IJCRR - 13(1), January, 2021
Pages: 169-173
Date of Publication: 05-Jan-2021
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
Evaluation of Laparotomy Fascial Wound Closure with Continuous Suture and Intermittent Aberdeen Knot
Author: Honeypalsinh H Maharaul, Harsh Patel, Darshan Gajera, Ketul Shah
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Background: The closure is a crucial factor in, laparotomy wound. Fascial layers provide a major tensile strength in wound closure. Poor wound, healing, and development of wound infection and, the incisional wound are the common complications of open abdominal surgery.
Objective: To evaluate abdominal wound closure in terms of the outcome of wound, infection, and wound pain.
Methods: Detailed, clinical history, clinical examination including per abdominal and per-rectal examination, routine blood investigations & chest x-ray screening was done. In all the patients undergoing laparotomy wound closure done with continuous suture and Aberdeen knot. All the patients were observed for complications after operation & followed up at 1 week, 15 days,3,6 months postoperatively.
Results: Most of the patients presented with intestinal obstruction (11) and peptic perforation (9) followed by ileal perforation (8) and appendicular perforation (6). There were 3 patients with liver abscess and Koch's abdomen, 2 patients with incisional hernia. 1 patient each of pseudocyst, CA descending colon, Ca stomach SMA thrombosis, rectal prolapse, abdominal Trauma, obstructed inguinal hernia, GOO. The most common complication was wound infection (5) followed by chronic wound pain (3), wound dehiscence (2). 1 patient developed an incisional hernia. None of the patients had stich granuloma or suture sinus formation.
Conclusion: In laparotomy, wound closure with continuous suture and Aberdeen knot reduces the incidence of infection, wound dehiscence, incisional hernia, suture sinus formation, and stitch granuloma & chronic wound pain. Thus, this method holds the promise for a safe technique of closure with minimal complication.
Keywords: Aberdeen knot, Continuous suture, Midline laparotomy, Abdominal Wall, Incisional Hernia, Seroma
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION
The closure is crucial,factor in a laparotomy wound. Fascial layers provide a major tensile strength in wound, closure. Poor wound healing and development of wound infection and incisional wound are common, complications of open abdominal surgery. Secure abdominal wound closure relies upon the repair of the musculofascial layer of the abdominal wall. The musculofascial layer of the abdominal wall comprises of external abdominal, internal abdominal, and transverse abdominal muscles and their aponeurosis. In the midline incision linea alba, right paramedian and right subcostal incision-anterior and a posterior layer of rectus, sheath of the musculofascial layers was included.
Continuous fascial closure with intermittent, Aberdeen knot normally practised and the, interrupted, closure is also practised by some surgeons with an assumption that it causes less, pain, and less wound infection. The wound is any discontinuity of tissue and for normal healing, it must be opposed with sufficient strength to allow the normal process of healing otherwise wound disruption may occur leading to complications.1 Wound complications may vary from seroma formation to hernia incidence of which is about 9-19%.2 There are various techniques of wound closure but there is no ideal technique or ideal suture material for particular closure and it all depends on surgeon’s preference. Closure technique varies for each surgeon either continuous or interrupted method, different fascial bites, variation in stitch interval.3,4 Here, we have tried to evaluate techniques of abdominal, fascial closure-continuous with intermittent Aberdeen, knot5 by using nonabsorbable polypropylene suture material in the midline, laparotomies.
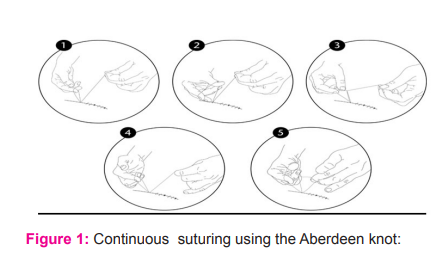
The Aberdeen knot is a self-locking, knot consisting of a combination of unique throws and, turns that is used to secure, the end of a continuous suture line (Stott 2009).6 To form an Aberdeen knot, a loop is formed in the future and passed through the tissue on each side of the incision, line. A second loop is then passed through the first loop. This is termed one throw. This step can be repeated any number of times to achieve the desired, number of throws. To lock the knot, an additional, throw called the turn is performed by passing the end of the suture, through the final loop. Depending on surgeon preference, the turn can be repeated (Figure 1).
