IJCRR - 13(2), January, 2021
Pages: 154-158
Date of Publication: 16-Jan-2021
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
Efficacy and Safety of Various Oral Isotretinoin Treatment Regimens in Moderate to Severe Acne Vulgaris: A Prospective, Randomised Controlled, Single-Blinded, Parallel-Group Comparative Study
Author: Anuj Kothari, Deval Vora, Mohit Saxena, Simran Singh Aujla
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Background: Isotretinoin is the most potent anti-acne agent available today and only one that addresses all pathogenic mechanism; However, it is associated with multiple dose-dependent side effects. Objective: To evaluate the efficacy and tolerability of various therapeutic regimens (daily; alternate and low dose) of oral isotretinoin in moderate to severe acne vulgaris. Methods: This randomised, prospective, single-blind, parallel-group study was carried out in 90 randomised with a group of 30 patients each categorized as Group A receiving a conventional daily dose of oral isotretinoin 0.5mg/kg/day for 24 weeks, Group B receiving alternate day dose of oral isotretinoin 0.5mg/kg for 24 weeks and Group C receiving low dose 20 mg daily regimen of oral isotretinoin for 24 weeks for the total duration of 24 weeks with every 2 weeks follow up visits for their efficacy and safety. Results: Out of total 90, only 6 patients lost to follow up during study period, so remaining 84 patients included in the final analysis as 27 patients in Group A, 28 patients in Group B and 29 patients in Group C. The comparison of mean initial acne load at each visit in all three groups suggested no significant difference at initial acne scores in various treatment groups, which was found to be significantly decreased at each follow-up and the end of therapy and no significant difference at the end of the therapy. Frequency of all the side effects was higher in treatment group A. Severity of the all the side effects including mucocutaneous and systemic were maximum in group A and minimum in group C. Conclusion: Looking at the efficacy and safety profile of various oral isotretinoin regimens, one can plan for reducing dose regimen of oral isotretinoin for severe acne and low dose isotretinoin for mild to moderate acne.
Keywords: Acne Vulgaris, Isotretinoin, Low Dose Treatment Regimens
Full Text:
Introduction
Acne vulgaris is a chronic inflammatory disease of the pilosebaceous unit, characterized by comedones, papules, pustules, nodules, cysts, abscesses, later on sometimes as widespread scarring.1 Acne is a multifactorial disease, although the basic cause is unknown. According to the severity of acne, there are various treatment modalities. It includes both topical and systemic therapy. In topical therapy, commonly used drugs are benzoyl peroxide, erythromycin, clarithromycin, clindamycin, tretinoin (0.025-0.05%), adapalene, azelaic acid. In systemic therapy commonly used drugs are oral antibiotics; tetracycline, minocycline, doxycycline, azithromycin and oral isotretinoin.
Isotretinoin is a 13-cis retinoic acid which is a derivative of retinol (Vitamin A). It represents the single most important advance in acne therapeutics. It is the most potent anti-acne agent available today and only one that addresses all pathogenic mechanism.2 Isotretinoin should only be given to healthy individuals. It is contraindicated in females of childbearing potential unless stringent contraception is secured as it is a known teratogen. Common adverse side effects are mucocutaneous and they are dose-dependent e.g. cheilitis (occurs in almost 100% of cases), dry skin, dry nose with epistaxis sometimes, ocular and vaginal dryness, increased susceptibility to impetigo and furunculosis. Other side effects are skin fragility, bone and joint pain, osteoporosis, visual disturbances, depression and rarely pseudotumor cerebri. Occasionally, patients may have mild to moderate hypertriglyceridemia and raised transaminases, anaemia, thrombocytopenia, all these are reversible. Thus, baseline blood counts, liver function tests and fasting lipid profile are suggested, with recommendations for follow-up monitoring ranging from every 4 to 8 weeks to less frequently if baseline values are normal.3
As proved by various studies, lower doses of isotretinoin are also effective in terms of side effects and cost, therefore other regimens should be used instead of a daily conventional dose of 0.5-1.0mg/kg/day. Thus, the present study was undertaken to compare the efficacy and tolerability of various therapeutic regimens (daily; alternate and low dose) of oral isotretinoin in moderate to severe acne vulgaris.4,5
Materials and Methods
This randomised, prospective, single-blind, parallel-group study was carried out with the primary objective to compare the efficacy of various oral isotretinoin treatment regimens (daily; alternate; and low dose) in moderate to severe acne vulgaris and to compare their side effects in Skin and Venereal Disease department of Guru Gobind Sing Hospital, Jamnagar, Gujarat for the total duration of 24 weeks.
