IJCRR - 13(2), January, 2021
Pages: 02-08
Date of Publication: 16-Jan-2021
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
Led Light Photobiomodulation Effect on Wound Healing Combined with Phenytoin in Mice Model
Author: Tarek Elwakil, Mahmoud S. Elbasiouny, Hatem Elnajar, Kawkababdelaziz
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Background: Impaired wound healing is a disastrous medical problem associated with chronic diseases and ageing. To accelerate skin regeneration many techniques have been researched laser and LED has been used for these purposes. Topical phenytoin is simple to use, safe, inexpensive and readily available drug and plays a significant role in the rate of healing of wounds. Objective: We aimed to evaluate irradiation of a LED light 670-nm for wound healing. Using ulcer mice model with and without the combination of phenytoin drug. Methods: Four groups 24 mice per group received treatment as follows. Group I: Ulcers followed up without any treatment modality.Group II: Ulcers subjected to topical Phenytoin spray twice daily, Group III: Ulcers irradiated with red LED 670 nm at a fluence of 5 J/cm2 . Group IV: Ulcers treated by combined topical Phenytoin spray and red LED670 nm at a fluence of 5 J/cm2 . All treatments started from the 1st day postoperatively and for up to three consecutive weeks or till complete healing of the ulcer. Results: The results showed the fastest healing in the combined group with more deposition of collagen fibres, larger amounts of granulation tissue, less oedema. The second best treatment was the red LED 670-nm only treated group as mice showed less evident features with fewer collagen fibres deposition. Conclusion: Red LED 670nm combined with phenytoin is an effective enhancer of wound healing that stimulates the secretion of growth factors in the wound bed and induce many changes during the skin healing process, especially in favouring neo collagen fibres to be better organized and led more deposition of collagen fibres.
Keywords: Wound healing, Biomodulation, Phenytoin, Laser therapy
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION
Many light based systems had effects on wound healing; these outcomes were noted irrespective of whether a laser, light emitting diode (LED) or broadband polarized light source used as a Low-level Laser therapy (LLLT) 1.
This form of therapy is currently being used to treat various conditions based on the principles of photobiomodulation2. That influences different biological processes, such as acceleration of wound healing. It is important to know that there is amost favorable light energy needed for wound healing, and higher or lower energy than the favorable value may have no beneficial effect3. Wound healing effects are generally observed at fluences between 1 and 10 J/cm2, while photoinhibitory effects are typically observed at higher fluenciestreatment 4.
Low level Laser therapy through Photobiomodulation may induce a decisive impact on the course of biological events that take place during wound healing, as it enhances collagen synthesis in the wound area with gradual fibroblastic proliferation and the amount of collagen being synthesized can be particularly affected during tissue regeneration 5 it has been demonstrated that collagen fibers appeared thicker and better organized by a 660 nm wavelength laser application6-9
Several studies have demonstrated that LLLT has a significant influence on a variety of cellular functions. Increased mitochondrial respiration and adenosine triphosphate (ATP) synthesis, cell proliferation, enhancement, and promotion of tissue regeneration following injury. Stimulation of cell proliferation results from an increase in mitochondrial respiration and ATP synthesis. It is assumed that this absorption of light energy may cause photodissociation of the inhibitory nitric oxide, leading to the enhancement of enzyme activity, increased electron transport, oxygen consumption, mitochondrial respiration, and ATP production6. In turn, LLLT, by altering the mitochondrial or cellular redox state, can induce the activation of numerous intracellular signaling pathways and alter the affinity of transcription factors concerned with cellular migration, proliferation, survival, tissue repair, and regeneration. 7
The basic light interaction behind the effects of LLLT is thought to be through the absorption of photon by chromophores, in particular cytochrome c oxidase (CCO), which is part in the respiratory chain positioned within the mitochondria several exogenous factors may interfere with the structural patternand the amount of collagen fibers being deposited during the healingprocess.8,9
The possibility of using phenytoin for wound healing was observed in a double -blind, placebo controlled clinical study involving the use of phenytoin inleg ulcers when the author demonstrated that phenytoin is effective in promoting healing. As it is readily available, safe, inexpensive, and easy to use,It was suggested as a drug for healing ulcers However, no evidence supporting these assumptions of positive healing effect of phenytoin 10. The RCTs reported Variable treatment outcomes may be attributed to different doses and forms, different healing assessment tools, topical application of phenytoin powder may improve the rate of healing and is not associated with any serious side effects 11.