This study is designed as an evaluation of abdominal wound closure in terms of the outcome of wound, infection, and wound pain. To minimize the influence of suture materials we used the same suture, materials at similar levels of fascial closure in all the patients.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
This is a Prospective, observational, cohort, study in 50 patients aimed to evaluate the outcome of laparotomy fascial wound closure with continuous suture and intermittent Aberdeen knot. Study was conducted at Dhiraj, Hospital with approval from Ethics committee (No: SVIEC/ON/ME01/BNPG18/D19094) from the date of period of Semptember 2017 to Semptember 2019.
Inclusion criteria
-
Both male and female, patients
-
Patients older than 18 years
-
The study includes both elective and emergency laparotomies
-
All vertical abdominal, incision closures will be included
-
Patients who voluntarily decide to take part in this study, and give written consent.
Exclusion criteria
-
All Medically and Anesthetically, unfit patients
-
Non-compliance
-
Patient not willing to, study.
Procedure
All patients admitted at Dhiraj general Hospital posted for laparotomy were explained about the risk factor. If the patient agrees, then the only Patient was being operated
A detailed history will be taken and all patients will be subjected to thorough clinical examination including per abdominal and per-rectal examination. Routine lab investigations like, blood and screening of chest will be done. All patients were undergoing laparotomy wound closure with continuous suture and Aberdeen knot.
All the patients will be analysed postoperatively according to proforma prepared and other post-operative complications such as
-
Incisional Hernia
-
Wound dehiscence
-
Suture sinus formation
-
Stitch granuloma
-
Chronic Wound pain
-
Wound infection
All patients where be followed up at 1 week, 15 days,3,6 months postoperatively.
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
Any contribution to the study and, knowledge of wound closure is important to surgical speciality and, this is a valuable contribution. Closure of abdominal incision has been greatly simplified by the realization that all incisions heal by forming a block of fibrous tissue.8
The strength of the abdominal wall depends on linea alba and anterior, rectus sheath. The technique of laparotomy wound closure is an important factor in preventing postoperative wound complications like wound infection, wound dehiscence, suture sinus formation, incisional hernia, and scar complications. However, there are many, systemic, and local factors responsible for delay in wound healing.
Systemic factors include diabetes, hypertension, anaemia. Local factors includes infection, hematoma formation. Mechanical factors such as postoperative vomiting, hiccough, explosive coughing and chest infection, gross gaseous distension.
The current study has shown that the mass closure technique for abdominal wounds, results in a lower incidence of wound infection, wound dehiscence and incisional hernia, chronic wound pain, suture sinus formation, and stitch granuloma than in layered technique.
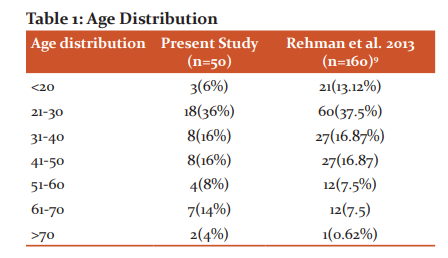
Age Distribution
Most of the patients in the present study, as well as Rehman et al.2013 9 study, belonged to the 21-30 years age group which is the most productive age group (Table 1). India is a developing country most are labourer class population belonging to this age group who are malnourished and presents often late for their symptoms.
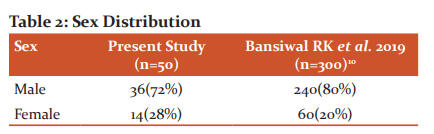
Sex Distribution
There was male predominance in both studies which may be attributed to the adverse sex ratio in India and the disease profile of a male patient who is working population with smoking habits and neglects their health (Table 2).
