IJCRR - 13(2), January, 2021
Pages: 113-117
Date of Publication: 16-Jan-2021
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
Characteristic of Hemopoetic Microelemental Status in Conditionally Healthy Elderly Men and Women Depending on the Age Range
Author: Boltaev Kamol Zhumaevich
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Introduction: Hypomicroelementosis is currently a significant problem for modern haematology. Objective: The purpose of this study is to carry out a comparative analysis of hematopoietic trace elements - iron, copper and zinc - in apparently healthy elderly men and women, depending on the age range. Methods: For these purposes, all surveyed men and women living both in urban and rural conditions were divided into two age ranges - surveyed - up to and over 70 years. Results: The results of the analysis showed that there is no statistically significant difference between the indicators of blood haemoglobin and hematopoietic microelements - iron, copper and zinc in the whole group of examined elderly men and the group of examined elderly men and examined elderly women in old age. Conclusion: The study did not reveal differences in the indices of hematopoietic microelements - iron, copper, and zinc in the examined conditionally healthy urban and rural elderly men, depending on the conditions of permanent residence.
Keywords: Hematopoiesis, Trace elements, Blood serum, Haemoglobin, Age
Full Text:
Introduction
Disturbances in the balance of trace elements in the human body lead to the development of diseases called microelementosis.1,2 It should be noted that the violation of the normal balance of trace elements in the body can be due to several reasons, namely deficiency, excess (overload), or imbalance.3,4 Studies indicate a wide spread of various forms of vitamin and microelement deficiency, in particular, among children, adolescents, women of fertile age, pregnant and lactating mothers, athletes, elderly people, the so-called polyhypovitamins and hypomicroelementosis.5 Among these nutritional deficiencies, hypomicroelementosis is currently a significant problem for modern haematology due to the significant frequency of these deficiencies and the variety and severity of their manifestations.3,6,7
Materials and Methods
We examined elderly persons (the age of the surveyed was from 61 to 75 years) and 65 elderly persons (the age of the surveyed was 75 to 90 years). All subjects were selected for study by the method of random selection. In the study, haematological, morphological, and biochemical methods of analysis were used to verify the diagnosis of anaemia. The results of the study were processed by the methods of variation statistics with the determination of the reliability of the compared values ??of the analyzed indicators.
Results and Discussion
We carried out in a comparative aspect the study of indicators of hematopoietic microelements - nutrients and iron metabolism in the examined conditionally healthy elderly men who permanently live in urban and rural conditions of the Bukhara region to find out whether the conditions of permanent residence affect certain indicators reflecting the state of various functional body systems.
As can be seen from the presented Table 1 there is no statistically significant difference between the haemoglobin values ??of blood and hematopoietic microelements - iron, copper, and zinc in the entire group of examined elderly men and the group of examined elderly men under the age of 70 - 133.5 ± 0.49 g/Land 132.6 ± 0.50 g/L, 14.9 ± 0.76 μmol/L and 17.5 ± 0.92 μmol/L, 12.1 ± 0.5 μmol/Land 14.0 ± 1.16 μmol/L and 16.8 ± 0.82 μmol/L and 18.9 ± 0.95 μmol/L, respectively.
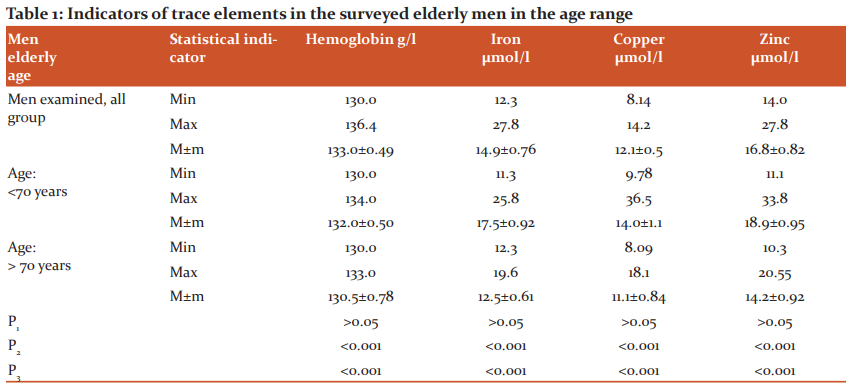
Note: p1-reliability between the indicators of trace elements in the surveyed under the age of 70 and the entire group of surveyed elderly men; p2-reliability between the indicators of microelements in those surveyed over the age of 70 and the entire group of surveyed elderly men; p3-reliability between the indicators of trace elements in those surveyed over the age of 70 and up to 70 years.