The possible mechanism of action by which phenytoin promotes wound healing has been contribute to An increase in the proliferation of fibroblasts hence increase in the deposition of collagen, increase in Neovascularisation enhanced granulation tissue formation. A decrease in the action collagenas and decrease in bacterial contamination that may be a primary antibacterial effect of phenytoin or if it is due to a secondary effect of phenytoin, such as neovascularisation and/or collagenisation and there has been at least one study which refutes its beneficial healing effect 12.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Animals Model
After the Research Ethics Committee of Cairo university with no. 281472, granted a total of 96 mice between 6 and 9 weeks of age and weighing 18–20 g, were used in this study. The animals were housed one per cage (to prevent cage-mate attacks on wounds) and had access to food and water, free access/ad-libitum. The mice were maintained on a 12-hour light/dark cycle under a room temperature of 21 °C.
To produce the surgical wound mice were anesthetized by an intraperitoneal injection of a ketamine–xylazine cocktail (90 mg/kg ketamine and 10 mg/kg xylazine) before wounding the dorsum of the anesthetized mice were shaved using an electric fur clipper, and the underlying skin was cleaned with sterile 70% isopropanol. The anticipated area of the wound to be created was outlined on the back of the animals with methylene blue using a circular stainless steel stencil, to ensure comparable wound size in all the mice. A full thickness excision wound diameter 12mm, along the markings using toothed forceps, a surgical blade and pointed scissors, the wound was left uncovered during the whole period of experiments. Their wounds were cleaned with 0.9% saline once a day in the morning. Animals was monitored daily looking for adverse effects of wounding on their general health.
Light source
The Phototherapy unit used in the study was the LED-based phototherapy system (Photo Therapeutics, Limited, Fazely, Tamworth, UK) which consists of a base unit fitted with interchangeable LED at 670nm nm (visible red). The illumination performed daily for three weeks, beginning 6h after the induced wound surgery, until 24h before sacrifice. The LED was be used in continuous and directly in non contact mode with the ulcer surface. The output power of LED was 40mW with fluence 5J /cm2 and Fluence rate (12mW/cm2) Spot size was defined by the area of the square window in the aluminum foil (1.5×1.5 cm) used to cover the mouse body. Each wound measured approximately 1.2×1.2 cm Time of irradiation/day (min) 6.6
Study design
Mice were randomly divided into four groups according to the therapy applied 24 mice per group. The study groups were divided into four groups receives treatment in form of phenytoin or LED or combination of both as follows. Group I (Control Group): Ulcers was followed up without any treatment modality. Group II (Phenytoin Group): Ulcers was be subjected to topical Phenytoin spray twice daily starting from the 1st day postoperatively and for up to three consecutive weeks or till complete healing of ulcer as denoted by its complete closure. Group III LED (670 nm) Group): Ulcers was be subjected to LED (red spectrum) daily illumination starting after 6 hours postoperatively and for up to three consecutive weeks or till complete healing of ulcer as denoted by its complete closure. The LED treatments were given at a fluence of 5 J/cm2. Group IV (Combined Phenytoin and LED (Red Spectrum) Group): Ulcers was be subjected to combined topical Phenytoin spray and LED (red spectrum) at the same conditions and parameters as mentioned in groups II and III.
Methods of Assessments
-
Wound area measurement
Maximum diameters of ulcers was measured daily by Vernier’s caliber and ulcer area was be calculated. The relative change in the surface area of ulcers with respect to the initial surface area was determined. Moreover, reepithelization and healthy granulation tissue was be grossly evaluated and timings of complete closure of wounds was be assessed for each. Ulcers were photodocumented at different timings of assessments by using a digital camera at the same distance and lighting conditions.
