IJCRR - 13(1), January, 2021
Pages: 10-15
Date of Publication: 05-Jan-2021
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
Prevalence of Diabetes Mellitus and Socio-demographic Survey in the Community of Western Uttar Pradesh, India in the Year 2019-2020
Author: Nadeem Rais, Akash Ved, Rizwan Ahmad, Kehkashan Parveen, Om Prakash
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Introduction: Diabetes is a chronic, metabolic disease characterized by elevated levels of blood glucose, which leads over time to serious damage to the heart, blood vessels, eyes, kidneys, and nerves. There are two types of diabetes and the most common is type 2 diabetes, usually in adults, which occurs when the body becomes resistant to insulin or doesn't make enough insulin.
Objective: This study aimed to estimate the prevalence of diabetes mellitus (DM) and its socio-demographic profile and screen the study population of diabetic patients in Western Uttar Pradesh.
Methods: The different mode of the survey was conducted between January 2019 to January 2020. A random screening was carried out with 3989 individuals of 1000 families at various geographical regions of western Uttar Pradesh. This was a cross-sectional house to house experience study that was conducted to find out the prevalence of diabetes mellitus at the community level.
Result: A total of 287 diabetic subjects were enrolled through a simple random sampling methodology. In the collected data, the prevalence of DM was found at 07.34%. Whereas the prevalence of type-1 DM and type-2 DM amongst known diabetics was found 06.62% and 93.37% respectively.
Conclusion: Incidents of DM were found varied person to person depending on their physical activities, knowledge, and myths/misconceptions about diabetes, food habits, etc. Current findings suggest that a relatively unfavourable risk profile of the diabetic subjects who also suffered from diabetic complications.
Keywords: Diabetes Mellitus, Prevalence, Community, Demographics profile, Uttar Pradesh
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION
Diabetes is a chronic problem that occurs either when the insulin production decreases from β cells of islets of Langerhans or when the pancreas cannot effectively use the insulin it produces. Insulin is a peptide hormone produced by beta cells of the pancreatic islets that regulates blood sugar level in the body. Hyperglycaemia, or raised blood sugar level, is the most common problem of uncontrolled diabetes and over time leads to serious damage to many of the body's systems, especially the nerves and blood vessels.1,2
India is currently experiencing a rapid epidemiological transition from communicable to non-communicable diseases viz. diabetes mellitus, hypertension, and ischaemic heart disease. Rapid industrialization and urbanization with a subsequent rise in standards of living, obesity, stress, sedentary lifestyle, addictions, etc. are posing a growing threat to the health of the nation. The number of people with diabetes in India currently around 40.9 million is expected to rise to 69.9 million by 2025 unless urgent preventive steps are taken.2 A very high prevalence of DM was observed in Saudi Arabia, the U.S., Switzerland, and Austria. Researchers believe there is a 250 per cent greater incidence of DM in the Middle East, Sub-Saharan Africa, India, Asia, and Latin America.3
Over recent decades, the prevalence of diabetes mellitus has been increasing worldwide due to factors like changes in lifestyle (sedentary living and eating habits) and obesity.4,5 The World Health Organization (WHO) estimated that India will have the largest number of diabetics in the world (every fourth diabetic is an Indian) and will become the diabetic capital of the world. 6,7,8 Although it has been recognized as a major cause of death and disability, many who suffer from diabetes are unaware that they are afflicted until they experience a debilitating side effect or complication of the disease.6 It is a fact that good clinical and self-care activities can delay diabetic complications and improve the quality of life. Therefore, in this present research, we attempted to determine the prevalence of diabetes mellitus and its socio-demographic profile and screen the study population of diabetic subjects in Western Uttar Pradesh.9-13 Having diabetes increases the risk of a myocardial infarction two times and the risk of suffering a stroke two to four times and it is also a leading cause of blindness, limb amputation, and kidney failure.14-16
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Study population
This was a cross-sectional house to house experience study that was conducted to find out the prevalence of diabetes mellitus at the community level. The study was carried out in the urban, semi-urban, and rural areas of Western Uttar Pradesh, India. Some developing and developed cities viz. Ghaziabad, Meerut, Bijnor, J.P. Nagar, and Moradabad of western Uttar Pradesh were selected for the study. The survey started in January 2019 and concluded in January 2020. The research protocol was approved by independent ethics committees. A random survey was performed with a total population of 3989 individuals Ghaziabad (N1=406), Meerut (N2=603), Bijnor (N3=1123), J.P. Nagar (N4=876), and Moradabad (N5=981) from 1000 families to know whether they had diabetes or not. The family members of already registered diabetic patients under treatment (oral antidiabetic drugs/injection regimen) or discontinuation were studied consciously (excluding pregnant women). 293 diabetic patients were selected for the study while 6 diabetic patients declined to answer any queries regarding diabetes. In this context, the detailed study of present final data of 287 diabetic patients of both gender and either age were carried out.