At the same time, a statistically significant difference is revealed between the studied indicators between the entire group of examined elderly men and men over the age of 70 - 133.5 ± 0.49 g/Land 130.5 ± 0.78 g / l; 14.9 ± 0.76 μmol/L and 12.5 ± 0.61 μmol/L; 12.1 ± 0.50 μmol/L and 11.1 ± 0.84 μmol/L; and 16.8 ± 0.82 μmol/L and 14.2 ± 0.92 μmol/L, respectively.
Similarly, we found a statistically significant difference in the studied indicators in the examined elderly men between older men under the age of 70 and over 70 years - 132.6 ± 0.50 g/l and 130.5 ± 0.78 g/l; 17.5 ± 0.92 μmol/L and 12.5 ± 0.61 μmol/L; 14.0 ± 1.16 μmol/L and 11.1 ± 0.84 μmol/L; and 18.9 ± 0.95 μmol/L and 14.2 ± 0.92 μmol/L, respectively. Table 2 also presents comparative data on indicators of hematopoietic trace elements studied by us in elderly women, depending on the age range.
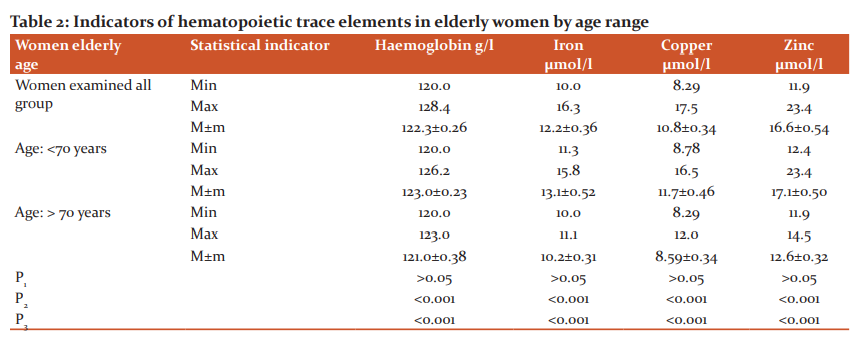
Note: p1 is the reliability between the parameters of haemoglobin and trace elements in the surveyed elderly women (the whole group) and surveyed elderly women under 70 years old; p2 - reliability between the parameters of haemoglobin and trace elements in all surveyed women and elderly women over the age of 70; ?3 - reliability between the surveyed elderly women under the age of 70 and over.
As can be seen from the data presented, we did not find significant differences between the studied indicators of blood haemoglobin and trace elements in the entire group of examined elderly women and elderly women under the age of 70 - 122.3 ± 0.26 g/l and 123.0 ± 0, 23 g/L and 12.2 ± 0.36 μmol/L and 13.1 ± 0.52 μmol/L; 10.8 ± 0.34 μmol/L and 11.7 ± 0.46 μmol/L and 16.6 ± 0.54 μmol/L and 17.1 ± 0.50 μmol/L.
At the same time, there is a statistically significant difference between the studied parameters of hemoglobin and trace elements in all surveyed elderly women and elderly women over the age of 70 - 122.3 ± 0.26 g/l and 121.0 ± 0.38 g/l; 12.2 ± 0.36 μmol/L and 10.2 ± 0.31 μmol/L; 10.8 ± 0.34 μmol/L and 8.59 ± 0.34 μmol/L; and 16.6 ± 0.54 μmol/L and 12.6 ± 0.32 μmol/L, respectively.
A significant difference between the studied indicators was also revealed between the indicators typical for the group of surveyed elderly women aged up to 70 years and the group of elderly women aged over 70 years - 123.0 ± 0.23 g/l and 121.0 ± 0.38 g/l; 13.1 ± 0.52 μmol/L and 10.2 ± 0.31 μmol/L; 11.7 ± 0.46 μmol/L and 8.59 ± 0.34 μmol/L; and 17.1 ± 0.50 μmol/L and 12.6 ± 0.32 μmol/L, respectively.
Thus, the study of the dependence of the indicators of total haemoglobin in blood and indicators of hematopoietic trace elements in the examined elderly men and women with different age ranges shows that there is a direct dependence of these indicators on age - in older people, there is a decrease in all studied indicators, which indicates a decreasing adaptive potential of an ageing organism.