Wound images were acquired every other day using a digital camera. Wound surface area was monitored by capturing the video images of each ulcer area together with a ruler (mm) using the digital camera and downloaded to a computer. The first image of each wound from the different groups was obtained on the day of injury (day 0). The subsequent images were captured on third, fifth, seventh, twelfth and fourteenth day post-injury. The wound area analysis was performed by Fiji (ImageJ) software and values were expressed in mm2. Repeated measurements were accurate to within 2%.
B. Histological Evaluations:
Animals were randomly sacrificed at each evaluation time by using an intraperitoneal overdose of ketamine at (3-5-7-10-12-14) day’s postoperativly postoperatively, as well as, after complete healing of ulcers as denoted by the complete ulcer closure. Standardized rectangular specimens were harvested across the wound using a double-blade cutting instrument then preserved in 10 % formalin and then embedded in paraffin. Serial tissue sections of 4-μm thickness were prepared, stained with hematoxylin and eosin (H&E), and observed for histological changes under a light microscope to assessreepithelialization, epidermis thickness, inflammatory cell infiltration, collagen deposition, and blood vessel proliferation. Staining with Methyl trichromon paraffin sections done to determine the amount of collagen at the wound the most representative findings was be documented by photomicrography.
Immunohistochemical Analysis: Basic fibroblast growth factor vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and tumor necrosis factor was investigated.
Data was be presented as means ± standard deviation (SD). Student’s t-Test was be used to determine significant differences between treatment groups. Differences between pairs of means was be analyzed by one–way analysis of variance (ANOVA) test. Values of P≤0.05 were being considered statistically significant.
Results
Results of Wound area measurements
In the present study, we compared the effect of red wavelength at 635 nm ranges delivered at a constant fluence (5 J/cm2) and fluence rate (12 mW/cm2) with and without the combination on of Phenytoin drug that increases angiongesis and promotes healing to study mice dermal wound healing response variation with wavelength. Wound areas was determined after surgery day after day during the ongoing wound healing process, wound areas decreased in all groups compared to the initial wound area measured after surgery. However, low level light therapy by red LED 635 nm combined with Phenytoin markedly influenced this parameter, there was no difference on day 3 post-OP, but on day 7 the wound area was 50% smaller (p < 0.05) in the combined LED 635 nm and Phenytoin group compared to not illuminated control to elucidates the effect of light (Fig.1). In contrast, red LED 635 nm light seemed to delay wound closure, and the difference was even greater compared to the Phenytoin group although these finding were not significant.
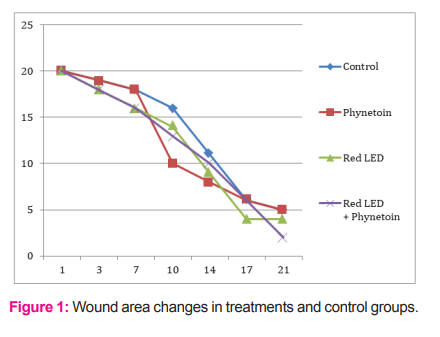
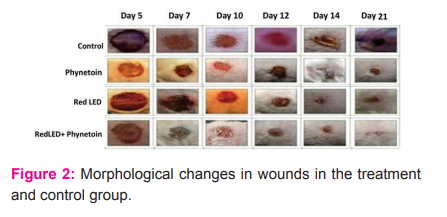
Results of Morphological wound Assessment
No significant difference could be detected regarding the degree of granulation (Fig. 2). However, light effected reepithelialisation as there was a strong trend to enhanced epithelialisation.
Wounds treated with different wavelengths exhibited wound contraction from day 1 until observation of day 21 after wounding. However, non-treated control wounds initially expanded on day 1 post-injury, and at day 2, control wounds were the same size as the original size on day 0. From day 4 onwards, control wound exhibited a gradual reduction in wound area.
Histological Evaluations:
Assessments were carried out at (3-7-14-21) days postoperatively where at those times healing/healed ulcers were excised and subjected to multiple cross-sections of H&E-stained sections of wound tissues obtained from control group and treated groups of mice the evaluations aimed for:haemorrhage, epidermis thickness, inflammatory cell infiltration, collagen deposition, and blood vessel proliferation.