Data collection method
Data of the total population were collected on individual Data Collection Forms1 (DCFs1) while data of diabetic patients were collected on individual Data Collection Forms2 (DCFs2) at baseline and written consent was obtained from all the patients participating in the study. DCFs1 included in the interview schedule pertained to personal information i.e. name, religion, age/gender, residence, marital alliance, and diabetic status. DCFs2 included in the interview schedule pertained to personal information, date of diagnosis of disease, patient’s medical history, knowledge and myths/ misconceptions about diabetes, diabetic complication, demography, education, occupation, antidiabetic treatment, food habits, blood glucose measurement frequency, diabetes among any family member, number of hypoglycaemic episodes, adverse drug reactions (ADRs) and lifestyle (i.e. physical activity, smoking or consumption of alcohol, etc.).17-19
Data handling and statistical analysis
All data were tabulated and descriptive statistical analyses were performed. Sub groupings were carried out where required and prevalence (%) was calculated. Values are expressed as mean±SEM (N=5) by using One-way Analysis of Variance (ANOVA) followed by Dunnett's Multiple Comparison Test P< 0.01.
RESULTS
Data Concerning the prevalence of diabetes according to gender, marital alliance, and type incidence amongst known diabetics with Prevalence of DM according to parental history is presented in Table 1.
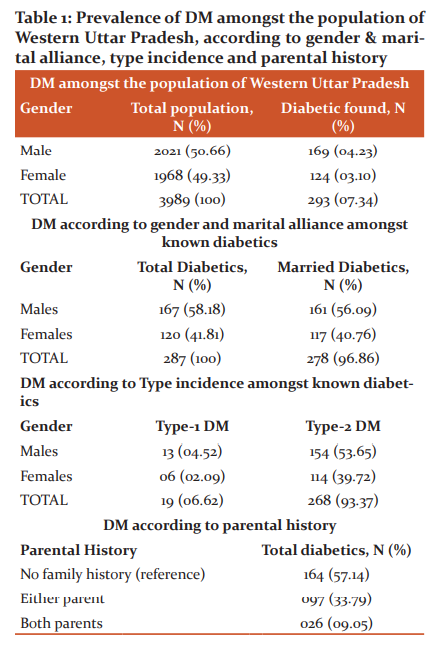
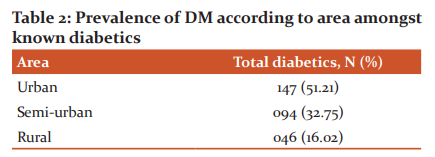
There are 3989 individuals from 1000 families in the five zoographical regions of Ghaziabad (406), Meerut (603), Bijnor (1123), J.P. Nagar (876), and Moradabad (981)} were selected for the study. The patients taken medications by oral ant-diabetic drugs/injection regimen under the supervision of physicians and discontinuation were studied consciously (excluding pregnant women). 293 diabetics were selected for the study while 6 diabetic patients declined to answer any queries regarding diabetes. This gave a final sample of 287 diabetic patients (considered as 100%) of both gender and either age to be studied. Out of 287 diabetics, 278 were found married with a percentage of 56.09% (males) and 40.76% (females). Type-1 and Type-2 incidence amongst known diabetics were06.62% and93.37% respectively. Parental history of diabetes was detected 33.79% (either parent) and 09.05% (both parents) while 57.14% diabetics were detected without any family history of diabetes. The prevalence of diabetes was significantly different between different zoographical zones urban 51.21%, semi-urban 32.75%, and rural 16.02%. The detailed descriptions are reported in Table 2.