After obtaining the approval from the Institutional Ethics Committee, the patient of age more than 12 years with moderate to severe acne vulgaris and willingness to participate in the study and taking oral isotretinoin were included in the study. Patient with mild acne vulgaris, married female planning to conceive, already pregnant or lactating females, history of hypersensitivity to isotretinoin therapy as well as drug-induced acne and unwilling to give consent for participation were excluded for the study.
The calculated sample size with 80% power and 95% confidence interval with a 10% drop out rate for this study found to be 90 were randomized in subgroups by simple random sampling method. Each group of 30 patients categorized as Group A receiving a conventional daily dose of oral isotretinoin 0.5mg/kg/day for 24 weeks, Group B receiving alternate day dose of oral isotretinoin 0.5mg/kg for 24 weeks and Group C receiving low dose 20 mg daily regimen of oral isotretinoin for 24 weeks.Along with oral isotretinoin all patients were also advised to apply topical 1% clindamycin gel twice daily.
Each participant was given pre-designed Case Record Form (CRF) to obtain a detailed history of age, sex, age of onset of disease, duration of disease, type of skin and relation of disease with diet, premenstrual flare, pregnancy, seasonal variation, sweating, stress and seborrhea. Psychosocial effects (shame, embarrassment, anxiety, anger, lack of confidence and impaired social contact) observed by the patients were also taken. The assessment of the acne was done according to the Pillsbury’s classification: Grade I: comedones, occasional papules(mild), Grade II: papules, comedones, few pustules (moderate), Grade III: predominant pustules, nodules, abscess (severe) and Grade IV: mainly cysts, abscesses, widespread scarring (cystic).
Total lesion count was calculated at the 1st visit as the baseline total acne load in each patient and after that on each subsequent visit. The response and adverse effects were recorded according to number and type of lesions on follow up at 2 weekly intervals for 6 months. Complete blood cell counts, liver function tests and serum lipid profile (cholesterol and triglycerides) were done initially and repeated every 4 weeks. The criterion for discontinuation of therapy was a blood test rising above the following values in the first 2 months: triglycerides > 400 mg/dL (4.52 mmol/L), alkaline phosphatase > 264/UL (female), > 500/UL (male), ALT > 62/UL, AST > 80/UL, cholesterol > 300 mg/dL (> 7.7 mmol/L). Improvement in lesions was recorded by measuring total acne load at each visit. A failure was defined as no improvement, requiring a subsequent increase in isotretinoin dosage or even additional treatment at the end of 24 weeks of treatment.
Results
A total of 90 patients with a mean age of 18.74 years were included in the present study. Out of these 90 patients, 6 patients lost to follow up during the study period. For the final result analysis, there were 84 patients. Of these 84 patients, 27 patients in Group A, 28 patients in Group B and 29 patients in Group C completed the study (Table 1).
Out of 84 patients, 6 (7.14%) patients were of 10 - 15 years, 46 (54.76%) were of 15-20 years and remaining 32 (38.10%) patients were of age more than 20 years. A total number of 40 (47.62%) patients had a family history of acne and 44 (52.38%) had no family history of acne. A total number of 29 (34.52%) patients were from a rural background and 55 (65.48%) patients were from the urban area.