Control group: Cross-sections of H&E-stained sections of skin wound from, untreated mice at day 3 showed necrosis associated with oedema and inflammatory infiltrate at day 7 showed necrosis associated with oedema and massive dermal inflammatory infiltrate, at day 14 ill developed granulation tissue appeared, At 21 days granulation tissue formation with inflammatory cells infiltration and congested newly formed blood capillaries were noticed.
Phenytoin treated group: at day 3 H&E-stained sections showed necrosis, oedema and inflammatory cells infiltration at day 7 it showed necrosis, dermal inflammatory cells infiltration and no haemorrhage, at day 14 showed granulation tissue formation with epithelization well developed neo angiogenic blood vessles and inflammatory cells infiltration. At day 21 showed epithelization granulation tissue formation collagen fibers.
The Red LED group: at day 3 H&E-stained sections showed necrosis, highly vascularized dermal blood vessel and dermal inflammatory (7days) showing dermal inflammatory infiltrate and congested dermal blood vessel (14 days) showing epithelization and granulation tissue formation
The combined phenytoin and Red LED group: at day 3 H&E-stained sections showed necrosis, dermal inflammatory cells infiltration and haemorrhage at day 7 showed necrosis and massive dermal inflammatory cells infiltration at
day 14 showed granulation tissue formation and inflammatory cells infiltration at day 21 showied well developed granulation tissue formation with few inflammatory infiltrate well oriented epithelization.
Results of the histopathological comparison scors
On days 3 and 7, the phenotyon and combined phenotyon and red LED groups had significantly higher angiogenesis than other two groups (p< 0.05). Treatment groups were not significantly different among each other of groups 1 and 2 in terms of angiogenesis is. Epithelialization There were no significant differences on days 3 and 21.Epithelialization on day 7 was higher in all the treatment groups compared with control group (p < 0.05). All treatment groups had significantly lower inflammation on day 14 compared with control group (p< 0.05). Red LED ligh and combined group had faster epithelialisation than the other treated groups There were no differences between groups on day 21 shown in Fig. 1
Collagen Analysis: It
Fibroblastic activity, and collagen deposition was determine the amount by Masson trichrom(MTC stain).were not statistically different between treatment groups and the control group Skin of mice from control group (14 days) showing haphazardly arranged, ill developed granulation tissue. Notice massive haemorrhage between the granulation tissue Skin of mice from treated with phenytoin (14 days) showing well oriented granulation tissue with collagen fibers deposition Skin of mice from treated with combined phenytoin and led (14 days) showing well oriented, well developed dense stained granulation tissue with collagen fibers deposition Skin of mice from treated with combined phenytoin and led (14 days) showing well oriented, well developed dense stained granulation tissue with collagen fibers deposition Skin of mice from treated with led (Red Spectrum) (14 days) showing well oriented, well developed dense stained granulation tissue with collagen fibers deposition Skin of mice from treated with led (Red Spectrum) (14 days) showing well oriented, well developed dense stained granulation tissue with collagen fibers deposition Skin of mice treated with LED (IR spectrum) (14 days) showing haphazardly arranged, ill developed granulation tissue kin of mice from treated with combined phenytoin and LED (Red Spectrum) (14 days) showing well oriented, well developed dense stained granulation tissue with collagen fibers deposition (fig. 3) .
