IJCRR - 8(4), February, 2016
Pages: 06-12
Date of Publication: 21-Feb-2016
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
A STUDY OF HEMATOLOGICAL PARAMETERS AND ANTHROPOMETRIC INDICATORS IN HYPERTENSIVE AND NORMOTENSIVE MALES
Author: Divya R., Ashok V.
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Introduction: Hypertension is one of the factors associated with stroke, congestive heart failure, heart or kidney failure. Overweight and obesity are the two most key determinants of health that leads to adverse metabolic changes including increase in blood pressure. The cellular components of blood contribute to the viscosity and volume of blood, thus playing a vital role in regulating blood pressure. Objectives: To compare the hematological parameters and anthropometric indicators in hypertensive and normotensive males. Materials and Methods: This was a hospital based case control study which included 60 normal healthy male subjects and 60 hypertensive male subjects. Blood pressure was measured in supine position by mercury sphygmomanometer. Hematological indices were estimated using an autoanlayser. The data collected were entered and analyzed using software Statistical Package for the Social Science 16.0 (SPSS 16.0). Results and Discussion: The mean levels of hemoglobin and hematocrit were significantly lower in the hypertensive group compared to the normotensives in our study. The anthropometric measurement waist hip ratio, showed a statistically significant positive correlation with systolic blood pressure. Multiple regression analysis showed waist hip ratio, hemoglobin and hematocrit were significant predictors of systolic blood pressure. Conclusion: The present study concludes that Waist hip ratio, a simple and inexpensive anthropometric measurement can be used as a significant predictor of systolic blood pressure. Also monitoring of hematological indices like hemoglobin and hematocrit is essential in the prevention of development of cardiovascular complications in hypertension.
Keywords: Hypertension, Anthropometric indicators, Hematological indices, BMI, WHR
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION Hypertension is defined as blood pressure more than 140/90 mm Hg as per US Seventh Joint National Committee on Detection, Evaluation and Treatment of Hypertension (JNC VII).1 The prevalence of hypertension in India is 23.10 % among men and 26.60% among women.2 Prevalence of hypertension in South India was found to be 20% according to the CURES 2007 study.3 Overweight and obesity are the two most important key determinants of health that leads to adverse metabolic changes including increase in blood pressure.
Obesity and weight gain are independent risk factors for hypertension. Also 60- 70% of hypertension in adults may be directly attributable to adiposity.4 Body mass index or BMI is propagated by the WHO as the most beneficial epidemiological measure of obesity. Waist hip ratio (WHR) and waist circumference (WC) are frequently used to forecast the danger of obesity linked morbidity and mortality as they account for regional abdominal adiposity.
Visceral fat is a more significant determinant of blood pressure elevation than is peripheral body fat.5 In longitudinal studies, a direct association exists between change in weight and change in blood pressure over time.4 Though hypertension and obesity are closely linked but there is no universal anthropometric marker due to distinct population features. Studies in urban population showed a strong relationship between different anthropometric indicators and blood pressure levels but very little is known about these relationships in rural Indian population.6, 7, 8
The cellular components of blood contribute to the viscosity and volume of blood, thus playing a vital role in regulating blood pressure. It has been newly realized that many hematological parameters varies with hypertension in comparison with normotensives. This gives a vision into the connection between blood cell defects and blood pressure. There are number of disputes in different studies with respect to variability of hematological parameters in hypertensive and normotensive subjects.9, 10, 11 The pathophysiology of hypertension is multifactorial which is affected by sympathetic over activity contributing to alterations in hematological parameters like hematocrit, viscosity and hypercoagulability of blood.
These factors change the kinetics of blood flow acting as contributory risk factor for coronary artery diseases, stroke and thromboembolism.12Thus the hematological parameters gives an insight to prognosis of disease also. So the present study was therefore undertaken to compare the hematological parameters and anthropometric indicators in hypertensive and normotensive males. The present study was carried out with the following objective: To compare the hematological parameters and anthropometric indices in normotensive and hypertensive males.