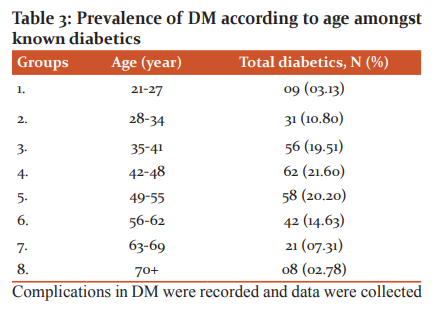
Diabetics in the study were distributed into 8 groups according to age (in years) from 21 to 70 plus, where we found that the age group of 21-27 was at the lowest risk (3.13%) of DM and the prevalence of diabetes increased significantly with advancing age till the age group of 42-48 (21.60%) then after this age group the prevalence of diabetes decreased significantly with advancing age (70+ years). The decreasing prevalence of DM after 54 years indicates the lethal effects of diabetes if not controlled. Detailed information is provided in Table 3.
Complications in DM were recorded and data were collected for the number of patients having one major complication, the number of patients with more than one complication, and the number of patients without any complication. The significant complications of diabetes were recorded as kidney disease, high blood pressure, neurological disorder cardiac disease, ophthalmic trouble, diabetic coma, etc, while 13.58% diabetics were reported without any complication. The detailed complications are reported in Table 4. Most of the diabetics were recorded as no exercise and sedentary work and data are 143 or 49.82%, while few diabetic peoples were aware of it and doing exercise regularly with strenuous work and data is 37 or 12.89%. Many of them accepted that physical activity plays a very important role in managing diabetes mellitus and found either doing regular exercise or strenuous work and data are 107 or 37.28%. The prevalence of DM according to lifestyles such as fast food/junk food (67.24%), smoking (35.54%), and consumption of liquor (4.52%) were recorded and detailed information is given in table5).

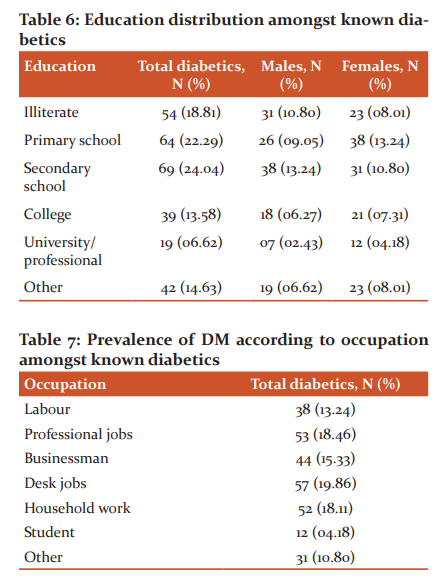
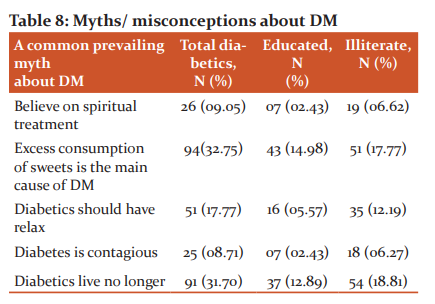
Out of 287 diabetics, patients are also elaborated based on literacy are having secondary school education, primary school education, college education, university/professional education, and illiterate patients and the collected data are 24.04%, 22.29%, 13.58%, 6.62%, and 18.81% respectively ( Table 6 and 7). The detailed information is reported in table 6. Out of 287 (100%) diabetics, the majority of subjects were found to have physically less active occupation like desk job (19.86%) > professional jobs (18.46%) > household work (18.11%) and further the prevalence was found gradually decreased with a physically active occupation like a businessman (15.33%) > labour (13.24%) > student (04.18%) while diabetics with other occupations were (10.80). The detailed information is given in Table 7. Because the majority of diabetics were uneducated or little educated, the prevalence of myths or misconceptions about diabetes mellitus was also at its peak. Out of 287 (100%) diabetics, 94(32.75%) subjects believed that excessive consumption of sweets is the main cause of DM. 91 (31.70%) subjects had negative faith that a diabetic lives no longer. 51 (17.77%) subjects were suggested to have relaxed. Despite this technical era, 26 (09.05%) subjects had faith in the spiritual treatment to get permanent benefit and25 (08.71%) diabetics thought that diabetes is contagious, and shown in Table 8.
