de caso-controle. Rev Bras Ter Intensiva 2019;31(1):64–70.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License