Materials andmethods This study was conducted in Sri ManakulaVinayagar medical college hospital(SMVMCH) Madagadipet, Puducherry. Study design: Hospital based case control study. Sample size: 120 subjects. We included 60 normal healthy male subjects of 35-55years of age. 60 hypertensive male subjects of 35-55 years of age. Data collection: A representative sample of local population comprising of 120 subjects aged 35-55 years were selected from 1. Hypertensive patients attending medicine OPD in SMVMCH. 2. Normotensives were attendants of patients, workers in SMVMCH. Inclusion criteria 1. Hypertensive subjects having blood pressure >140/90 mmHg. 2. Normotensive subjects having blood pressure ≤120/80mmHg.
Exclusion criteria Subjects with any systemic illness, subjects on drug medications (steroids, α methyl dopa) for past three months Subjects who fulfilled the inclusion and exclusion criteria were included in the study. After explaining the nature of the study, informed consent was obtained from the study subjects.
Methodology 1. Measuring Blood pressure: Blood pressure was measured by a mercury sphygmomanometerin supine position. Blood pressure was measured two times. The average of two readings was taken as correct systolic and diastolic blood pressure.13, 1 The classification of blood pressure is as follows4 Normal BP: 160/100 mmHg. 2. Hematological parameters: From the subjects 2 ml of blood were withdrawn to which anticoagulant solution was added and fed into the ABX Pentra DF120 Hematology analyser from Horiba Medicals Pvt Ltd. The RBC’s, WBC’s and PLT’s are measured by an electronic impedance variation principle. The hemoglobin(Hb) freed by the lysis of the red blood cells combines with potassium cyanide to form a cyanmethemoglobin compound.
Absorbance is then measured by spectrophotometry, at a wave length of 550 nm.MCV (Mean Corpuscular Volume) is calculated directly from the RBC histogram.MCH (Mean Corpuscular Hemoglobin) is calculated from the Hb value and the RBC count. MCHC (Mean Corpuscular Hemoglobin Concentration) is calculated according to the Hb and HCTvalues.The hematocrit is measured as a functionof the numeric integration of the MCV.14 3. Body weight: Body weight was measured while the subject minimally clothed and without shoes, standing steady on a weighing scale and it was recorded to the nearest 0.1kg.15 4. Height: Height was measured to the nearest 0.1 cm while the subject was standing barefoot in erect position with a wallmounted stadiometer.15 5. Body mass index:
BMI was measured by weight in kilograms divided by square of height in meters (kg/m2). (BMI in the range of 18.50 to 24.99 kg/m2 is considered to be normal.15 6. Waist circumference: Waist circumference was measured in centimeters over light clothing at a point mid-way between the lower rib and iliac crest.15 7. Hip circumference: Hip Circumference was measured in centimeters over light clothing at the widest girth of the hip. For waist and hip circumference two consecutive readings were made at each site on a horizontal plane without compression of the skin. The mean was taken as the final reading. 15 8. Waist Hip Ratio: It was calculated by dividing waist circumference by hip circumference.15
Statistical analysis The data collected were entered and analyzed using software Statistical Package for the Social Science 16.0 (SPSS 16.0). All parameters were presented as mean ± standard deviation (mean ± SD). Comparison of parameters between hypertensive subjects and normal healthy controls was done with student ‘t’ test. Correlation analysis was done with Pearson’s correlation method. A linear regression analysis was performed to evaluate the independent predictors of hypertension. A p value of less than 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
RESULTS Table 1 presents the demographic characteristics and the anthropometric indices of the study participants. A significant difference however existed between the cases and controls with respect to systolic blood pressure and diastolic blood pressure (p<0.001).The mean values of blood indices are presented in Table 2. Within the hypertensive and normotensive groups, the mean levels of hemoglobin and hematocrit were significantly higher in controls compared to hypertensive patients. Correlation analysis showed a statistically significant positive correlation between WHR and systolic blood pressure (Table 3).
Hemoglobin and hematocrit showed a negative correlation with systolic blood pressure among the cases. Systolic blood pressure was also found to be positively correlated with the duration of hypertension among the cases (Table 3). Pearson’s correlation analysis showed a statistically significant positive correlation between age and duration of hypertension. Hemoglobin and hematocrit showed a negative correlation with duration of hypertension among the cases (Table 4). Correlation analysis of Waist hip ratio with other anthropometric indicators like body mass index and waist circumference are shown in Table 5. Waist hip ratio showed a statistically significant positive correlation with the body mass index and waist circumference among the hypertensive subjects.
