IJCRR - 13(1), January, 2021
Pages: 165-168
Date of Publication: 05-Jan-2021
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
Effect of Dual Task Training on Balance and Gait Over Regular and Diversified Land Surfaces in Independent Elderly
Author: S. Anandh, G. Varadharajulu, Mahendra M. Alate, Dhirajkumar A. Mane
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Introduction: Although most falls involve multiple factors, causes of falling are often categorized into intrinsic (personal) and extrinsic (environmental) factors. The dual-task method, which requires participants to perform multiple tasks simultaneously, has been used to investigate the effects of cognitive tasks or additional motor task on postural control and vice versa. The perfect implementation of this intervention will give the evaluative report of functional capacity levels and safety limits in the social life of the elderly population.
Objective: To test the effects of combined dual tasking with the dual components of cognition-motor and motor-motor administered in both regular and diversified environments using the outcome parameter Tinetti balance assessment tool (Balance & Gait).
Methods: 192 subjects randomly selected into two groups (dual-tasking on even & uneven surfaces) were included for the study. Tinetti balance assessment tool was used in 3 sessions of training. A 10-minute warm-up exercises followed by dual-task activity training which includes two components. i.e., cognitive-motor and motor-motor activity.
Results: It was observed that the elderly slow down with gait parameters on diversified land surfaces and when performing a concurrent dual-task. Also, the elderly err on the side of safety and focus their anticipatory resources towards controlling balance. It is so important for physiotherapists to be aware of these strategies and incorporate them into the management of fall prevention among the elderly.
Conclusion: The Dual-task activity training administered in both environmental conditions with safe progressive incremental levels is a motivational response for the elderly and easily predicts the physical difficulty levels.
Keywords: Regular land surface, Diversified land surface, Tinetti balance assessment tool, Balance, Gait, Dual-task training
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION
A UN Population Fund and Help age India analysis stated that by 2026 the total quantity of the older adults will increase to 173 million. According to Population Census 2011 in India, there are nearly 104 million elderly persons (aged 60 years or above) in India(53 million females and 51 million males). Most common disability among the aged persons was found to be a locomotor disability and visual disability as per Census 2011. The probability of age-related disorders and disabilities will have a great impact on individuals, families & health care providers. Exercises developed for rehab of older adults should be sensible, safe & comfortably a gradual approach if applicable & suitable as per individual needs will improve quality of life since the fear of suffering cripples his / her life. Attention is the “magic sauce” for altering our brains. With increasing age, the act of walking demands a higher level of control processing, and gait becomes less automatic.1,2
The increase in attentional demands during walking would reduce the resources available for the performance of a concurrent dual-task interfering balance.3 This makes it imperative for further investigations in the effect of dual-tasking on gait / postural control among the elderly, given the strong link between gait disturbance and fall prediction.4 These differences are more pronounced when walking on diversified uneven surfaces challenging the elderly with confirming risk.
Geriatric wellness is a multi-dimensional, multi-disciplinary area with an assessment designed to evaluate an older person’s functional activity, physical health, cognition and mental health under various socio-environmental circumstances. The geriatric assessment differs from a typical medical evaluation by including non-medical domains; by emphasizing functional capacity and quality of life. Completing survey questions and completing similar procedures not only saves a lot of time but gives a valuable glimpse into the patients' encouragement and awareness. Traditionally, rehabilitation programs emphasize training balance under single-task conditions to improve balance and reduce the risk of falls.
Recent research suggests that older adults that perform poorly under dual-task conditions are at increased risk of falls. Falls, the leading cause of accidental death away older adults over 65 years of age, are a serious clinical problem. Non-fatal falls often lead to physical injury (e.g. fracture), reduced levels of activity, loss of confidence, and altered lifestyle in elderly people. Falls are costly and have potentially devastating physical, psychological and social consequences.
So, this study gives insight on how this incremental physiotherapy intervention involving dual-task activity training (cognitive-motor and motor-motor) under regular and diversified environmental conditions applied to both rural and urban older adults more than 65 years of age. The perfect implementation of this intervention will give the evaluative report of functional capacity levels and safety limits in the social life of the elderly population.
The study aims towards formulating a self-reliant approach for the elderly to self-assess and train themselves towards their threshold levels of exercise capacity. The Dual-task activity training administered in both environmental conditions (regular & diversified) with safe progressive incremental levels have proved to be a challenging responsibility for the elderly. The cause of fall is categorized into Intrinsic (Personal) and/or Extrinsic (Environmental) factor. Attention changes with environment inclusive of additional interference of Psycho-Social factors are more in Physical activity in the elderly. The need for higher attentional demands with environmental demands in the performance of the automatic act of walking needs to be understood. To date, the effects of dual-tasking on diversified land surfaces have received less attention. So, possible risk components on balance & gait need to be ruled out.