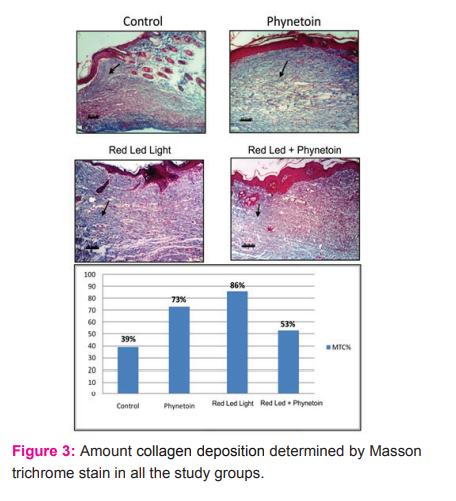
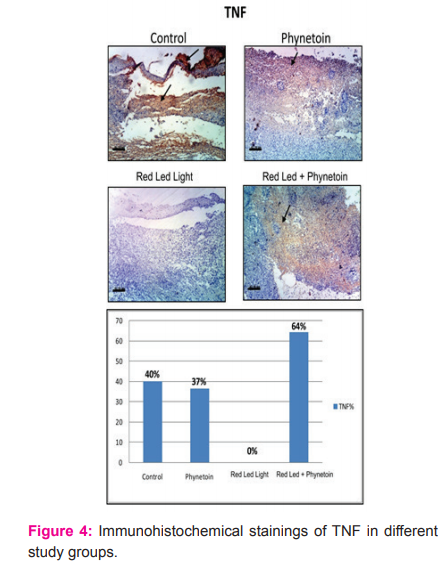
Results of immunehistochemical study of the Inflammatory Mediators
Immunohistochemical staining of TNF in skin of control mice showing strong positive expression of TNF in skin of mice treated with H showing moderate positive expression of TNF skin of mice treated with H showing moderate positive expression of TNF skin of mice treated with HL showing no expression of TNF (negative immunoreaction for TNF). skin of mice treated with HL showing no expression of TNF (negative immunoreaction for TNF). skin of mice treated with R showing strong positive expression of TNF skin of mice treated with R showing moderate positive expression of TNF skin of mice treated with RH showing weak positive expression of TNF skin of mice treated with RH showing moderate positive expression of TNF
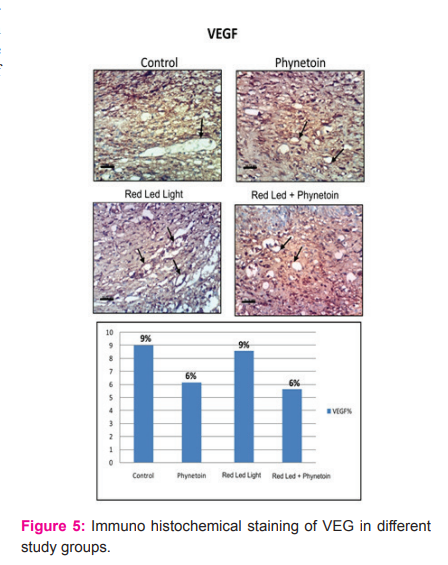
Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF):
Immunohistochemical staining of VEGF in skin of control mice showing weak positive expression of VEGF Whereas the skin of mice treated with phenytoin showing moderate positive expression of VEGF The skin of mice treated with combined phenytoin and LED (Red spectrum) showing moderate positive expression of VEGF skin of mice treated with combined phenytoin and LED (Red spectrum) showing strong positive expression of VEGF skin of mice treated with LED (Red spectrum) showing strong positive expression of VEGF skin of mice treated with LED (Red spectrum) showing strong positive expression of VEGF skin of mice treated with LED (IR spectrum) showing moderate positive expression of VEGF skin of mice treated with combined phenytoin and LED (IR spectrum) showing strong positive expression of VEGF skin of mice treated with combined phenytoin and LED (IR spectrum) showing strong positive expression of VEGF (fig 4).
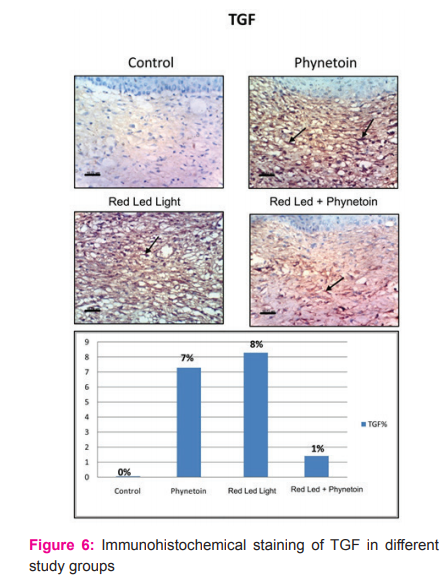
Immunohistochemical staining of TGF in skin of mice from control group showing no expression of TGF. In skin of mice treated with phenytoin showing positive expression of TGF in skin of mice treated with combined phenytoin and LED (Red spectrum) showing positive expression of TGF
skin of mice treated with combined phenytoin and LED (Red spectrum) showing positive expression of TGF skin of mice treated with LED (Red spectrum) showing strong positive expression of TGF skin of mice treated with LED (Red spectrum) showing strong positive expression of TGF
-
skin of mice treated with LED (IR spectrum) showing moderate positive expression of TGF skin of mice treated with combined phenytoin and LED (IR spectrum) showing strong positive expression of TGF skin of mice treated with combined phenytoin and LED (IR spectrum) showing strong positive expression of TGF (fig 5, 6).