Discussion
Diabetes mellitus is a leading public health problem and a major cause of morbidity and mortality worldwide. Its prevalence is on the rise in many areas of the developing world, especially in India, in response to increasing prosperity and sedentary lifestyles. In this study, the overall prevalence of diabetes in the study population was 07.34%. The prevalence of diabetes mellitus was higher among subjects with a family history of diabetes mellitus, who had a sedentary lifestyle or light grade physical activity. This community-based cross-sectional prevalence study was conducted in urban, semi-urban, and rural areas of the western Uttar Pradesh with a significant difference (51.21% urban, 32.75% semi-urban and 16.02% rural). These data provide a firm basis for further qualitative and quantitative studies to explore socio-demographic profile and many risk factors affecting the outcomes of diabetes, especially Type 2 DM, which will yield new perspectives and knowledge regarding diabetes management. To the best of our knowledge, no similar study has been conducted in Western Uttar Pradesh, India.8 The overall prevalence of diabetes in our study population was 7.34%, out of which 4.23% diabetics were males and 3.10 % diabetics were females. This is lower than earlier studies from other areas of the same state by Singh PS et al. in which prevalence was 8.03%.7 This difference could be explained, because of the change in lifestyle, and age composition of the selected population of earlier studies. The International Diabetes Federation had estimated that in 2010 the global population with diabetes between the ages of 20-79 was285 million (6.4%) and it had projected that this would grow to 439 million (7.7%) by 2030.2 However, the Diabetes Atlas, 6th edition figures show that in 2013 there are 382 million people have diabetes in the world and by 2035 this will rise to 592 million. Diabetes caused 5.1 million deaths in 2013; every six seconds a person dies from diabetes.9
Many cross-sectional studies conducted in India and other countries have shown that there is a rise in the prevalence of diabetes globally. There is a rapid increase in the prevalence of diabetes in India and other Asian countries. It has been predicted that India will be having a maximum number of diabetes cases in the year 2025.10 Many other Indian studies on diabetes like Rao et al, 2010 and Mohan et al, 2006 have seen that prevalence did not differ concerning gender; however, few studies have shown higher prevalence among the females.11-13 The prevalence of type 2 diabetes rates continues to increase with an increasing number of patients at risk of serious diabetes-related complications. In large metropolitan cities in India (Mumbai, Delhi, Calcutta, Chennai, Bangalore, and Hyderabad), the prevalence of diabetes among adults (aged ≥20 years) ranges from 8-18%.12,13,17-24
CONCLUSION
We recommend modifying the risk profile through early screening, education, awareness, and lifestyle modification strategies to improve the quality of life for diabetics. Early intervention for the prevention of complications can improve the outcome for diabetics and reduce the associated mortality and morbidity.
Funding
No funding sources
Ethical Approval and Consent to Participate The authors have no ethical conflicts to disclose. Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Acknowledgements
Authors are thankful to Dr Tauheed Ishrat, Associate Professor, Department of Anatomy and Neurobiology, The University of Tennessee Health Science Center, TN, USA for his sustained encouragement, meticulous supervision, and valuable suggestions at all stages of completion of this manuscript.
References:
-
-
Diabetes. https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/diabetes. June 2020.
-
Sicree R, Shaw J, Zimmet P. Diabetes, and impaired glucose tolerance. In: Gan D, editor. Diabetes Atlas. International Diabetes Federation. 3rd ed. Belgium, 2006, pp15-103.
-
Ginter E, Simko V. Diabetes type2 pandemic in the 21st century. Bratis Lek Listy. 2010; 111(3):134-137.
-
Roman SH, Harris MI. Management of diabetes mellitus from a public health perspective. Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am 1997; 26(3):443-474.
-
Gruber W, Lander T, Leese B, Songer T, Williams R. The Economics of Diabetes and Diabetes Care. International Diabetes Federation. Brussels: Belgium;1998.
-
Mayur P, Ina MP, Yash MP, Suresh KR. Profile of the subjects with Diabetes: A hospital-based observational study from Ahmedabad, Western India. Electr Physic 2011:378-384.