It is a community-based rehabilitation approach dealing with an elderly population under personal supervision and assistance. Elderly are taking care of their grandchildren and participate in IADL activities all alone for which functional enhancement is far mandatory. The whole elderly population indeed is well-bounded with many Psycho-Socio-Economic issues and lack of caretakers. So, this research will have a good response from the community-dwelling elderly.
Thus, we aimed to examine the effects of performing a dual-task activity on gait and balance in functionally independent elderly ambulating on regular and diversified land surfaces.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
The study type is Interventional study design with a sample size of 96 subjects using a random sampling method. The period of study continued for more than a year. The study was carried out in Krishna Institute of Medical Sciences, Karad, (KIMS/IEC-043/2011).
Outcome measures
Tinetti Balance Assessment Tool consisting of: Balance score: 16 / Gait score: 12 and so the total score: Balance + Gait = 28
Inclusion criteria
All functionally independent elderly, above the age of 65-75 years including both genders with normal vitals were included in the study; Retired senior citizens restricted to their residence most of the time; No history of fall for the past 12 months; Ability to walk 20m without human assistance; Ability to speak/read/communicate.
Exclusion criteria
Medically unstable patients and Patients with Pacemaker; Chronic illness &Life threatening medical issues; All types of disabilities including severe musculoskeletal pathologies, neurological conditions, vestibular dysfunction that would affect participation; Uncooperative and Psychiatric elderly patients; Participants scored less below 23 on the MMSE; Subjects who are doing part-time work, Farm work or any other regular work are restricted from the study.
Procedure
Ninety-six elderly males and females from 65 to 75 years of age community-dwelling that fulfilled involvement standards for inclusion voluntarily participated in the study. The participants recruited were orally briefed about the study procedure by the primary investigator and were told orally about the place to try, date and time of the trial. Demographics, anthropometrics and comorbidities were assessed at the baseline using a standard questionnaire. Diversified surface: A natural uneven surface under a smooth surface of natural grass with the solid muddy surface with minor ups and downs exposed to sunlight (Usually an area not exposed). Regular surface: A solid pavement area or a track (usually an area exposed prior or similar safe area).
To retain privacy, a letters and numbers token was allocated to each capable individual. To guarantee to counterbalance, all subjects were significantly changed to test procedure baskets. A randomized preference of directories (A-regular and B-diversified), wherein the ordering of testing has been random, offered a contrast.
The treatment lasted about 60 minutes. There have been sufficient rest periods when appropriate. Before the study, the participants had verbal guidance about what they were supposed to do and, if supposed, they performed no more than three practical experiments to get to know the research process.
Exercise Procedure
1. All participants are made to perform daily tasks& cognitive tasks for practice followed by free exercises of extremities and spine: 5 minutes. Personal activities (Folding Bedsheet/counting currency & Dressing self): 5 minutes. Cognitive exercises (Loud reading, Writing / Drawing while listening to music & brushing teeth with non-dominant hand): 5 minutes.
2. Dual-task activity: 15 minutes inclusive of the following: Reading / Talking while walking: 05 minutes. Follow the light/cues while walking: 05 minutes and Obstacle walking: 5 minutes
3. Followed by Balance and Gait assessment. The results recorded were considered for statistical analysis and interpretation.
RESULTS
The table shows the level of risk in the elderly as they ambulate and simultaneously performing a motor and/or a cognitive task on regular and diversified surfaces. Extremely Significant with p-Value < 0.0001 / Odds Ratio - 116.44 / 95% CI: 7.011 - 1933.8 / Chi. Square - 44.308 (Table 1).

The Table 2 shows the level of Balance (Poor & Better) in elderly as they ambulate and simultaneously performing a motor and/or a cognitive task on regular and diversified surfaces. Extremely Significant with p-Value < 0.0001 / Odds Ratio - 116.44 / 95% CI: 7.011 - 1933.8 / Chi. Square - 44.308
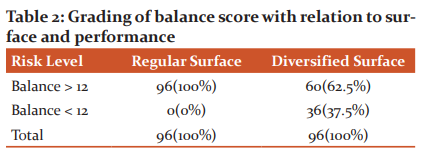
Table 3 shows the Gait score (Poor & Better) in the elderly as they ambulate and simultaneously performing a motor and/or a cognitive task on regular and diversified surfaces. Extremely Significant with p-Value <0.0001 / Odds Ratio - 132.58 / 95% CI: 7.990 - 2200.1 / Chi. Square - 48.941

DISCUSSION
The result of this study demonstrates that surface type and task related to attentional complexity affect the gait parameters and balance in the elderly. Some previous studies have reported deficits during walking on regular surfaces while performing a dual-task in older adults 5,6, our findings extend these observations to diversified surfaced walking. Significantly, the use of participants' multiple gastric techniques when actively conduct a dual-task in an unstable area supports the need to guarantee that they learn and practise on diversified walking surfaces while conducting a dual-task whilst rehabilitating.
