IJCRR - 13(1), January, 2021
Pages: 98-102
Date of Publication: 05-Jan-2021
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
Influence of Exercise Environment on Attentional Awareness and Emotional Changes Among Elderly
Author: S. Anandh, Smita Patil, G. Varadharajulu, Mahendra M. Alate, Dhirajkumar A. Mane
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Introduction: Emotional wellbeing in the elderly is an essential track of the quality of life. The progress of any intervention for the elderly depends on mood characteristics and attention related to cognitive health which spirals further accordingly. In residential aged care and retired home-dwelling elderly attention and mood effect varies with individual and situation from time to time.
Objective: To explore the effects of exercise environment on Positive / Negative mood effect & Attention awareness among elderly without mobility limitation on Indoor versus Outdoor environment.
Methods: 102 literate elderly participants within the age group of 65 - 75 years sedentary and independent were recruited from the general public of Karad, Satara district of Maharashtra. Research environment setting: Outdoor environment was grassland with partly interspersed with trees. The indoor environment is a paved path within the walls or building pathways and not expose to greenery. Measures: Baseline and Posttest measures after 8 weeks adaptation to the exercise environment using PANAS questionnaire to record the scores of positive and negative mood effect and Mindful attention awareness scale (MAAS) to record attention awareness. The participants were made to undergo dual-task activity exercises and mindful walking in their prescribed environment during the 8 weeks of the adaptation period.
Results: The Pretest and Posttest measures have been analyzed and found that the outdoor environment has a significant influence on positive mood effect and improved attention awareness in the elderly.
Conclusion: Emotional wellbeing won't work upon compulsion and it has to be explored to reach pleasantness.
Keywords: Outdoor environment, Indoor environment, Positive mood effect, Negative mood effect, Emotional wellbeing, Mindful attention awareness
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION
Emotional wellbeing in the elderly is an essential track of the quality of life. The progress of any intervention depends on the mood characteristics of the participants and it spirals further accordingly. In aged elderly, it’s a major feature to be worked upon in a simple way of research. Ageing influences upon attention demands in association with cognitive function interfering with physical activity participation. It’s a common belief that a positive emotional state contributes to confidence and better physical functioning promoting well-being on the whole.1,2 Attention restoration is influenced by the individual’s adaptation to the environment as per his/her wish and positive or negative mood status gained. So, it is necessary to find out the interrelationship between attention awareness and mood status which directly influences participation in physical activity.3,4
A sensible and gradual approach whichever is suitable to the elderly will improve the quality of life. Fear of suffering cripples human beings. Any possibility of enriching happiness makes older adults smarter through positive emotions balancing personality traits. Regulation of emotions is influenced by cognitive function resulting in an optimally functional state. Emotional optimism protects older populations against permanent institutional care decreasing functional decline.5-7
Enhancing cognition maintains a balance between existential reality and psychological reality in the elderly which is possible through improving attentional awareness. Attention and Mood effect directly interferes with physical activity participation and level of performance in the elderly. Also, the personality variables of the elderly may get altered with the environmental stimulus which influences commonsense (Intelligence). The Studies on influences of mood-related life orientation and positive or negative emotion among older people on health outcomes are not common (Ble, Volpato, 2003).5 The timely mood effect and lack of attention lead to falls and injuries which is a neglected area of research. So, the purpose of this study has been designed to examine the association of Positive / Negative emotions and Mindful attention awareness in older people.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Data was obtained from regular Screening and Counseling for Physical Activity and Mobility in Older People conducted by senior citizens survey in the area. A total of 102 physically independent elderly citizens in the age group of 65 - 75 years who were sedentary but able to move outdoors independently took part in the study. The emotion was analyzed with Positive effect and Negative effect schedule (PANAS - GEN) Questionnaire.6 Attention was assessed by the Mindful Attention Awareness Scale (MAAS).7,8 The study was carried out in Krishna Institute of Medical Sciences, Karad, (KIMS/IEC-043/2011). The study was carried out in Krishna Institute of Medical Sciences, Karad, (KIMS/IEC-043/2011). The Study design is a Pretest - Post-test design done in two groups. Group A participants have undergone mindful physical activity training in the Indoor Environment. Group B participants have undergone mindful physical activity training in the Outdoor environment. In the Outdoor exercise environment, the participants have an opportunity to expose to the green type of scenery amid trees and fields. An indoor exercise environment is a closed environment specifically not exposed to greenery.9-12
Physical activity training
Baseline and Posttest measures after 8 weeks of adaptation to the environment have been assessed and recorded as per group A and B. The participants were made to undergo dual-task activity exercises in their prescribed environment during the 8 weeks (5 days per week) of the adaptation period. Besides, they have to undergo mindful walking for 20 minutes at a comfortable pace. Dual-task activity training includes cognitive-motor task activities for 15 minutes. It includes Talking while walking for 5 minutes; following cues/light while walking for 5 minutes and Obstacle walking for 5 minutes. Warm-up and Cool down includes mindful breathing practice for 5 minutes session and free exercises of spine & extremities for 5 minutes.