-
DISCUSSION
Various treatment methods are used for the aim of developing wound care products and strategies such as local or systemic agent use, and even surgical treatment 13- 15. The use of light in wound healing experimental studies and clinical applications remains popular among clinicians. Mechanism of Actions of light have been widely investigated to understand the molecular basis and to extend their clinical use 16. Topical phenytoin had been knownhelpful for a broad variety of wounds. Clinical studies using topical phenytoin as a treatment suggest that it may be useful for the therapy of both acute and chronic wounds of diverse etiologies17. To our knowledge no other study had tested the combination between phenytoin and LED light therapy for wound healing. The cellular, biochemical, and molecular effects start to build up early in healing wound, as in the cicatricial context 18. Therefore, the present study aimed to characterize the process of fibrous tissue formation in later stages of tissue healing. In addition to this aspect, an investigation was conducted to ascertain whether the combination of phenytoin and laser stimulation could affect tissue repair on the basis of cellular level.
The use of laser therapy for wound healing was initially described as early as 1960. Because of its ability to either stimulate or inhibit tissue responses, the term “biostimulation” was changed to “biomodulation. Several reports have shown that major components of the healing process are affected by several wavelengths, which include: fibroblastic proliferation, proliferation of keratinocytes, collagen synthesis and deposition, and increased angiogenesis 19.
Collagen synthesis and other components of the connective tissue are important for the healing process at early stages. However, this process has to be self-controlled in order to prevent the formation of hypertrophic scars. The positive biomodulation of laser therapy on fibroblastic proliferation, and on collagen synthesis and deposition are well described in current literature. In the present investigation, a number of fibroblasts were observed on irradiated subjects when compared to their controls. These cells were predominantly young and very active in collagen production. Despite the fact that the collagen organization observed in the present study suggested that laser therapy influences collagen synthesis but does not significantly affect collagen organization 20. Our results indicated that non-coherent LED light 670-nm had better stimulatory effects when combined with phenotoyn and was superior to it when used alone. On the cellular level, LED light 670-nm modulates fibroblast proliferation, increases collagen bond and synthesis, promotes angiogenesis, improves energy metabolism and produces biological effects during the healing phase.
The collagen deposition varied according to the period and according to the group analysed; it was minor in the great majority of animals in the four groups on the 10th day of examination. Our results harmonize with the findings of previous research that employed wavelengths of 660 and 780 nm and a dosage of 5 J/cm2 on four points and found a small and moderated number of immature and fragmentary collagen fibres on the 14th day of treatment using optical microscopy 21.
Conclusions
The combined phentoyn and LED light have a positive healing effect on dorsal mice wounds regardless of the radiation dose. LED light was considered more effective compared to phenotyon in terms of fibroblast proliferation and collagen fiber density. However, further randomized clinical studies are required to determine the effect of combination of these two modalities of therapy on wound healing in humans.
Founding
This studies as no fund from any authorities and there is no any conflict of interest.
References:
-
WiererJr JJ, Tsao JY, Sizov DS. Comparison between blue lasers and light?emitting diodes for future solid?state lighting. Laser & Photonics Reviews. 2013 ,7(6):963-93.
-
Lucas C, Criens-Poublon LJ, Cockrell CT, de Haan RJ. Wound healing in cell studies and animal model experiments by Low Level Laser Therapy; were clinical studies justified? A systematic review. Lasers in medical science. 2002 , 1;17(2):110-34.
-
Avci P, Gupta A, Sadasivam M, Vecchio D, Pam Z, Pam N, Hamblin MR. Low-level laser (light) therapy (LLLT) in skin: stimulating, healing, restoring. InSeminars in cutaneous medicine and surgery 2013, 32, 1, pp. 41). NIH Public Access.