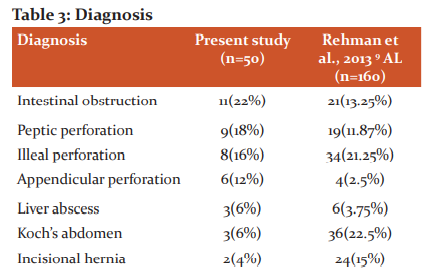
Diagnosis
Our institute is a tertiary institute hence the variety of patients presents to our surgical department which is comparable to Rehman et al., 2013 9 study (Table 3). Also, India being developing tuberculosis and malnutrition are endemic hence more patients with tuberculosis and perforation.

Comorbid conditions
India is a third-world country with most people belonging to either lower or extremely higher socioeconomic status thus anaemia and chest infection are common in the lower class and Diabetes Mellitus and Hypertension common in the Upper class (Table 4).
Complications
Wound infection
In the present study wound infection was 10% as compared to other studies. McNeill had a 3.92% wound infection with continuous closure. Khan et al., 20091 reported a 4.75% wound infection while Gurjar et al., 201413 reported a 4% wound infection. The part played by the wound, sepsis is important, as this is the major avoidable cause of wound failure. Inadequate treatment or, the immuno-compromised state may lead to serious, systemic complications like septicaemia, shock, and multi-organ failure.
The higher rate of wound infection in the present study may be attributed to the poor nutritional status of the study population, and late presentation to our centre with comorbidities like DM, Hypertension, anaemia
Wound dehiscence
In the present study wound dehiscence was 4% which is similar to Gurjar et al., 201413 (4%) while Khan et al., 20091 reported 0.94%. Wound dehiscence is a grave, complication with poor prognosis. Faulty suture
the technique is entirely responsible for early dehiscence but only partly responsible for a late, incisional hernia, the other culprit being deep wound sepsis often associated with intraperitoneal drainage. Wound dehiscence rates are higher with conventional layered closure than single-layered closure. The suture, holding capacity of the anterior rectus sheath, alone was 2.25 kg compared with 3.93 kgs after, full-thickness, musculoaponeurotic. The structures found to have the greatest suture holding capacity was the linea alba 7.93kgs as compared with,4.12kg for full-thickness without linea alba.14
In our study, the incidence of wound dehiscence is higher than Khan et al., 20091. This is because, in our study, we had a large number of patients who were elderly, had intraabdominal sepsis, and presented late. Most of these patients were anaemic, DM, Hypertension, and most of them were operated on an emergency basis and also had a higher incidence of post-operative wound infections. These predisposing factors were responsible for delayed wound healing and subsequent dehiscence as compared to the western countries where the incidence is less.
Chronic wound Pain
Chronic wound pain was present in 6% of patients in the present study as compared to 3% in Gurjar et al., 201413. This may be attributed to intermittent knotting and nerve entrapment in a knot.
Incisional hernia
The incisional hernia was 2% in the present study compared to 9.8% in McNeill and 3% in Gurjar et al., 201413 while it was similar to Khan et al., 20091 (2.35%)
Incisional develops from, the scar of a surgical incision, when a patient is examined by making him lie flat on the bed and is asked to lift his legs or to cough, any bulges in the scar is considered as, Incisional hernia. Incisional hernias are mainly due to faulty incision and faulty technique of closure, other, important determinants are sex (males more predisposed) and, age (elderly more predisposed) of the patients, chest infection, and wound infection. As age advances, breakdown of collagen fibres takes place weakening the old-healed scars, predisposing for hernia, thus indicating the need to use non-absorbable, suture material to support it, using chromic catgut in conventional, layered closure proved to be a drawback in causing incisional hernia and thus proving the advantages of using polypropylene in preventing incisional hernia by holding more tissue with, little tension for a long period after the wound heals. As in the present study closure technique involve intermittent Aberdeen knot tension gets distributed and thus chances of incisional hernia get reduced.