RESULTS
Demographic data
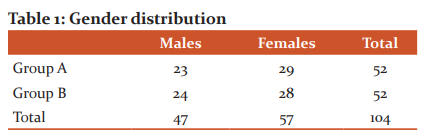
A total of 102 participants were included in the study which consisted of 47 males and 57 females. Group A consisted of 23 males and 29 females. Group B consisted of 24 males and 28 females (Table 1).
The mean age in group A was 68.92±2.8 and Group B was 69.11±2.63. The unpaired t-test analysis showed that the age difference in both groups was not significant (Table 2).

Outcome Measures
The within-group analysis shows that in Group A the pre-intervention score was 27.30±3.184 and post-intervention was 29.78±3.33 which was statistically extremely significant (p<0.0001). Group B analysis showed that the pre-intervention score was 28.80±4.559 and post-intervention was 32.53±2.44 which is statistically extremely significant (p<0.0001). This was done using a paired t-test (Table 3).

The between-group analysis showed that pre interventional there was no significant difference statistically (p=0.0545) but post interventional there was an extremely significant difference in Group B as compared to Group A (p<0.0001) indicating that positive mood score was improved in Group B (outdoor exercise) as compared to Group A (indoor exercise). This was done using the unpaired t-test. Thus, outdoor exercise environments in better than indoor exercise environments.
The within-group analysis shows that in group A the pre-intervention score was 16±3.003 and post-intervention was 14.36±2.90 which was statistically extremely significant (p<0.0001). Group B analysis showed that the pre-intervention score was 14.36±4.559 and post-intervention was 10.36±1.44 which is statistically extremely significant (p<0.0001). This was done using a paired t-test (Table 4).
The between-group analysis showed that pre interventional there was no significant difference statistically (p=0.0057) but post interventional there was an extremely significant difference in Group B as compared to Group A (p<0.0001) indicating that negative mood score was improved in Group B (outdoor exercise) as compared to Group A (indoor exercise). This was done using the unpaired t-test. Thus, outdoor exercise environments in better than indoor exercise environments.

The within-group analysis shows that in group A the pre-intervention score was 49.5±3.67 and post-intervention was 62±3.94 which was statistically extremely significant (p<0.0001). Group B analysis showed that the pre-intervention score was 49.88±2.9 and post-intervention was 75.38±4.4 which is statistically extremely significant (p<0.0001). This was done using a paired t-test (Table 5).
The between-group analysis showed that pre interventional there was no significant difference statistically in MAAS score (p=0.5571) but post interventional there was an extremely significant difference in Group B as compared to Group A (p<0.0001) indicating that MAAS score was improved in Group B (outdoor exercise) as compared to Group A (indoor exercise). This was done using the unpaired t-test.


These results indicate, 1. A pre-test to Post-test results of the outdoor environment is better compared to the indoor environment about Positive (Increased) & Negative Decreased) mood scores. 2. A pre-test to Post-test results of the outdoor environment is better compared to the indoor environment about the Attentional awareness MAAS score (Increased).