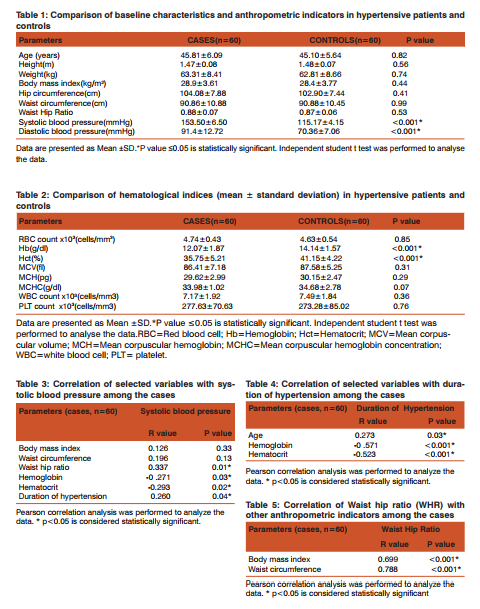
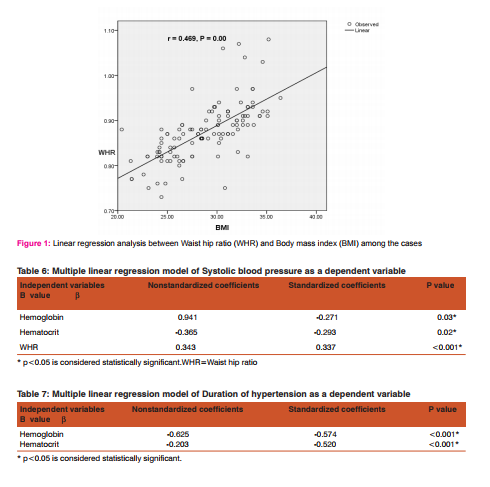
The association was found to be stronger with waist circumference (r = 0.778) than the body mass index(r = 0.699). Figure 1 shows the regression curve of Waist hip ratio (WHR) with Body mass index (BMI) in the hypertensive subjects. A linear regression analysis was performed to evaluate the independent predictors of systolic blood pressure. Regression analysis with systolic blood pressure as a dependent variable showed a linear relationship with WHR, hemoglobin and hematocrit levels among the cases (Table 6). Further regression analysis with duration of hypertension as a dependent variable showed a linear relationship with hemoglobin and hematocrit levels among the cases (Table 7).
DISCUSSION Our study showed significant differences in the mean levels of hematocrit and hemoglobin concentration between hypertensive and the normotensive subjects. The mean levels of hemoglobin and HCT were significantly lower in the hypertensive group compared to the normotensives in our study. Although a number of studies have shown significant differences in the levels of hemoglobin, RBC, MCV, HCT and MCH between hypertensive and normotensive individuals, there are also a few studies that has not shown any significant difference between the two groups.9, 11, 16 According to Richard D.
Gordon, sympathetic activity is responsible for an increase in renal afferent arteriolar constriction which in turn causes an increase in renin secretion and eventually, a rise in aldosterone secretion. Renin, via the effect of angiotensin on aldosterone, is a key factor for sodium and water retention in the body. The subsequent increase in blood volume thereby causes haemodilution and may be responsible for decreased hemoglobin and hematocrit level in hypertensives.17, 18, 19
The other probable mechanism responsible for decrease in hemoglobin levels in hypertension may be reduced production of erythropoietin and resistance of the bone marrow to erythropoietin stimulation.20 Hypertension if not treated promptly leads to cardiac and renal failure.21Congestive cardiac failure may also cause a low hemoglobin level due to hemodilution in later stages. Ultimately, the fall in hemo- globin concentration due to hypertension leads to an increase in cardiac output and heart failure.22 According to Julius S sympathetic stimulation in hypertensives is associated with elevation of plasma renin levels. Increased renin circulation leads to sodium and water retention in the body, which leads to hemodilution and may be the cause for low hemoglobin concentration in hypertensives.23
The anthropometric measurement waist hip ratio, showed a statistically significant positive correlation with systolic blood pressure in hypertensive individuals. (Table 3) This finding is in accordance with the study by Hartz et al, 24 in which it was revealed that Waist hip ratio is a strong independent indicator of hypertension, particularly in men aged 40-59 years. However, in our study BMI and waist circumference did not independently correlate with blood pressure. Multiple regression analysis showed that variables like WHR, Hb, Hct were significant predictors of systolic blood pressure.