We also carried out in a comparative aspect the study of indicators of hematopoietic microelements - nutrients and iron metabolism in the examined conditionally healthy senile men, permanently residing in urban and rural conditions of the Bukhara region.
The distribution of the surveyed conventionally healthy elderly men shows that they are distributed approximately the same in a rather narrow age range of 81-84 years, and thus, the indices of hematopoietic microelement status and iron metabolism derived by us in the surveyed can also be extrapolated with a high degree of reliability to the entire sample of those examined old men. This circumstance is of interest in connection with the existing in the literature ideas about the relationship between the age of a person and the biological variability of certain studied indicators, defined for these age groups as reference or reference.
The results of a comparative study of indicators of iron metabolism in conditionally healthy urban and rural senile men are presented in Table 3.
As can be seen from the table, the average total haemoglobin of blood in the examined urban men of old age is 133.2 ± 0.1 g / l with a reference interval of this indicator from 130.0 g / l (min) to 136.7 g/l ( max). In the surveyed rural men of old age, the average value of this indicator is 130.5 ± 0.2 g/l with a reference interval of this indicator from 130.0 g/l (min) to 132.1 g/l (max). As can be seen in the indicators of total haemoglobin in conditionally healthy men permanently living in urban and rural conditions, there is a statistically significant difference - 133.2 ± 0.1 g/l and 130.5 ± 0.2 g/l, respectively (p <0.001).
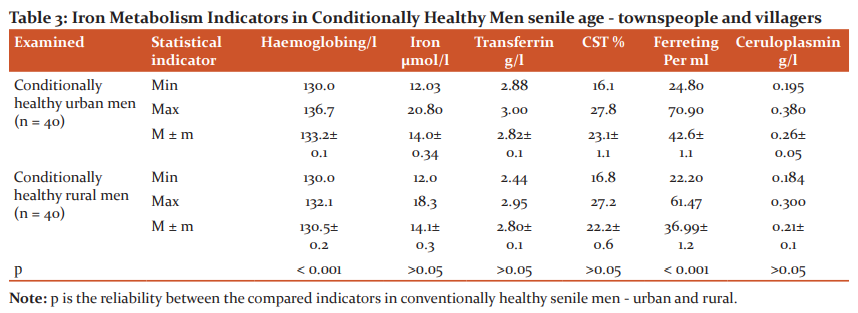 The average index of serum iron content in the examined conditionally healthy urban men of old age averages 14.0 ± 0.34 μmol/L with a reference interval of this indicator from 12.03 μmol/L (min) to 20.08 μmol/L (max ), in the surveyed rural, conventionally healthy elderly men, this indicator averages, according to our data, -14.1 ± 0.3 μmol/L with a reference interval of this indicator from 12.0 μmol/L (min) to 18.3 μmol/L (max). Thus, it can be seen that this indicator in urban and rural senile men does not significantly differ - 14.0 ± 0.34 μmol/L and 14.1 ± 0.3 μmol / L, respectively (p> 0.05).
The average index of serum iron content in the examined conditionally healthy urban men of old age averages 14.0 ± 0.34 μmol/L with a reference interval of this indicator from 12.03 μmol/L (min) to 20.08 μmol/L (max ), in the surveyed rural, conventionally healthy elderly men, this indicator averages, according to our data, -14.1 ± 0.3 μmol/L with a reference interval of this indicator from 12.0 μmol/L (min) to 18.3 μmol/L (max). Thus, it can be seen that this indicator in urban and rural senile men does not significantly differ - 14.0 ± 0.34 μmol/L and 14.1 ± 0.3 μmol / L, respectively (p> 0.05).
The indicator of total transferrin in blood serum in the examined urban, conventionally healthy elderly men, on average, according to our data, is 2.82 ± 0.1 g/l with a reference interval of this indicator from 2.88 g/l (min) to 3.00 g/l (max) and in rural conditionally healthy elderly men, according to our data, this indicator averages - 2.80 ± 0.1 g/l with a reference interval of this indicator from 2.44 g/l (min) to 2.95 g/l (max). It can be seen that this indicator, on average, also does not differ statistically significantly - 2.82 ± 0.1 g/l and 2.80 ± 0.1 g/l, respectively (p> 0.05) in the surveyed conventionally healthy urban and rural men old age.
At the same time, it should be noted that in both urban and rural conventionally healthy senile men, the average level of serum transferrin is reduced compared to the similar content of transferrin in young people, in whom this indicator is normally distributed within the reference interval - 3.00- 3.50 g/l.