The study proves significant results among elderly participants exercising in the outdoor environment with highly significant improvement showing a higher degree of positive mood effect and attentive awareness.
DISCUSSION
Mindful attentional awareness scores
The outdoor environment is always beneficial in ways like exposure to sunlight and participation in enjoyable activities. The natural environment is found to have a healing effect and reduce mental tiredness among most of the participants in common 11 - 13. The sensory impressions and stimulus received in both indoor and outdoor environments are found to be different. Nature is closely linked with the individual’s identity and behaviour with growth since childhood. The voice of the birds expresses emotion representing freedom. The elderly express their sense of wellness or discomfort in their unique ways which have to be observed properly and to be understood.12
Positive mood scores
It was found that even the socially deprived participants and the oldest old had a better positive response in the outdoor environment. In comparison, in the Indoor Environment, the participants had less motivation to participate and so resulted in a negative effect with reduced attentional awareness. The subjects were found free to communicate in outdoor and have shown more of physical gestures.13
Effect of outdoor environment
Maintaining high levels of cognitive functioning is an important aspect of successful ageing and it is related to the attention awareness and mood effect of the individual related to successful training methods. The subjects were found continuing the task out of self-interest and modified as per their convenience in the outdoor environment.14
Negative mood scores
Even though intellectual functioning predicts negative effect, morbidity, or mortality, there is no evidence that it predicts a positive effect in aged (9, 10). A comfortable environment with required socialization has been found better to improve the normalization pattern of their thoughts and feelings improving attentional awareness of their physical activity pattern. It means the suppression of feelings increased stress and restricts attention irrespective of any reason.10,11
It was found difficult to relate intelligence with positive or negative effect as all the subjects were rural elderly with required literacy and similar life status. The mood effect was found changing invariably with each individual which was unexplained among 50% of the participants during the research. It might be possibly due to their likes or dislikes and daily life situations.9,8
The elderly exercising in the outdoor environment was found to have better memory response as they were in contact with nature which provided a sustained positive stimulus comparatively to the indoor environment.14 It was found that subjects had shared their experiences and past or present memories with others in an outdoor environment. This helps the elderly to integrate information and so resulting in better cognitive abilities which are evident through the findings in the research. The participants exercising in an outdoor environment were ready to take up challenging dual-task activities with better progression.
CONCLUSION
Results suggest associations between green space and mental wellbeing, particularly hedonic wellbeing. We discovered adequate evidence for associations between urban greenspace and life satisfaction; however, the evidence for the remainder of the green space characteristics, including greenspace (land use) type, accessibility, viewing and visiting patterns, was limited or inadequate. Psychological or emotional wellbeing won’t work upon compulsion and it has to be explored to reach pleasantness. The study concludes that easier modes of promoting attentional awareness with adaptive situations and activities result in gaining confidence and promoting positive mood effect resulting in elderly wellness. Large, well-designed trials in which the effects of long-term physical activity interventions conducted indoors and out in nature on mental and physical wellbeing are compared in different groups of people are urgently needed. Easily transferable outcome measures (e.g., assessment of the health-related quality of life), administered both immediately after activity and after a period of rest to assess the sustainability of the effects of the activity is also required. Measures to assess the adherence to different physical activity programs should also be included.
LIMITATIONS:
A large portion of the variance in different forms of mood effect is unexplained as it passes in the subconscious state among every participant. This mood effect gets transformed with their feelings and thought process and finally, the primary effect is found lost. So an environment providing positive stimulus is advisable to maintain a stable mood among the elderly. Future research is required considering the cognitive, attentional, dispositional, and behavioural factors applicable to mood change and emotional stability of each elderly.
FUTURE DIRECTIONS:
The influence on emotional change depends on the intensity of the situation and cannot be handled similarly to all individuals. So, empowering the elderly to cope with their emotional changes and to promote attention is a crucial need.
ETHICAL ISSUE: Ethical clearance was taken from institutional ethical committee, KIMSDU, Karad.
FUNDING SOURCES: Krishna Institute of Medical Sciences Deemed To Be University, Karad.