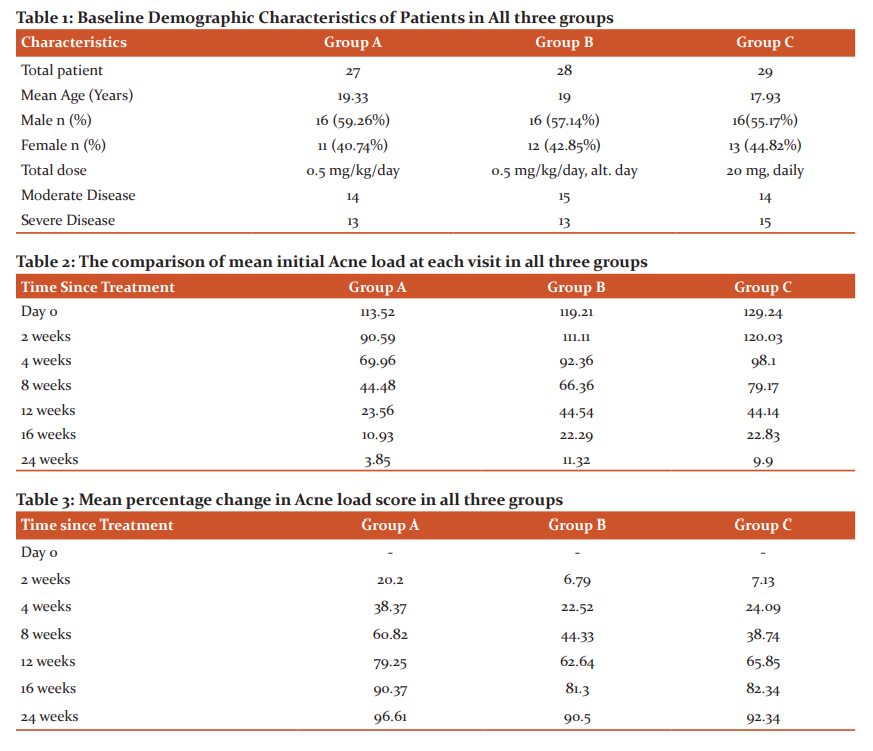
Out of 84 patients, 21 (25.00%) patients had <1-year duration, 25 (29.76%) patients had 1-2-year duration and 38 (45.24%) patients had >2-year duration.The face is the most common site involved in all patients (100%). Out of 84 patients, 31 (36.90%) patients had a lesion on the trunk along with face and 53 (63.10%) patients had no involvement of trunk. Normal skin type was present in 20 (23.81%) patients; oily skin was present in 55 (65.48%) patients and dry skin was present in 9 (10.71%) patients (Figure 1).
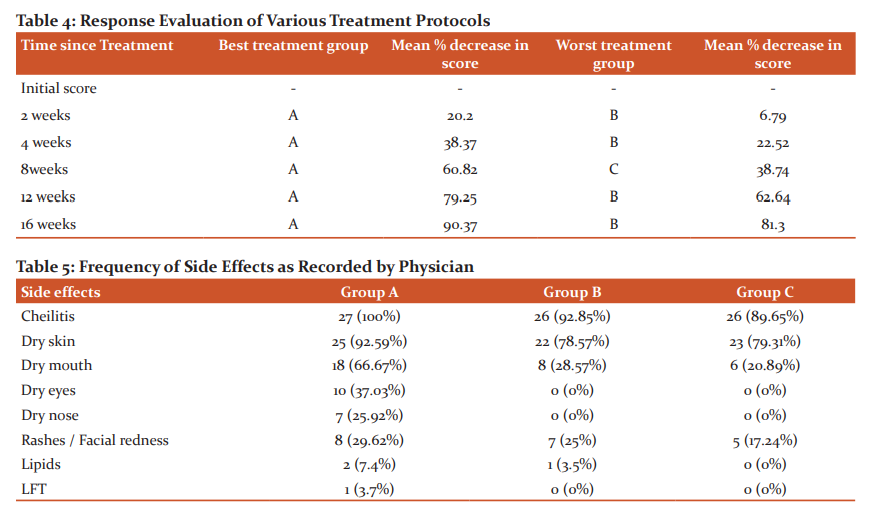
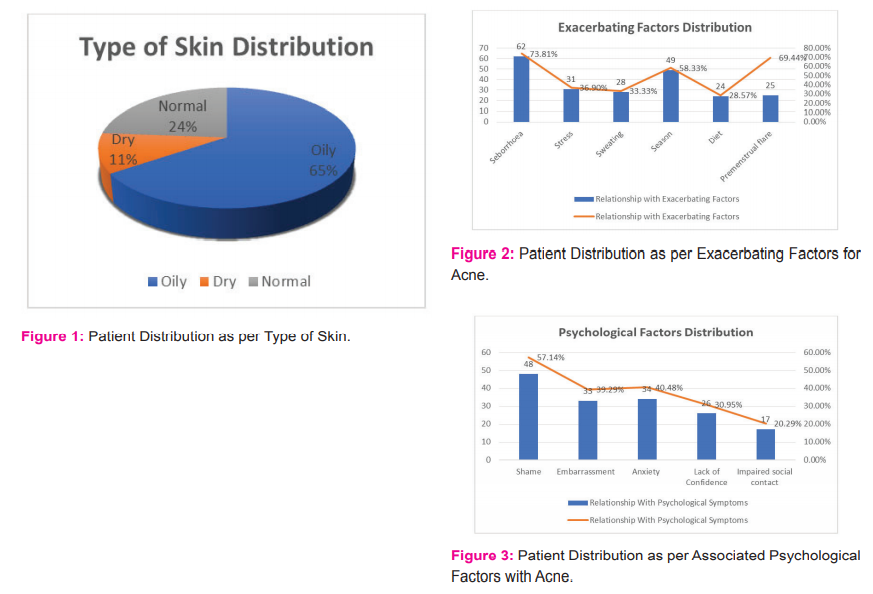
Out of 84 patients, 80 (95.24%) patients had one or more exacerbating factors (stress, seborrhea, sweating, diet, seasonal change and premenstrual flare). No exacerbating factors were present in 4 (4.76%) patients (Figure 2). Psychological factors were present in 69 (82.14%) patients. A total number of 48 (57.14%) patients had complained of shame, 33 (39.29%) patients had embarrassment, 34 (40.48%) patients had anxiety, 26 (30.95%) patients had lack of confidence and 17 (20.92%) impaired social contact (Figure 3).
The comparison of mean initial Acne load at each visit in all three groups suggested no significant difference at initial acne scores in various treatment groups (Table 2). Scores in each group were found to be significantly decreased at each follow-up and the end of therapy. At the end of the therapy in all the three groups, there was no significant difference between different treatment groups. Mean percentage change in score was comparable in all the three groups (Table 3). Treatment group A performed best in term of response till the end of treatment as compared to the rest of the treatment groups. The earliest response was noted in treatment group A (Table 4).