Visceral fat, measured as WHR, showed a positive correlation with Waist circumference, body mass index (Table 5).Various mechanisms may explain the association between visceral obesity and arterial blood pressure. 25, 26The greater quantity of visceral fat may favor an increase in sympathetic activity mediated by the associated insulin resistance, besides potentializing the activity of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system due to the increased angiotensinogen secretion by visceral adipocytes, when compared to the subcutaneous fat.27, 28The visceral fat accumulation could also exert a mechanical effect, inducing renal compression and promoting arterial blood pressure exacerbation.29, 30 In our study the best association was found between Waist hip ratio and Waist circumference.
This correlation’s magnitude is similar to the one that was found by Beauloye et al.88 But in a study by Freedman et al indicate that arterial blood pressure changes in a certain population do not necessarily correlate to obesity changes. 31These evidences suggest that anthropometric’s influence on hypertension is quite complex and needs to be better investigated. Also the results suggest that visceral fat as measured by waist hip ratio exerts greater influence in systolic blood pressure levels.
CONCLUSION The present study concludes that Waist hip ratio, a simple and inexpensive anthropometric measurement can be used as a significant predictor of systolic blood pressure. It may be useful as an assessment tool in screening programs to assess the risk of hypertension. In addition, we also conclude that monitoring of hematological indices like hemoglobin and hematocrit is essential in the prevention of development of cardiovascular complications in hypertension.
ACKNOWLEDGMENT We are grateful to the Sri Manakula Vinayakar Medical College and Hospital for providing the facilities to perform this study. We acknowledge the immense help received from the scholars whose articles are cited and included in references of this manuscript. We are also grateful to authors / editors / publishers of all those articles, journals and books from where the literature for this article has been reviewed and discussed.
References:
1. The seventh report of the Joint National Committee on prevention, detection, evaluation and treatment of high blood pressure. JAMA2003; 289:2560-71.
2. Jyotsna Singh. World Health Organisation. Global Health Statistics. India has low rates of hypertension reveals WHO study. New Delhi, DHNS: 2012.
3. Mohan V, Deepa M, Farooq S, Datta M, Deepa R. Prevalence, awareness and control of hypertension in Chennai-the Chennai Urban Rural Epidemiology Study(CURES-52). J Assoc Physicians India 2007; 55:326-32.
4. Fauci A, Branwald E, Kasper L, Larry L. Hypertensive vascular disease. In: Naomi DL, Gordon HW eds. Harrison’s principles of internal medicine. 17th ed. Newyork: McGraw Hill Publishers: 1463-1480.
5. Deshmukh PR, Gupta S, Dongre A, Bharambe M, Maliye C. Relationship of anthropometric indicators with blood pressure levels in rural Wardha. Ind J Med Res 2006; 123:657-64.
6. Bose K, Ghosh A, Roy S, Gangopadhyay S. Blood pressure and waist circumference: an empirical study of the effcts of waist circumference on blood pressure among Bengaleemale jute workers of Belur, West Bengal, India. J Physiol Anthropol Appl Human Sci 2003; 22:169-73.
7. Shanthirani CS, Pradeepa R, Deepa R, Premalatha G, Saroja R, Mohan V. Prevalence and risk factors of hypertension in selected South Indian population – the Chennai Urban Population Study. J Assoc Physicians India 2003; 51:20-27.
8. Gupta R, Mehrishi S. Waist-hip ratio and blood pressure correlation in an urban Indian population. J Indian Med Assoc 1997; 95(7):412-415.
9. Cirillo, M Laurenzi, M Trevisan and J Stamler. Hematocrit, blood pressure, and hypertension. The Gubbio Population Study.Hypertension 1992; 20:319-326.
10. Chien S. Blood rheology in hypertension and cardiovascular disease. Cardiovasc Med 1977; 2:356-360.
11. Dan SJ, David C, Irwin J, Herbert J, Timothy C, Cecil M et al. Mean red cell volume as a correlate of blood pressure. Circulation 1996; 93: 1677.