This can be associated with the phenomenon of a general decrease in the protein-synthetic function of the liver with age. At the same time, our comparative analysis of the serum isotransferrin spectrum, i.e. quantitative analysis of various molecular isoformtransferrin, showed that the isotransferrin spectrum of blood serum in conventionally healthy elderly men has its characteristics. Thus, as a percentage of the total pool of serum transferrin, the share of transferrin completely saturated with iron - cholotrans-Ferrin is 60% or more, while in conventionally healthy young people, the share of cholotransferrin in the total pool of serum transferrin averages 36-45%.
This indicates that although the total amount of serum transferrin in conventionally healthy elderly men is less than in young people, due to the higher content of functionally active molecules of cholotransferrin, the circulating pool of transferrin in the blood serum of elderly people can provide the bone marrow with the necessary amount of iron for the needs of haemoglobin formation.
According to our data, the CST in the surveyed urban conditionally healthy elderly men averaged 23.1 ± 1.1%, with the reference interval of this indicator from 16.1% (min) to 27.8% (max), in the surveyed rural men of senile age, the average CST is - 22.2 ± 0.6% with the reference interval of this indicator from 16.8% (min) to 27.2% (max). A comparative study of indicators reflecting the saturation of the total pool of transferrin with iron (the coefficient of saturation of transferrin with iron) in conventionally healthy urban and rural elderly men shows that there are also no significant differences - 23.1 ± 1.1% and 22.2 ± 0.6 % respectively.
Such a degree of saturation of the total pool of transferrin with iron, apparently, fully provides physiological erythropoiesis in elderly people. The study of such an important indicator of iron metabolism as the indicator of serum ferritin shows that, on average, the level of ferritin in the blood serum in the examined healthy urban senile men age is 42.6 ± 1.1 ng/ml with a reference interval of this indicator from 24.8 ng/ml (min) to 70.90 ng/ml (max).
In the surveyed rural, conventionally healthy elderly men, the level of serum ferritin averaged 36.99 ± 1.2 ng/ml, with a reference interval of this indicator from 22.20 ng/ml (min) to 60.4 ng/ml (max). At the same time, a comparative analysis of such an important indicator of iron metabolism as the content of ferritin in the blood serum, which reflects the state of the iron depot in the body, unambiguously indicates that iron stores in conventionally healthy senile men who constantly live in urban conditions are significantly higher than in conventionally healthy senile men permanently residing in rural conditions - 42.6 ± 1.1 ng/ml and 36.99 ± 1.2 ng/ml, respectively (p <0.001).
This phenomenon can be explained by the fact that the serum ferritin index, reflecting the reserve stock of iron, is one of the most conservative indicators, which changes little even in the age aspect, and the conditions of permanent residence, i.e. the nature and structure of nutrition, the frequency of visits on health issues (preventive examinations, etc.) among people living in the city is better than among people living in the countryside, as indicated by studies on the status of iron, for example, in women of fertile age, which also revealed differences in the iron depot in residents of the city and village, in particular. In quantitative terms, iron stores in conventionally healthy old-age urban men are about 80 mg of elemental iron greater than in conventionally healthy rural men of old age.
On average, the content of such an informative indicator, reflecting the state of metabolism of the essential trace element - copper in the body - the level of the copper transport protein of the blood serum ceruloplasmin, on average in the examined urban men of old age is 0.26 ± 0.05 g/l with a reference interval of this indicator from 0.195 g/l (min) to 0.380 g/l (max). In the examined conditionally healthy rural men of old age, the content of this protein in the blood serum averaged 0.201 ± 0.1 g/l with a reference interval of this indicator from 0.184 g/l (min) to 0.300 g/l (max).
Comparison of such an indicator as serum ceruloplasmin, which regulates copper metabolism in the body, shows that there is no significant difference in the values ??of this indicator either - 0.26 ± 0.05 g/L and 0.201 ± 0.01 g/L, respectively (p> 0,05).
In Table 4, we present in a comparative aspect the indices of hematopoietic microelements - iron, copper, and zinc in conventionally healthy senile men permanently living in urban and rural conditions of the Bukhara region in a comparative aspect.