Most common side effects were cheilitis and dry skin. Dry mouth was more common in treatment group Aand least common in treatment group C. Dry eyes, dry nose and facial redness/rashes were noted mostly in Group A. Lipids were raised in treatment group A and B only while Liver function tests were deranged in only treatment group A. In group B and C this side effect was almost equal. Frequency of all the side effects was higher in treatment group A. Severity of the all the side effects including mucocutaneous and systemic were maximum in group A and minimum in group C. All the side effects were successfully managed and no patient required discontinuation of therapy (Table 5).
Discussion
Age of maximum involvement of acne in girls was seventeen and amongst boys was eighteen years.4 Epstein also reported that the greatest incidence of acne to be in the sixteen to twenty years of age group5, which is comparable to the present study. Bloch and Hamilton in 1964 reported that males had a more common and more severe form of acne as compared to the females due to more androgens secretion by males which is comparable to our study. Oily skin in acne patients may be correlated with the excess sebum production which was also observed by Pochi and Strauss6 which very much correlates with our study findings of having most people with oily skin type. Pochi & Strauss also noted that the output of sebum on the forehead was quantitatively more than the other body area. As the face is the presenting body part. People are more conscious; therefore, such cases make a major bulk amongst acne group. This is well depicted in our study by 100% involvement of the face.6
Pandey et al., 1980 also conducted that acne was found more common in urban boys than in their rural counterparts as seen in our study. It may be because urban patients are more conscious of themselves.7 A survey in Germany showed that acne has been present in one or both parents of 45% of schoolboys with acne, in only 8 % of parents without acne, which is more or less similar to our study findings.