-
Gupta A, Dai T, Hamblin MR. Effect of red and near-infrared wavelengths on low-level laser (light) therapy-induced healing of partial-thickness dermal abrasion in mice. Lasers in medical science. 2014, 29(1):257-265.
-
Arany PR, Nayak RS, Hallikerimath S, Limaye AM, Kale AD, Kondaiah P. Activation of latent TGF-β1 by low power laser in vitro correlates with increased TGF-β1 levels in laser-enhanced oral wound healing. Wound repair and regeneration. 2007, 15(6):866-874.
-
Chaves ME, Araújo AR, Piancastelli AC, Pinotti M. Effects of low-power light therapy on wound healing: LASER x LED. Anaisbrasileiros de dermatologia. 2014;89(4):616-23.
-
deFreitas LF, Hamblin MR. Proposed mechanisms of photobiomodulation or low-level light therapy. IEEE Journal of selected topics in quantum electronics. 2016 Jun 9;22(3):348-64.
-
Fortuna T, Gonzalez AC, Sá MF, Andrade ZD, Reis SR, Medrado AR. Effect of 670 nm laser photobiomodulation on vascular density and fibroplasia in late stages of tissue repair. International wound journal. 2018 Apr;15(2):274-82.
-
Medrado AP, Soares AP, Santos ET, Reis SR, Andrade ZA. Influence of laser photobiomodulation upon connective tissue remodeling during wound healing. Journal of Photochemistry and Photobiology B: Biology. 2008 Sep 18;92(3):144-52.
-
Hao XY, Li HL, Su H, Cai H, Guo TK, Liu R, Jiang L, Shen YF. Topical phenytoin for treating pressure ulcers. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 2017(2).
-
Bhatia A, Prakash S. Topical phenytoin for wound healing. Dermatology Online Journal. 2004;10(1).
-
Swamy SM, Tan P, Zhu YZ, Lu J, Achuth HN, Moochhala S. Role of phenytoin in wound healing: microarray analysis of early transcriptional responses in human dermal fibroblasts. Biochemical and biophysical research communications. 2004 Feb 13;314(3):661-6.
-
Kay?r S, Demirci Y, Demirci S, Ertürk E, Ayaz E, Do?an A, ?ahin F. The in vivo effects of Verbascumspeciosum on wound healing. South African Journal of Botany. 2018, 1;119:226-9.
-
Asfaw M and Fentahun T. Treatment trials of epizootic lymphangitis with local medicinal plants: a review. Online Journal of Animal and Feed Research,2020, 10(4): 158-161.
-
Al Johny BO. Efficacy of silver nanoparticles synthesized on Commiphoragileadensis (Balsam) extract against infectious bacteria. Journal of Experimental Biology and Agricultural Sciences, 2019. 7(3): 301-307
-
Fushimi T, Inui S, Nakajima T, Ogasawara M, Hosokawa K, Itami S. Green light emitting diodes accelerate wound healing: characterization of the effect and its molecular basis in vitro and in vivo. Wound Repair and Regeneration. 2012 Mar;20(2):226-35.
-
Pendse AK, Sharma A, Sodani A, Hada S. Topical phenytoin in wound healing. International journal of dermatology. 1993 Mar;32(3):214-7.
-
Fortuna T, Gonzalez AC, Sá MF, Andrade ZD, Reis SR, Medrado AR. Effect of 670 nm laser photobiomodulation on vascular density and fibroplasia in late stages of tissue repair. International wound journal. 2018 Apr;15(2):274-82.
-
Chung TY, Peplow PV, Baxter GD. Laser photobiostimulation of wound healing: defining a dose response for splinted wounds in diabetic mice. Lasers in surgery and medicine. 2010 Nov;42(9):816-24.
-
Grbavac RA, Veeck EB, Bernard JP, Ramalho LM, Pinheiro AL. Effects of laser therapy in CO2 laser wounds in rats. Photomedicine and Laser Therapy. 2006 Jun 1;24(3):389-96.
-
Meirelles GCS, Santos JN, Chagas PO, Moura AP, Pinheiro ALB (2008) A comparative study of the effects of laser photobiomodulation on the healing of third-degree burns-a histological study in rats. Photomed Laser Surg 26(2):159–166. doi:10.1089/pho.2007.2052
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License