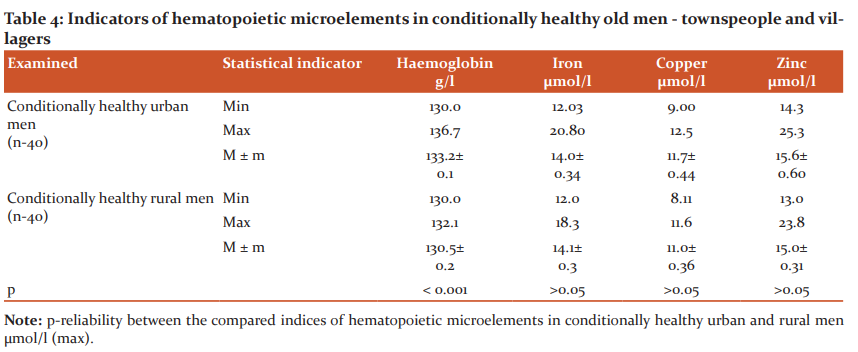 As can be seen from the presented table, the hematopoietic microelement status in the examined conditionally healthy urban and rural elderly men is characterized as follows - the average level of such an important essential microelement as copper in urban elderly men is 11.7 ± 0.44 μmol/Lwith the reference interval of this indicator from 9.00 μmol/L (min) to 12.5 μmol/L(max), in rural areas it is 11.0 ± 0.36 μmol/L with a reference interval of this indicator from 8.11 μmol/L (min ) up to 11.6
As can be seen from the presented table, the hematopoietic microelement status in the examined conditionally healthy urban and rural elderly men is characterized as follows - the average level of such an important essential microelement as copper in urban elderly men is 11.7 ± 0.44 μmol/Lwith the reference interval of this indicator from 9.00 μmol/L (min) to 12.5 μmol/L(max), in rural areas it is 11.0 ± 0.36 μmol/L with a reference interval of this indicator from 8.11 μmol/L (min ) up to 11.6
And the average level of another important hematopoietic essential microelement zinc in the blood serum of the examined urban elderly men is 15.6 ± 0.60 μmol/L with a reference interval of this indicator from 14.3 μmol/L (min) to 25.3 μmol/L (max) and in rural elderly men, the average level of zinc in the blood serum was 15.0 ± 0.31 μmol/Lwith a reference interval of this indicator from 13.0 μmol/L (min) to 23.8 μmol/L (max).
Conclusion
Thus, as can be seen from the presented table, we did not reveal differences in the indices of hematopoietic microelements - iron, copper, and zinc in the examined conditionally healthy urban and rural elderly men, depending on the conditions of permanent residence. At the same time, certain correlations were noted in the content of these hematopoietic nutrients- microelements, and in both of those examined, the average content of iron in the blood serum prevails over the content of copper in the blood serum, and the level of zinc in the blood serum exceeds the content of iron and copper in the serum blood.
Conflict of interest. We have no conflicts of interest.
Acknowledgment. We thank the staff of the Bukhara Regional Multidisciplinary Medical Center.
Funding information. None.
References:
-
Bakhramov SM, Boltaev KZ, Zharylkasynova Z, Kalmenov GT, Kazakbaeva KM. Analysis of the incidence of various forms of anaemia among adolescents and adults. Uzbekiston tibiyot zhurnal 2001;4:53–54.
-
Skalny AV, Kaminskaya GA, Krekesheva TI, Abikenova SK, Skalnaya MG, Berezkina ES, et al. The level of toxic and essential trace elements in the hair of petrochemical workers involved in different technological processes. Envir Sci Poll Res 2017;24(6):5576-5584.
-
Boltaev KZh, Akhmedova NSh. Characteristics of the phenomenon of the development of polydeficiency states during aging. Probl Biol Med 2020;1:24-26.
-
Buglanov AA, Mamatkhonov OA. Exchange of hematopoietic nutrients in healthy women of fertile age in Uzbekistan. Hematol Blood Transf 2005;3:25-27.
-
Fofana IY, Prilepskaya VN. The content of folic acid, zinc and copper in blood serum in pregnant women with urogenital mycoplasma infection. Med Advice 2015;11:39-45.
-
Skalnaya, M.G. Establishing the boundaries of the physiological (normal) content of some chemical elements in the hair of residents of Moscow using centile scales. Bulletin of the St. Petersburg State Med Acad 2004;4:82-88.
-
Skalnaya, M. Involvement of macro-and trace elements in dysregulation mechanisms of obesity and type II diabetes pathogenesis in pre-and postmenopausal women. Cell Biol Toxicol 2008;24(1):39-46.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License