In the present study majority of the patients gave a history of shame, embarrassment, anxiety, anger, lack of confidence and impaired social contact due to acne. Jowest et. al. (1988)also reported that acne is associated with stress, shame, lack of confidence and lack of employment. In our study majority of patients had one or more exacerbating factors (stress, seborrhea, sweating, solar radiation, diet, seasonal change and premenstrual flare). Likewise, stress is responsible for exacerbating the disease and sweating to exacerbate the acne due to hydration of the pilosebaceous follicle.8,9 Premenstrual flare-up was observed in around 60-70% of females due to hydration of the pilosebaceous follicle10 which is comparable with our study. The role of diet in the etiopathogenesis of acne vulgaris has remained controversial. Rasmussen and Smith10,11 in 1983 reported that there was a relationship between acne and diet. Our finding is comparable with Rasmussen and Smith et al. and diet as an exacerbating factor were present in 24 (28.57%) patients which mainly included oily food, milk, spicy food and chocolates.
Comparing the effects and side effects of various regimens we found that the low-dose isotretinoin is almost equal in efficacy to high dose but with the advantage of lesser side-effects and more cost-effective than the full-dose protocol. All our results were comparable to the previous studies of conventional and low doses of oral isotretinoin.
Conclusion
Looking at the efficacy and safety profile of various oral isotretinoin regimens one can plan for reducing dose regimen of oral isotretinoin i.e. initially give higher doses for early remission followed by low dose maintenance therapy for a prolonged period with lesser side effects especially in cases of severe acne. For mild to moderate acne, we can directly use low dose isotretinoin which is an effective and safe treatment option.
Acknowledgements: Our humble thanks and gratitude towards all the patients who gave consent to participate in the study as well as the administration and staff of GGG hospital Jamnagar. A special mention to Dr Atul Rajpara, for guidance related to the publication of the manuscript.
Source of Funding: None
Conflict of Interest: Nil
References:
-
Dreno B, Poli F. Epidemiology of acne. Dermatology 2003;43:1042–1048.
-
Harper JC, Thiboutot DM. Pathogenesis of acne: Recent research advances. Adv Dermatol 2003;19:1-10.
-
Cunliffe W, Gollnick H. Acne. In: Arndt KA, LeBoit PE, Robinson JK, Wintroub BU, eds. Cutaneous Medicine and Surgery. Philadelphia, Pa: WB Saunders Co; 1996:461-480.
-
Ghodsi SZ, Orawa H, Zouboulis CC. Prevalence, severity, and severity risk factors of acne in high school pupils: a community-based study. J Invest Dermatol 2009; 129(9):2136-2141.
-
Epstein E. Incidence of facial acne in adults. Derm Digest 1968;7:49-58.
-
Pochi PE, Strauss JS. Sebum Production causal sebum level. J Invest Dermatol 1964; 43:383-88.
-
SS Pandey, P Kaur, G Singh. Has Acne Urban Bias? Indian J Dermatol Venerol Lep 1980;46:80-82.
-
Kenyon FE. The psychosomatic aspect of acne. Br J Dermatol 1966;76:344-351.
-
Williams M, Cunliffe WJ. The explanation for premenstrual acne. Lancet 1973;11:1055-1057.
-
Cunhiffe WJ, Cotterill JA. The Acnes. London WB Saunders, 1975.
-
James E, Rasmussen MD, Smith SB. Patient Concepts and Misconceptions About Acne. Arch Dermatol 1983;119(7):570-572.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License