-
Prem SS, Himanshu S, Khwaja SZ, Prafulla KS, Sudhir KY, Rajesh KG, Tony P. Prevalence of type 2 diabetes mellitus in the rural population of India- a study from Western Uttar Pradesh. Int J Res Med Sci 2017;5(4):1363.
-
Poulomi S, Kapil M. Study of Prevalence and Pattern of Sensorineural Hearing Impairment in Stage 5 Chronic Kidney Disease Patients on Haemodialysis- at a Tertiary Health Care Setup in India. Int J Curr Res Rev 2020;12(04):08-13.
-
Diabetes in South-East Asia: An update for 2013 for the IDF Diabetes Atlas, 6th edition.
-
International Diabetes Federation. Diabetes Atlas. 4th edition 2009. Available from URL:www.diabetesatlas.org.
-
-
Rao CR, Kamath VG, Shetty A, Kamath A. A study on the prevalence of diabetes in coastal Karnataka. Int J Diabetes 2010;30:80-85.
-
Mohan V, Deepa M, Deepa R, Shanthirani CS, Farooq S, Ganesan A, Datta M. Secular trends in the prevalence of diabetes and impaired glucose tolerance in urban South India- the Chennai Urban Rural Epidemiology Study (CURES-17). Diabetologia 2006;49:1175-1178.
-
Ramachandran A, Snehalatha C, Latha E, Vijay V, Viswanathan M. Rising prevalence of NIDDM in an urban population in India. Diabetologia. 1997; 40:232-237.
-
World Health Organization. Fact Sheet No.312: What is Diabetes? Available from URL:http://www.who.iny/mediacentre/factsheets/fs312/en.pdf.
-
International Diabetes Federation. Diabetes Atlas. 3rd ed 2006. Available from www.diabetesatlas.org.
-
Cubbon RM, Wheatcroft SB, Grant PJ, Gale CP, Barth JH, Sapsford RJ, Ajjan R, Kearney MT, Hall AS. Temporal trends in mortality of patients with diabetes mellitus suffering acute myocardial infarction: a comparison of over 3000 patients between 1995 and 2003. Eur Heart J 2007;28:540-545.
-
Iyer SR, Iyer RR, Upasani SV, Baitule MN. Diabetes mellitus in Dombivli-an urban population study. J Assoc Physicians India 2001; 49:713-716.
-
Misra A, Pandey RM, Devi JR, Sharma R, Vikram NK, Khanna N. High prevalence of diabetes, obesity and dyslipidaemia in urban slum population in Northern India. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 2001;25:1722-1729.
-
-
Prabhakaran D, Shah P, Chaturvedi V, Ramakrishnan L, Manhapra A, Reddy KS. Cardiovascular risk factor prevalence among men in a large industry of Northern India. Nat Med J India 2005;18:59-65.
-
Ramachandran A, Snehalatha C, Kapur A, Vijay V, Mohan V, Das AK, Rao PV, Yajnik CS, Prasanna KKM, Nair JD. Diabetes epidemiology study group in India. High prevalence of diabetes and impaired glucose tolerance in India: national urban diabetes survey. Diabetologia 2001;44:1094-1101.
-
Mohan V, Shanthirani CS, Deepa R. Glucose intolerance (diabetes and IGT) in a selected South Indian population with special reference to family history, obesity and lifestyle factors- The Chennai urban population study (CUPS 14). J Assoc Physic India 2003;51:771-777.
-
Ramachandran A, Snehalatha C, Baskar ADS, Mary S, Kumar CKS, Selvam S, Catherine S, Vijay V. Temporal changes in the prevalence of diabetes and impaired glucose tolerance associated with lifestyle transition occurring in the rural population in India. Diabetologia 2004;47:860-865.
-
Ramachandran A, Mary S, Yamuna A, Murugesan N, Snehalatha C. High Prevalence of diabetes and cardiovascular risk factors associated with urbanization in India. Diabetes Care 2008;31:893-898.
-
Bai PV, Krishnaswami CV, Chellamariappan M. Prevalence and incidence of type-2 diabetes and impaired glucose tolerance in a selected Indian urban population. J Assoc Physic India 1999;47:1060-1064.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License