CONFLICT OF INTEREST: Nil.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT:
We are grateful for the support which we received from the Department of community health Physiotherapy, Faculty of Physiotherapy, Krishna Institute of Medical Sciences Deemed To Be University, Karad, and Director of Research office, Krishna Institute of Medical Sciences Deemed to be University, Karad., Department of musculoskeletal sciences, Faculty of Physiotherapy, KIMSDU, Karad as well as Faculty of Physiotherapy, KIMSDU, Karad.
References:
-
Allerhand M, Gale CR, Deary IJ. The dynamic relationship between cognitive function and positive well-being in older people: A prospective study using the English Longitudinal Study of Aging. Psychol Ageing 2014 Jun;29(2):306.
-
Jin C, Zheng Z, Xian W, Bai M, Jin L, Li Y, Yang X, Sheng Y, Ai W, Liu H. Gender differences in positive life orientation among the nursing home elders in China: a cross-sectional study. Arch Gerontol Geriatr 2017;72:86-90.
-
Cabrita M, Lamers SM, Trompetter HR, Tabak M, Vollenbroek-Hutten MM. Exploring the relation between positive emotions and the functional status of older adults living independently: a systematic review. Ageing Mental Health 2017;21(11):1121-8.
-
Yew SH, Lim KM, Haw YX, Gan SK. The association between perceived stress, life satisfaction, optimism, and physical health in the Singapore Asian context. Asi J Humanities Soc Sci 2015;3(1):56-66.
-
Barbic SP, Bartlett SJ, Mayo NE. Emotional vitality: the concept of importance for rehabilitation. Arch Phy Med Rehab 2013;94(8):1547-54.
-
Vera-Villarroel P, Urzua A, Jaime D, Contreras D, Zych I, Celis-Atenas K, Silva JR, Lillo S. Positive and Negative Effect Schedule (PANAS): Psychometric properties and discriminative capacity in several Chilean samples. Eval Health Prof 2019;42(4):473-97.
-
Schultz PP, Ryan RM. The “why, what,” and “how” of healthy self-regulation: Mindfulness and well-being from a self-determination theory perspective. In Handbook of mindfulness and self-regulation 2015 (pp. 81-94). Springer, New York, NY.
-
Schultz PP, Ryan RM, Niemiec CP, Legate N, Williams GC. Mindfulness, work climate, and psychological need satisfaction in employee well-being. Mindfulness 2015;6(5):971-85.
-
Parto M, Besharat MA. Mindfulness, psychological well-being and psychological distress in adolescents: Assessing the mediating variables and mechanisms of autonomy and self-regulation. Procedia-Social Behav Sci 2011;30:578-82.
-
De Vries NM, Van Ravensberg CD, Hobbelen JS, Rikkert MO, Staal JB, Nijhuis-Van der Sanden MW. Effects of physical exercise therapy on mobility, physical functioning, physical activity and quality of life in community-dwelling older adults with impaired mobility, physical disability and/or multi-morbidity: a meta-analysis. Ageing Res Rev 2012;11(1):136-49.
-
Thompson Coon J, Boddy K, Stein K, Whear R, Barton J, Depledge MH. Does participating in physical activity in outdoor natural environments have a greater effect on physical and mental wellbeing than physical activity indoors? A systematic review. Envt Sci Tech 2011;45(5):1761-72.
-
Triguero-Mas M, Donaire-Gonzalez D, Seto E, Valentín A, Smith G, Martínez D, Carrasco-Turigas G, Masterson D, Van den Berg M, Ambròs A, Martínez-Íñiguez T. Living close to natural outdoor environments in four European cities: adults’ contact with the environments and physical activity. Int J Envt Res Public Health 2017;14(10):1162.
-
Brown DK, Barton JL, Pretty J, Gladwell VF. Walks4Work: Assessing the role of the natural environment in a workplace physical activity intervention. Scandinavian J Work Envt Health 2014;11:390-9.
-
Sheppard DP, Matchanova A, Sullivan KL, Kazimi SI, Woods SP. Prospective memory partially mediates the association between ageing and everyday functioning. Clin Neurops 2020;34(4):755-74.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License