A well-balanced gait pattern demands attention in elderly which is achieved through dual-task training to bring out a natural automated process of walking.7 The physiological changes and lack of physical activity lead to increased levels of physical demand.8 Environmental and extrinsic features influence upon other inputs and behave as a suppressive or enhancing feature for rhythmic gait pattern.
To be out of fear/risk of falls, the training should be a little challenging considering multiple risks involved in daily activities. There is a need for executive functioning skills along with relevant inhibitory factors to improve gait pattern and balance. So dual-task training will be a better choice of intervention. A favourable regular land surface has been found beneficial to improve inhibitory skills. The results proved that the elderly managed to walk better for a comfortable distance without any pitfalls.
Gait: Walking is a primary activity determining morbidity and attentional deficits in the elderly. Progressive dual-task training under the regular land surface has been found beneficial in the elderly with fear / minimal problems encountered with balance 9-12. Also, the participants were found to have an improved level of motivation and confidence for continuous participation. Uneven diversified land surfaces cannot be implemented for a longer duration due to safety considerations or evoking unnecessary stimulus which leads to reduced levels of motivation.
The study gives significant results about dual-task training inclusive of cognitive and motor component to keep the elderly aroused and attentive during any activity enhancing gait balance. The findings from this study support that gait changes do occur when performing a concurrent cognitive and/or motor dual-task, or while walking on a diversified land surface compared to a regular land surface in older community-living adults which is found statistically significant with p-value < 0.0001.
CONCLUSION
Based upon these findings, physiotherapists working to promote motor skill acquisition and prevention of secondary impairments in the elderly must ensure that they are introducing progressive safe dual-task activity on even regular surfaces and multi-task conditions on further progression into their patient’s management.
LIMITATIONS
The fact that only one type of diversified surface was used does not allow us to infer what would occur on all other types of diversified surfaces. The research can progress as per individual anthropometrics and utilization of advanced technology are some of the limitations. However, this work does add to the literature and offers insight and direction for future work exploring these factors.
Ethical issue: ethical clearance was taken from institutional ethical committee, kimsdu, karad.
Funding sources: krishna institute of medical sciences deemed to be university, karad.
Conflict of interest: nil.
Acknowledgement: We are grateful for the support which we received from the Department of community health Physiotherapy, Faculty of Physiotherapy, Krishna Institute of Medical Sciences Deemed To Be University, Karad, and Director of Research office, Krishna Institute of Medical Sciences Deemed to be University, Karad.
References:
-
Yogev-Seligmann G, Giladi N, Gruendlinger L, Hausdorff JM. The contribution of postural control and bilateral coordination on the impact of dual-tasking on gait. Exp Brain Res 2013 Apr 1;226(1):81-93.
-
Martin E, Bajcsy R. Analysis of the effect of cognitive load on gait with off-the-shelf accelerometers. Proc Cogn 2011;7:1-6.
-
Holtzer R, Wang C, Verghese J. The relationship between attention and gait in ageing: facts and fallacies. Motor Control 2012 Jan 1;16(1):64-80.
-
Verghese J, Ambrose AF, Lipton RB, Wang C. Neurological gait abnormalities and risk of falls in older adults. J Neurosci 2010 Mar 1;257(3):392-8.
-
LeMonda BC, Mahoney JR, Verghese J, Holtzer R. The association between high neuroticism-low extraversion and dual-task performance during walking while talking in non-demented older adults. J Int Neuropsychological Soc 2015 Aug;21(7):519.
-
Wrightson JG, Ross EZ, Smeeton NJ. The effect of cognitive-task type and walking speed on dual-task gait in healthy adults. Motor Control 2016;20(1):109-21.
-
Yogev-Seligmann G, Sprecher E, Kodesh E. The effect of the external and internal focus of attention on gait variability in older adults. J Motor Behav 2017;49(2):179-84.
-
Young WR, Olonilua M, Masters RS, Dimitriadis S, Williams AM. Examining links between anxiety, reinvestment and walking when talking by older adults during adaptive gait. Expt Brain Res 2016;234(1):161-72.
-
Wollesen B, Schulz S, Seydell L, Delbaere K. Does dual-task training improve walking performance of older adults with the concern of falling?. BMC Geriatr 2017 Dec 1;17(1):213.
-
Wollesen B, Mattes K, Rönnfeldt J. Influence of age, gender and test conditions on the reproducibility of dual-task walking performance. Ageing Clin Expt Res 2017 Aug;29(4):761-9.
-
Beurskens R, Bock O. Does the walking task matter? Influence of different walking conditions on dual-task performances in young and older persons. Human Movement Sci 2013;32(6):1456-66.
-
Martin KL, Blizzard L, Wood AG, Srikanth V, Thomson R, Sanders LM, Callisaya ML. Cognitive function, gait, and gait variability in older people: a population-based study. J Gerontol Series A: Biomed Sci Med Sci 2013;68(6):726-32.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License