12. Al-Muhana F, Larbi E, Ali A, Sultan A, Ateeq S Soweilem L et al. Haematological, lipid profile and other biochemical parameters in normal and hypertensive subjects among the population of the eastern province of Saudi Arabia. East Afr Med J 2006; 83(1):44-48.
13. Badaruddoza, Navneet K, Basanti B. Inter-relationship of waist-to-hip ratio (WHR), bodymass index (BMI) and subcutaneous fat with blood pressure among university-going Punjabi Sikh and Hindu females.International Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences 2010; 2(1):5-11.
14. Corberand JX, Segonds C, Fontanilles AM, Cambus J, Fillola G, Laharrague P. Evaluation of the PENTRA 120 Hematology Analyzer in a university hospital setting. Clin Lab Haem 1999; 21:3-10.
15. Tambe B, Phadke V, Kharche S, Joshi R. Correlation of blood pressure with body mass index and waist to hip ratio in middle aged men. Internet Journal of Medical Update 2010; 5(2):26-30.
16. Bruschi G, Minari M, Bruschi E, Tacinelli L, Cavatorta A. Similarities of essential and spontaneous hypertension. Volume and number of blood cells. Hypertension 1986; 8:983-89.
17. Gordon RD, Küchel O, Liddle GW, Island DP. Role of the Sympathetic Nervous System in Regulating Renin and Aldosterone Production in Man. J Clin Invest 1967; 46(4):599–605.
18. Williams GH. The renin-angiotensin system and hypertension. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol Suppl 1982; 7:31-40.
19. Esler M, Julius S, Zwelfer A, Randall O, Harburg E, Gardiner H. Mild high–renin in essential hypertension: Neurogenic human hypertension. N Engl J Med 1977;296:405– 411.
20. Kes P, Jukic B, Kes V. The cardiorenal syndrome and erythropoietin. Acta Med Croatica. 2008; 62(1):21-31.
21. Silverberg DS, Wexler D, Iaina A, Schwartz D. The interaction between heart failure and other heart diseases, renal failure, and anemia. Semin Nephrol. 2006; 26(4):296-306.
22. Androne AS, Katz SD, Lund L. Hemodilution is common in patients with advanced heart failure. Circulation. 2003; 107:226–229.
23. Julius S. Corcoran Lecture. Sympathetic hyperactivity and coronary risk in hypertension. Hypertension. 1993; 21:886-893.
24. Hartz, A, Rupley D, Rimm A. The association of girth measurements with disease in 32,856 women. Am J Epidemiol 1984; 119:71-80.
25. Kabir M, Catalano KJ, Ananthnarayan S, Kim SP, Vancilters GW, Dea MK et al. Molecular evidence supporting the portal theory: a causative link between visceral adiposity and hepatic insulin resistance. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 2005; 288(2):454-61.
26. Després J. Obesity and lipid metabolism: relevance of body fat distribution. Curr Opin Lipidol 1991;2(1):5- 15.
27. Karlsson C, Lindell K, Ottosson M, Sjostrom L, Carlsson B, Carlsson L. Human adipose tissue expresses angiotensinogen and enzymes required for its conversion to angiotensin II. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 1998;83(11):3925-9.
28. Lee S, Bacha F, Gungor N, Arslanian SA. Waist circumference is an independent predictor of insulin resistance in black and white youths. J Pediatr 2006;148(2):188-94.
29. Hall JE, Jones DW, Kuo JJ, da Silva A, Tallam LS, Liu J. Impact of the obesity epidemic on hypertension and renal disease. Curr Hypertens Rep 2003;5(5):386-92.
30. Silverberg DS, Wexler D, Iaina A, Steinbruch S, Wollman Y, Schwartz D. Anemia, chronicrenal disease and congestive heart failure-the cardio renal anemia syndrome: the need for cooperation between cardiologists and nephrologists. Int Urol Nephrol 2006; 38(2):295- 310.
31. Beauloye V, Zech F, Tran HT, Clapuyt P, Maes M, Brichard SM. Determinants of early atherosclerosis in obese children and adolescents. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2007; 92(8):3025-32.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License