Stitch Granuloma and Suture Sinus Formation
It is defined as a chronic, granulating infection or micro abscess that results in a
persistent fistulous tract. The incidence of suture sinus formation is predisposed by the use of, multifilament suture material. Due to lodgement of, infective foci in the crevices of suture material. We did not have any patient with stitch granuloma or suture sinus formation as we had used monofilament suture material as compared to 3% (stitch granuloma) and 2% (Suture sinus) in Gurjar et al., 2014.13
CONCLUSION
In laparotomy, wound closure with continuous suture and Aberdeen knot reduces the incidence of infection, wound dehiscence, incisional hernia, suture sinus formation, and stitch granuloma & chronic wound pain. Thus, this method holds the promise for a safe technique of closure with minimal complication.
Conflict of interest: nil
Source of funding: nil
Acknowledgement: Immeasurable appreciation and deepest gratitude for the help and support are extended to my mentor Dr. Vipul Gurjar who in a way or other has contributed to making this study possible.
References:
-
Khan NA, Almas D, Shehzad K, Chaudhry AK, Mian MA. Comparison between delayed-absorbable polydioxanone and non-absorbable (Prolene) suture material in abdominal wound closure. Pak Armed Forces Med 2009; 23(6):123-6.
-
Hodgson NCF, Malthaner RA, Ostbye T. The search for an ideal method of abdominal fascial closure. Ann Surg 2000;231:436–442.
-
O’Dwyer PJ, Courtney CA.Educational Review: factors involved in abdominal wall closure and subsequent incisional hernia. Surg J R Coll Surg EdinbIrel 2003; 4:17–22.
-
Kreszinger M, Delimar D, Kos J, Jovanov N, Vnuk D, Maticic D, et al. Wound strength after midline laparotomy: a comparison of four closure techniques in rats. Vet Arhiv 2007;77:397–408.
-
Farquharson M, Moran B. Farquharson’s textbook of operative general surgery. Surgery of the skin and subcutaneous tissue, 9th edn. London, 2005; 12:5–7.
-
Mimi, Leong, Linda G. Philips. Wound Healing. Chapter 8 in Sabiston's Textbook of surgery, 17th ed, 183-207.
-
Kiran K Singisetti, George P Ashcroft. The Aberdeen ‘continuous interrupted’ surgical suturing technique. Ann R Coll Surg Engl 2009; 91:344–350.
-
Bentley PG, Owen WJ, Girolami PL, Dawson JL. Wound closure with Dexon (PGA), Ann R Col Surg Engl 1978; 60:123-127.
-
Zabd-Ur-Rehman AR, Naveed M, Javeed MU, Akbar A. Comparison of Wound Dehiscence in Interrupted with Continuous Closure of Laparotomy. PJMHS 2013;7(3): 828.
-
Rajesh KB, Tarun M, Rajeev S, Sanjay G, Simrandeep S, Kumar A, Ashok KA, Comparative study of abdominal wound dehiscence in continuous versus interrupted fascial closure after emergency midline laparotomy. Int Surg J 2019 Mar;6(3):886-891.
-
McNeill PM, Sugerman HJ. Continuous Absorbable vs Interrupted Nonabsorbable Fascial Closure. Arch Surg 1986;121: 45-48.
-
Khan MI, Khalil J, Khan MA. Internal tension sutures, a novel method of midline laparotomy closure in high-risk patients. Pak J Surg 2017; 33(3):165-169.
-
Vipul G, Halvadia BM, Bharaney RP, Vicky A, Shah SM, Samir R, et al. Study of Two Techniques for Midline Laparotomy Fascial Wound Closure. Indian J Surg 2014;76(2):91–94.
-
Leaper DJ, Pollock AV, Evans M. Abdominal wound closure, a trial of nylon, polyglycolic acid and steel sutures. Br J Surg 1977; 64: 603-606.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License